©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Clin Oncol. Jan 24, 2026; 17(1): 112801
Published online Jan 24, 2026. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.112801
Published online Jan 24, 2026. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.112801
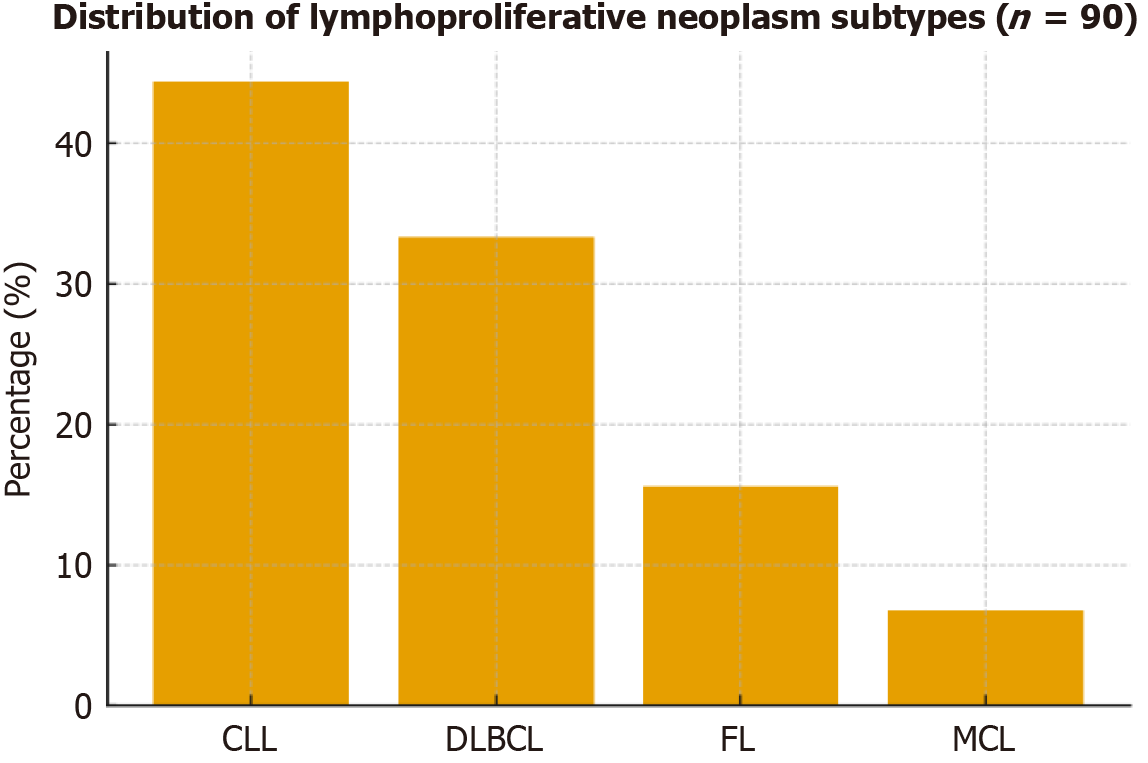
Figure 1 Distribution of lymphoma subtypes in patients (n = 90).
Bar chart for distribution of lymphoproliferative neoplasm subtypes (chronic lymphocytic leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma). CLL: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; FL: Follicular lymphoma; MCL: Mantle cell lymphoma.
