©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Nov 24, 2024; 15(11): 1428-1434
Published online Nov 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i11.1428
Published online Nov 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i11.1428
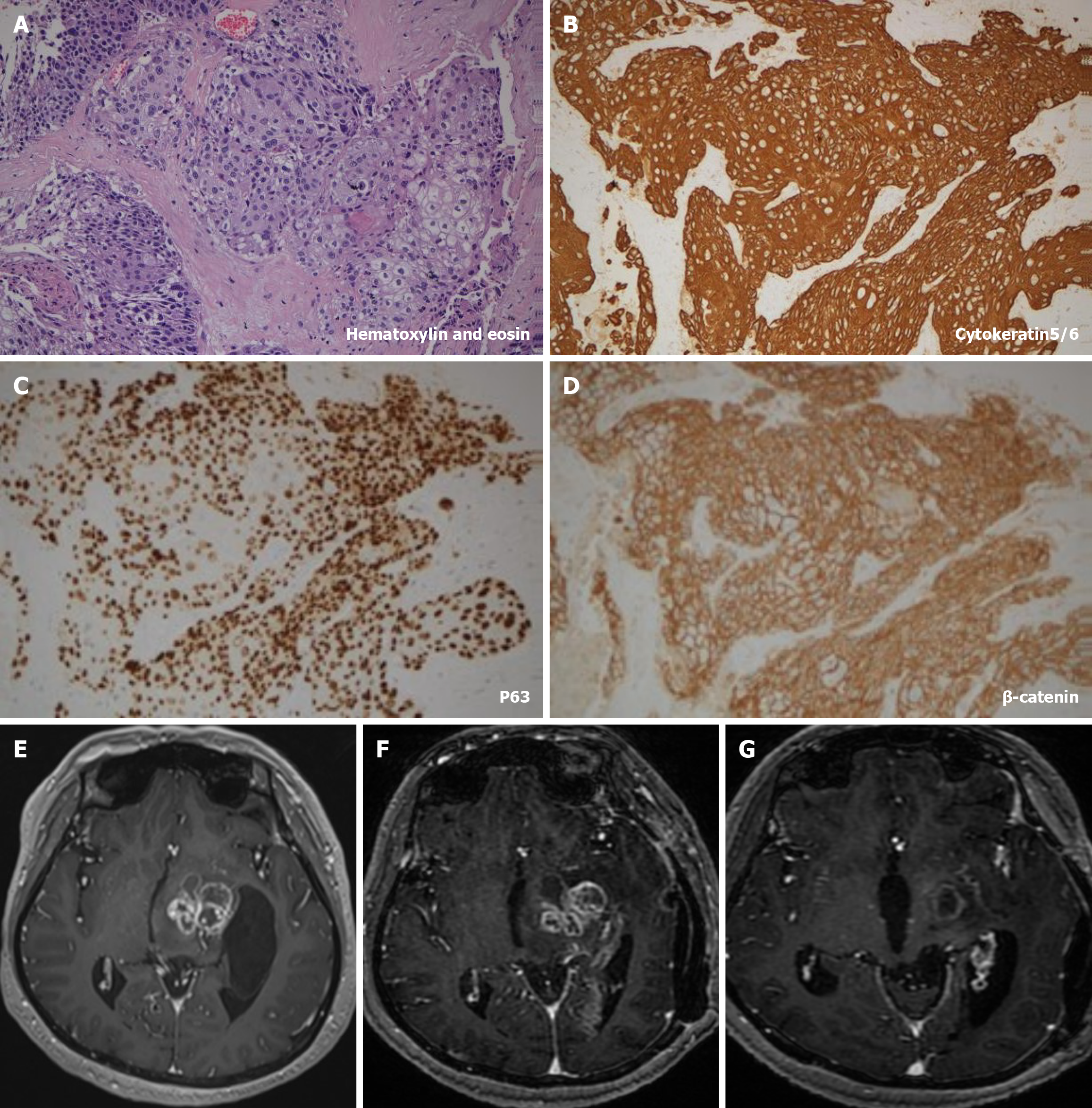
Figure 1 Brain magnetic resonance imaging and immunohistochemical features.
