©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Clin Oncol. Jan 24, 2026; 17(1): 113600
Published online Jan 24, 2026. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.113600
Published online Jan 24, 2026. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.113600
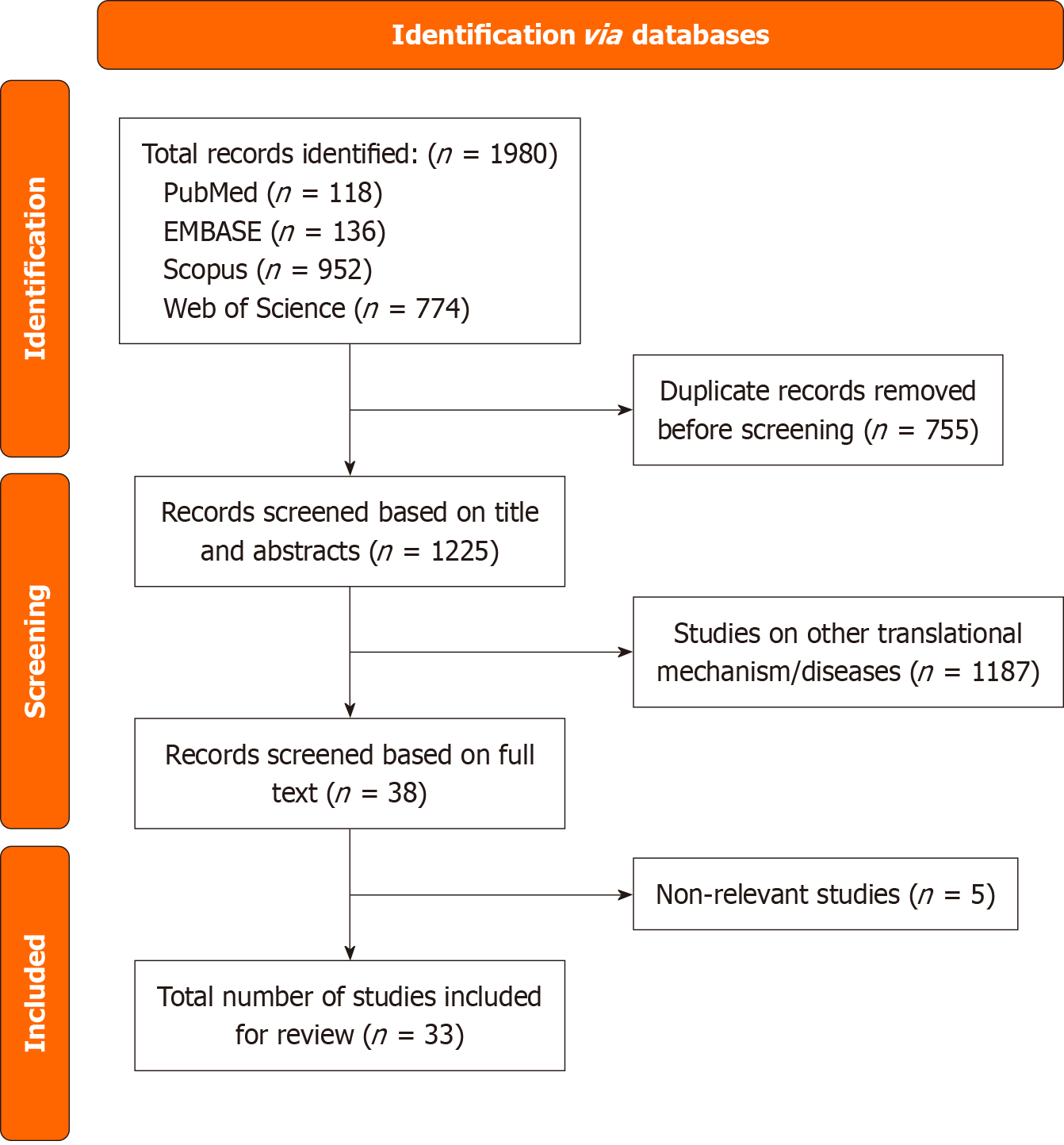
Figure 1 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses flow chart outlining the literature search and study selection process.
All cartoons in this figure were prepared using BioRender (Supplementary material).
