Published online Jan 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i1.163
Peer-review started: September 9, 2023
First decision: November 16, 2023
Revised: November 27, 2023
Accepted: December 5, 2023
Article in press: December 5, 2023
Published online: January 6, 2024
Processing time: 114 Days and 22.6 Hours
Endophthalmitis occurring in silicone oil-filled eyes is a very rare occurrence, with reported incidence rates ranging between 0.07% and 0.039%. Traditional methods of management of infectious endophthalmitis include the removal of silicone oil, washout of the vitreous cavity, administration of intravitreal antibiotics, and re-injection of silicone oil.
Herein, we report the case of a 39-year-old man with unilateral endophthalmitis after pars plana vitrectomy and silicone oil tamponade. Intravitreal injections of full-dose antibiotics and anterior chamber washout were used to treat the patient. No signs of retinal toxicity were observed during the follow-up period.
Intravitreal full-dose antibiotic injections and anterior chamber washout are promising alternatives to traditional therapies for endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eyes.
Core Tip: Endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eyes occurs very rarely. Traditional methods of management of infectious endophthalmitis include removal of the silicone oil, washout of the vitreous cavity, administration of intravitreal antibiotics, and re-injection of silicone oil. Here, we report the case of a 39-year-old man with unilateral endophthalmitis following vitrectomy and silicone oil tamponade surgery. The patient underwent two anterior chamber washouts and received three intravitreal antibiotic injections, resulting in successful control of the endophthalmitis.
- Citation: Yan HC, Wang ZL, Yu WZ, Zhao MW, Liang JH, Yin H, Shi X, Miao H. Endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eye: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(1): 163-168
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i1/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i1.163
Infectious endophthalmitis after vitrectomy and silicone oil tamponade is a rare occurrence. High surface tension and low permeability of silicone oil may limit the free movement of pathogens. Traditional methods of management of infectious endophthalmitis include the removal of silicone oil, washout of the vitreous cavity, administration of intravitreal antibiotics, and re-injection of silicone oil. Herein, we report a case of unilateral endophthalmitis after vitrectomy and silicone oil tamponade surgery.
A 39-year-old man presented with increasing pain in his left eye on the first day following vitrectomy at the Peking University People’s Hospital in Beijing, China.
Symptoms started on the first postoperative day with decreased vision. The patient was diagnosed with vitreous hemorrhage and tractional retinal detachment in the left eye due to diabetic retinopathy. Consequently, the patient underwent a standard 25-gauge pars plana vitrectomy involving membrane peeling, endo-laser photocoagulation, and silicone oil tamponade. On the morning of the first postoperative day, the patient’s vision in his left eye was counting fingers (CF)/20 cm, his intraocular pressure (IOP) was 15 mmHg, and the retina was reattached. Ofloxacin and Prednisolone Acetate Ophthalmic Suspension eye drops were administered four times daily, along with tropicamide administered twice daily.
The patient’s right eye was rendered blind due to more advanced diabetic retinopathy.
The patient had a history of diabetes spanning over 20 years. There were no significant findings in the family history.
The patient’s vision was CF/15 cm. Silt-lamp examination revealed flare and 2+ cells, accompanied by the presence of a hypopyon in the anterior chamber. The red reflex was observed; however, the retina could not be observed as clearly as in previous observations.
An aqueous humor specimen was obtained through anterior chamber tap for microbiological analysis. Due to economic constraints, a polymerase chain reaction test was not conducted. However, the aqueous humor culture results were negative.
