©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2025; 17(12): 112207
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.112207
Published online Dec 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.112207
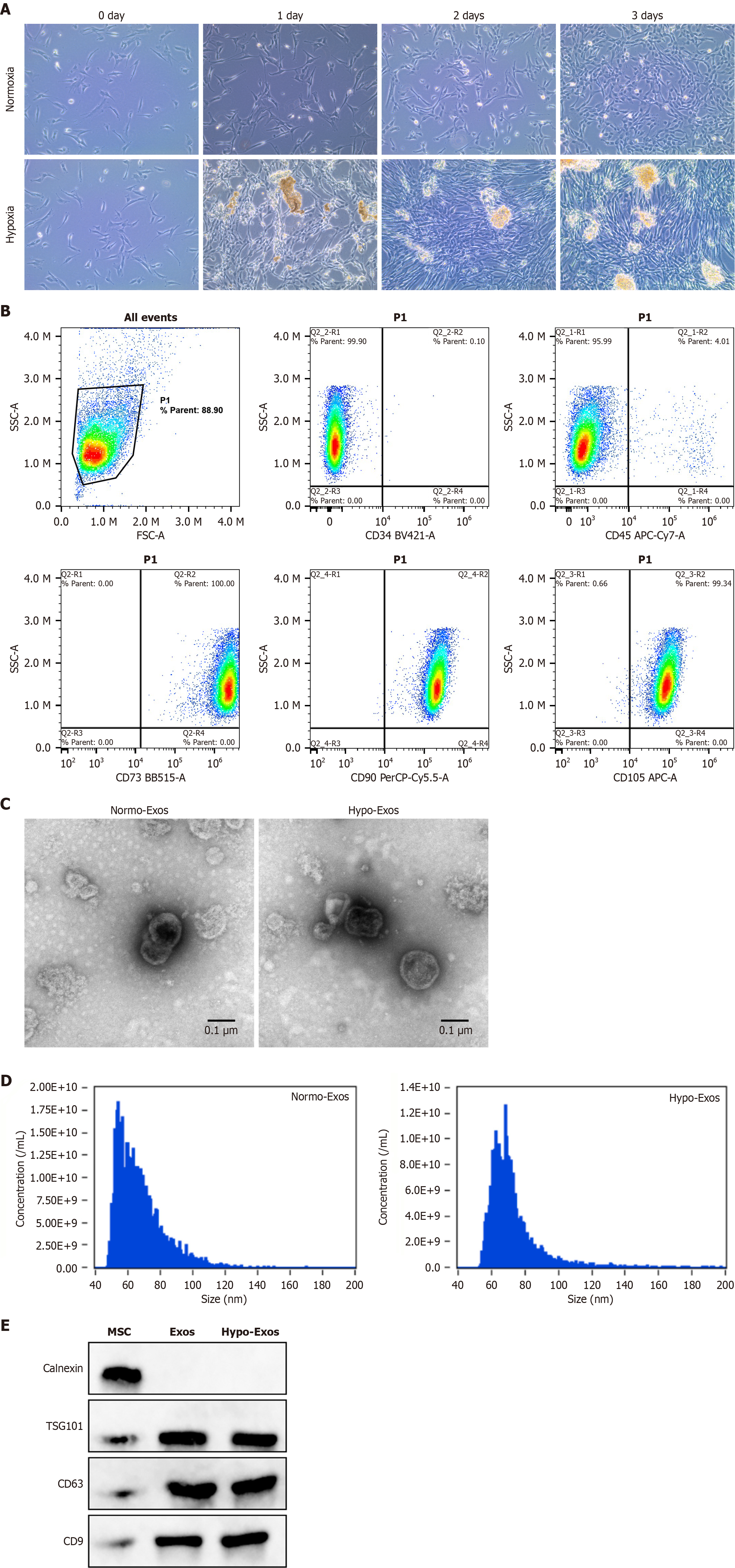
Figure 1 Identification of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and characterization of exosomes.
A: Representative bright-field microscopy image of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (HUC-MSCs); B: HUC-MSCs identification by flow cytometry phenotyping; C: Representative electron microscopy image of HUC-MSC-derived exosomes; D: Size distribution of exosomes (Exos) determined by nanoparticle tracking analysis; E: Western blot analysis of the surface markers of HUC-MSCs and exosomes. Hypo-Exos: Hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; Normo-Exos: Normoxic exosomes; TSG101: Tumor susceptibility gene 101.