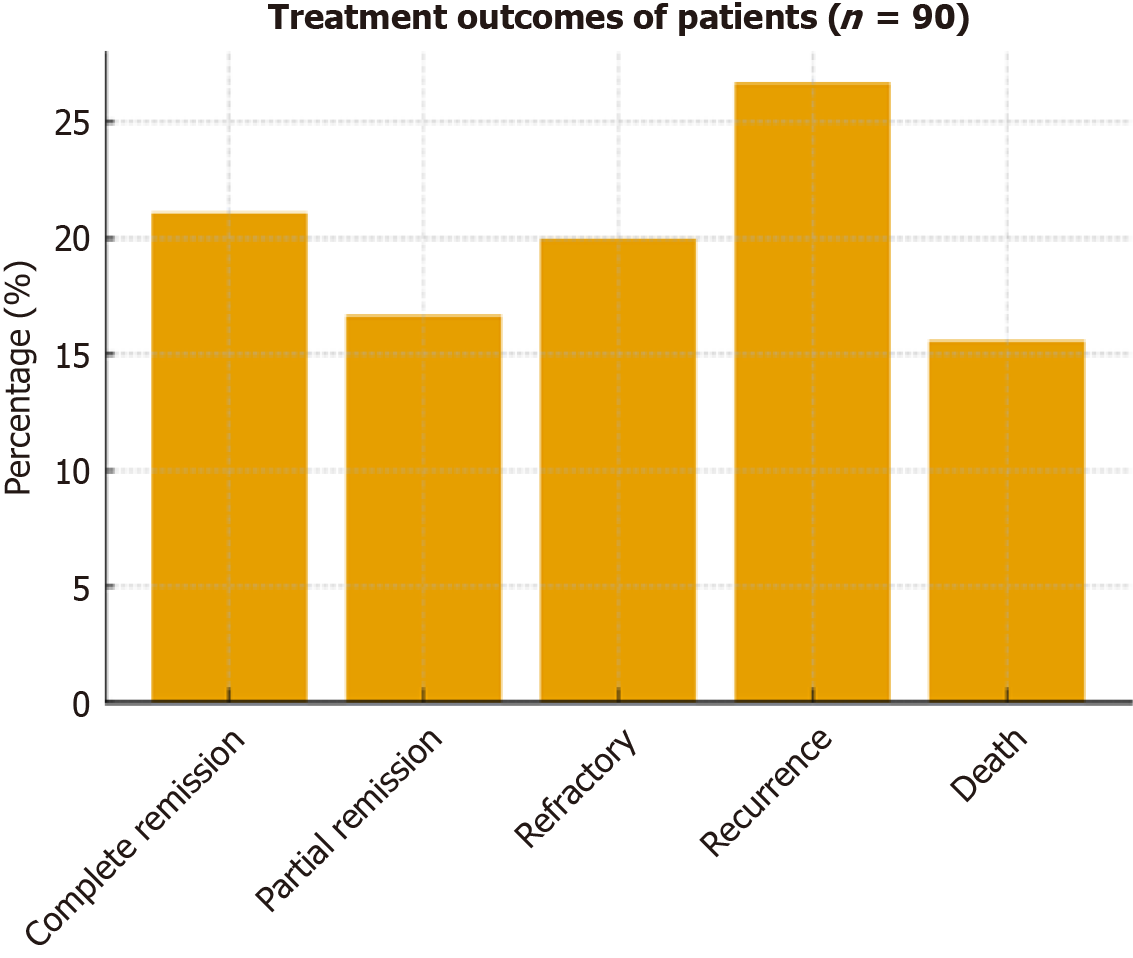
Figure 2 Treatment outcomes in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
Bar chart for treatment outcomes (complete remission, partial remission, refractory, recurrence, death).
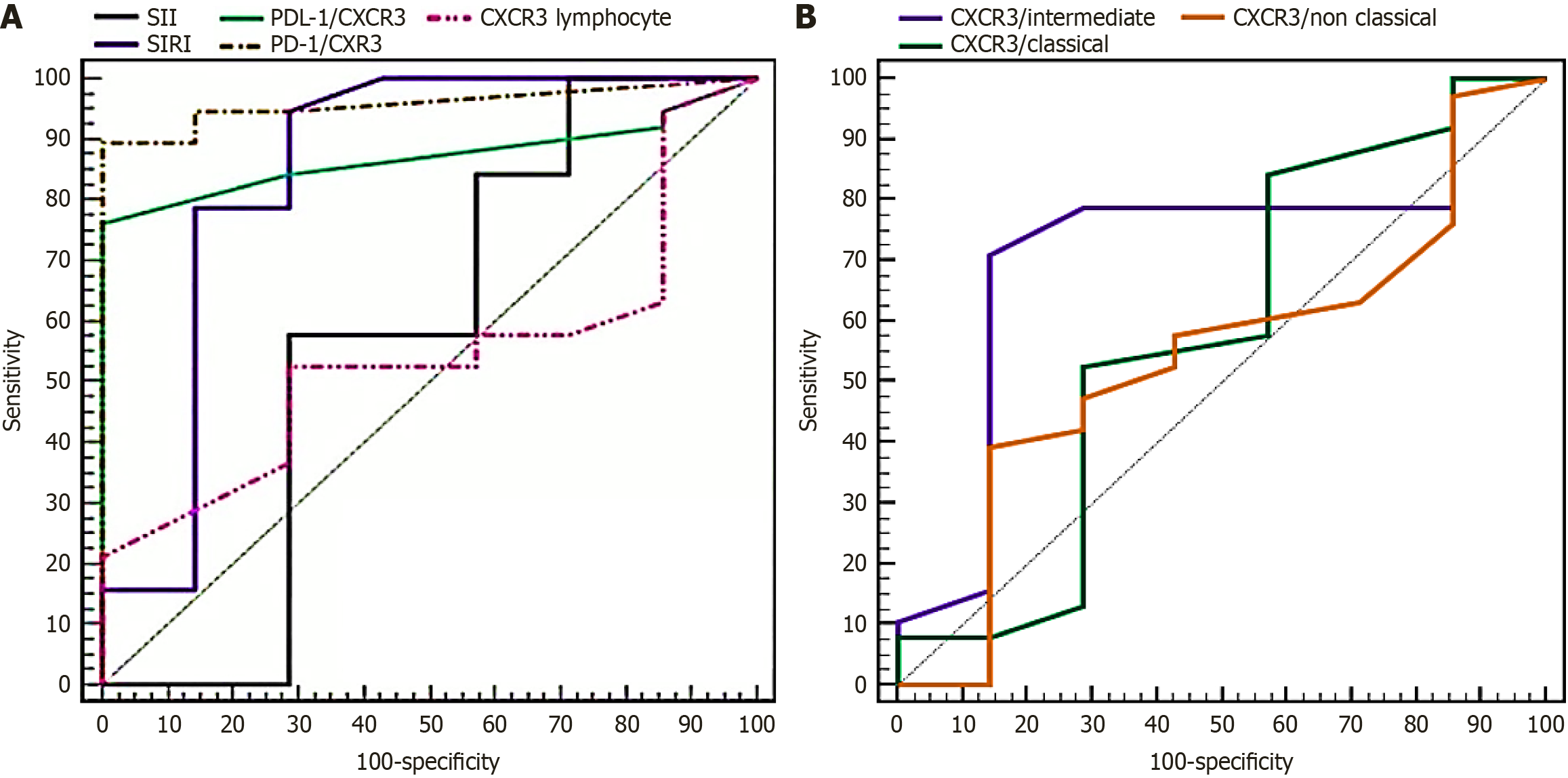
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves for biomarkers predicting stage IV lymphoma.
A: Receiver operating characteristic curves for the systemic inflammation response index, programmed death-ligand 1/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3), and programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3; B: Receiver operating characteristic curves for CXCR3/monocyte subsets. SII: Systemic immune-inflammation index; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1.
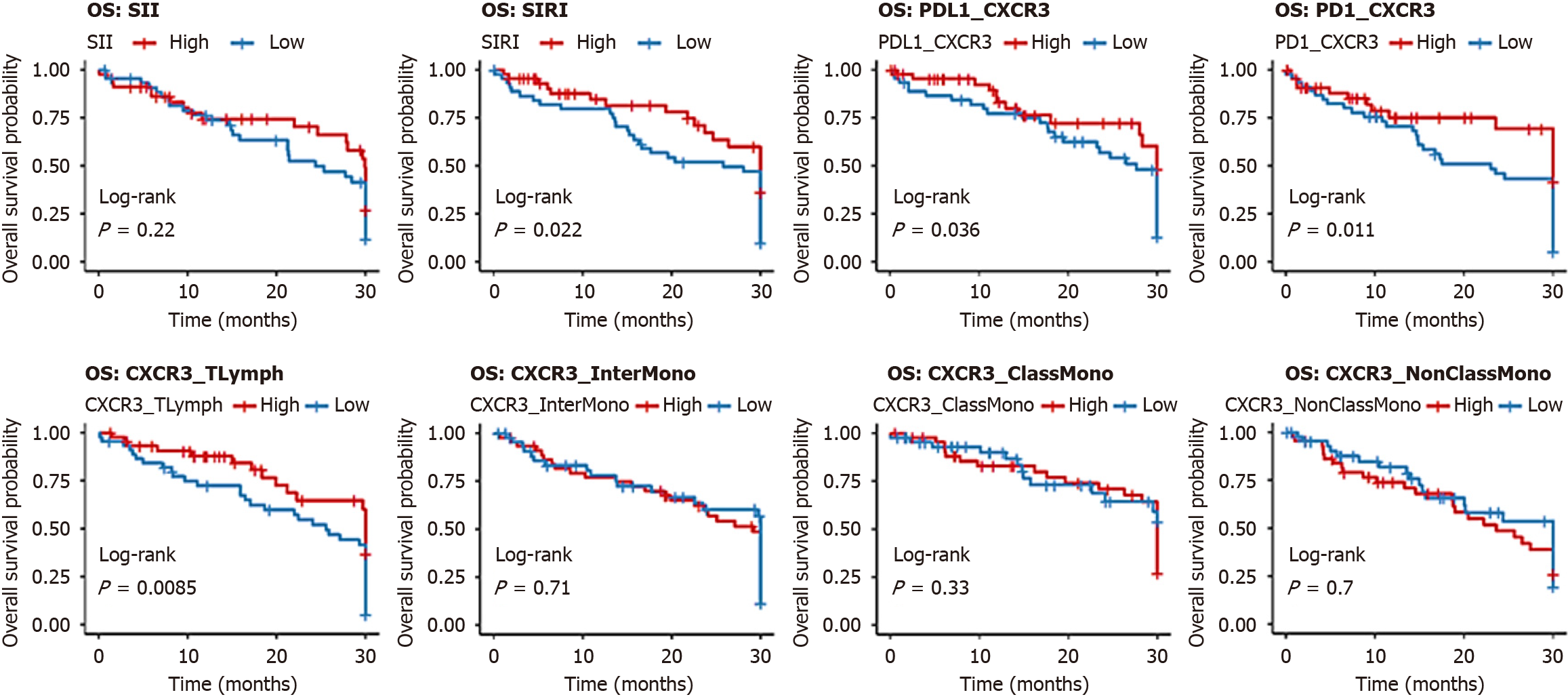
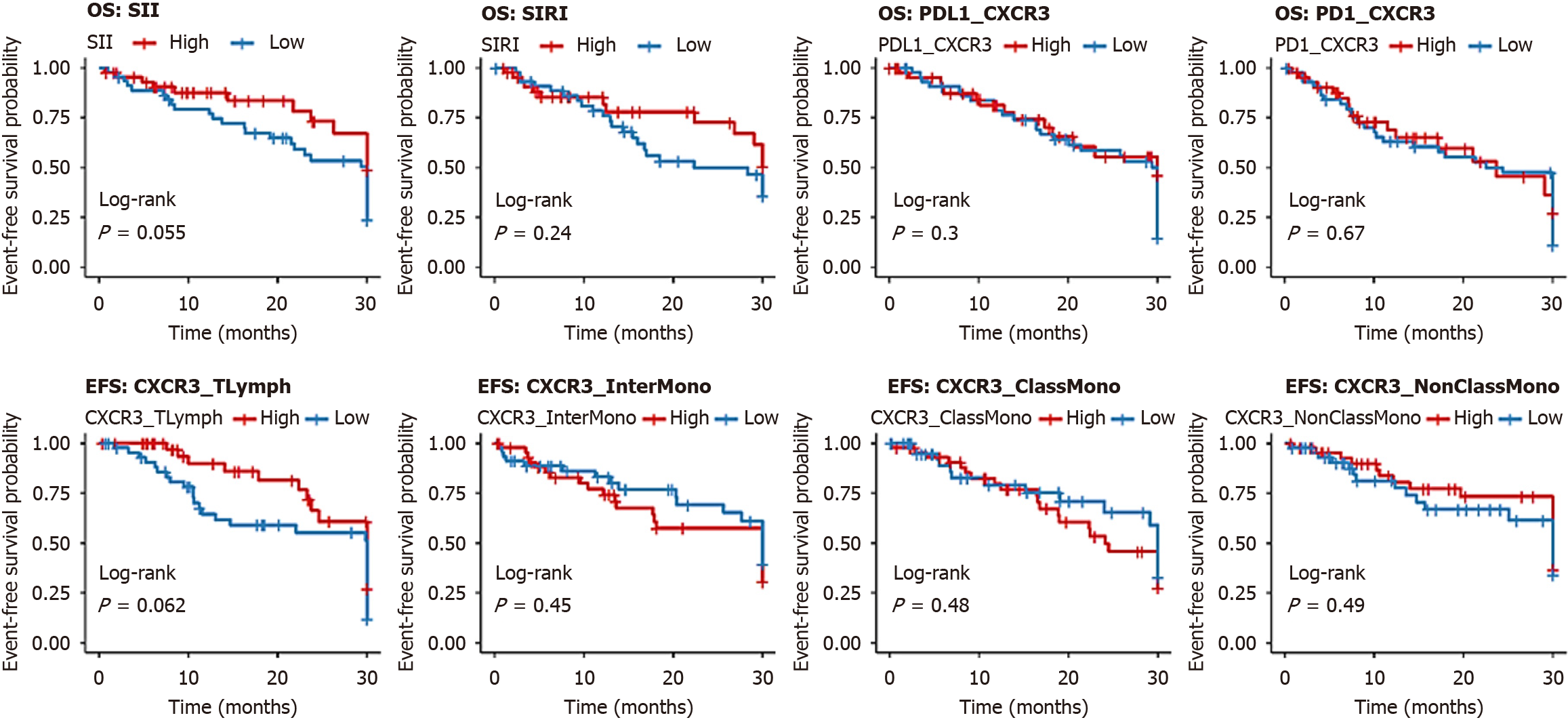
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival by biomarker levels in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
Eight panels (4 grid × 2 grid) show overall survival curves for low (n = 45, blue) vs high (n = 45, red) levels of the systemic immune-inflammation index, systemic inflammation response index, programmed death-ligand 1/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3), programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3, CXCR3/T lymphocytes, CXCR3/intermediate monocytes, CXCR3/classical monocytes, and CXCR3/non-classical monocytes. Log-rank P-values and χ2 statistics are annotated, with risk tables showing the number at risk over time. OS: Overall survival; SII: Systemic immune-inflammation index; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1.
