©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Virol. Jun 25, 2025; 14(2): 106479
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.106479
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.106479
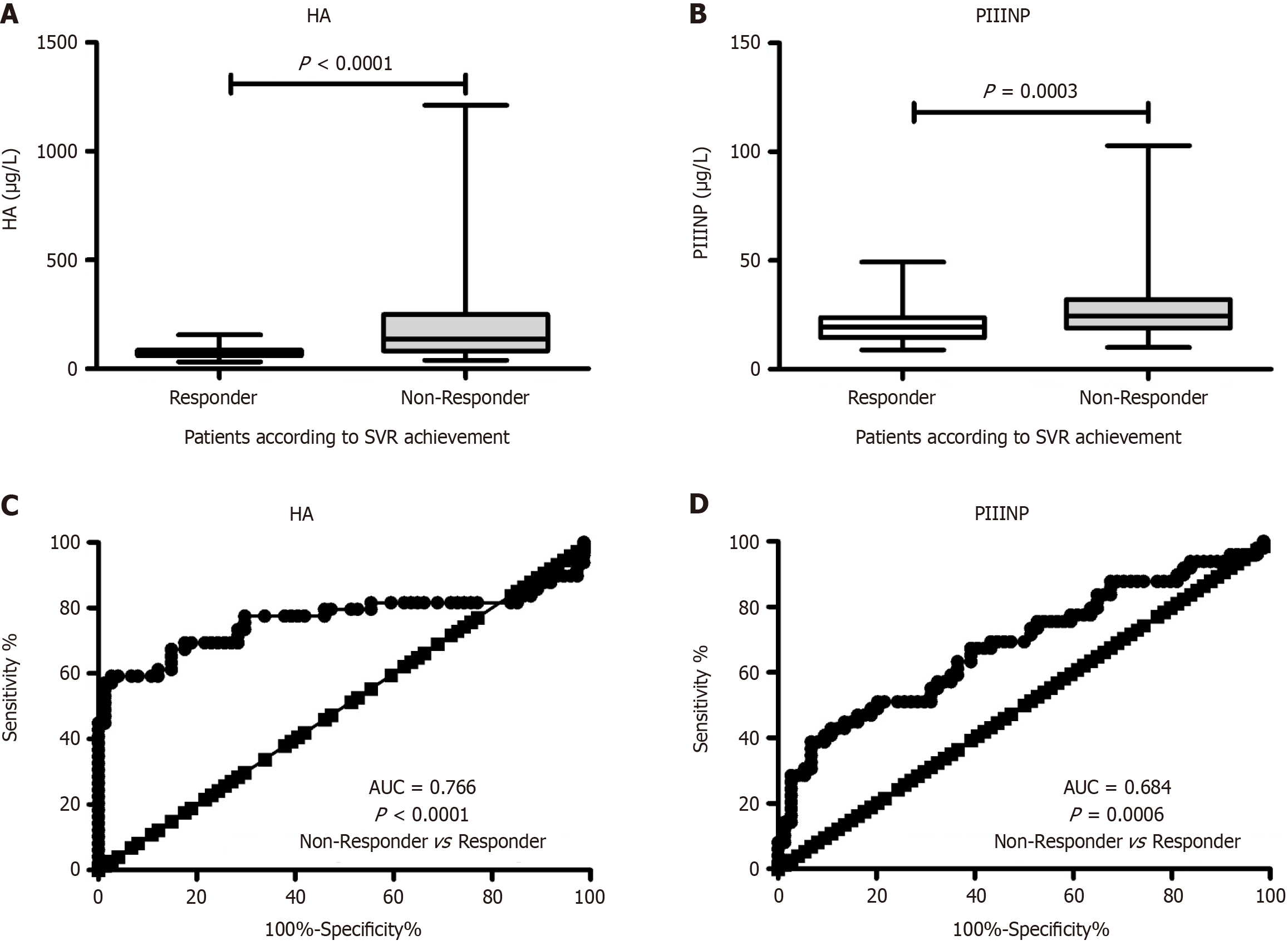
Figure 1 Elevated baseline hyaluronic acid and type III procollagen N-peptide was associated with treatment failure.