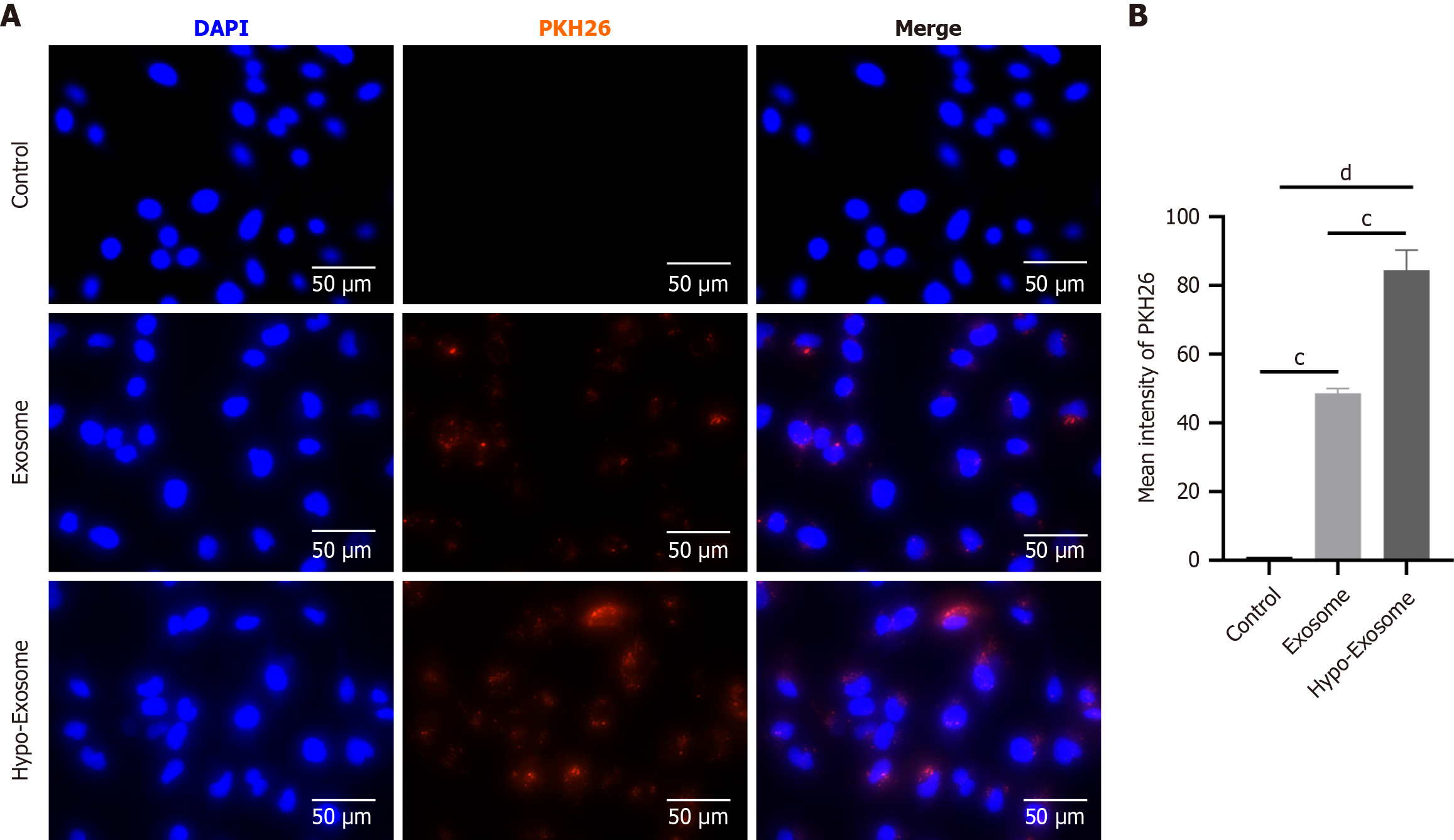
Figure 2 Hypoxic preconditioning promoted the internalization of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells exosomes.
A: Uptake of the red fluorescence dye PKH26-labeled normoxic exosomes and hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (Hypo-Exosome) into H9C2 cells; B: Statistical evaluation of fluorescence intensities. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the man (n = 3). cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001.