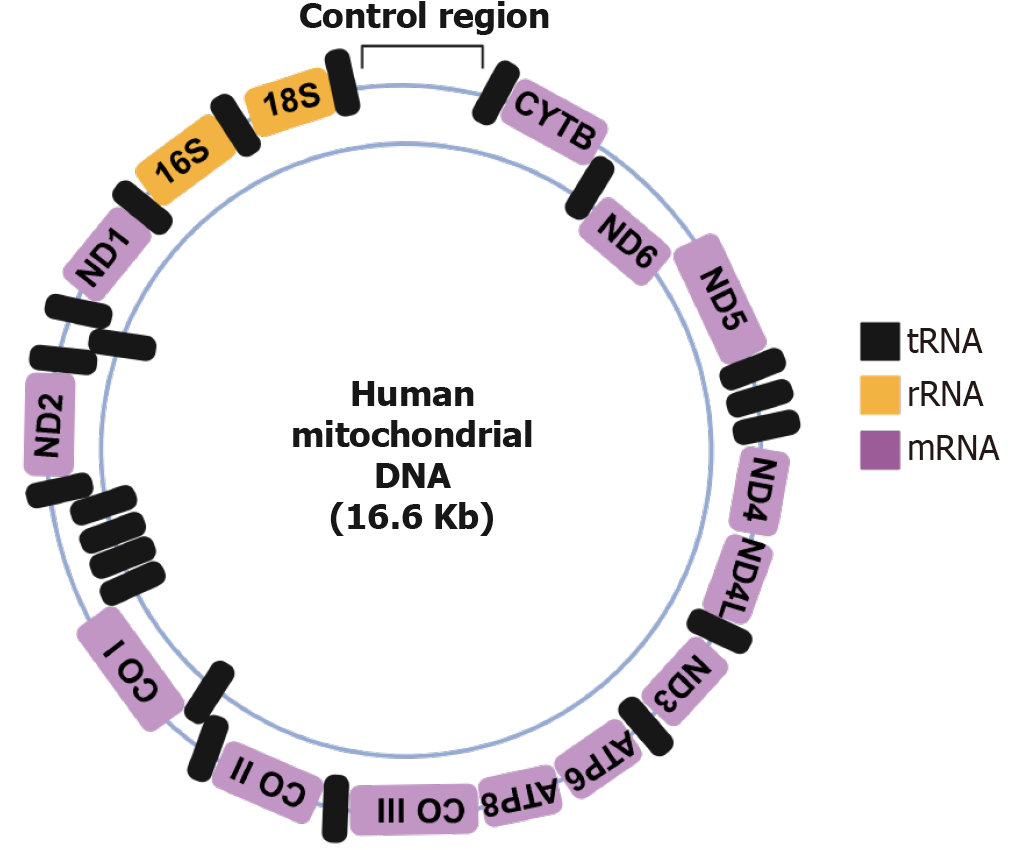
Figure 2 Structure of mitochondrial DNA.
tRNA: Transfer RNA; rRNA: Ribosomal RNA; mRNA: Messenger RNA. All cartoons in this figure were prepared using BioRender (Supplementary material).
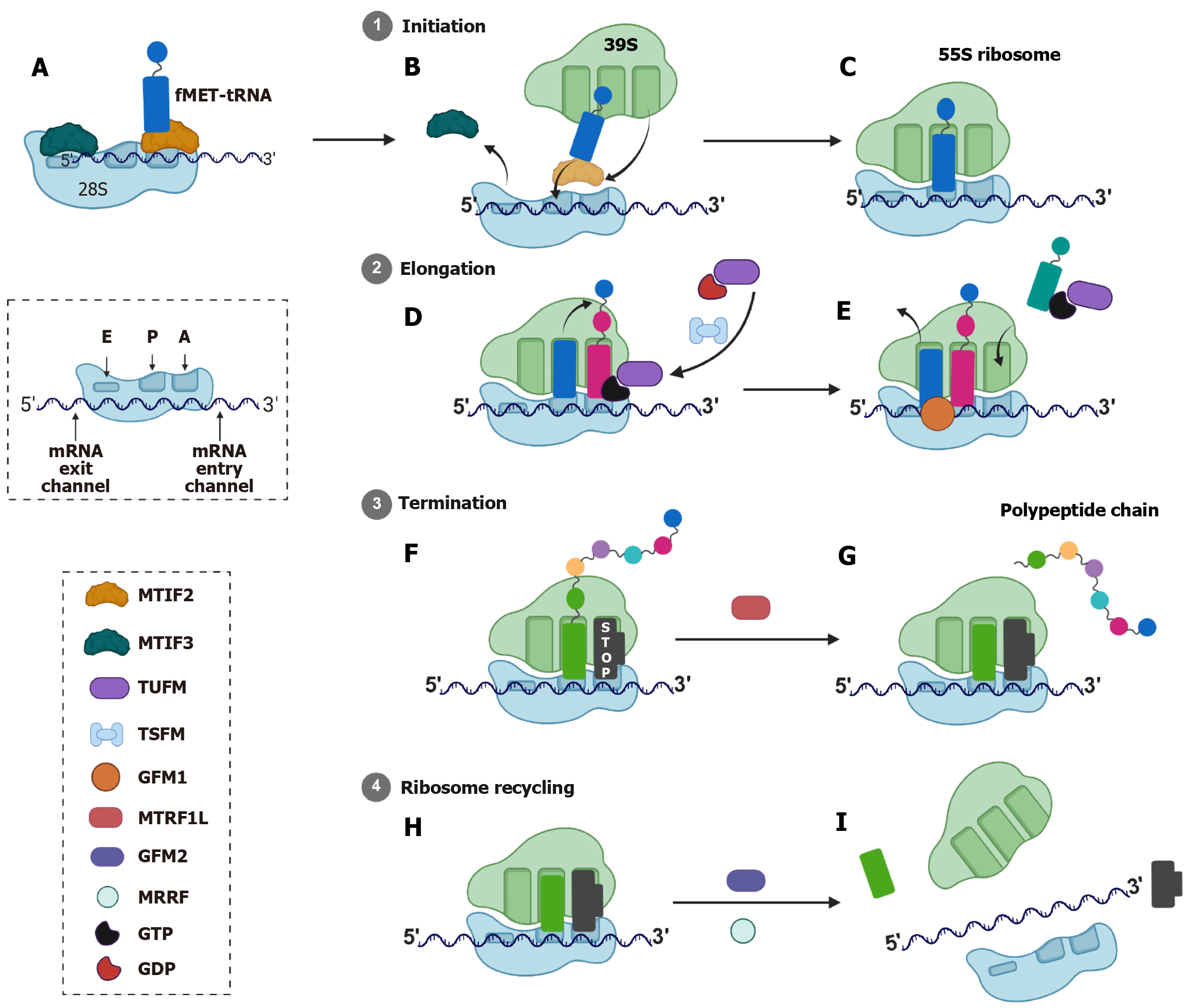
Figure 3 Schematic representation of mitochondrial translation.
A-C: Initiation: The small mitochondrial ribosomal subunit (28S) associates with messenger RNA (mRNA) and initiator formylmethionyl-transfer RNA, facilitated by initiation factors mitochondrial initiation factor 2 and mitochondrial initiation factor 3 The large subunit (39S) then joins to form the complete 55S mitoribosome; D and E: Elongation: Aminoacyl-transfer RNAs are delivered to the ribosome by the elongation factor mitochondrial elongation factor Tu, and peptide bond formation occurs. Mitochondrial elongation factor Ts helps in the exchange of guanosine triphosphate with guanosine triphosphate for mitochondrial elongation factor Tu, and mitochondrial elongation factor G1 assists in the translocation step; F and G: Termination: Release factors (Mitochondrial release factor 1A) promote polypeptide chain release upon reaching a stop codon; H and I: Ribosome recycling: Ribosome recycling factors (mitochondrial ribosome recycling factor, mitochondrial elongation factor G2) facilitate dissociation of the ribosomal subunits and release of mRNA. Inset (left): The ribosome’s E, P, and A sites and the entry/exit channels for mRNA. Inset (bottom left): Legend of translation factors and cofactors involved in each step. fMET: Formylmethionyl; tRNA: Transfer RNA; mRNA: Messenger RNA; MTIF: Mitochondrial initiation factor; TUFM: Mitochondrial elongation factor Tu; TSFM: Mitochondrial elongation factor Ts; GFM1: Mitochondrial elongation factor G1; MTRF1 L: Mitochondrial release factor 1A; GFM2: Mitochondrial elongation factor G2; MRRF: Mitochondrial ribosome recycling factor; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; GDP: Guanosine diphosphate. All cartoons in this figure were prepared using BioRender (Supplementary material).