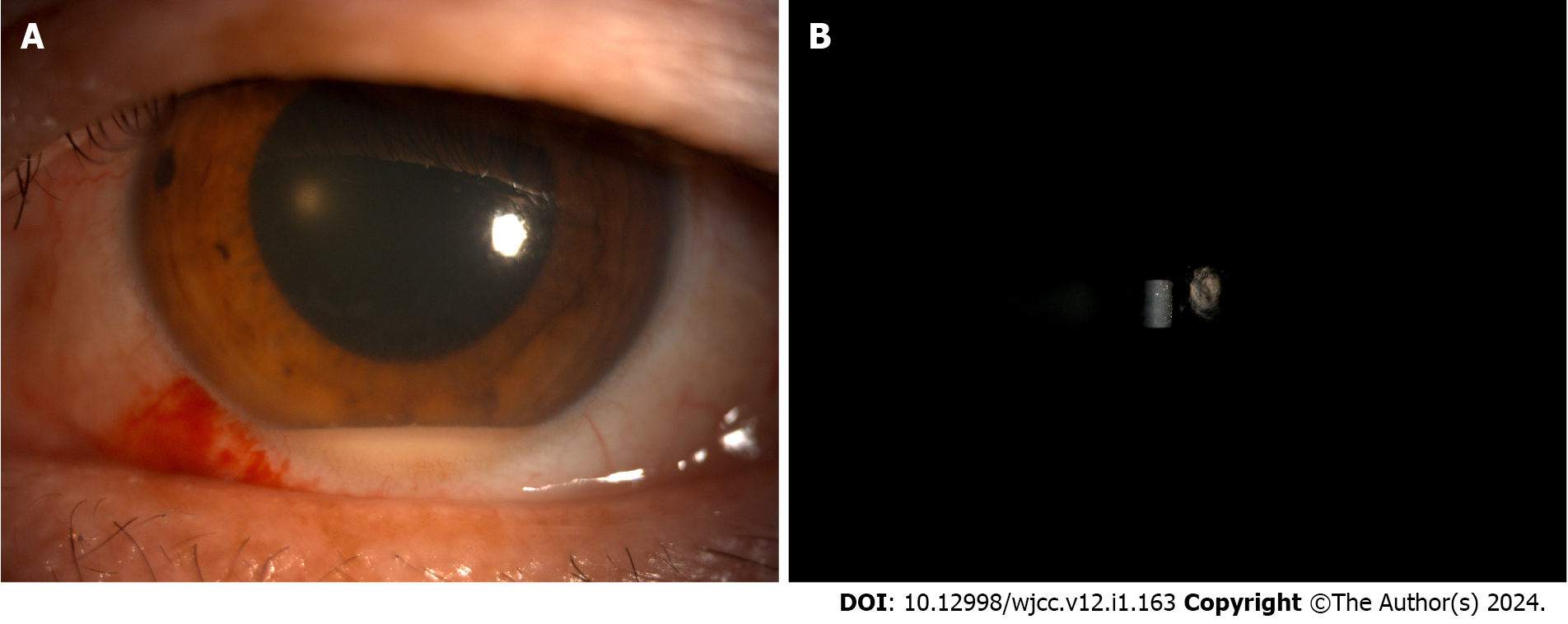
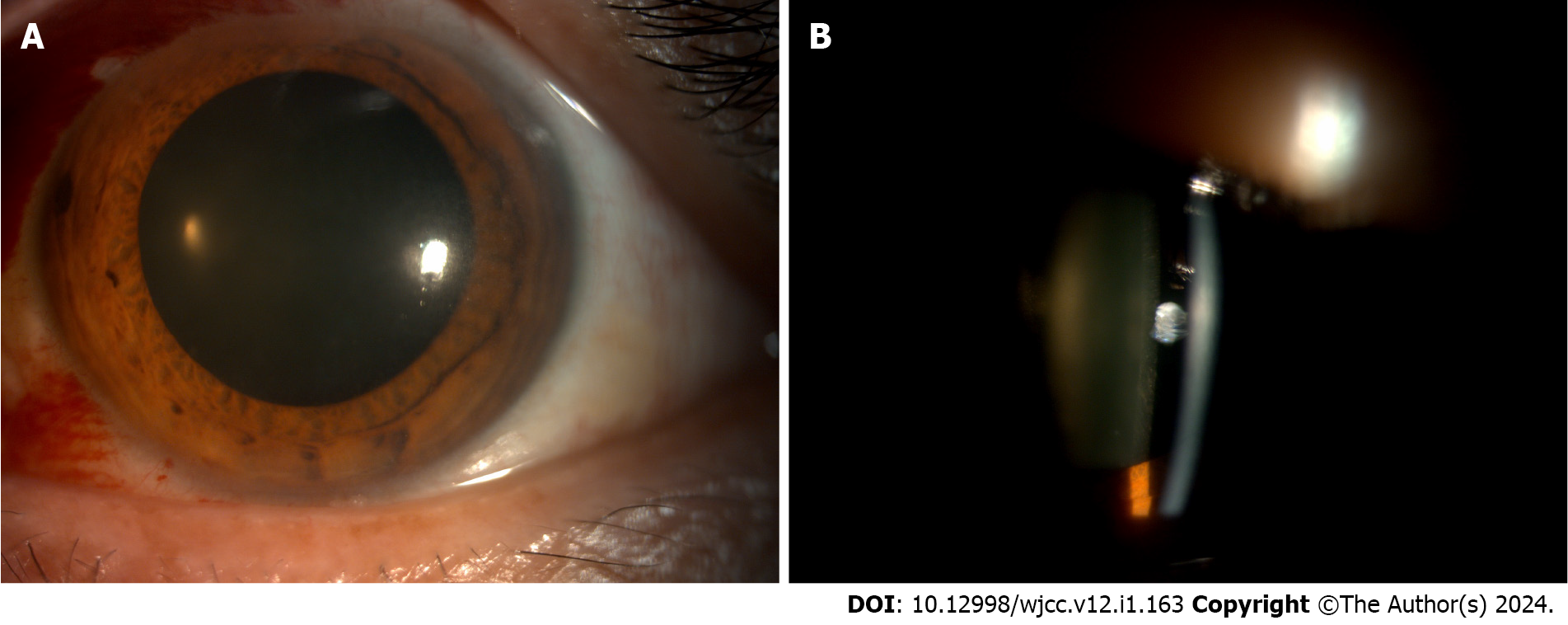
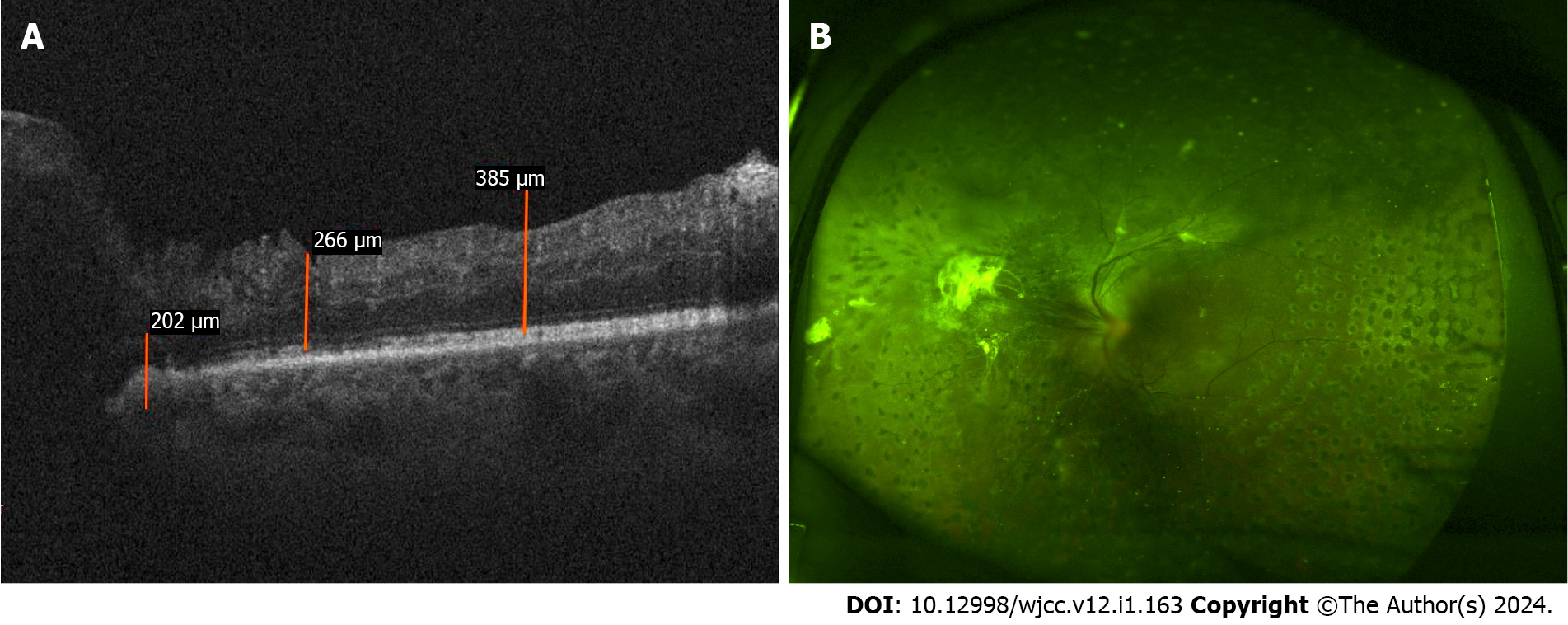
Follow-up imaging examinations included silt-lamp assessments on different postoperative days. On the second day after the surgery, the silt-lamp examination revealed a hypopyon and cells in the anterior chamber (Figure 1). By the fifth day post-surgery, the examination revealed a decreased hypopyon (Figure 2). One week after the surgery, the silt-lamp examination indicated a clear anterior chamber (Figure 3). The optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus examination conducted 3 mo later showed diabetic macular edema in the nasal region of the posterior pole. However, most of the structure appeared normal, with successful reattachment of the retina observed (Figure 4).
Endopthalmitis in the left eye with silicone oil.
Vancomycin (1 mg) was injected into the silicone oil through the pars plana, and intravenous imipenem was administered every 8 h.