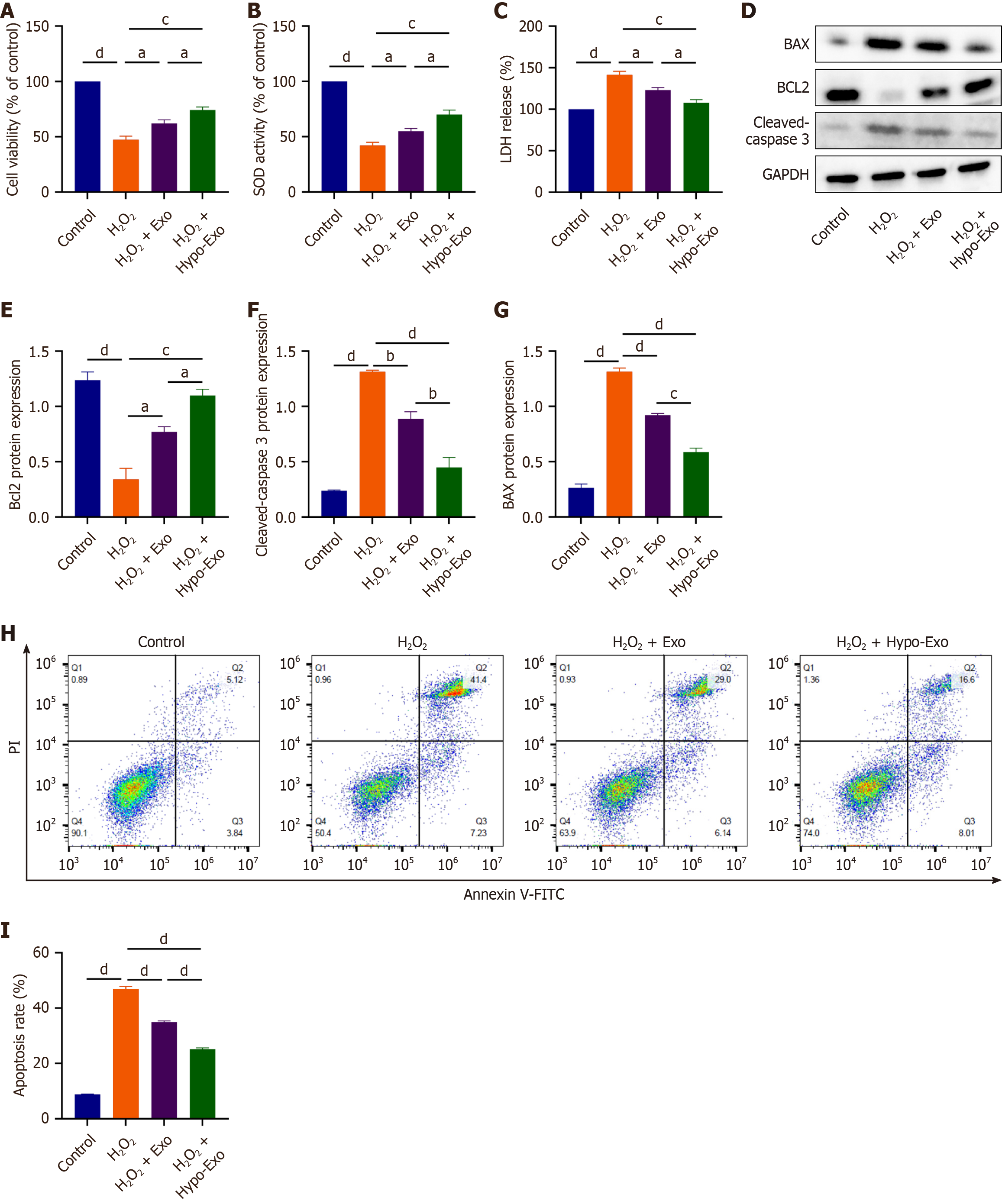
Figure 3 Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells exosomes ameliorated oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in H9C2 cells.
A: Different effects of normoxic counterparts (normo-Exos) and hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (hypo-Exos) on the viability of H9C2 cells; B: Different effects of normo-Exos and hypo-Exos on superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced H9C2 cells; C: Different effects of normo-Exos and hypo-Exos on lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release in H2O2-induced H9C2 cells; D: Expression of apoptosis-related protein was determined by western blotting; E-G: Quantitative analysis of the western blotting; H: Level of apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry; I: Statistical evaluation of flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001.
