©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2025; 17(9): 109715
Published online Sep 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i9.109715
Published online Sep 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i9.109715
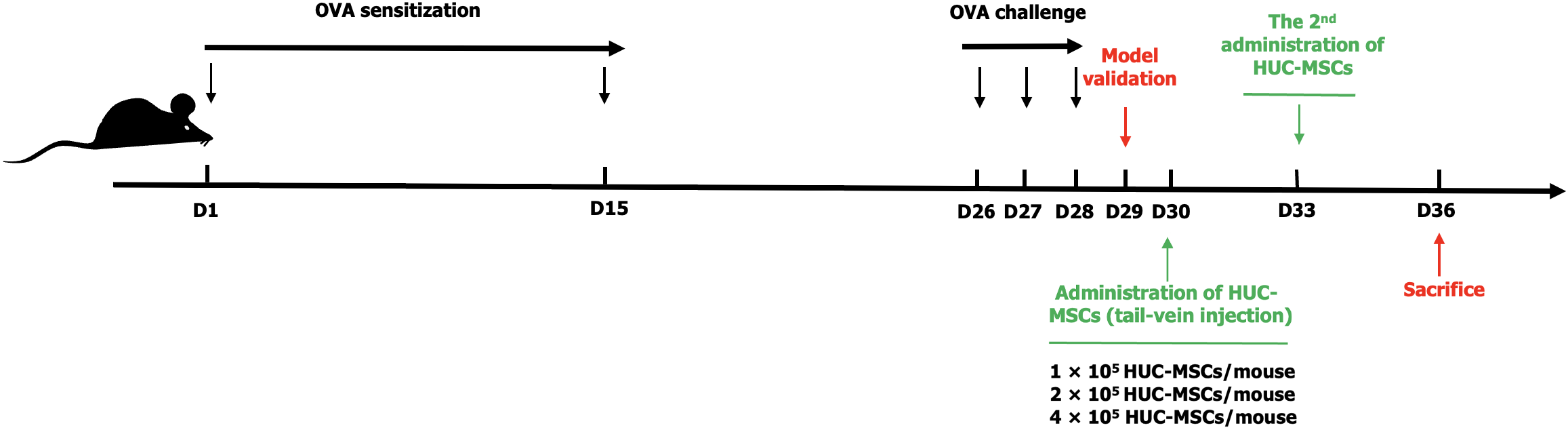
Figure 1 Schematic flow diagram of anti-asthma experiment with different dosages of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment.
OVA: Ovalbumin; HUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
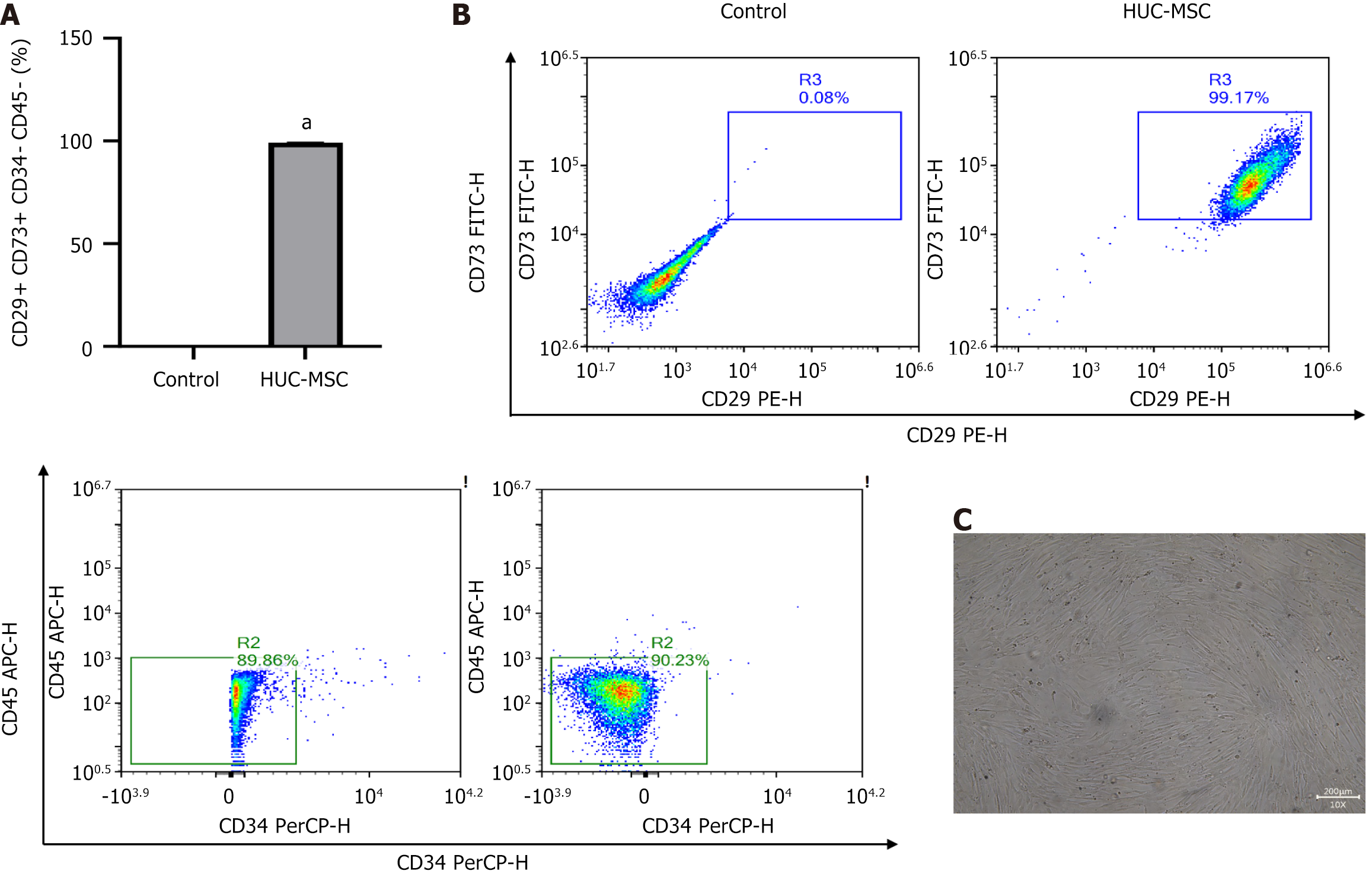
Figure 2 Immunophenotypic analysis of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
A and B: Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell cells were incubated with specific antibodies against the cell surface antigens CD29, CD73, CD34, and CD45 by flow cytometry; C: Representative images of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. HUC-MSC: Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
