©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2023; 11(7): 1521-1527
Published online Mar 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1521
Published online Mar 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1521
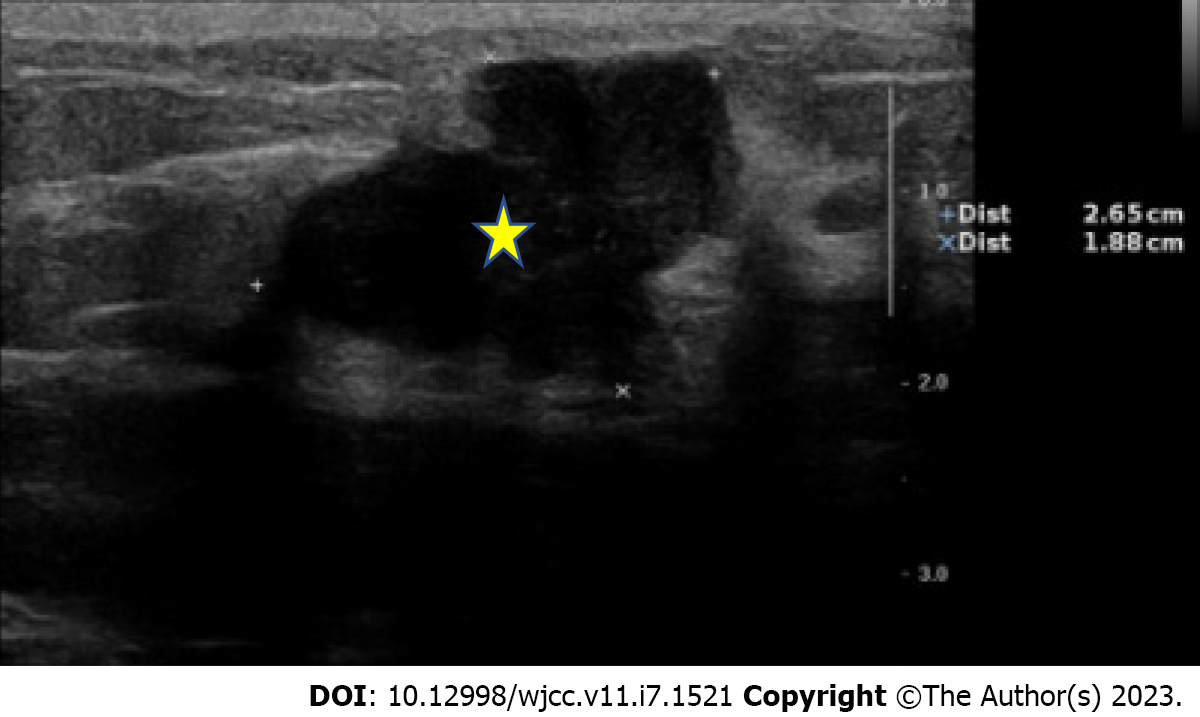
Figure 1 A 26.
5 x 18.8 mm asymmetric, lobular mass (yellow star) with circumscribed margin, at the 12 o'clock position of left breast, (12/2 cm), possibly atypical fibroadenoma or neogrowth.
