©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2025; 16(12): 111544
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.111544
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.111544
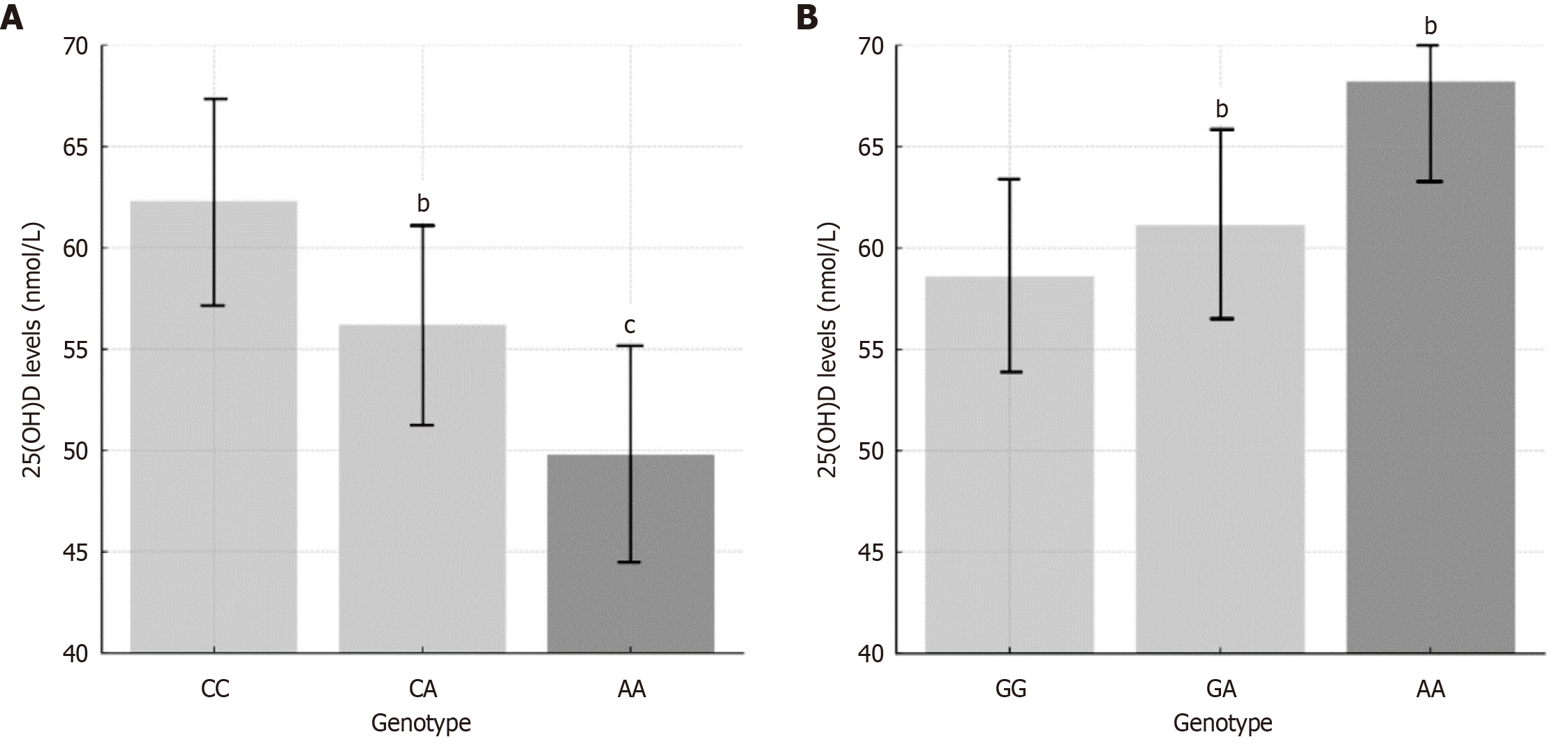
Figure 1 Association between group-specific component gene rs7041 and 25-hydroxylase gene rs10741657 polymorphisms and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.
