©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2025; 17(9): 108049
Published online Sep 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i9.108049
Published online Sep 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i9.108049
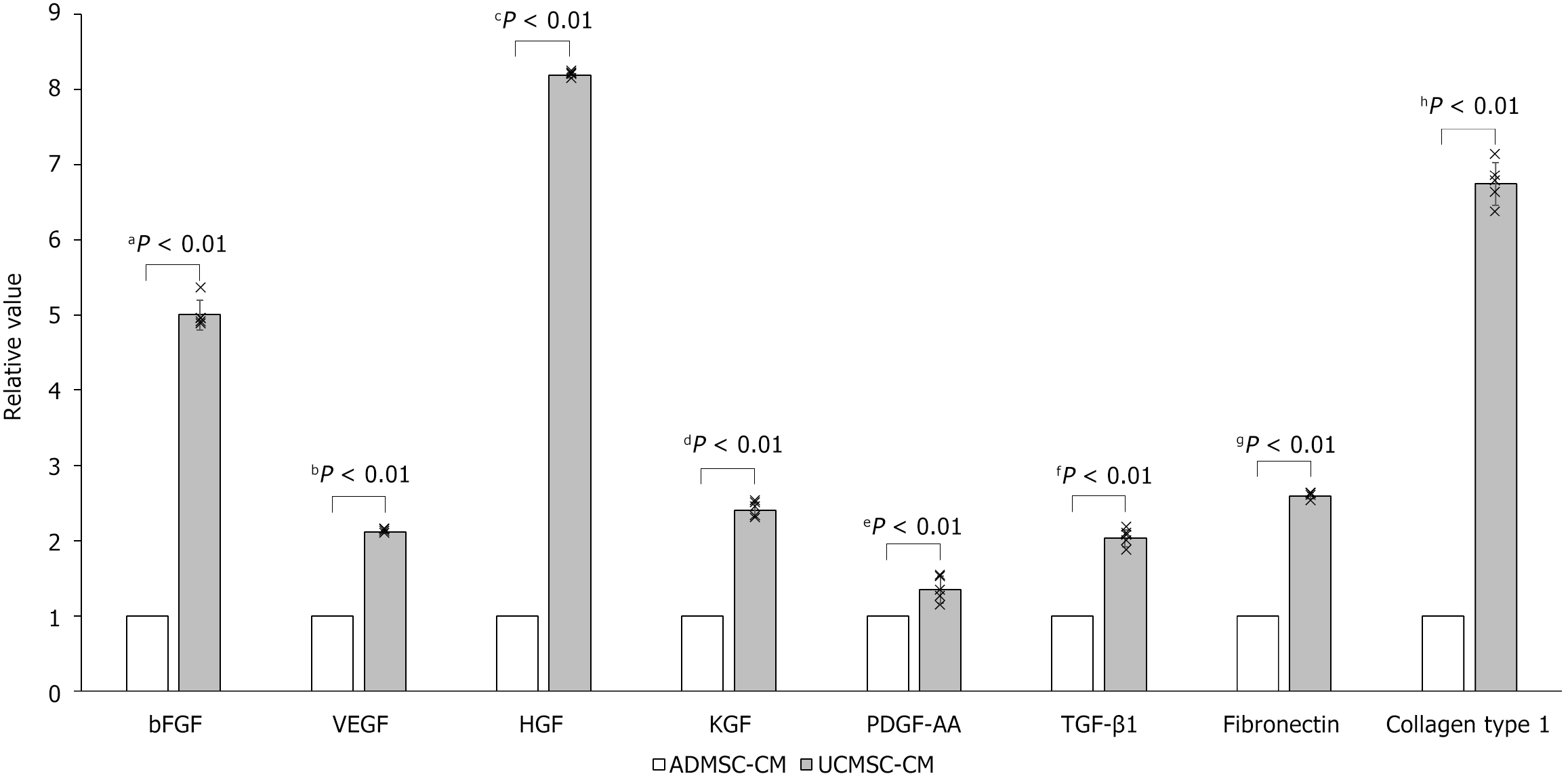
Figure 1 Comparison of effective factors for the prevention and treatment of skin aging in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
Data were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; KGF: Keratinocyte growth factor; PDGF-AA: Platelet-derived growth factor-AA; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-beta 1; ADMSC-CM: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium; UCMSC-CM: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
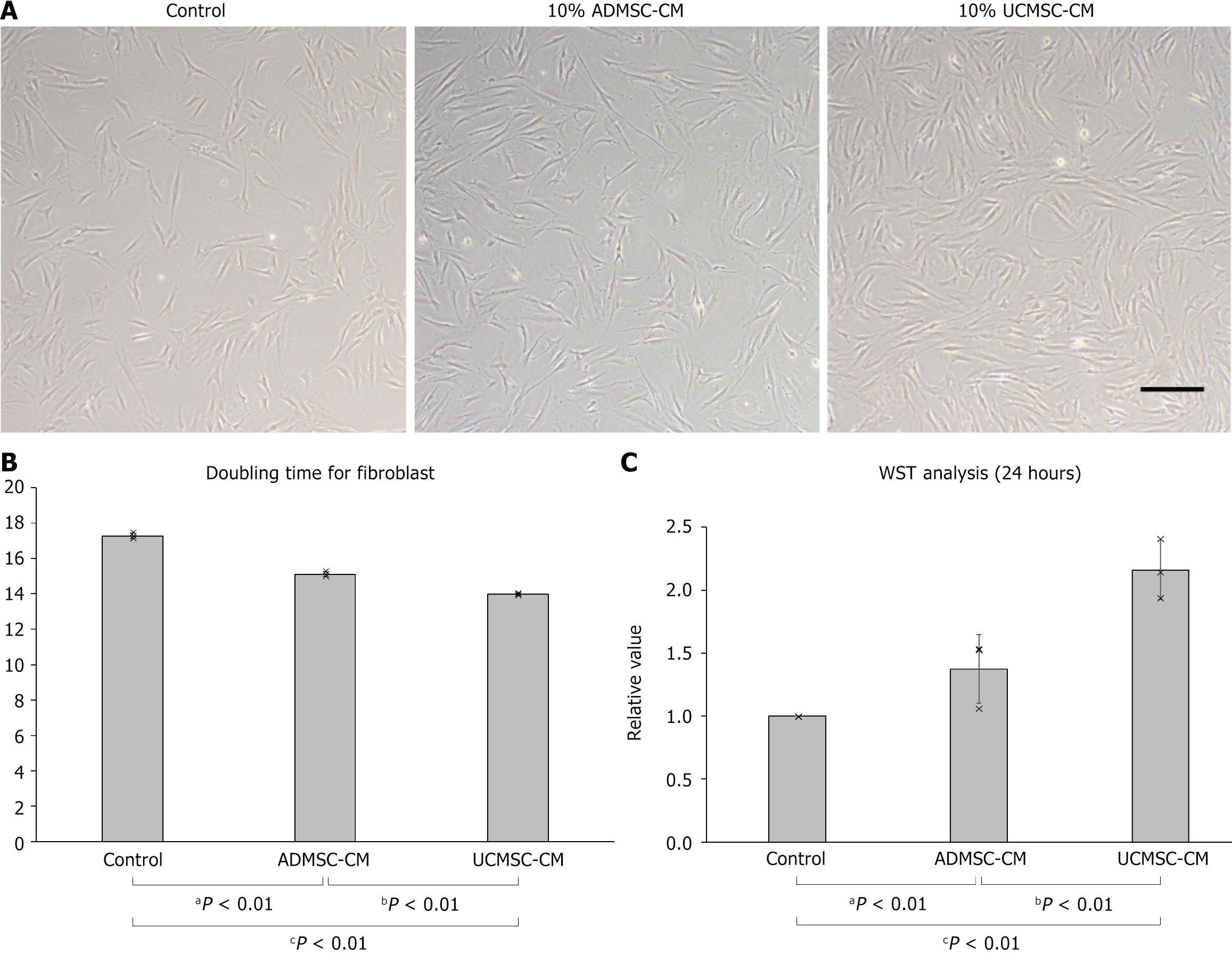
Figure 2 Enhanced proliferation ability of skin fibroblasts by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