A-D: Hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining of pathological sections from the patient: cytokeratin5/6 (+), P63 (+), β-catenin (+); E: Preoperative brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image of the patient; F: Postoperative brain MRI; G: Brain MRI figure following radio and chemotherapy.
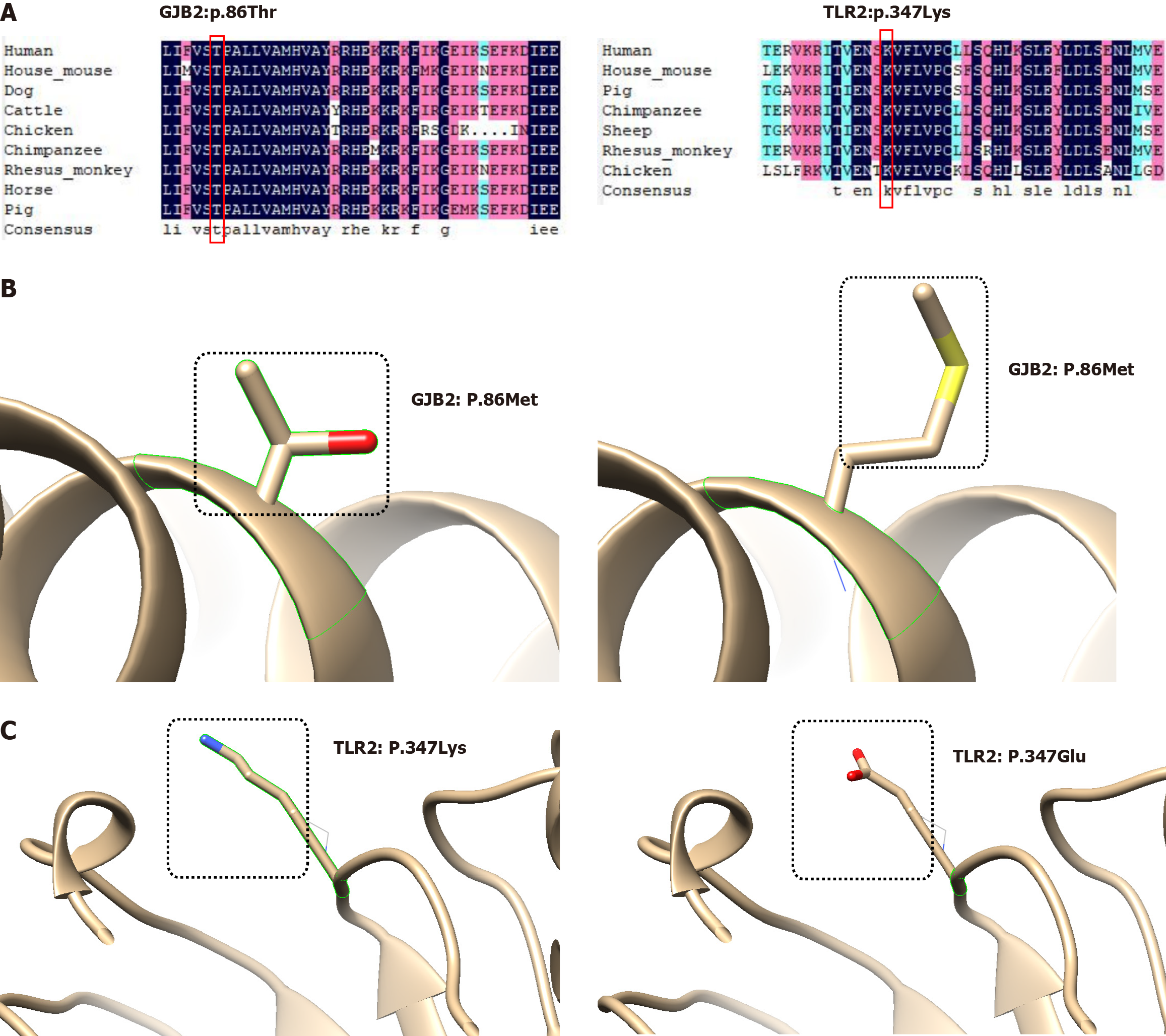
Figure 2 Bioinformatics analyses of the two risk variants.
