©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Dec 22, 2025; 16(4): 111245
Published online Dec 22, 2025. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v16.i4.111245
Published online Dec 22, 2025. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v16.i4.111245
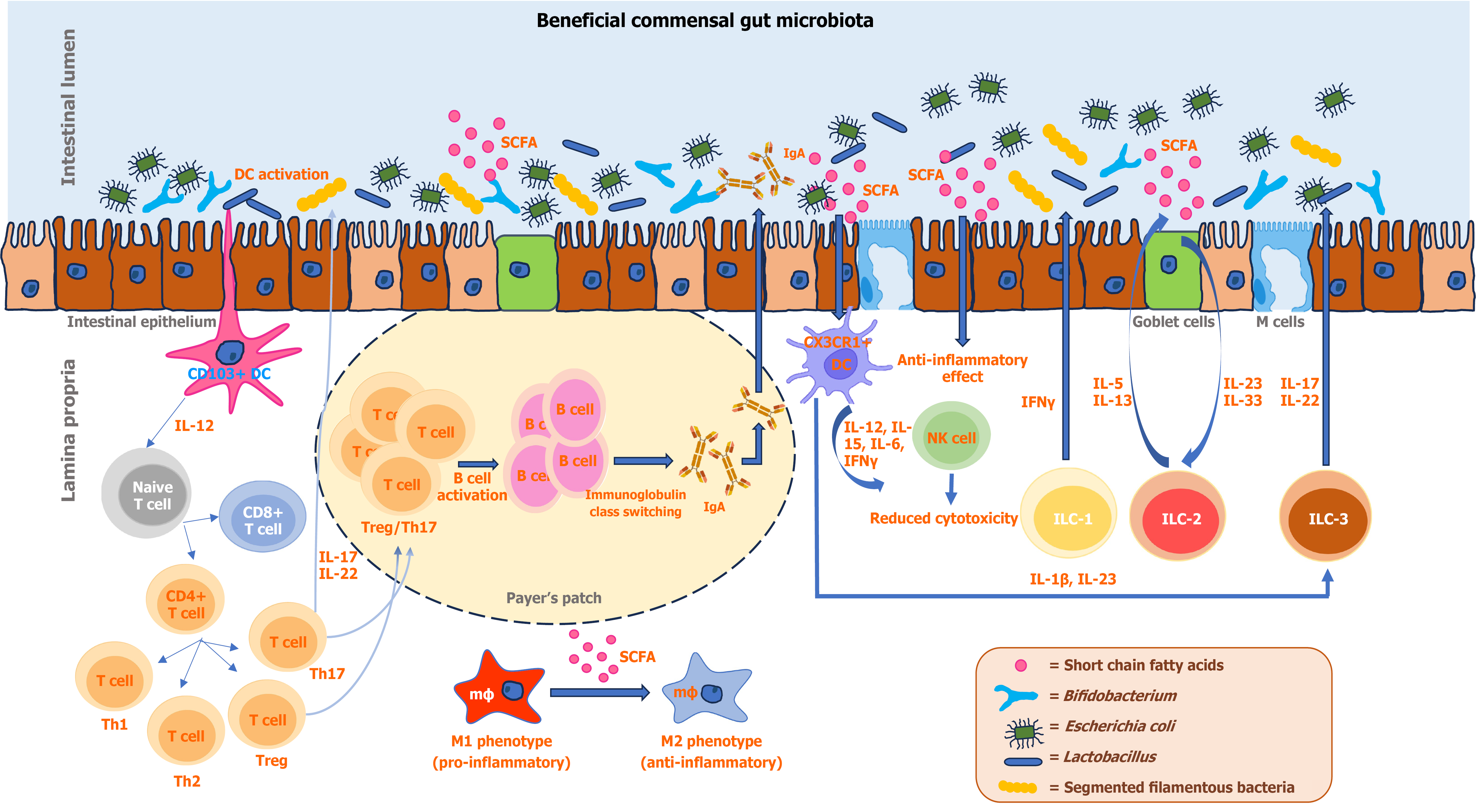
Figure 1 A simplified summary of the interaction of the beneficial gut commensals and gut resident immune cells.
For simplicity, only some key members of the gut microbiota community have been mentioned here. DC: Dendritic cells; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IgA: Immunoglobulin A; IL: Interleukin; ILC: Innate lymphoid cell; mϕ: Macrophage; NK: Natural killer; SCFA: Short chain fatty acids; Treg: Regulatory T; Th: T helper.