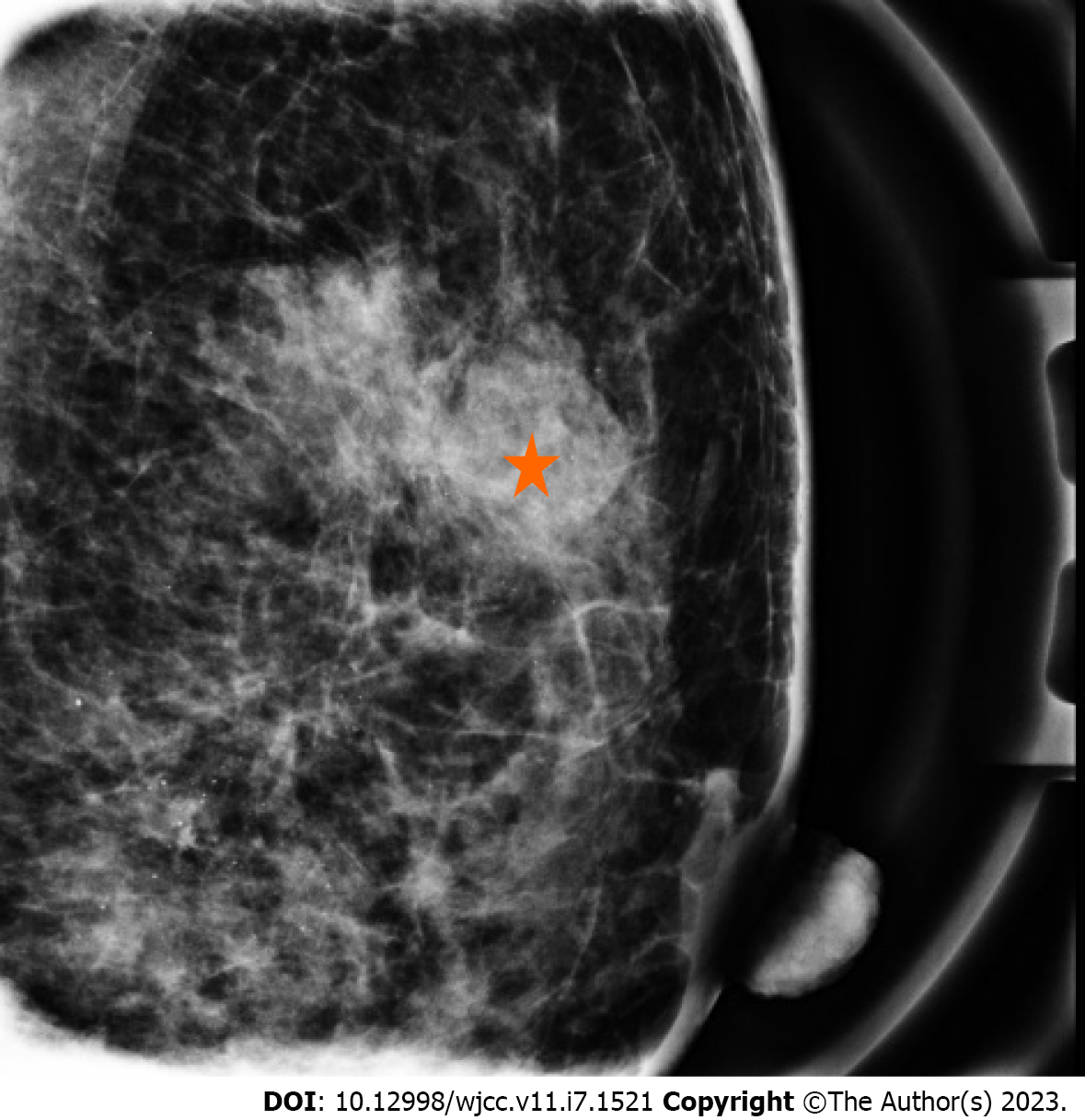
Figure 2 A partial circumscribed lobular mass (red star), sized approximately 3.
20 cm, in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast, A~M/3, about 2 cm away from the nipple on the medio-lateral view, with amorphous and punctate microcalcifications in the upper inner quadrant.