A: Analysis of the conservation of Gap junction protein beta 2 (GJB2): P86Thr and Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2): P347Lys across species; B: Local depictions of the three-dimensional protein structure of GJB2 prior to and after mutation; C: Local depictions of the three-dimensional protein structure of TLR2 prior to and after mutation. Black boxes indicate the altered amino acid. GJB2: Gap junction protein beta 2; TLR2: Toll-like receptor 2.
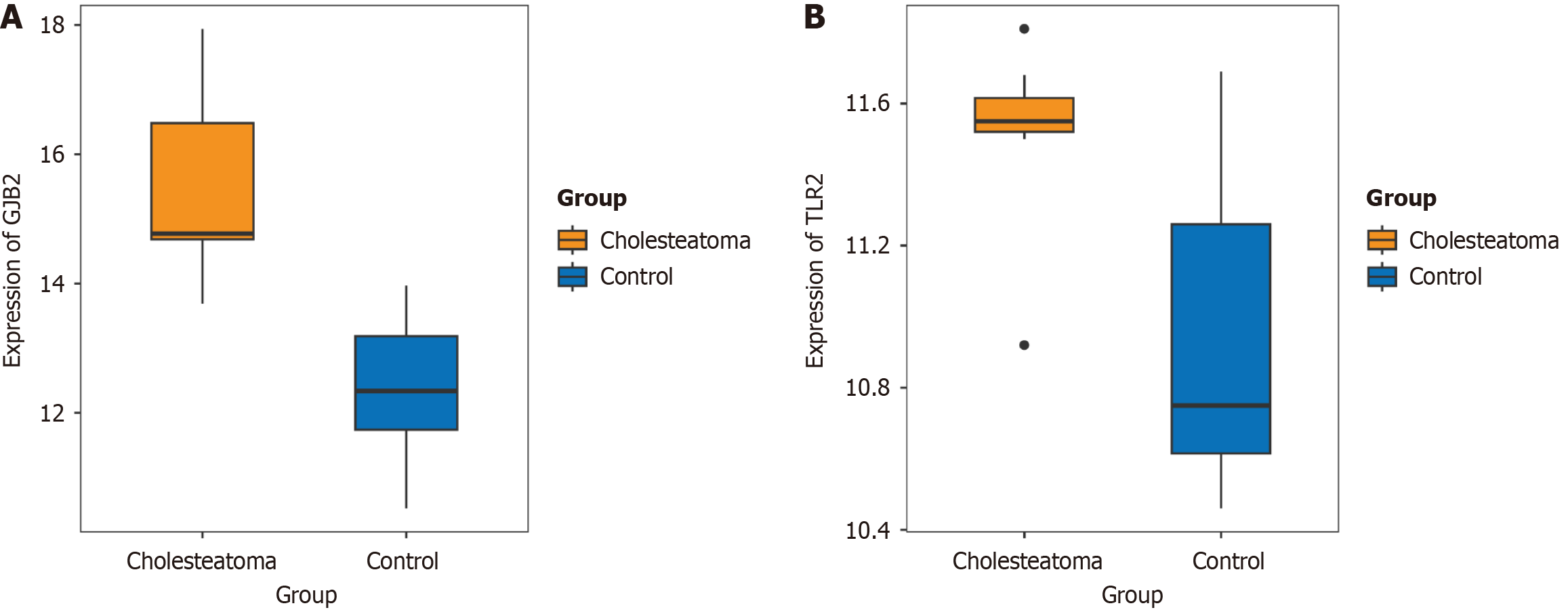
Figure 3 The expression of Gap junction protein beta 2 and Toll-like receptor 2 in the GSE42256 dataset.
A and B: Gap junction protein beta 2 and Toll-like receptor 2 were significantly over-expressed in the cholesteatoma group compared with normal population. GJB2: Gap junction protein beta 2; TLR2: Toll-like receptor 2.
- Citation: Song ZN, Cheng Y, Wang DD, Li MJ, Zhao XR, Li FW, Liu Z, Zhu XR, Jia XD, Wang YF, Liang FF. Whole exome sequencing identifies risk variants associated with intracranial epidermoid cyst deterioration: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(11): 1428-1434
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i11/1428.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i11.1428