©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2025; 16(12): 110909
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.110909
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.110909
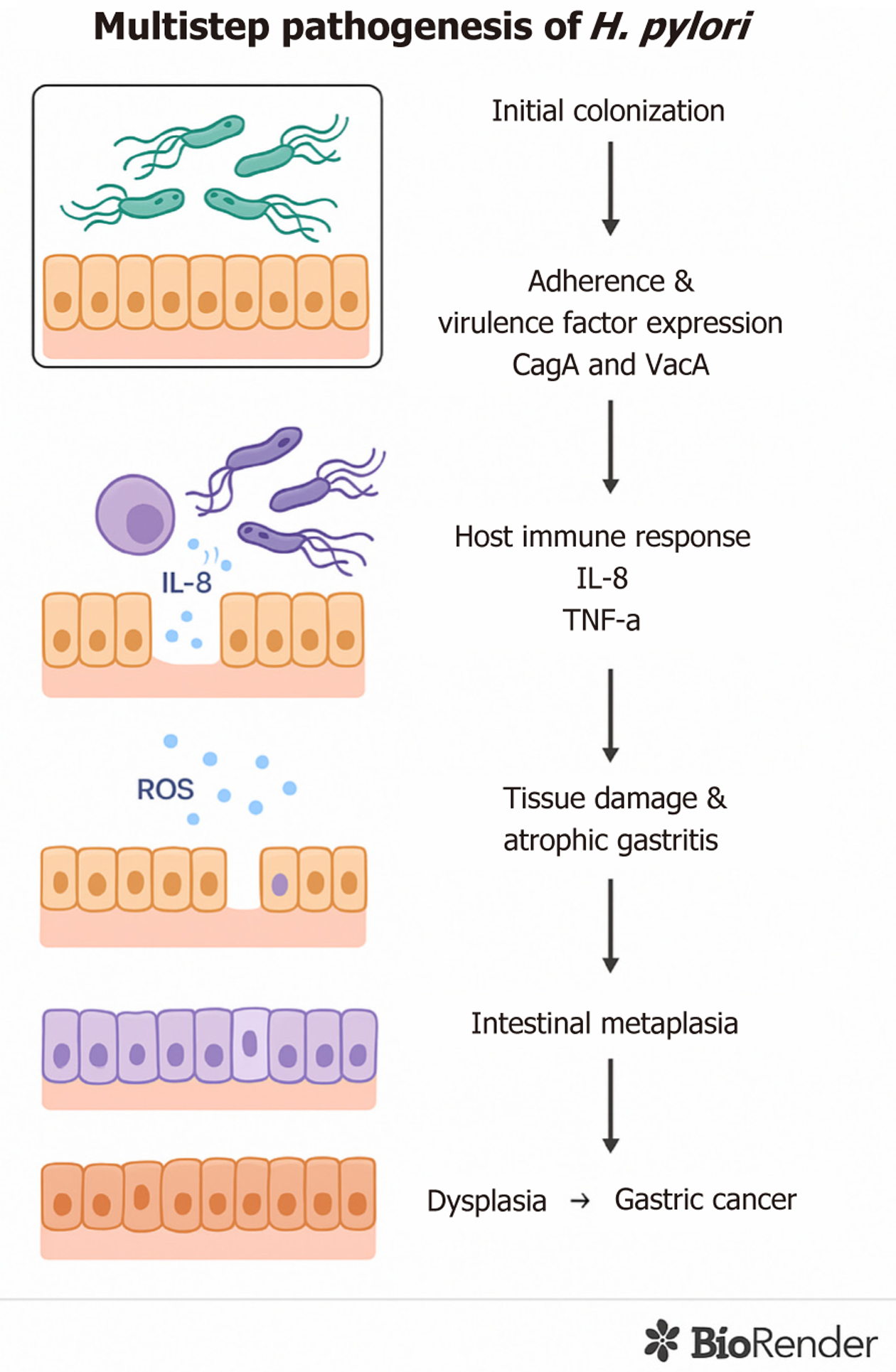
Figure 1 Multistep pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer.
The diagram illustrates the progressive stages of Helicobacter pylori infection: From initial colonization and virulence factor expression (CagA and VacA) to activation of host immune responses (e.g., interleukin-8, tumor necrosis factor-alpha), chronic inflammation, tissue damage, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and eventual dysplasia leading to gastric cancer. IL: Interleukin; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Ansari S, Ahmed N. Pathogenicity of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(12): 110909
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i12/110909.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.110909