©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2025; 17(10): 111241
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i10.111241
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i10.111241
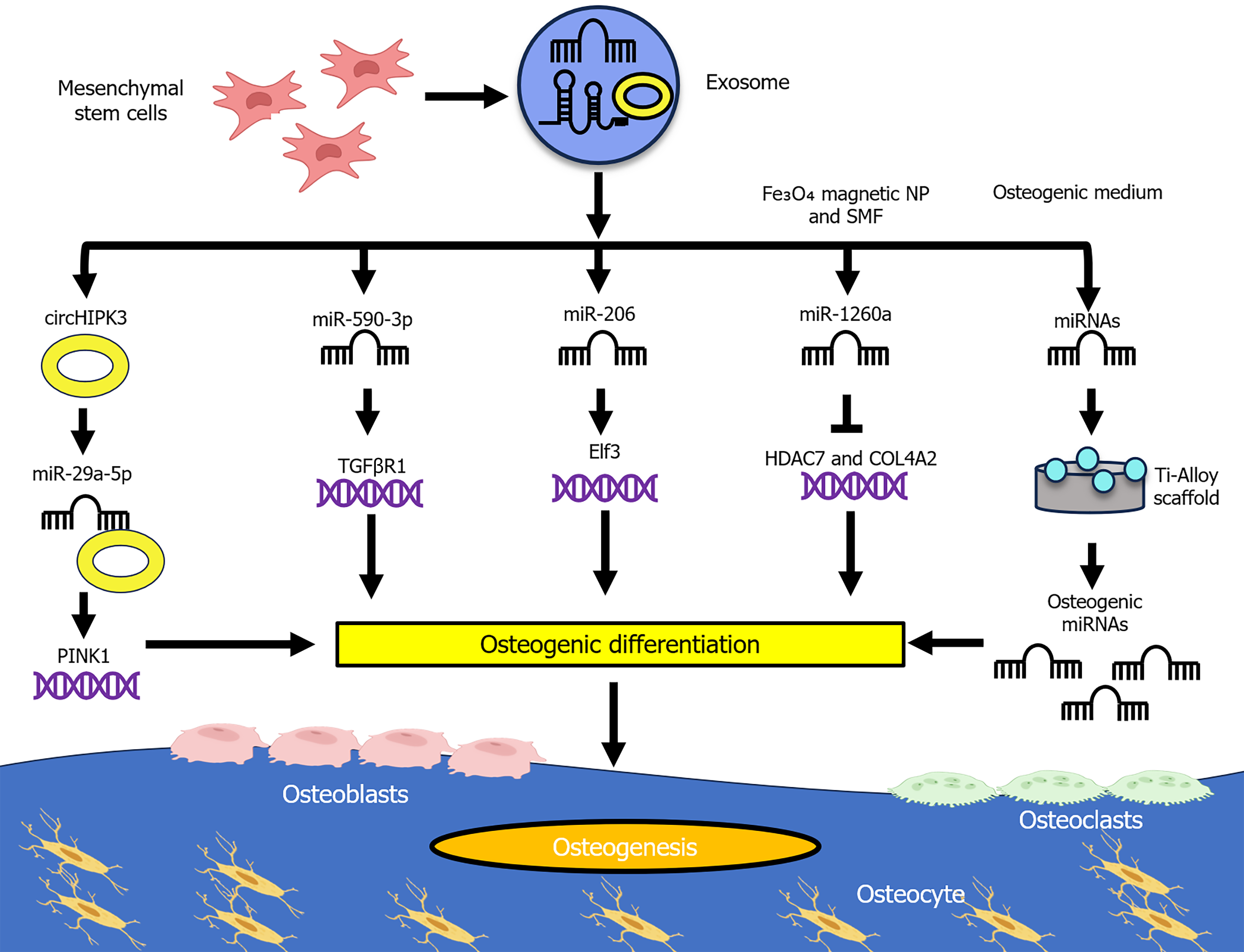
Figure 1 Role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNA in bone homeostasis.
A schematic diagram illustrates the role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNAs in osteogenesis, thereby contributing to the maintenance of bone homeostasis. NP: Nanoparticles; SMF: Static magnetic field; PINK1: Phosphatase and tensin homolog induced putative kinase 1; TGFβR1: Transforming growth factor beta receptor 1; Elf3: E74-like factor 3; HDAC7: Histone deacetylase 7; COL4A2: Collagen type IV alpha 2 chain.
