©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 16, 2025; 13(32): 110897
Published online Nov 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i32.110897
Published online Nov 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i32.110897
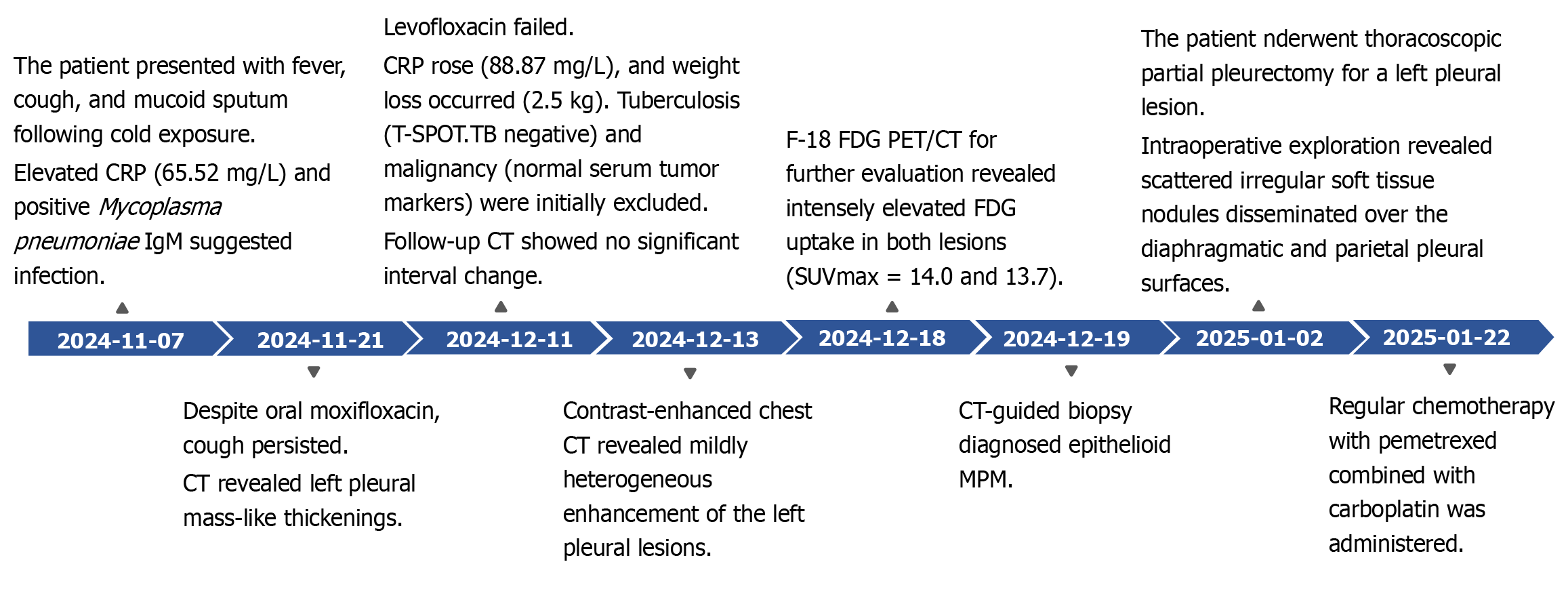
Figure 1 Diagnostic and therapeutic timeline.