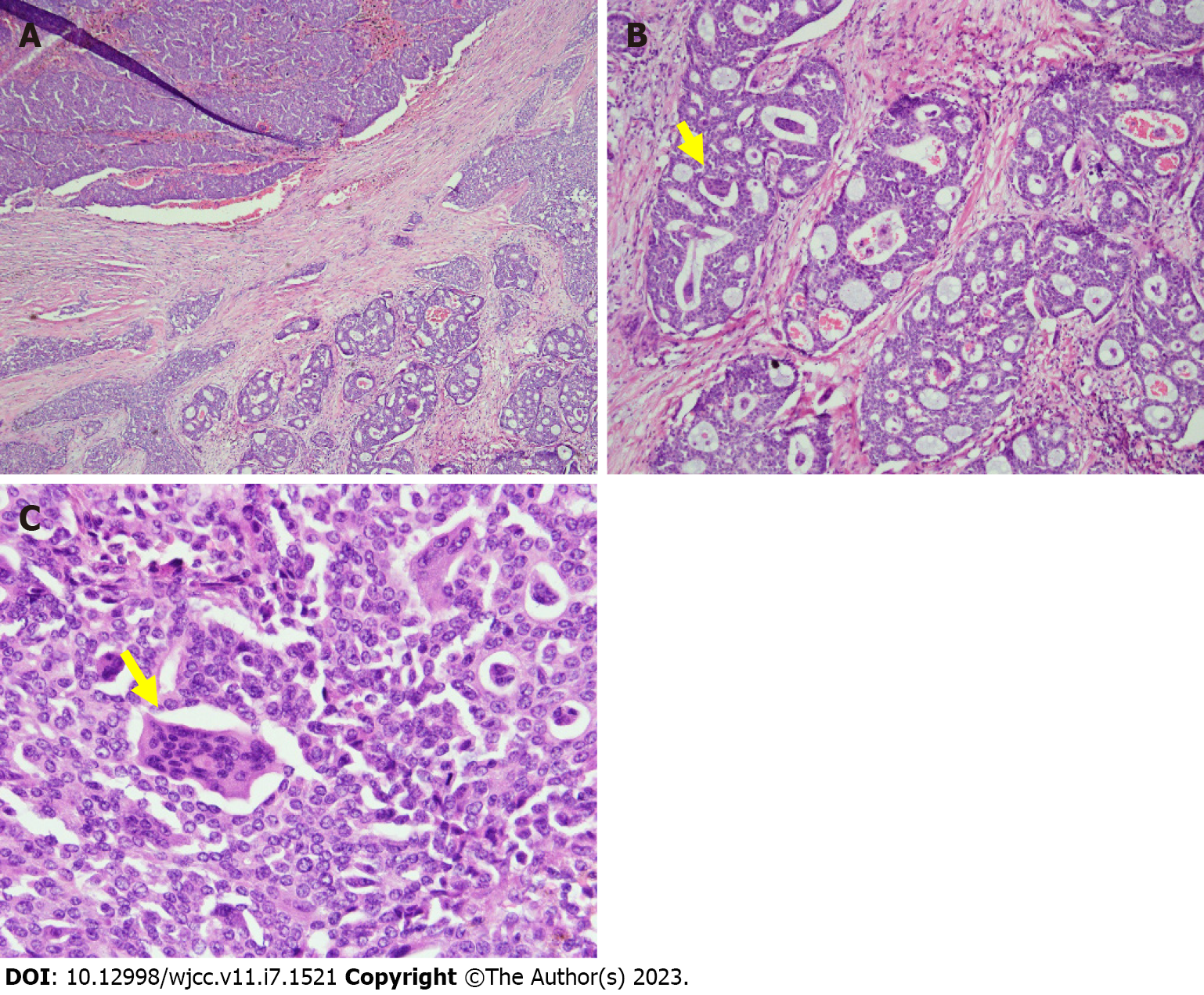
Figure 3 Breast Histopathology.
A: Low-power view of the infiltrative mammary tumor, composed of ducts, nests, and cribriform patterns; B: Medium-power view demonstrates osteoclast-like stromal giant cells (yellow arrow) and red blood cell extravasation; C: High-power view, multinucleated OGCs (yellow arrow) embedded in invasive breast carcinoma.