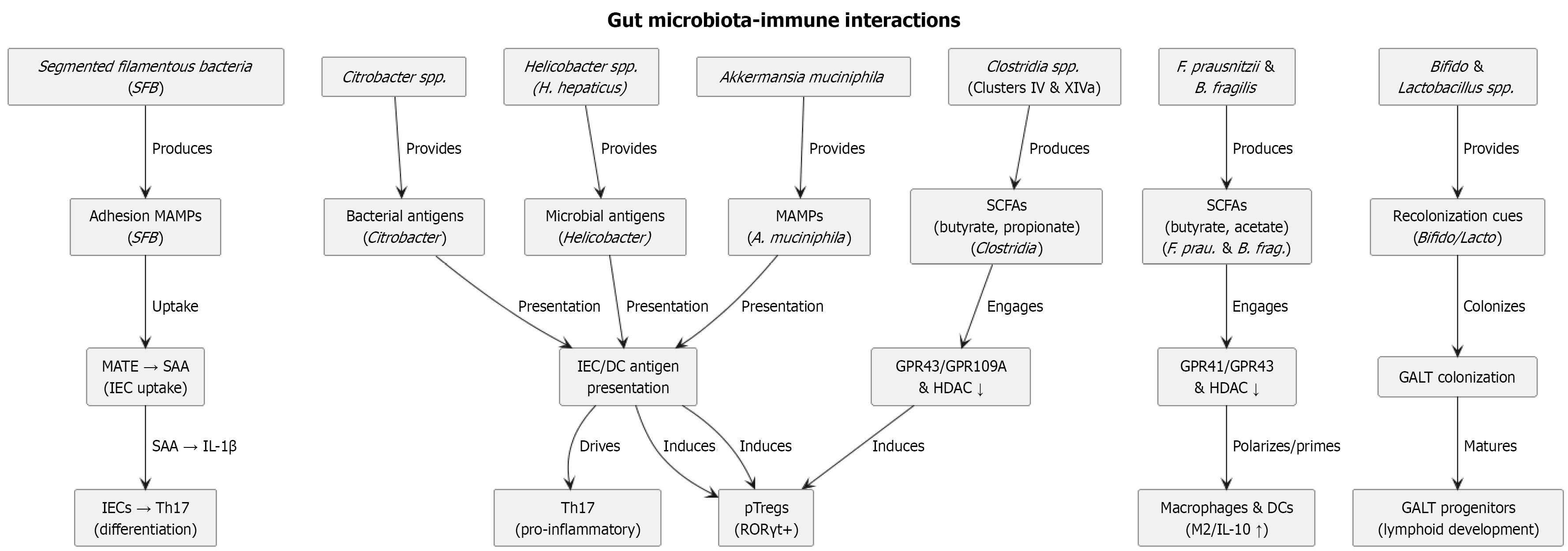
Figure 2 Schematic diagram depicts the gut microbiota-immune interactions.
Each microbial taxon (left) produces a specific metabolite or microbial-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) (next column) that is sensed by a defined host receptor or mechanism (center), leading to activation of intestinal epithelial or antigenpresenting cells and subsequent engagement of distinct immune cell subsets (right), which culminate in specific functional outcomes (far right). For example, segmented filamentous bacteria adhesion MAMPs are taken up via intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) microbial adhesion-triggered endocytosis transporters to induce serum amyloid A and Interleukin (IL)-1β for T helper 17 (Th17) differentiation; Citrobacter antigens presented by IECs/dendritic cells (DCs) drive proinflammatory Th17 responses; Clostridiaderived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (butyrate, propionate) engage G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 43/GPR109A and inhibit histone deacetylases to expand RORγt+ peripheral Tregs; Helicobacter antigens presented by DCs promote pTreg differentiation; Akkermansia muciniphila MAMPs via antigen-presenting cell cues support pTreg maintenance; Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bacteroides fragilis SCFAs polarize macrophages/DCs toward IL-10 – producing M2 phenotypes through GPR41/GPR43 signaling and histone deacetylase inhibition; and Bifidobacterium/Lactobacillus recolonization cues drive gut-associated lymphoid tissue colonization and lymphoid tissue maturation. B. fragilis: Bacteroides fragilis; Bifido/Lacto: Bifidobacterium/Lactobacillus; DC: Dendritic cell; F. prausnitzii: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; GALT: Gut-associated lymphoid tissue; HDAC: Histone deacetylase inhibition; IEC: Intestinal epithelial cell; IL: Interleukin; MAMP: Microbial-associated molecular pattern; SAA: Serum amyloid A; SFB: Segmented filamentous bacteria; Th: T helper.
- Citation: Ghosh N, Sinha K. Guardians within: Cross-talk between the gut microbiome and host immune system. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2025; 16(4): 111245
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v16/i4/111245.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v16.i4.111245