The patient presented with an acute onset. Following relevant laboratory and imaging investigations, along with an outpatient computed tomography -guided biopsy that confirmed the diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma, the patient underwent surgery in our hospital's Department of Thoracic Surgery. This was followed by standard adjuvant chemotherapy and immunotherapy. CRP: C-reactive protein; CT: Computed tomography; F-18 FDG PET/CT: F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
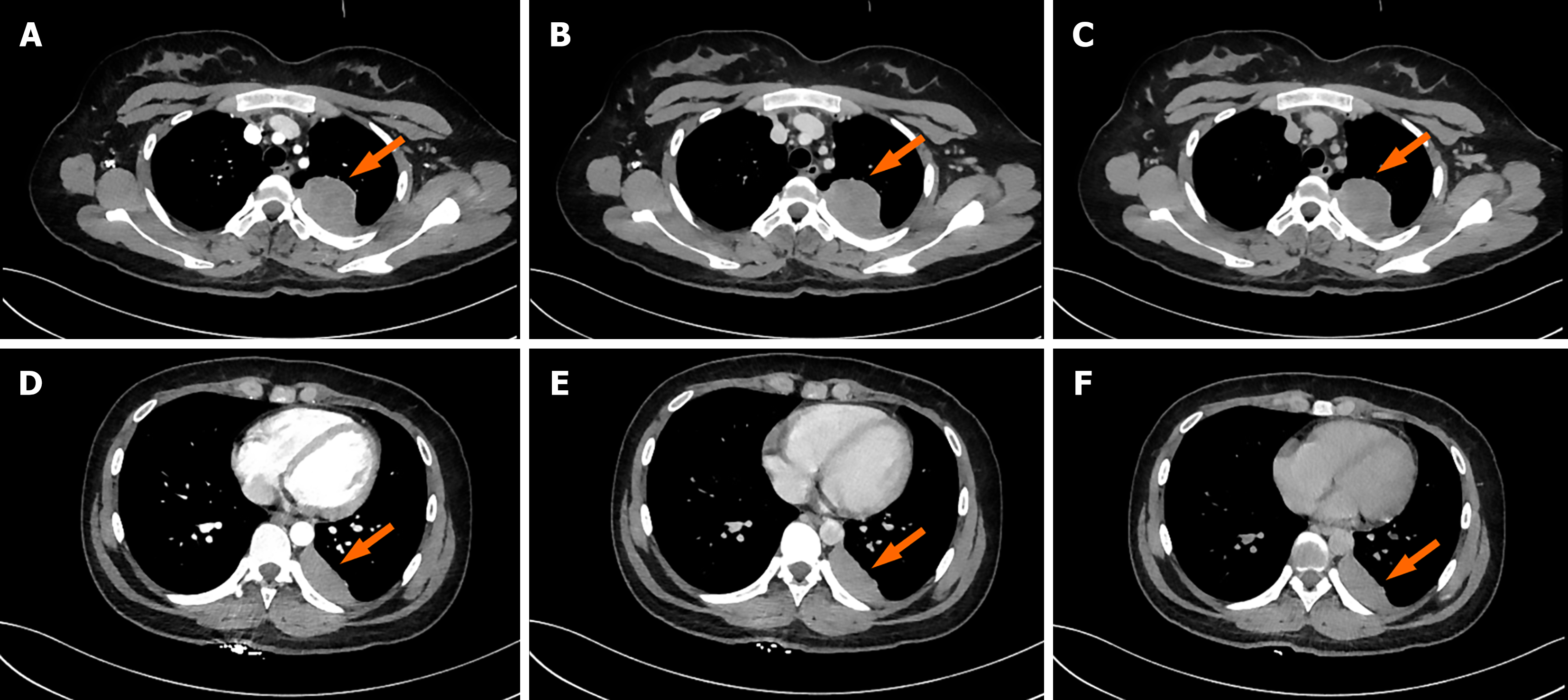
Figure 2 Chest triphasic contrast-enhanced images.
Lesion 1: A: Arterial phase; B: Venous phase; C: Delayed phase. Lesion 1 (arrow) demonstrated triphasic contrast-enhanced computed tomography values of 61 HU, 63 HU, and 59 HU in the arterial, venous, and delayed phases, respectively. Lesion 2: D: Arterial phase; E: Venous phase; F: Delayed phase. Lesion 2 (arrow) showed enhancement values of 61 HU, 69 HU, and 64 HU across the corresponding phases.
