©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2023; 11(33): 8065-8070
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8065
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8065
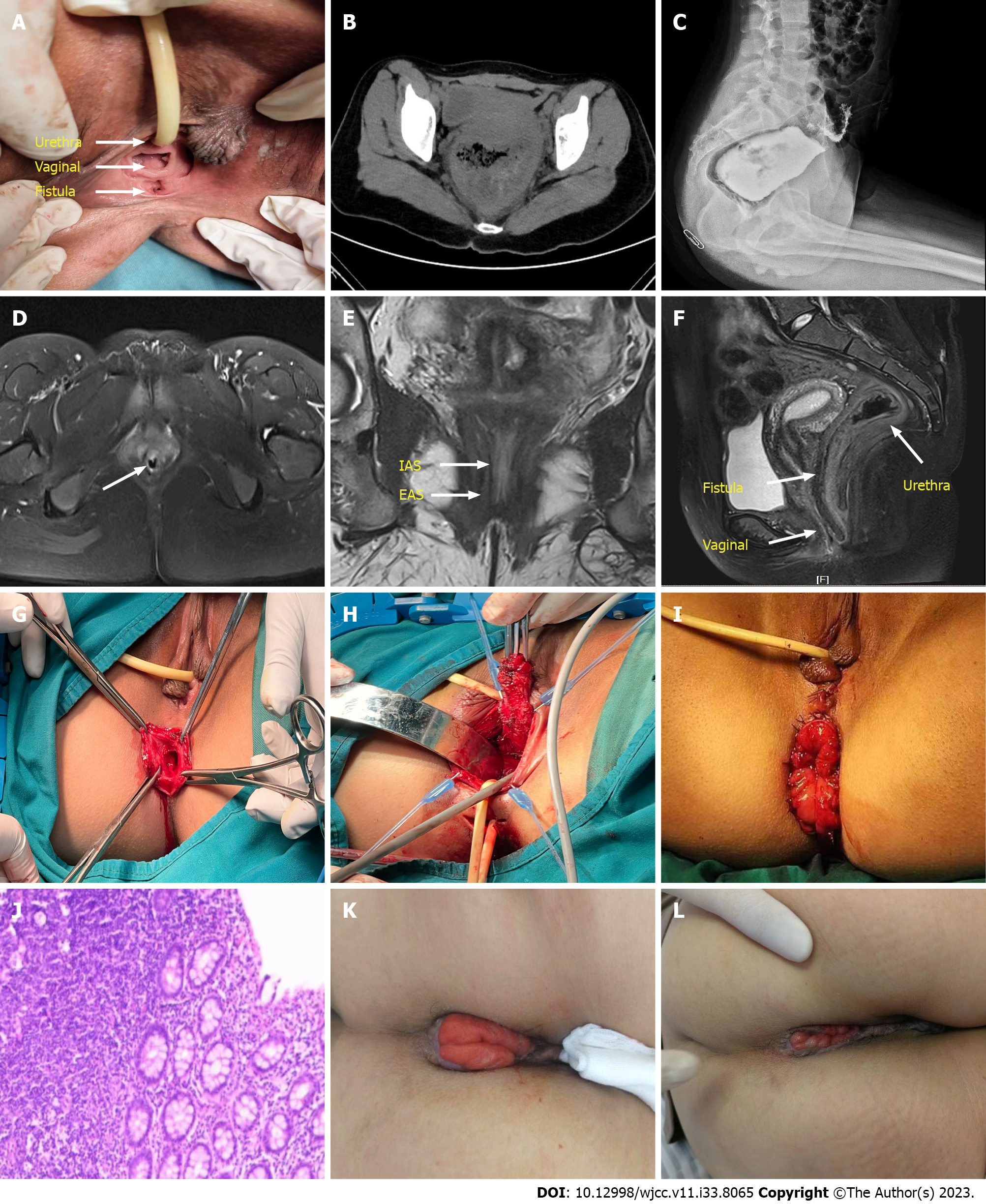
Figure 1 Preoperative physical examination, imaging examination, operation process and postoperative follow-up were performed in this case.
A: The vestibular fossa shows a defecation fistula, the position of the vagina, the urethral opening and the position of the fistula; B: Abdominal computed tomography showed rectal dilation with intestinal wall thickening, with a maximum diameter of approximately 10 cm; C: X-ray: The distal end of the rectum was blind, approximately 6 cm from the anal notch; D: Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) cross-section closed the upper segment of the anal canal space, not completely closed; E: Pelvic MRI coronal view showed that the thickness of the internal sphincter was approximately 1 mm, part of the internal sphincter was discontinuous, and the thickness of the external sphincter was approximately 2 mm; F: Pelvic MRI sagittal view shows the position of the rectum, vagina and fistula, and the fistula is adjacent to the posterior wall of the vagina; G: Opening of the atretic anal canal reveals lacunae and muscle fibers; H: Free the fistula and rectum, pay attention to protect the superficial perineal striated muscle and the central tendon of the perineum, and carefully separate it from the posterior wall of the vagina to avoid causing damage to the vagina; I: Reconstruction of the vagina and perineal body, repair of vestibular wounds, intermittent suture of the space between the posterior wall of the vagina and the central tendon of the perineum, intermittent suture of the bulbospongeus muscle, counterposition suture of the vestibular mucosa and submucosal tissue, repair of the hymen. The whole end of the new rectum was sutured to the subcutaneous dermis of the anus; J: Pathology: Moderate chronic inflammation of the mucosa, loose and swollen submucosa, and congestion of the gut wall; K: At the 2-mo follow-up, the rectal mucosa was slightly retracted; L: At the 4-mo follow-up, the rectal mucosa was almost retracted. IAS: Internal sphincter; EAS: External sphincter.
- Citation: Wang J, Zhang XY, Chen JH, Jin HY. Treatment of adult congenital anal atresia with rectovestibular fistula: A rare case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(33): 8065-8070
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i33/8065.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8065