The second day after the operation, the patient reported a vision decrease, which was measured at CF/10 cm. Slit-lamp examination revealed a hypopyon of 2 mm, which was more severe than in previous examinations. The fundus view was not clear. Full-dose of ceftazidime (2 mg) and vancomycin (1 mg) were injected intravitreally, and anterior chamber washout was performed as well, with the irrigation solution containing vancomycin 20 μg/mL, and ceftazidime 40 μg/mL. The sample of hypopyon was sent for culture again and the results were negative (Figure 1). Given the lack of early pathogenic evidence and concerns regarding the patient’s condition, the administration of intravitreal dexamethasone injection was postponed.
On the third day after the operation, there was no change in vision (CF/10 cm), the IOP measured 25 mmHg, the hypopyon could still be seen in the anterior chamber, and a fibrin membrane was observed in the pupil, in front of the lens. An anterior chamber washout was performed again. Ceftazidime (2 mg), vancomycin (1 mg), and dexamethasone (0.4 mg) were injected intravitreally, and fibrinous material was sent for culture, resulting in another negative test. It is noteworthy that the patient’s overall systemic condition remained stable upon presentation with endophthalmitis, devoid of symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Additionally, the blood sugar level normalized following hypoglycemic drugs administration.
After 3 d of treatment, the patient’s vision improved to CF/40 cm, and by the fifth day, the IOP measured 15 mmHg. Silt-lamp examination showed decreased hypopyon. The funds visibility improved significantly (Figure 2).
One week post-surgery, the best corrected visual acuity improved to 20/100, with IOP at 13 mmHg, a quiet anterior chamber, and a successfully reattached retina (Figure 3).
Subsequent follow-ups revealed further improvement of the vision. The patient went to a local hospital for examination; OCT revealed no significant abnormalities in the retinal structure, apart from diabetic macular edema in the nasal region of the posterior pole, and there were no indications of retinal toxicity (Figure 4).