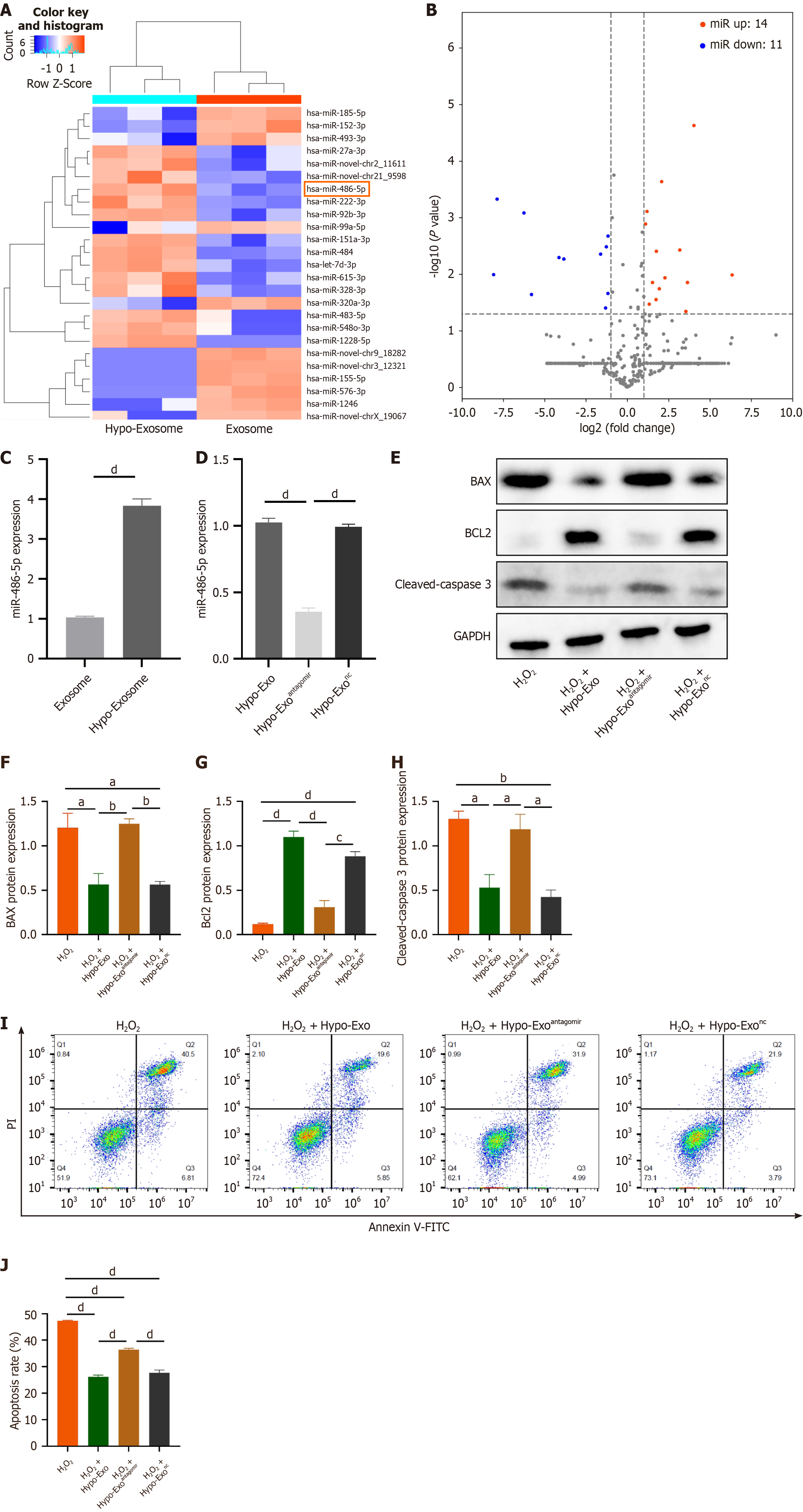
Figure 4 miR-486-5p mediated the cell protective effects of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes.
A: Heat map based on high-throughput microRNAs sequencing representing the 25 identified microRNAs with the most significant abundance differences between normoxic counterparts (normo-Exos) and hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (hypo-Exos); B: Volcano plot showing log2 (fold change) on the X-axis and -log10 (P value) on the Y-axis; C: MiR-486-5p expression level in normo-Exos and hypo-Exos determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction; D: MiR-486-5p antagomir or negative control transfected into hypo-Exos altered the miR-486-5p expression level in hypo-Exos; E: Expression of apoptosis-related protein was determined by western blotting; F-H: Quantitative analysis of the western blotting; I: Level of apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry; J: Statistical evaluation of flow cytometry. All data are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001.