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier curves for event-free survival by biomarker levels in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
Eight panels (4 grid× 2 grid) show event-free survival curves for low (n = 45, blue) vs high (n = 45, red) levels of the systemic immune-inflammation index, systemic inflammation response index, programmed death-ligand 1/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3), programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3, CXCR3/T lymphocytes, CXCR3/intermediate monocytes, CXCR3/classical monocytes, and CXCR3/non-classical monocytes. Log-rank P-values and χ2 statistics are annotated, with risk tables showing the number at risk over time. OS: Overall survival; SII: Systemic immune-inflammation index; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; EFS: Event-free survival.
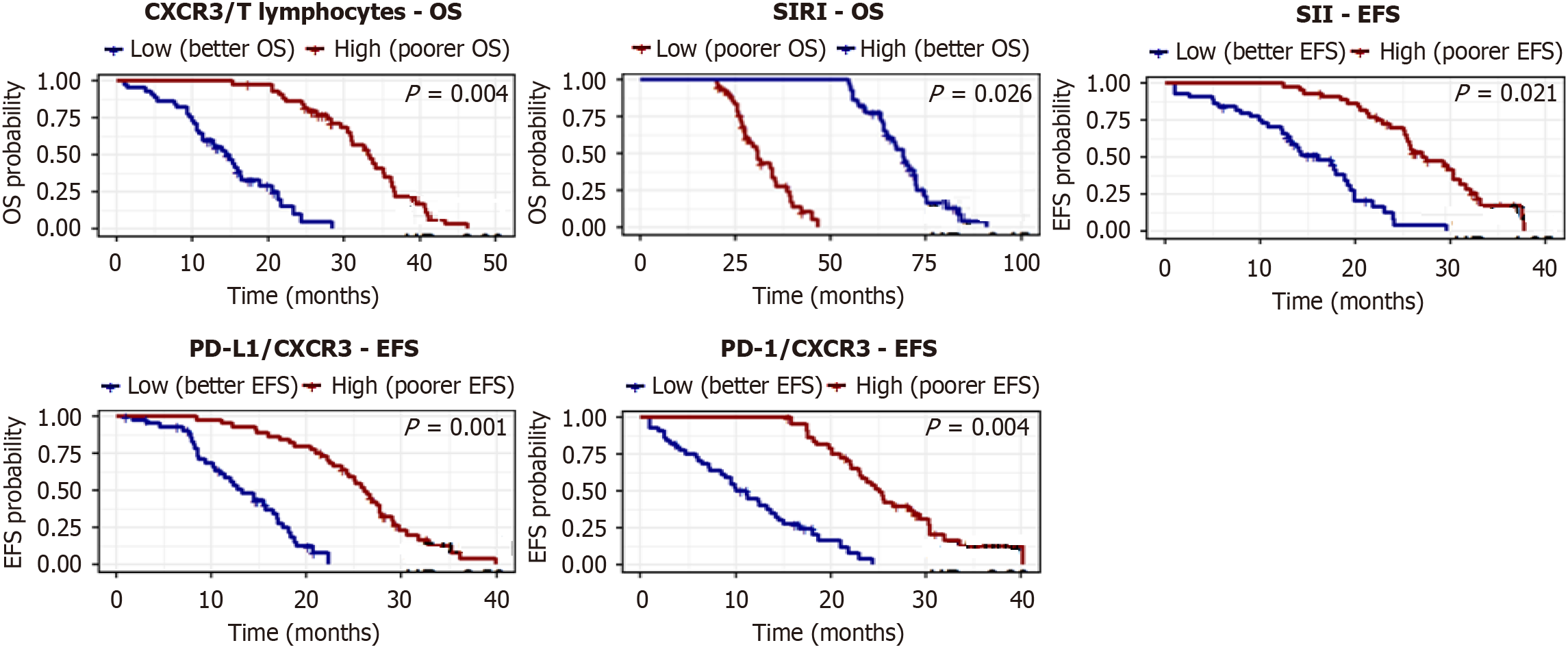
Figure 6 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for overall survival and event-free survival stratified by high vs low biomarker levels in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
Panels show overall survival for C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3)/T lymphocytes and the systemic inflammation response index, and event-free survival for the systemic immune-inflammation index, programmed death-ligand 1/CXCR3, and programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3. P-values are from log-rank tests, with risk tables below each curve. Biomarkers with the lowest P-values from multivariate Cox regression. CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; OS: Overall survival; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index; SII: Systemic immune-inflammation index; EFS: Event-free survival; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1.