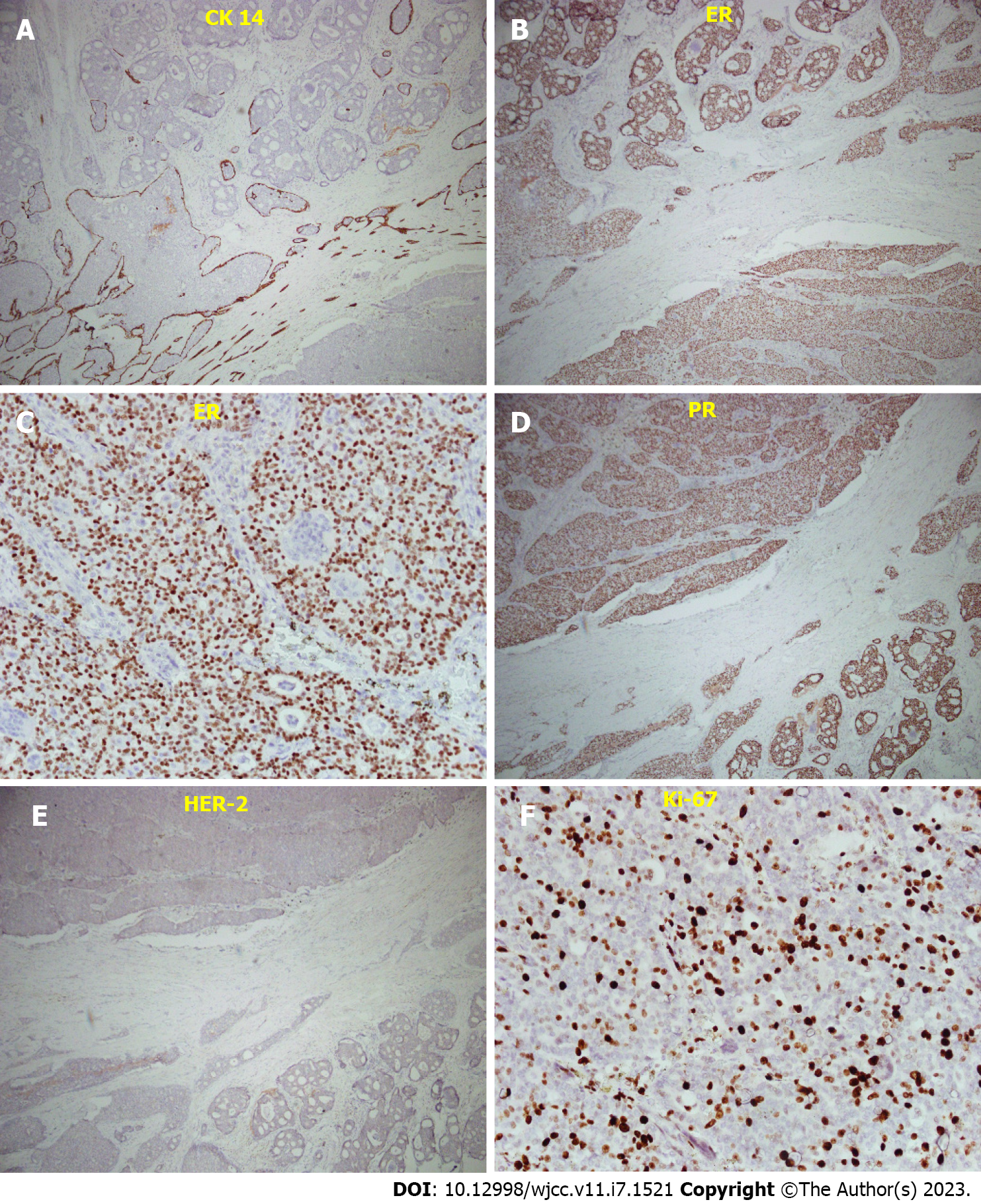
Figure 4 Immunostaining of the breast tissue.
A: CK14 immunostaining, showing a loss of myoepithelial cell; B: Median-power view of ER staining, percentage 80%; C: High-power view of ER staining; D: Median-power view of PR staining, 80%; E: Median-power view of HER-2 stain, showed negative result; F: Ki-67 staining, < 30%, less proportional to the mitotic count. ER: Estrogen receptor, PR: Progesterone receptor.
- Citation: Wang YJ, Huang CP, Hong ZJ, Liao GS, Yu JC. Invasive breast carcinoma with osteoclast-like stromal giant cells: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(7): 1521-1527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i7/1521.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1521