Infectious endophthalmitis is a severe disease of the eye, and its clinical features include ocular pain, decreased vision, conjunctival congestion, anterior segment inflammation, vitreous inflammation, and reduced red light reflex. It is mainly caused by exogenous pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Surgery, trauma, or ocular surface infection, which can cause damage to the structure of the eyeball, can lead to infectious endophthalmitis. Pathogens can also transmit through the blood, which is a condition called endogenous endophthalmitis. Studies show that the incidence of infectious endophthalmitis following cataract surgery is 0.13%-0.7%, and between 0.03 and 0.13% after pars plana vitrectomy surgery[1]. Gentile et al[2] reported that infectious endophthalmitis is mainly caused by Gram-positive bacteria (85.1%), and the most common pathogenic bacterium is Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eyes after pars plana vitrectomy is very rare, reported to have an incidence between 0.07% and 0.039%. Non-infectious sterile endophthalmitis and infectious endophthalmitis have both been reported. Non-infectious sterile endophthalmitis is always associated with inadvertent lens contact during surgery. Most infectious endopthalmitis cases described in the literature are culture-negative. Sborgia et al[3] summarized some studies of endophthalmitis with silicone oil endotamponade, reporting that approximately 38% of cases involving silicone-filled eyes yielded positive results, while 62% yielded negative results; the majority of positive findings originated from aqueous humor samples.
Pathogens associated with infectious endophthalmitis include Pseudomonas aeruginosa, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Mucor[1,4,5]. Steinmetz et al[6] reported two cases of endophthalmitis with silicone oil-filled eyes after pars plana vitrectomy. The clinical features were highly suspected as infectious endophthalmitis and appeared 3-4 d after surgery; however, microbiology test results were negative. Intravitreal injections of half and full-dose antibiotics (ceftazidime and vancomycin) were used to treat the two patients. The symptoms in both patients were resolved within one week. In the current case report, the patient developed pain in the eye and reduced vision one day after the surgery. Physical examination revealed significant inflammation in the anterior chamber. Although the microbial results of the sample of anterior chamber aqueous culture were negative, based on empirical judgment, the probability of infectious endophthalmitis is high.
When infectious endophthalmitis happens in a silicone oil-filled eye, routine treatment should include removal of the silicone oil, intravitreal washout and antibiotics administration, and refilling with silicone oil. In a reported case of Mucor associated endophthalmitis, the patient refused further treatment, resulting in loss of vision[7]. Steinmetz et al[6] first experimented with the use of intravitreal antibiotic therapy in silicone oil-filled eyes, and successfully controlled the disease. They hypothesized that the slow release of antibiotics within the silicone oil played a key role in managing the disease. In our study, intravitreal injections of antibiotics were used to treat the patient, and the symptoms were alleviated. However, unlike previous cases reported, our case achieved remission after multiple intravitreal injections. We hypothesize that this is due to vancomycin and ceftazidime being water-soluble drugs, contrary to the hypothesis that antibiotics can be slowly and temporarily released in silicone oil.
Al Taisan et al[4] evaluated the retinal toxicity of vancomycin, ceftazidime, and ganciclovir in rabbits undergoing pars plana vitrectomy and silicone oil tamponade. They considered that both full and half-doses of these drugs had retinal toxicity, while a quarter dose was safe. Eng et al[8] showed that injection of full dose ganciclovir in silicone oil-filled eyes had no retinal toxicity. Steinmetz et al[6] reported no evident retinal toxicity at both half and full doses of vancomycin or ceftazidime. Imamura et al[9] measured the drug toxicity of vancomycin and ceftazidime in silicone oil-filled eyes and other eyes of rhesus monkeys. Their findings revealed that administering the full dose of these drugs in the silicone oil-filled eyes did not induce retinal toxicity in the rhesus monkeys. Additionally, there were no significant differences in the amplitude or implicit time of each electroretinogram (ERG) pattern observed before and after intravitreal injection of antibiotics across all groups. In addition, the study found that the half-life of vancomycin and ceftazidime in silicone oil-filled eyes is shorter than that of eyes in the control group. They hypothesized that vancomycin and ceftazidime were hydrophilic antibiotics that could thus be insoluble in silicone oil, resulting in rapid drug excretion and shortened half-life. Therefore, the frequency of intravitreal injections (using vancomycin/ceftazidime) would likely need to be higher in silicone oil-filled eyes compared to normal eyes[9]. In the current case, three intravitreal injections of antibiotics were administered, and subsequent follow-ups did not reveal any evidence of retinal toxicity.