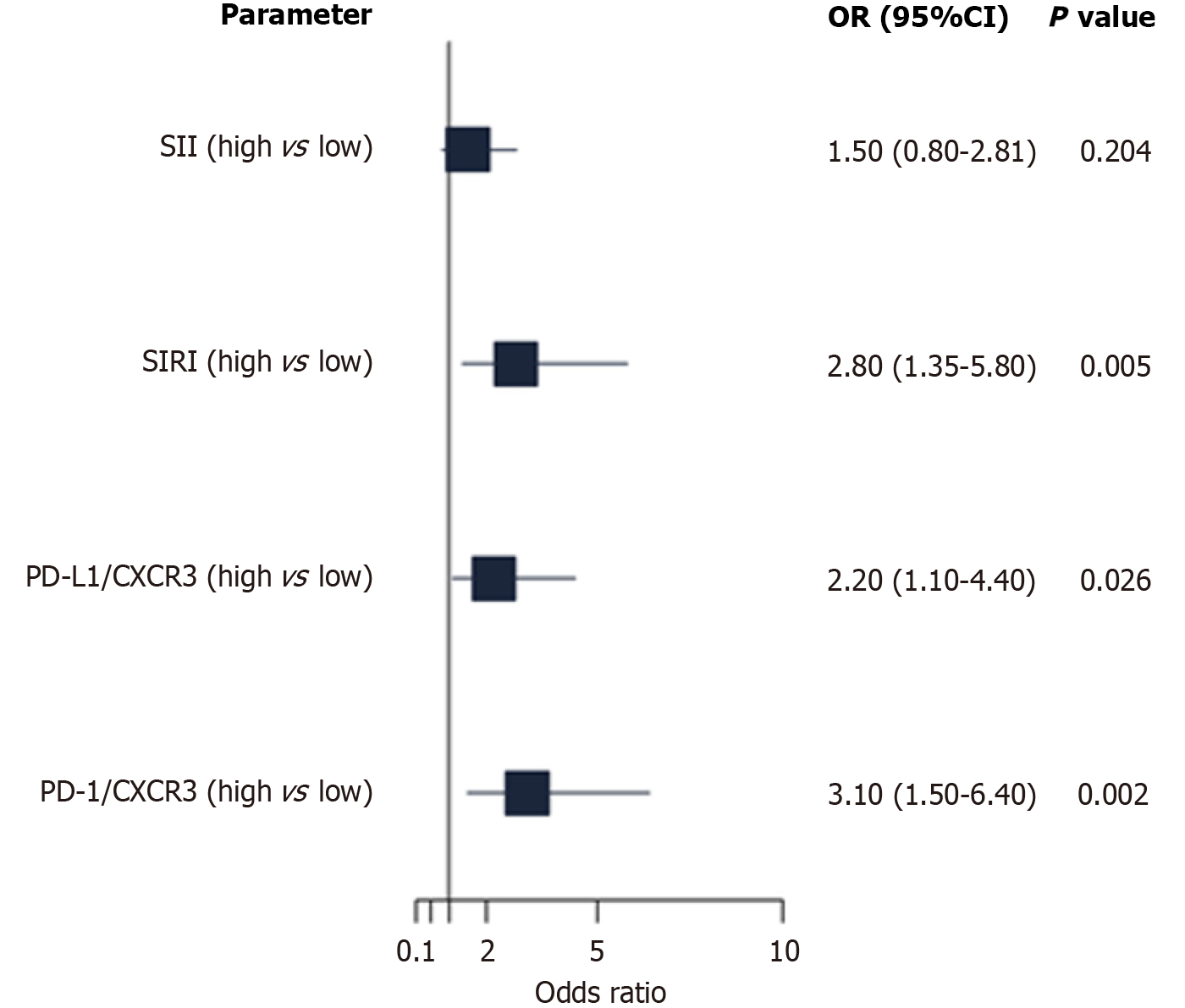
Figure 7 Forest plot of odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals from multivariate logistic regression for stage IV lymphoma in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
Parameters include the systemic immune-inflammation index, systemic inflammation response index, programmed death-ligand 1/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3), and programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3. Dark blue indicates a non-significant association (P ≥ 0.05) for the systemic immune-inflammation index, and dark red indicates significant associations (P < 0.05) for systemic inflammation response index, programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3, and programmed cell death protein 1/CXCR3, adjusted for age, sex, and subtype. SII: Systemic immune-inflammation index; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
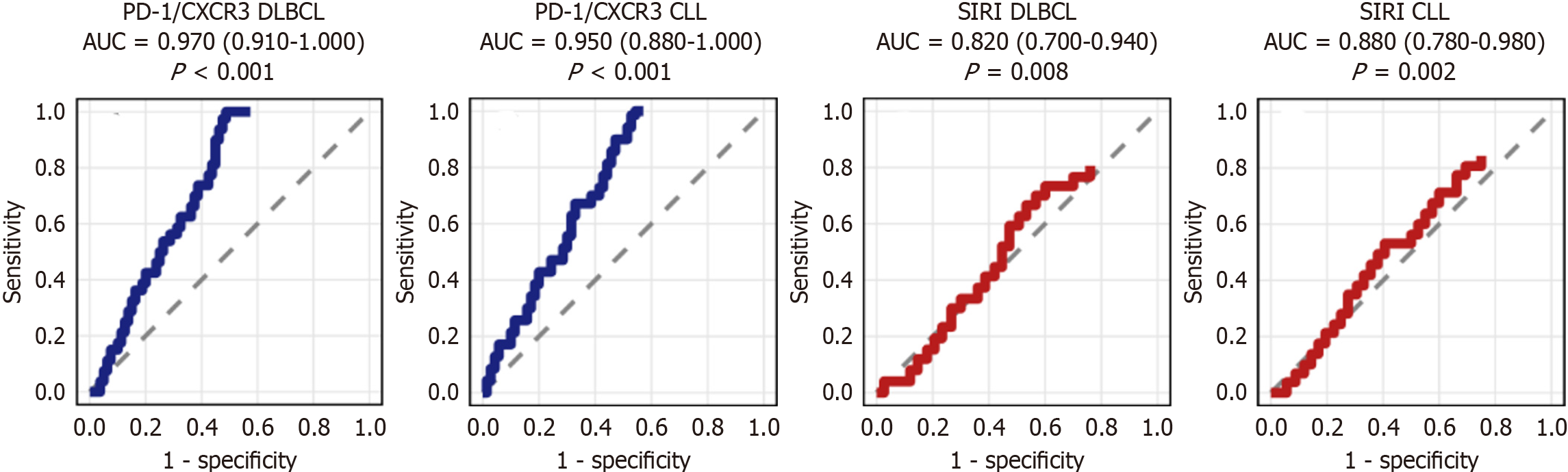
Figure 8 Receiver operating characteristic curves for the diagnosis of stage IV lymphoma stratified by subtype in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
The panels show programmed death-ligand 1/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [DLBCL; area under the curve (AUC) = 0.970], programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/CXCR3 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (AUC = 0.950), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) in DLBCL (AUC = 0.820), and SIRI in CLL (AUC = 0.880). Zigzag stepped lines represent real receiver operating characteristic curves from discrete classification thresholds. Dark blue indicates PD-1/CXCR3; dark red indicates SIRI. All AUCs are statistically significant (P < 0.001 for PD-1/CXCR3, P = 0.008 for SIRI in DLBCL, P = 0.002 for SIRI in CLL). The dashed diagonal line represents chance performance (AUC = 0.5). PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; AUC: Area under the curve; CLL: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index.