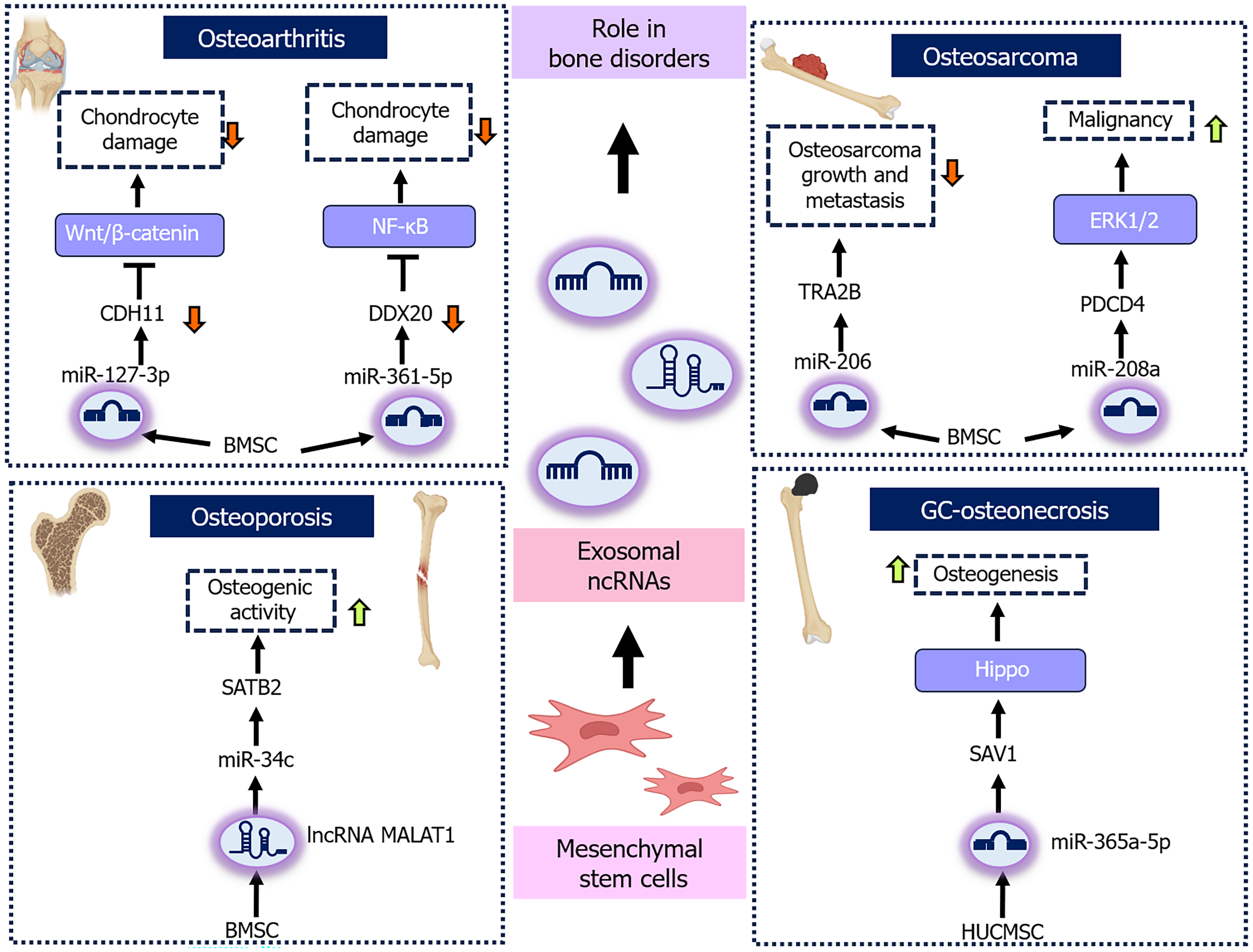
Figure 2 Molecular mechanisms regulated by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNAs in bone related disorders.
The diagram depicts various molecular pathways and targets through which mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNAs exert regulatory roles in bone-related disorders, including osteoarthritis, osteosarcoma, glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis, and osteoporosis. Wnt: Wingless/integrated; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; CDH11: Cadherin-11; DDX20: Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp-box polypeptide 20; BMSC: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-related kinases 1/2; TRAB2: Transformer 2β; PDCD4: Programmed cell death protein 4; SATB2: Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; MALAT1: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; ncRNAs: Non-coding RNAs; GC: Gastric cancer; SAV1: Salvador homolog 1; HUCMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Chidambaram D, Subashini V, Nanthanalaxmi M, Selvamurugan N. Role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNAs in bone and bone-related disorders. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(10): 111241
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i10/111241.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i10.111241