©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Clin Oncol. Jan 24, 2026; 17(1): 111294
Published online Jan 24, 2026. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.111294
Published online Jan 24, 2026. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.111294
Figure 1 Modulation of immune cell function using nanotechnology.
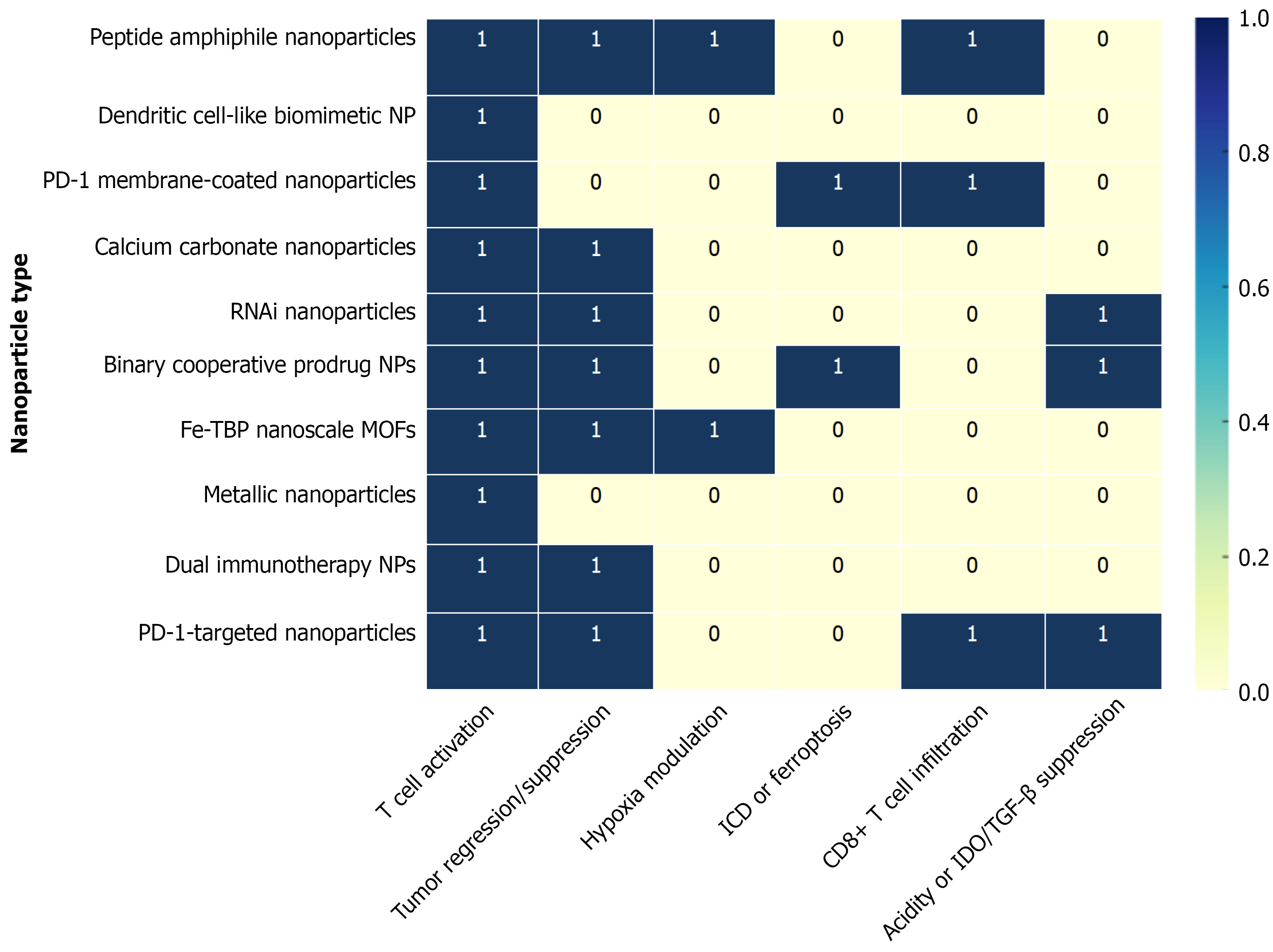
Figure 2 Heatmap showing specific nanoparticle classes and their principal immunotherapeutic mechanisms in the oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor microenvironment.
Rows represent nanoparticle types (e.g., peptide amphiphile, dendritic cell-like, PD-1 membrane-coated, calcium carbonate, metallic nanoparticles) and columns indicate key functions: T cell activation; tumor regression; hypoxia modulation; immunogenic cell death/ferroptosis; CD8+ T cell infiltration; and suppression of immunosuppressive pathways (e.g., IDO/TGF-β). The matrix links each nanoparticle to its main mode of action, illustrating how nanotechnology can target multiple barriers within the oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor microenvironment to enhance immunotherapy efficacy. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; ICD: Immunogenic cell death; MOF: Metallic organic framework.
- Citation: Jain A, Verma S, Jadhav A, John S, Gupta S. Role of nanotechnology in modulating the tumor microenvironment to enhance immunotherapy efficacy. World J Clin Oncol 2026; 17(1): 111294
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v17/i1/111294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v17.i1.111294