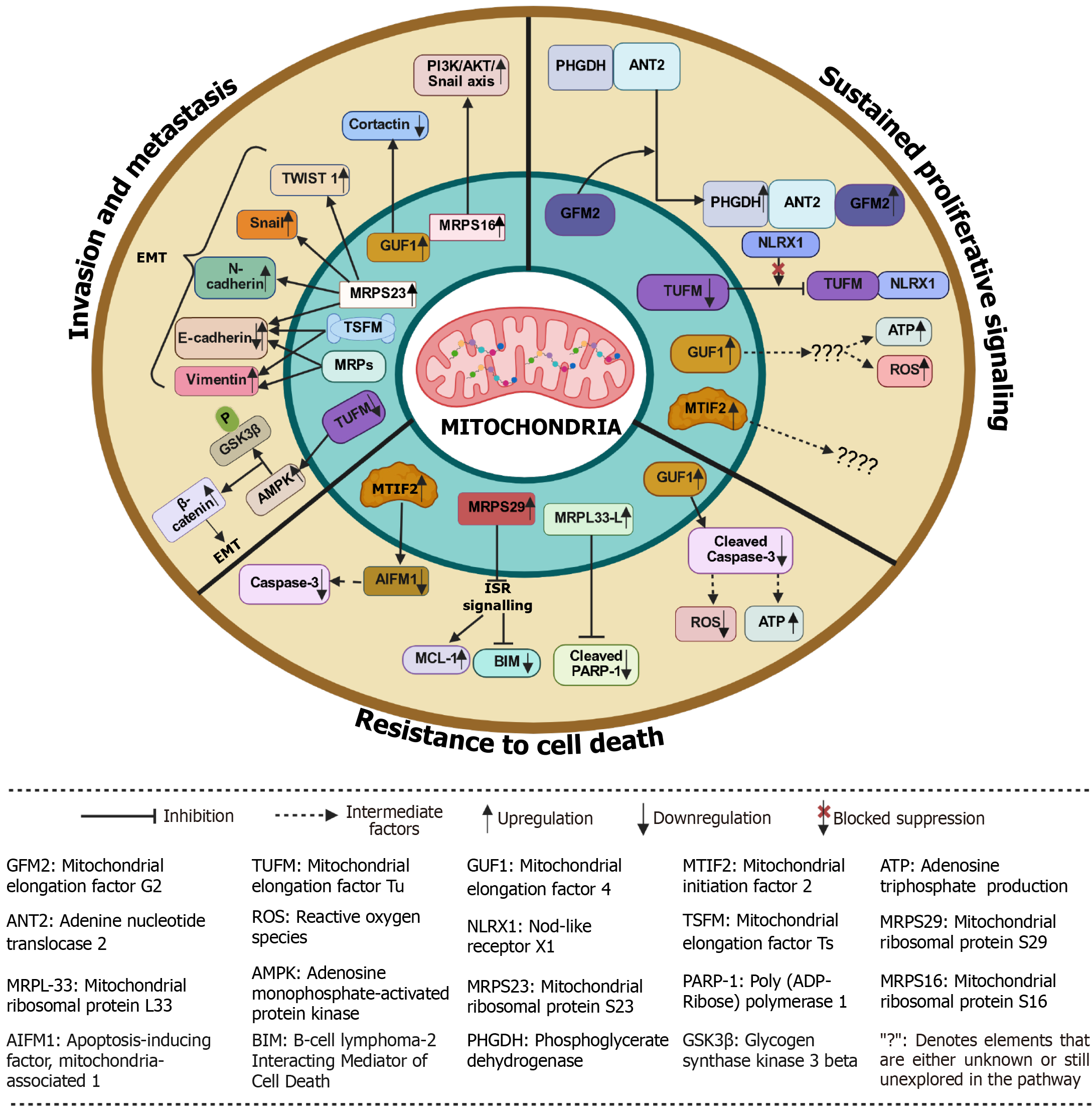
Figure 4 Mechanism of mitochondrial translation factors.
The inner blue circle contains all the translation factors. The outer orange circle represents the downstream mechanism of the translation factors. All cartoons in this figure were prepared using BioRender (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Agarwal N, Sharma U, Shree A, Kumar RR, Gorain JK, Vishwas V, Jahan F, Singh A, Palanichamy JK, Pushpam D, Bakhshi R, Chopra A, Sahoo RK, Batra A, Sharawat SK, Bakhshi S. Pleiotropic regulation of mitochondrial translational factors in governing proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis during cancer progression. World J Clin Oncol 2026; 17(1): 113600
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v17/i1/113600.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.113600