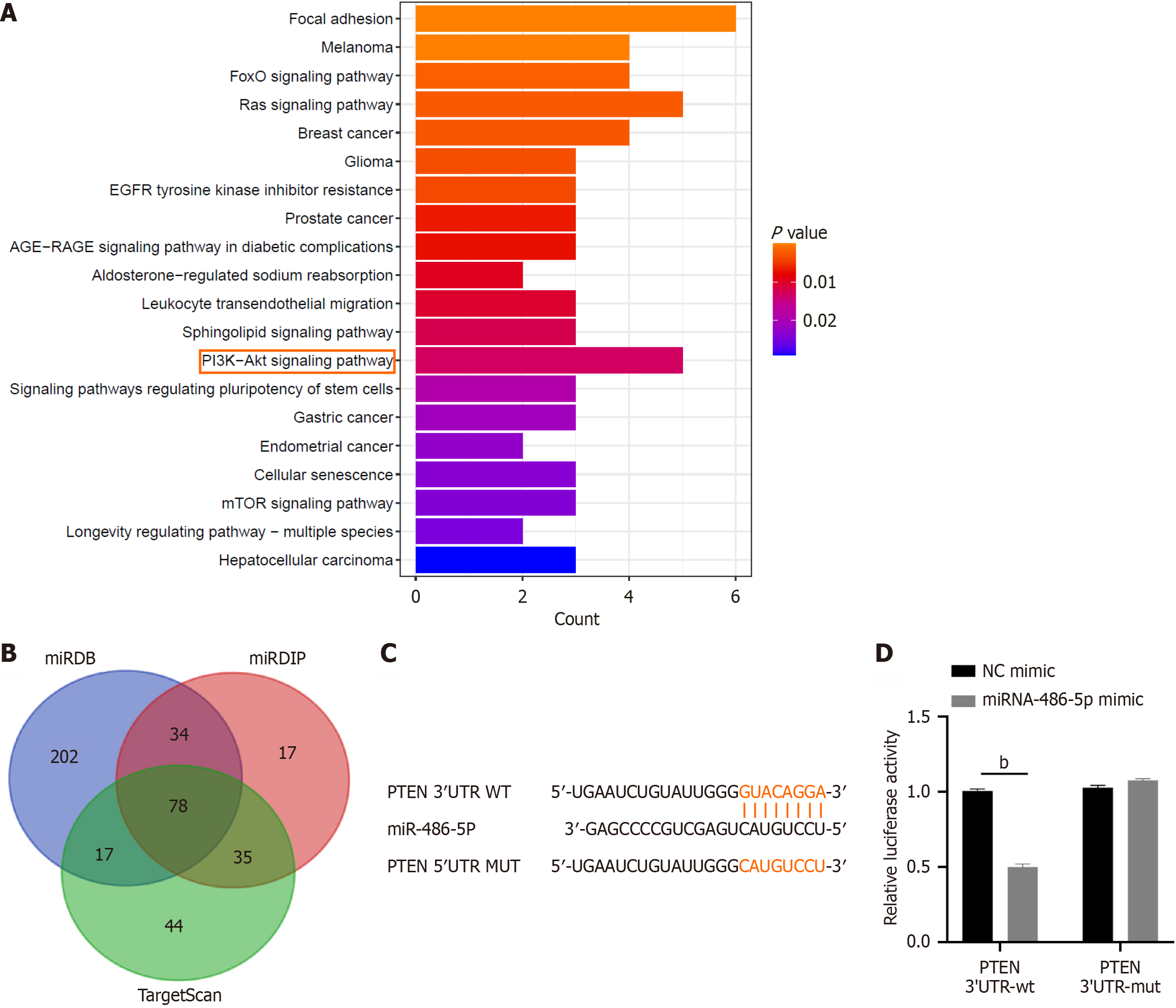
Figure 5 Potential signaling pathway and target genes involved in the protective effects of exosomal miR-486-5p.