Numerous studies have shown that high levels of blood sugar could damage the function of neutrophils and macrophages, especially affecting phagocytosis and chemotaxis. The degree of neutrophil impairment is directly correlated with the severity of hyperglycemia. The process of inflammation could lead to impairment of the tissue, as seen in endophthalmitis[10,11]. Therefore, further caution with the ocular treatment of patients with diabetes should be given. In the current study, although the anterior chamber aqueous culture was negative, intravitreal injections of antibiotics were administered as a precaution against potential severe endophthalmitis in the presence of pre-existing diabetes.
A limitation of this study is that the patient has not returned for recent outpatient visits. Although improvements in vision and other examinations suggest enhanced retinal function, the assessment of retinal function through ERG examinations has not been conducted.
Conventional treatments for endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eyes include the removal of silicone oil, washing out of the vitreous cavity, administration of intravitreal antibiotics, and re-injecting the silicone oil. In our case, intravitreal full-dose antibiotic injections and washing out of the anterior chamber were used instead of traditional therapies, and the signs and symptoms of the endophthalmitis gradually subsided. The management of endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eyes may necessitate an increased frequency of antibiotic intravitreal injections. Furthermore, in scenarios where patients exhibit anterior segment inflammatory reactions post-surgery, especially those with diabetes or poor immunity, prompt aggressive treatment should be administered, even if infectious endophthalmitis is not confirmed. Further studies are needed to explore the management of endophthalmitis in silicone oil-filled eyes.
We appreciate the patient’s informed consent for the publication of the photographs used in this report.
| 1. | Sinisi F, Della Santina M, Loiudice P, Figus M, Casini G. The Role of Silicone Oil in the Surgical Management of Endophthalmitis: A Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2022;11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Gentile RC, Shukla S, Shah M, Ritterband DC, Engelbert M, Davis A, Hu DN. Microbiological spectrum and antibiotic sensitivity in endophthalmitis: a 25-year review. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:1634-1642. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 121] [Cited by in RCA: 146] [Article Influence: 12.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Sborgia L, Albano V, Sborgia G, Boscia F, Alessio G. Citrobacter koseri: A Cause of Silicone Oil Related Endophthalmitis after Post Pars Plana Vitrectomy. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2023;2023:3494521. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Al Taisan AA, Semidey VA. CULTURE-POSITIVE ACUTE POSTVITRECTOMY ENDOPHTHALMITIS IN A SILICONE OIL-FILLED EYE. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2022;16:622-624. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Zimmer-Galler IE, Santos A, Haller JA, Campochiaro PA. Management of endophthalmitis in a silicone oil-filled eye. Retina. 1997;17:507-509. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Steinmetz RL, Vyas S, Ashmore E, Brooks HL. Acute-onset postoperative endophthalmitis in silicone oil–filled eyes managed with intravitreal antibiotics alone. Journal of VitreoRetinal Diseases 2018; 2: 107-110. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 7. | Dogra M, Bhutani G, Gupta V. Mucormycosis Endophthalmitis in a Silicone Oil-Filled Eye of an Immunocompetent Patient. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2019;27:1293-1295. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Eng KT, Lam WC, Parker JA, Yücel YH. Retinal toxicity of intravitreal ganciclovir in rabbit eyes following vitrectomy and insertion of silicone oil. Can J Ophthalmol. 2004;39:499-505. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Imamura T, Kakinoki M, Hira D, Kitagawa T, Ueshima S, Kakumoto M, Terada T, Kawamoto I, Murase M, Ohji M. Pharmacokinetics of Intravitreal Vancomycin and Ceftazidime in Silicone Oil-Filled Macaque Eyes. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021;10:1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Gondhale H, Jaichandran VV, Jambulingam M, Anand AR, Srinivasan S, Raman R, Sharma T. Distribution and risk factors of postoperative endophthalmitis in people with diabetes. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021;69:3329-3334. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Ansari AS, de Lusignan S, Hinton W, Munro N, McGovern A. The association between diabetes, level of glycaemic control and eye infection: Cohort database study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11:421-429. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Mohamed SO S-Editor: Qu XL L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Qu XL