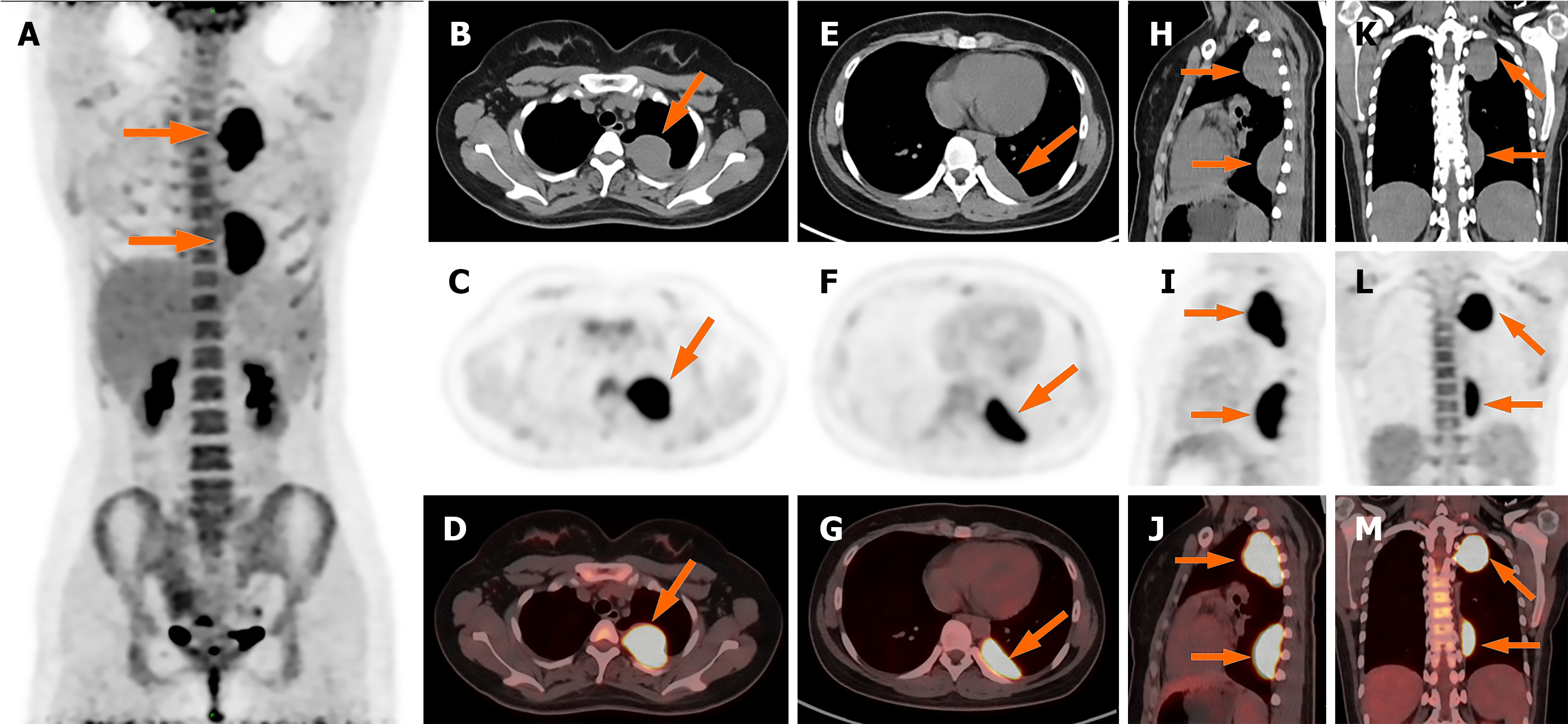
Figure 3 Whole body positron emission tomography/computed tomography images.
A: Maximum intensity projection image showed increased F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in the lesion (arrow). No other FDG-avid lesions were detected elsewhere in the body. Lesion 1: B-M: Axial (B–D); Lesion 2: Axial (E–G), sagittal (H–J), and coronal (K–M) PET/CT demonstrated abnormally elevated FDG uptake in the lesions (SUVmax 14.0 and 13.7, respectively).