A: Fibroblasts cultured for 72 hours in fibroblast medium containing 10% adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (ADMSC-CM) or umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium (UCMSC-CM). Scale bar = 250 μm; B: Doubling time, calculated from cell growth curves, of fibroblasts cultured in fibroblast medium with 10% ADMSC-CM or UCMSC-CM; C: WST analysis results of fibroblast culture in fibroblast media with 10% ADMSC-CM or UCMSC-CM. ADMSC-CM: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium; UCMSC-CM: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
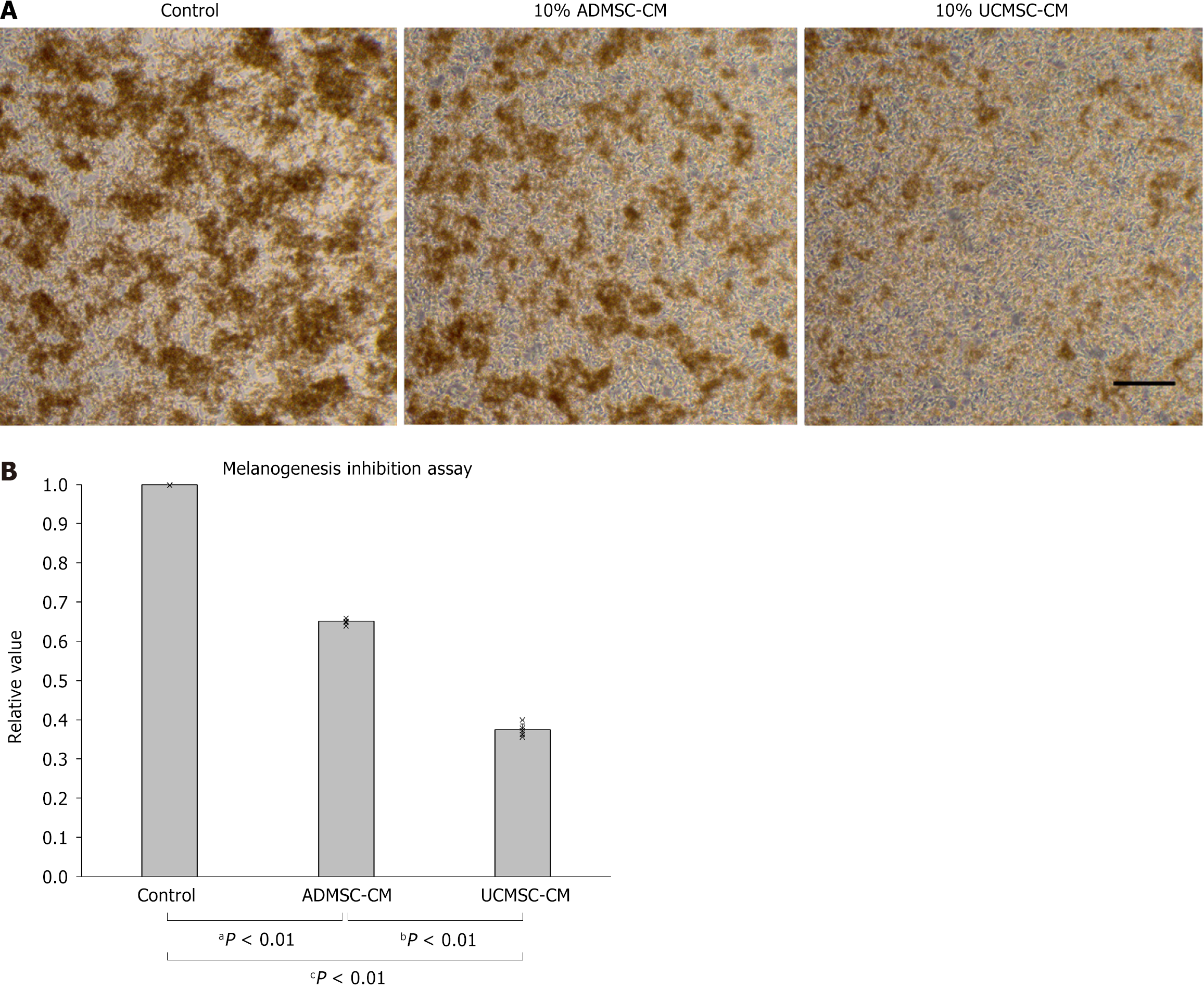
Figure 3 Inhibition of melanin production by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
A: B16F1 cells cultured in B16F1 culture media with α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and 10% adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell or umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium. Scale bar = 250 μm; B: Comparison of the amount of melanin synthesized by B16F1 cells cultured with 10% adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell or umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium. Data were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. ADMSC-CM: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium; UCMSC-CM: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
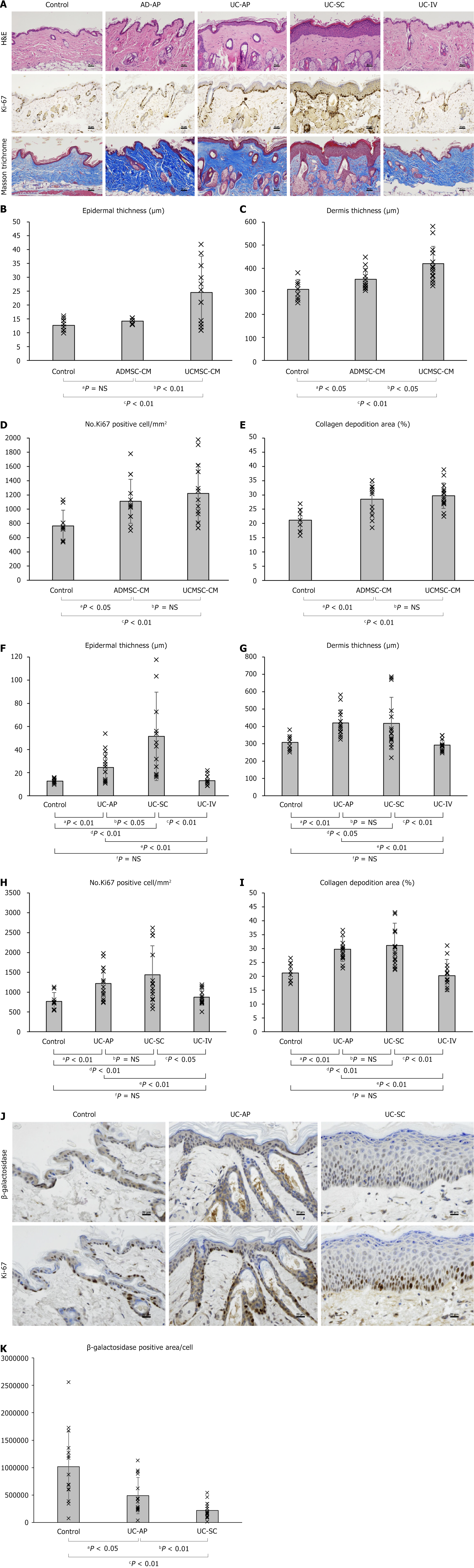
Figure 4 In vivo effectiveness test of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
A: Representative histological images of aged mouse skin stained with hematoxylin-eosin, Ki-67, and Masson’s Trichrome stains. Scale bar = 50 μm; B-E: Quantitative analysis of epidermal thickness (B), dermal thickness (C), number of Ki-67-positive cells per unit area (D), and collagen deposition area (E) according to the type of reagent; F-I: Quantitative analysis of epidermal thickness (F), dermal thickness (G) number of Ki-67-positive cells per unit area (H), and collagen deposition area (I) according to the method used for umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium administration; J: Serial sections of aged mouse skin stained with Ki-67 and β-galactosidase. Scale bar = 20 μm; K: Quantification of β-galactosidase expression per epidermal cell. All quantitative data (B-I and K) were obtained from color-based image analysis of stained tissue sections. NS: Not significant; AD-AP: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium application; UC-AP: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium application; UC-SC: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium subcutaneous injection; UC-IV: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium tail-vein injection; ADMSC-CM: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium; UCMSC-CM: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium.
- Citation: Ahn H, Han HS, Lee KH. Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media for preventing and treating skin aging. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(9): 108049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i9/108049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i9.108049