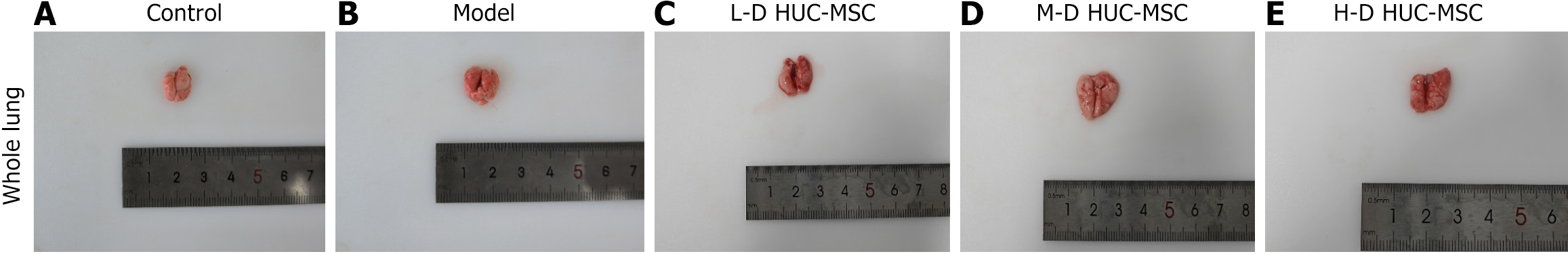
Figure 3 Gross lung photography of ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice treated with different dosages of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
A-E: Gross lung images of a group of control, model, and three different dosages of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells treatment. L-D HUC-MSC: Low dosage (1 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; M-D HUC-MSC: Medium dosage (2 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; H-D HUC-MSC: High dosage (4 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
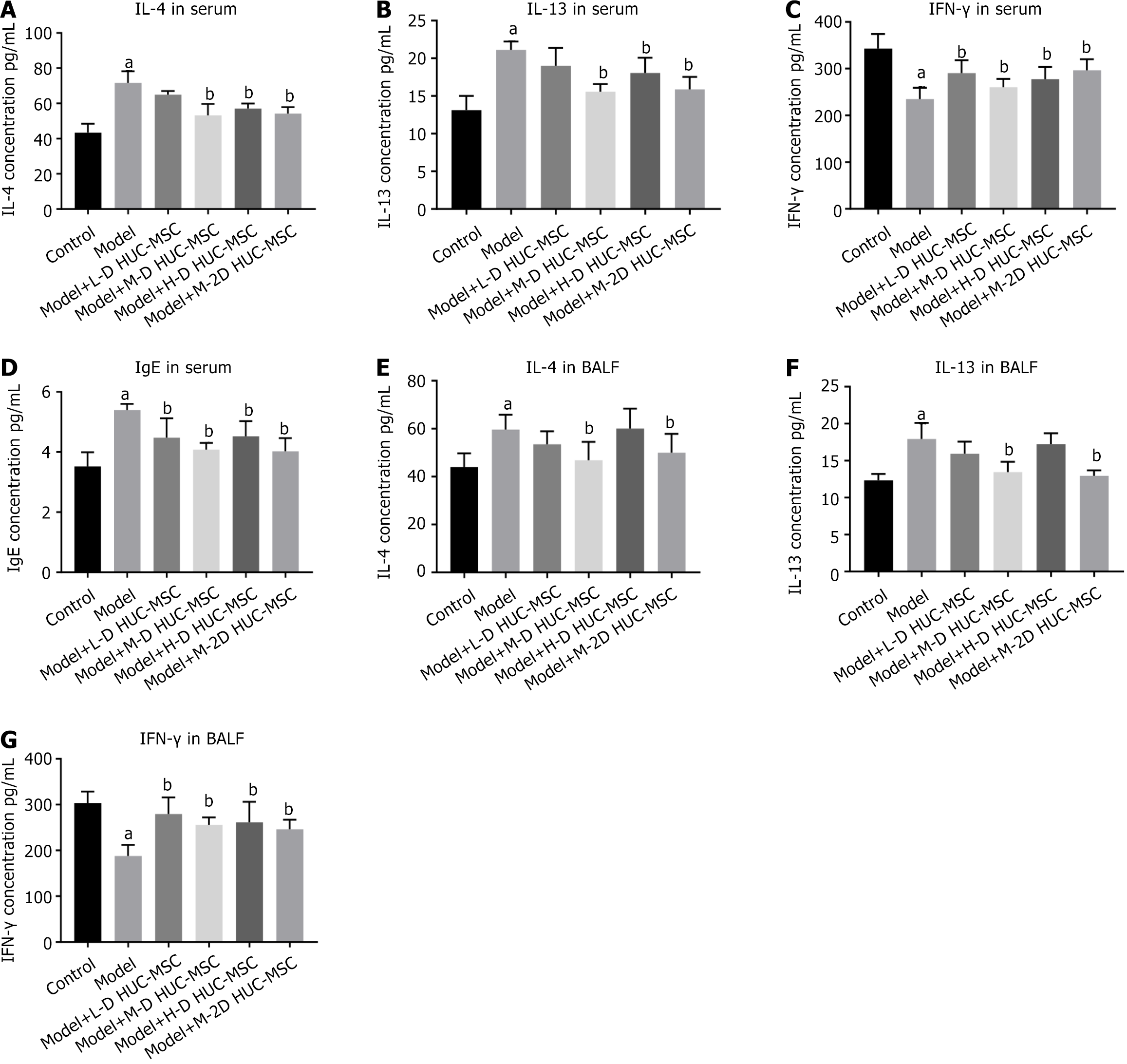
Figure 4 Effect of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on the levels of inflammatory cytokines.
A-D: Interleukin-4 (IL-4) (A); IL-13 (B); interferon-gamma (C), and immunoglobulin E (D) in serum of mice with ovalbumin-induced asthma; E-G: IL-4 (E), IL-13 (F), interferon-gamma (G) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of mice with ovalbumin-induced asthma. aP < 0.05 indicate a significant difference from the control group; bP < 0.05 indicate a significant difference from the model group. Bonferroni correction was applied to evaluate cytokines in multiple treatment groups. IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; IgE: Immunoglobulin E; BALF: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; L-D HUC-MSC: Low dosage (1 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; M-D HUC-MSC: Medium dosage (2 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; H-D HUC-MSC: High dosage (4 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; M-2D HUC-MSC: Medium dosage (2 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell twice.