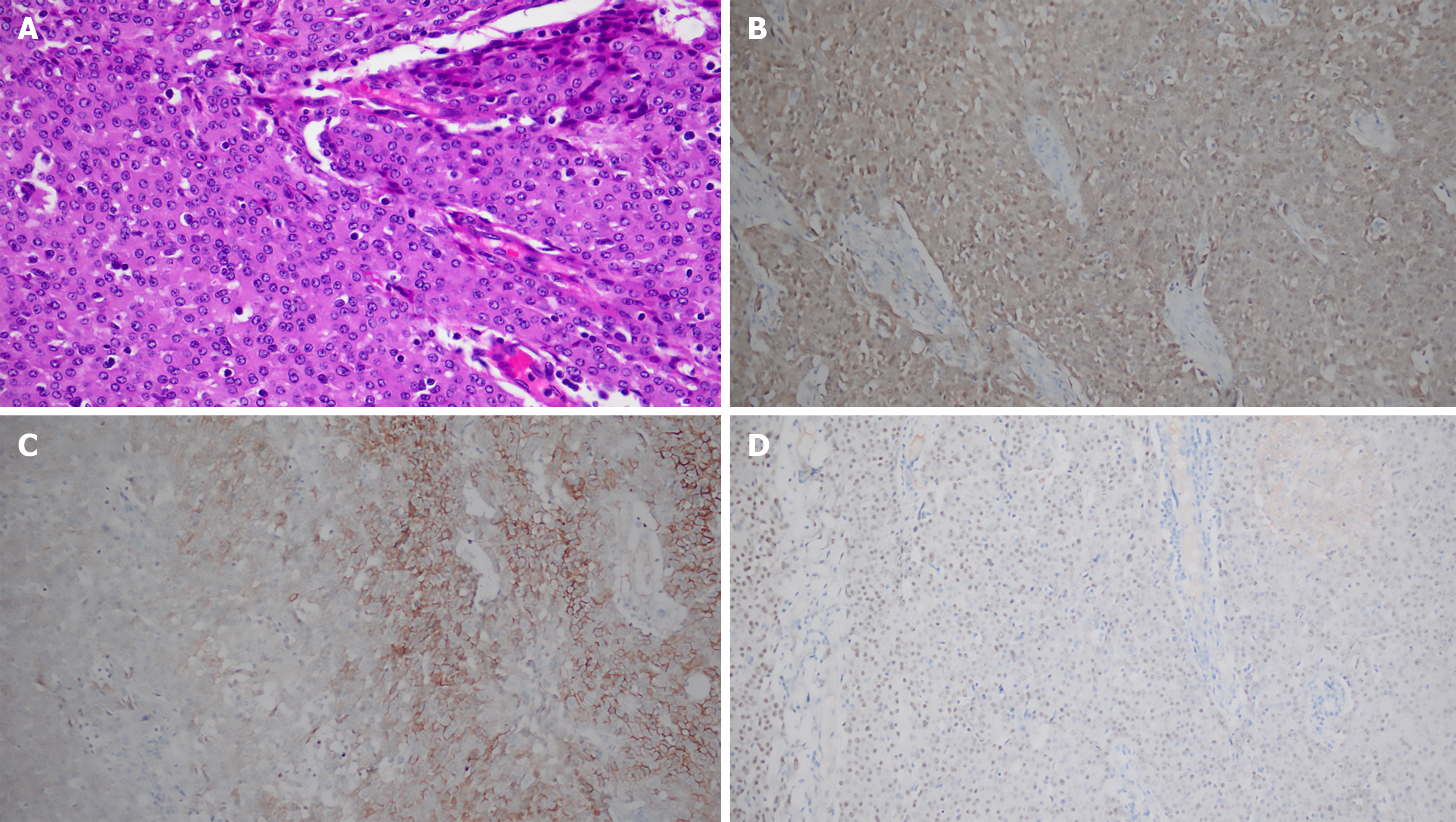
Figure 4 Histopathological analysis of the resected specimen.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (× 400): Epithelioid tumor cells arranged in sheets, exhibiting large cell volume, eosinophilic cytoplasm, and marked nuclear atypia; B-D: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) (× 200); B: Calretinin: Strong and diffuse cytoplasmic/nuclear positivity in tumor cells; C: D2-40: Partial membranous positivity in tumor cells; D: WT-1: Focal nuclear positivity in tumor cells. The combined morphological and IHC profile (Calretinin+/CK5/6+/WT-1 focal+/TTF-1–) supports the diagnosis of epithelioid malignant pleural mesothelioma.
- Citation: Aisikaer A, Sun MM, Shen J. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography in risk-factor-negative young female with malignant pleural mesothelioma: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(32): 110897
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i32/110897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i32.110897