A: Distribution of hyaluronic acid serum levels between non-responders and responders according to sustained virological response after treatment; B: Distribution of type III procollagen N-peptide serum levels between non-responders and responders according to sustained virological response after treatment; C; As revealed by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis hyaluronic acid have a good ability in predicting treatment response; D: As revealed by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis type III procollagen N-peptide have a good ability in predicting treatment response. HA: Hyaluronic acid; PIIINP: Type III procollagen N-peptide; SVR: Sustained virological response; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
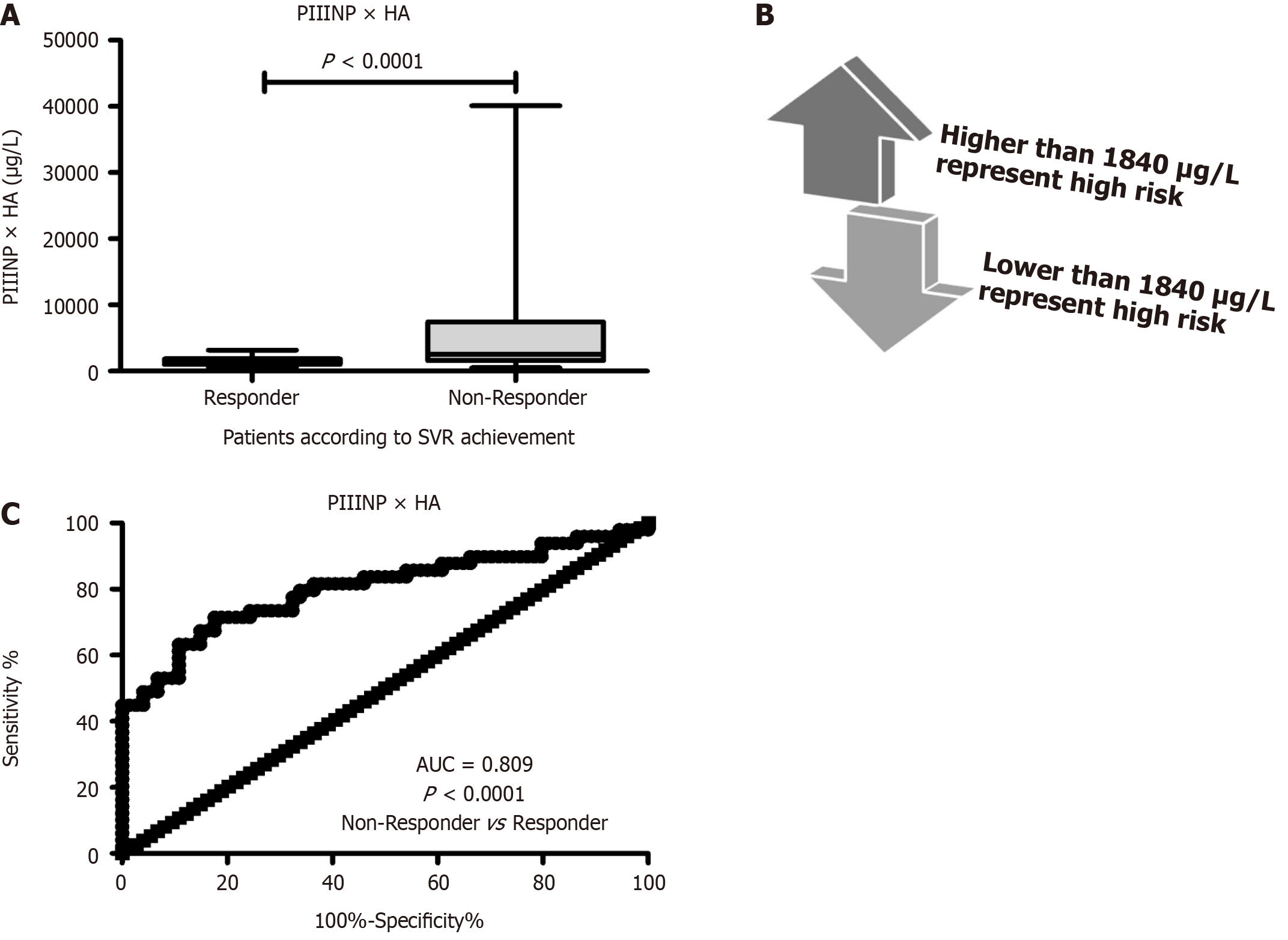
Figure 2 Index development and treatment failure prediction.
A: Multiplication of hyaluronic acid (HA) by type III procollagen N-peptide (PIIINP) values is the beast model for significant prediction of treatment failure; B: The best cut-off points of HA × PIIINP model is 1840 μg/mL; C: At this value, HA × PIIINP model has good and significant ability for early distinguishing non-responders from patients with sustained virological response 24. HA: Hyaluronic acid; PIIINP: Type III procollagen N-peptide; SVR: Sustained virological response; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
- Citation: Abdelrazek MA, Elghwab AI, Tabll AA, Elsayed EH, El Behery M. Evaluation of hyaluronic acid and type III procollagen peptide as predictors for treatment response to direct-acting antivirals. World J Virol 2025; 14(2): 106479
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v14/i2/106479.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.106479