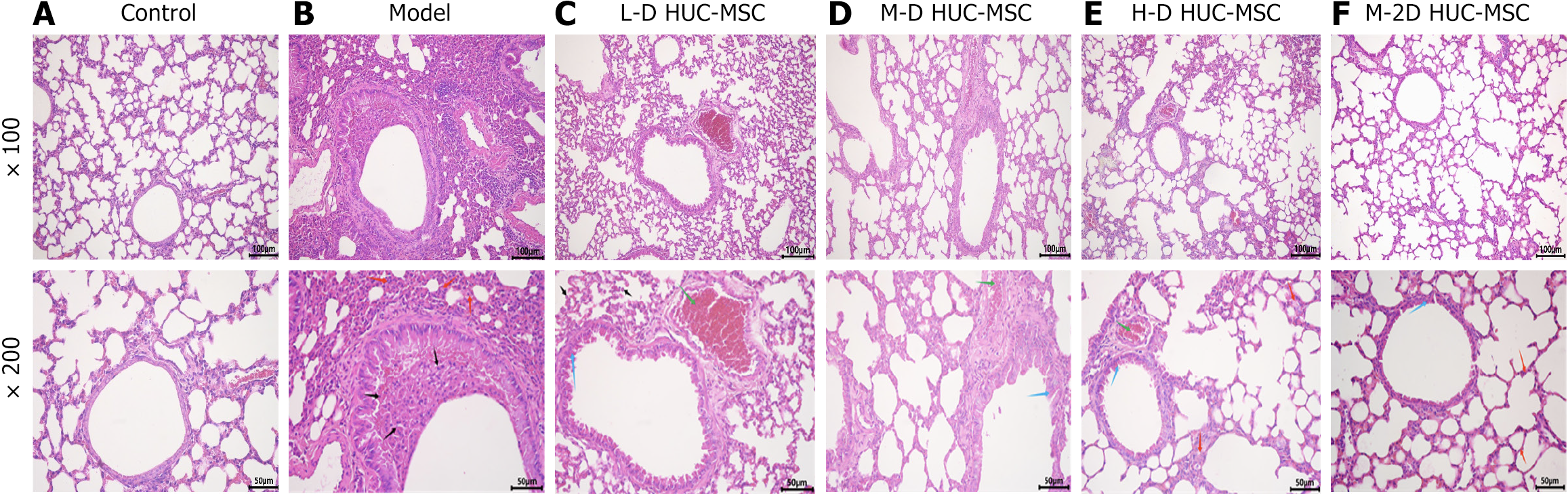
Figure 5 Pathological features of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell in attenuating airway inflammation in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice.
A-F: Hematoxylin and eosin staining images of control, model, low dosage, medium dosage, high dosage, and two medium dosage human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell treated lung tissue of mice. Hematoxylin and eosin staining showed that the control group displayed normal lung tissue architecture and cellular morphology, with no inflammatory cell infiltration. Conversely, the model group demonstrated pronounced inflammatory cell infiltration (indicated by black arrows), thickening of the alveolar walls (indicated by red arrows), sparse inflammatory cells (black arrows), desquamation of bronchial epithelial cells (indicated by blue arrows), and vascular congestion (indicated by green arrows) across the various dose groups. Notably, the group receiving a double medium dose of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell exhibited significant improvement in the condition of the alveolar walls compared to the model group (red arrows). L-D HUC-MSC: Low dosage (1 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; M-D HUC-MSC: Medium dosage (2 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; H-D HUC-MSC: High dosage (4 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; M-2D HUC-MSC: Medium dosage (2 × 105) of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell twice.