A: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses showed the top 20 significantly enriched signaling pathways of miR-486-5p; B: Venn diagram illustrates the number of targets of miR-486-5p among three bioinformatics platforms; C: MiR-486-5p regulated phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) by directly targeting the 3’ untranslated region (UTR); D: Relative luciferase activity was measured in HEK293T cells transfected with luciferase reporter vectors containing either the wild-type or mutant binding site of miR-486-5p in the 3’ UTR of PTEN, along with a miR-486-5p mimic or negative control (n = 3). bP < 0.01.
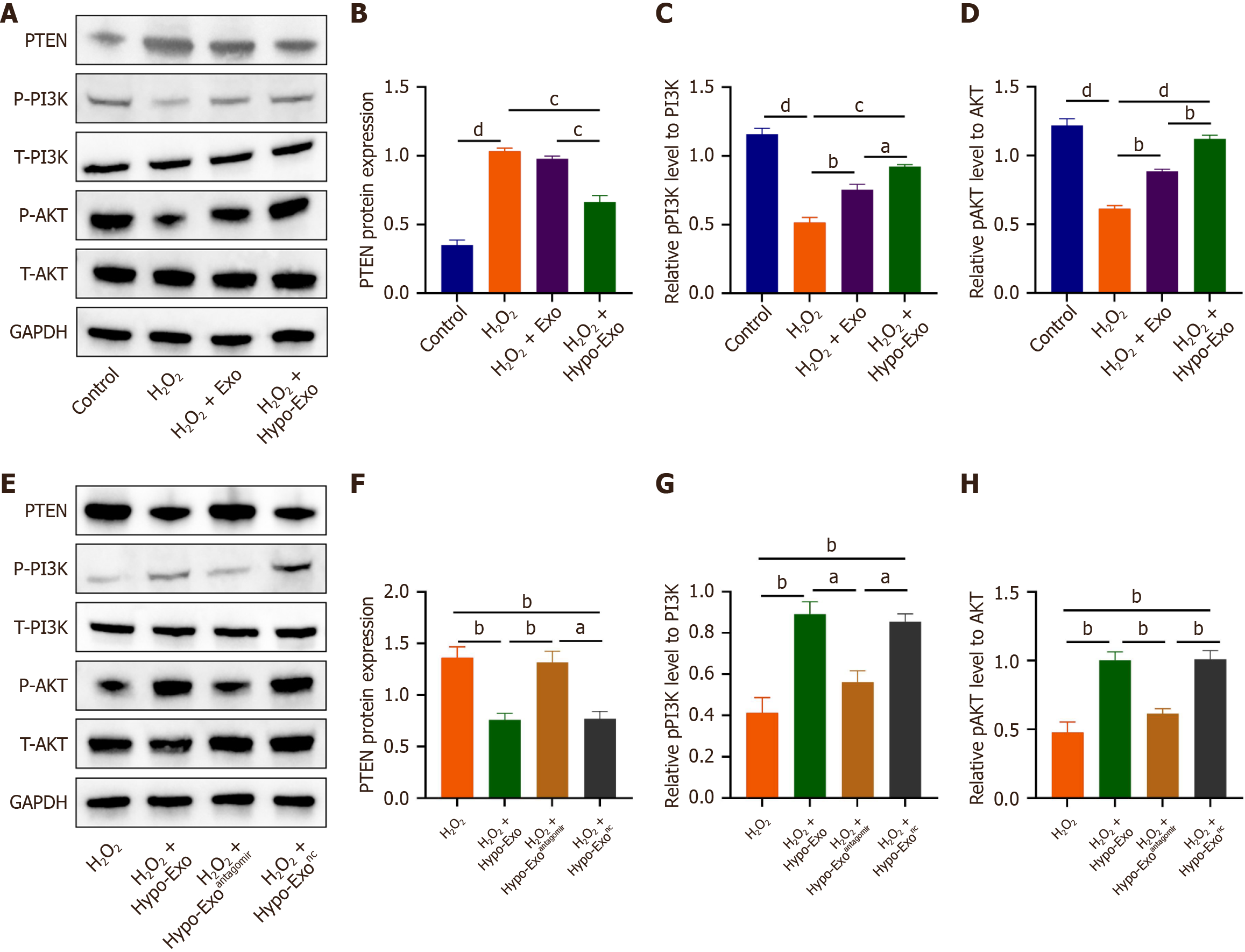
Figure 6 Exosomal miR-486-5p activated the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway by phosphatase and tensin homolog inhibition.
A-H: Expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathway protein was determined by western blotting (A and E). Quantitative analysis of the western blotting. All data are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001.
