©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2025; 16(12): 110351
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.110351
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.110351
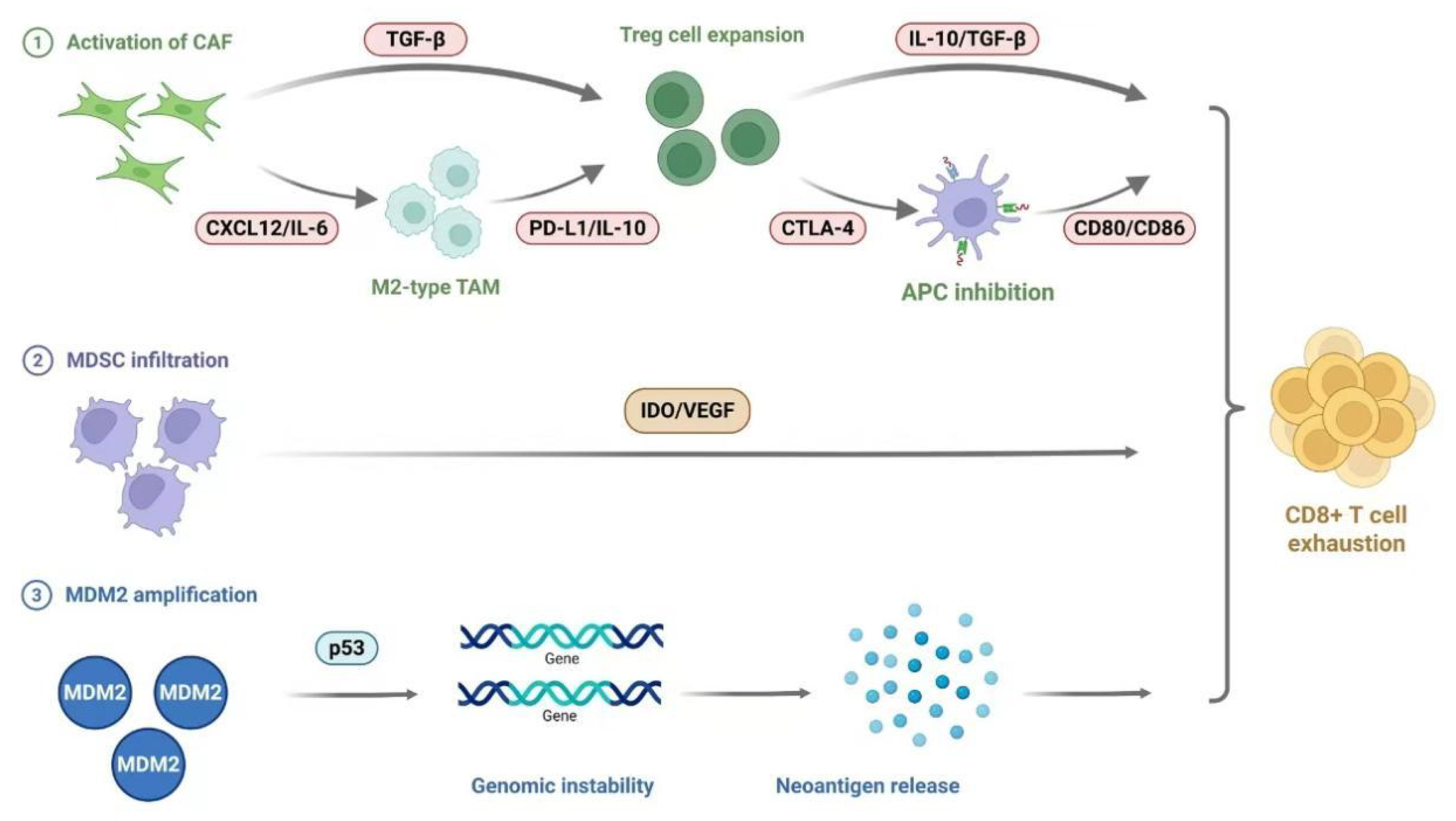
Figure 1 Molecular mechanisms of hyperprogressive disease.
CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; CXCL: C-X-C chemokine ligand; IL: Interleukin; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; APC: Antigen-presenting cell; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MDM2: Mouse double minute 2 homolog.
- Citation: Zhang XM, Zhao FY, Gao LF, Xu T, Yang F, Qian NS. Immune therapy-related hyperprogressive disease: Molecular mechanisms, biomarkers, and clinical strategies. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(12): 110351
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i12/110351.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.110351