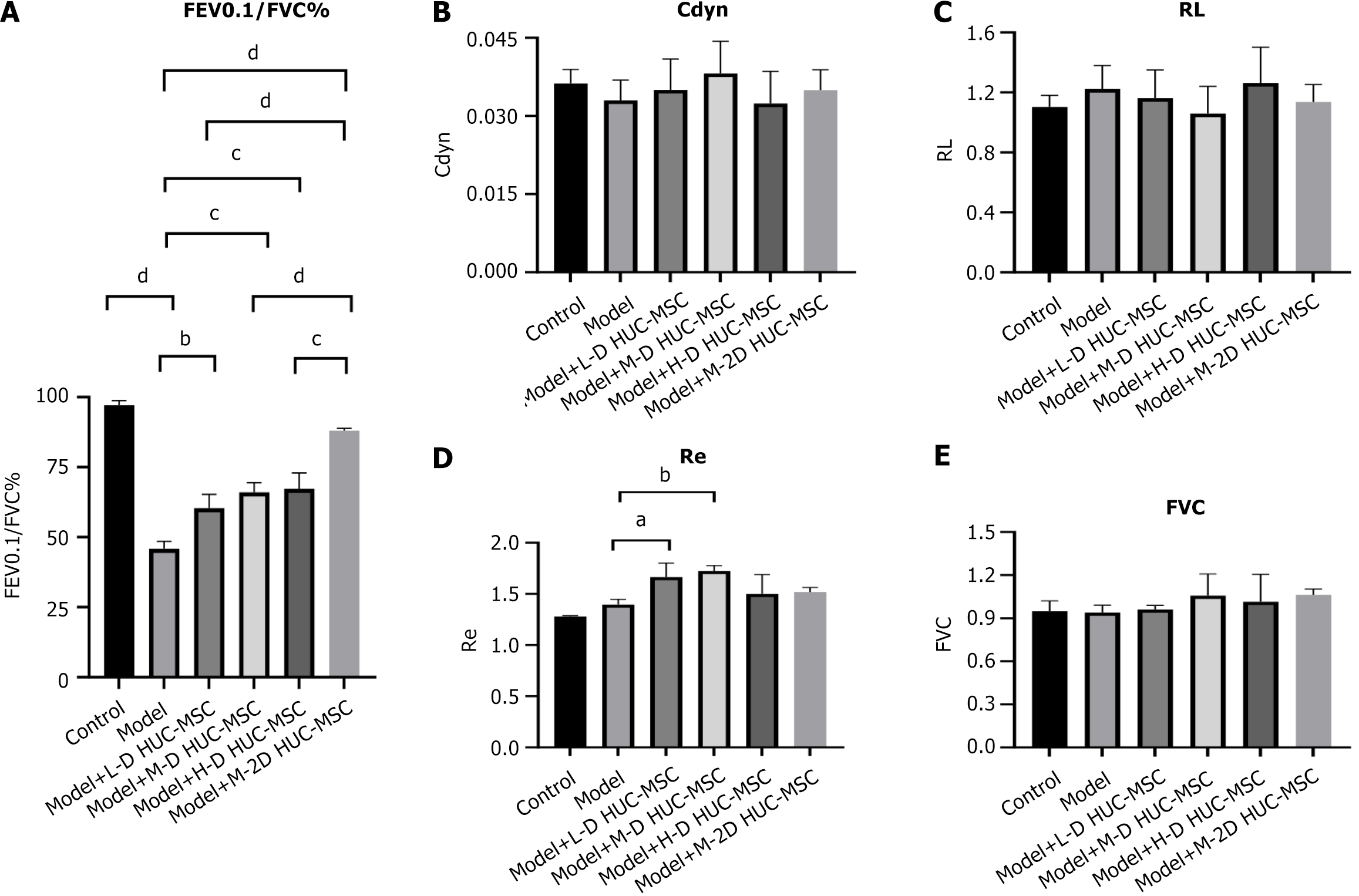
Figure 6 Effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the lung function of acute ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice.
A: Forced expiratory volume 0.1/forced vital capacity; B: Dynamic lung compliance; C: Airway resistance; D: Respiratory system elastic resistance; E: Forced vital capacity. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. Bonferroni correction was applied to evaluate lung function metrics in multiple treatment groups. FEV: Forced expiratory volume; FVC: Forced vital capacity; Cdyn: Dynamic lung compliance; RL: Airway resistance; Re: Respiratory system elastic resistance.
- Citation: Chen QH, Zheng JY, Zhu YQ, Zhang JY, Lin CY, Zhuang XE, Cheng J, Huang XY. Exploring the critical therapeutic window: Dose-frequency optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for preclinical asthma treatment. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(9): 109715
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i9/109715.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i9.109715