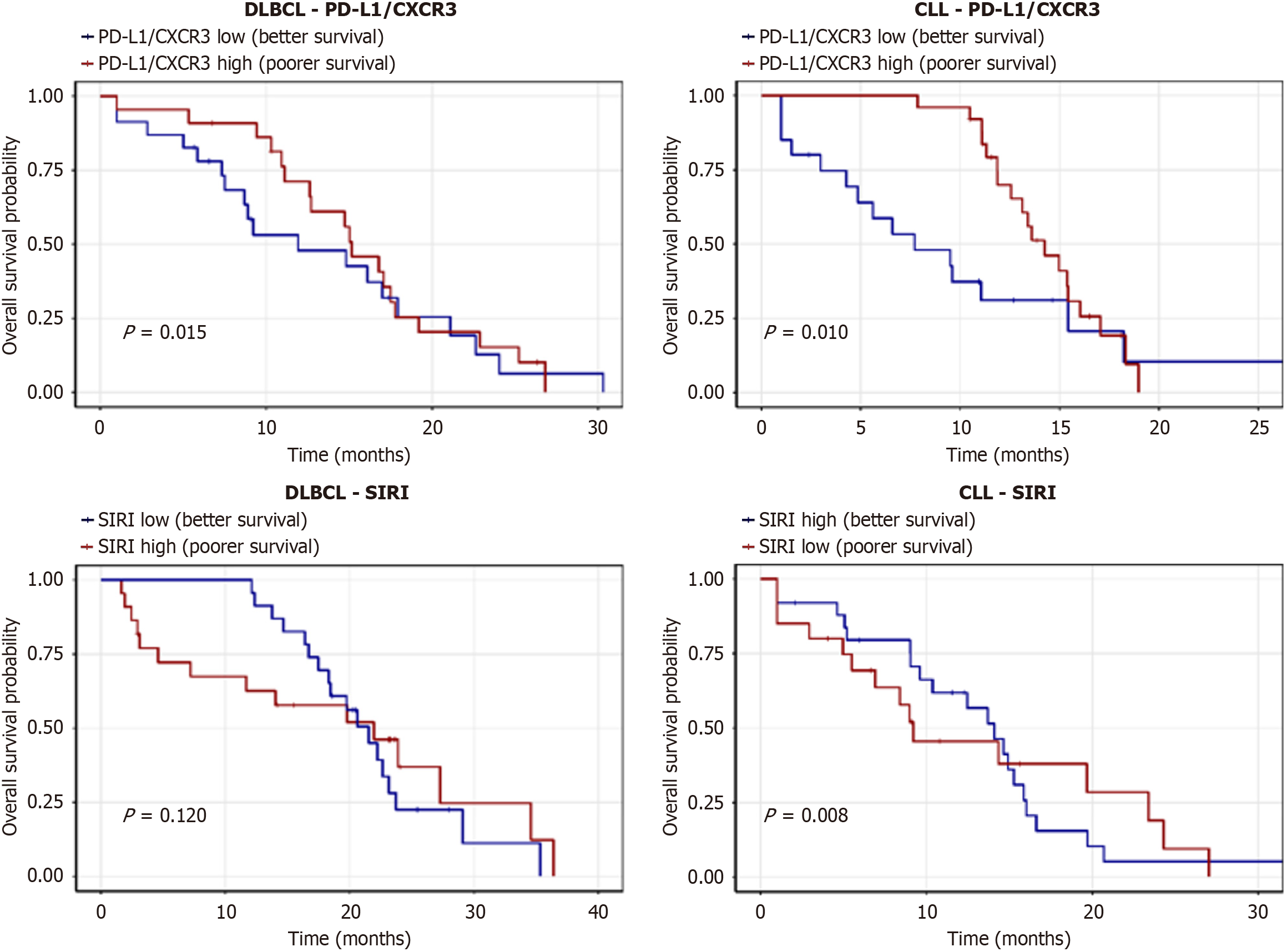
Figure 9 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for overall survival stratified by biomarker levels and subtype in patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms (n = 90).
Panels show programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3) (low vs high) for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and the systemic inflammation response index (SIRI; high vs low) for DLBCL and CLL. Dark blue indicates the group with longer overall survival (low PD-L1/CXCR3 in both subtypes, high SIRI in CLL), and dark red indicates the contrast group (high PD-L1/CXCR3, low SIRI in CLL, and high SIRI in DLBCL, where non-significant). P-values are from log-rank tests, with risk tables below each curve. Mean overall survival values are 285 ± 1.5 months for low PD-L1/CXCR3 in DLBCL, 30.0 ± 1.0 months in CLL, 20.0 ± 2.0 months for high SIRI in DLBCL, and 25.0 ± 1.5 months in CLL. DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; CCL: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index.
- Citation: Sherief DE, Nosair N, Abdelhameed AM, Sadaka E, Othman AAA, Elgamal R. Prognostic significance of PD-L1/PD-1 co-expression and CXCR3-driven inflammatory signatures in Egyptian patients with lymphoproliferative neoplasms. World J Clin Oncol 2026; 17(1): 112801
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v17/i1/112801.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.112801