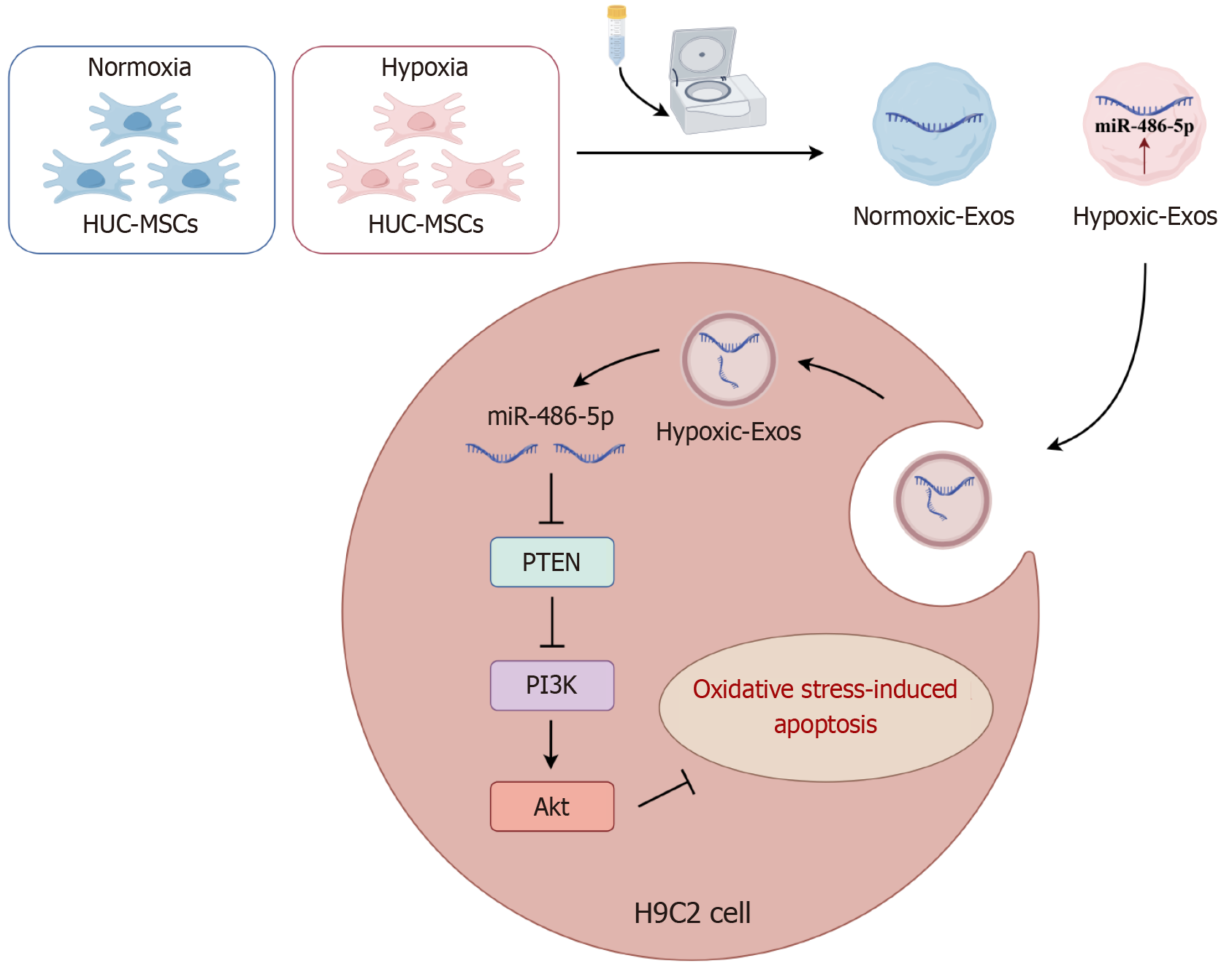
Figure 7 Hypoxic preconditioned human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes alleviate H9C2 cells apoptosis and oxidative stress through the miR-486-5p targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway.
Akt: Protein kinase B; HUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stems; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog.
- Citation: Zeng ZF, Rao J, Xia XB, Chen XY, He HX, Liu B, Chen Q, Liu YD, Wang GJ, Cheng PC, Wang JN, Wang P, Yu Y, Wang ZN. Hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through miR-486-5p. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(12): 112207
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i12/112207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i12.112207