A: Box plot showing serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels corresponding to the group-specific component rs7041 genotype (CC, CA, AA) in the study population. The 25(OH)D levels of AA genotype carriers were significantly lower than those of CC genotype carriers (cP < 0.001); B: Box plots showing serum 25(OH)D levels stratified by 25-hydroxylase rs10741657 genotype (GG, GA, AA). Serum 25(OH)D levels were higher in the AA genotype compared to the GG genotype (bP < 0.01). 25(OH)D: 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
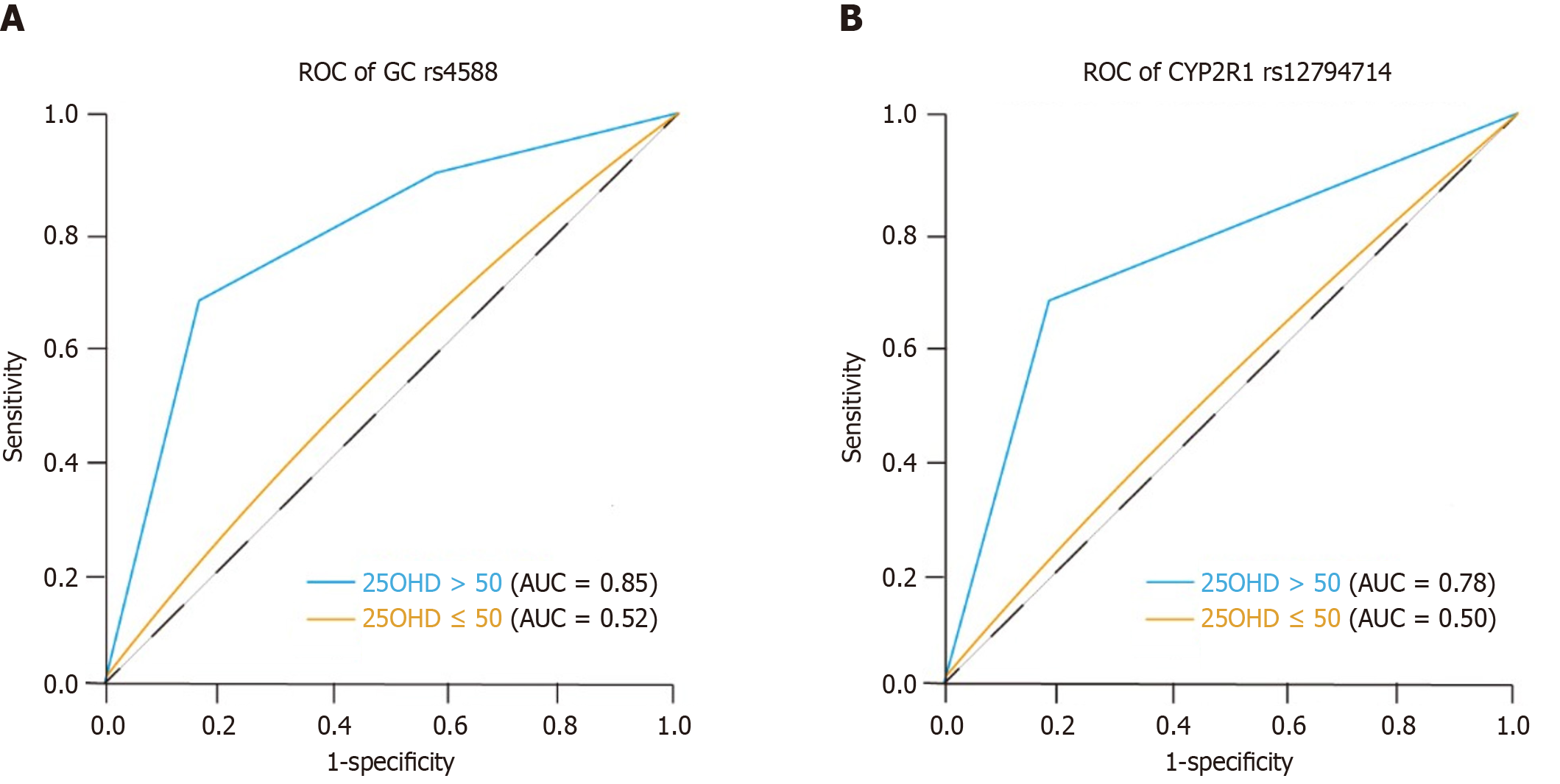
Figure 2 Stratified analysis of gene polymorphisms and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk/radiotherapy response by serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.
A: The association between the group-specific component gene rs4588 TT genotype and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk was significant only in the subgroup with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels > 50 nmol/L [odds ratio (OR) = 2.15, 95%CI: 1.32-3.51, P = 0.002]; B: The association between the 25-hydroxylase gene rs12794714 AA genotype and radiotherapy resistance was significant only in the subgroup with serum 25(OH)D levels > 50 nmol/L (OR = 2.43, 95%CI: 1.45-4.08, P < 0.001). AUC: Area under the curve; CYP2R1: 25-hydroxylase; GC: Group-specific component; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; 25(OH)D: 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
- Citation: Liu L, Shi DY, Tan J, Xu S, Liu CR. Group-specific component and 25-hydroxylase gene polymorphisms in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Associations with susceptibility and radiotherapy response. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(12): 111544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i12/111544.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.111544