Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Mar 15, 2025; 16(3): 100329
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.100329
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.100329
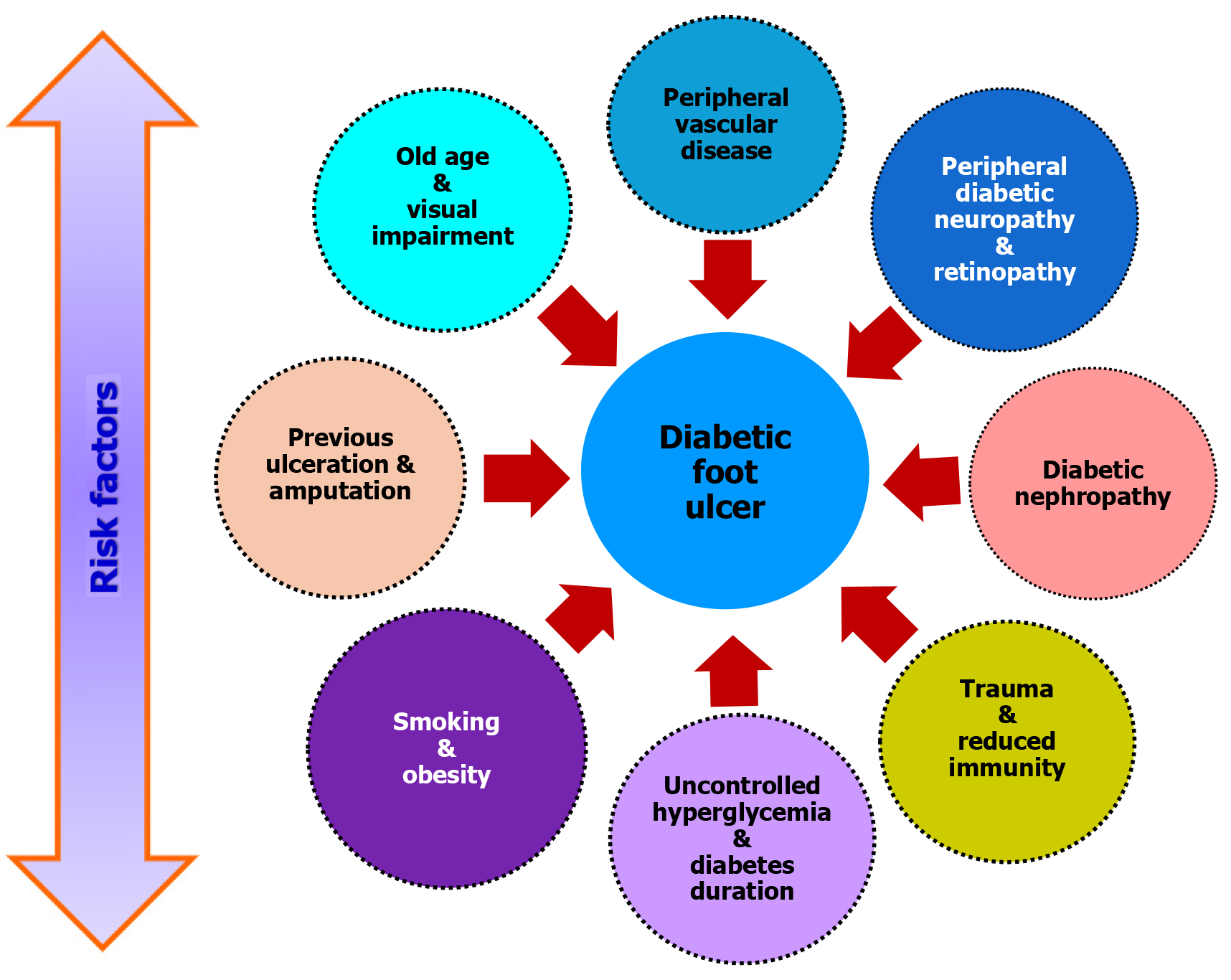
Figure 1 Risk factors of diabetic foot ulcer.
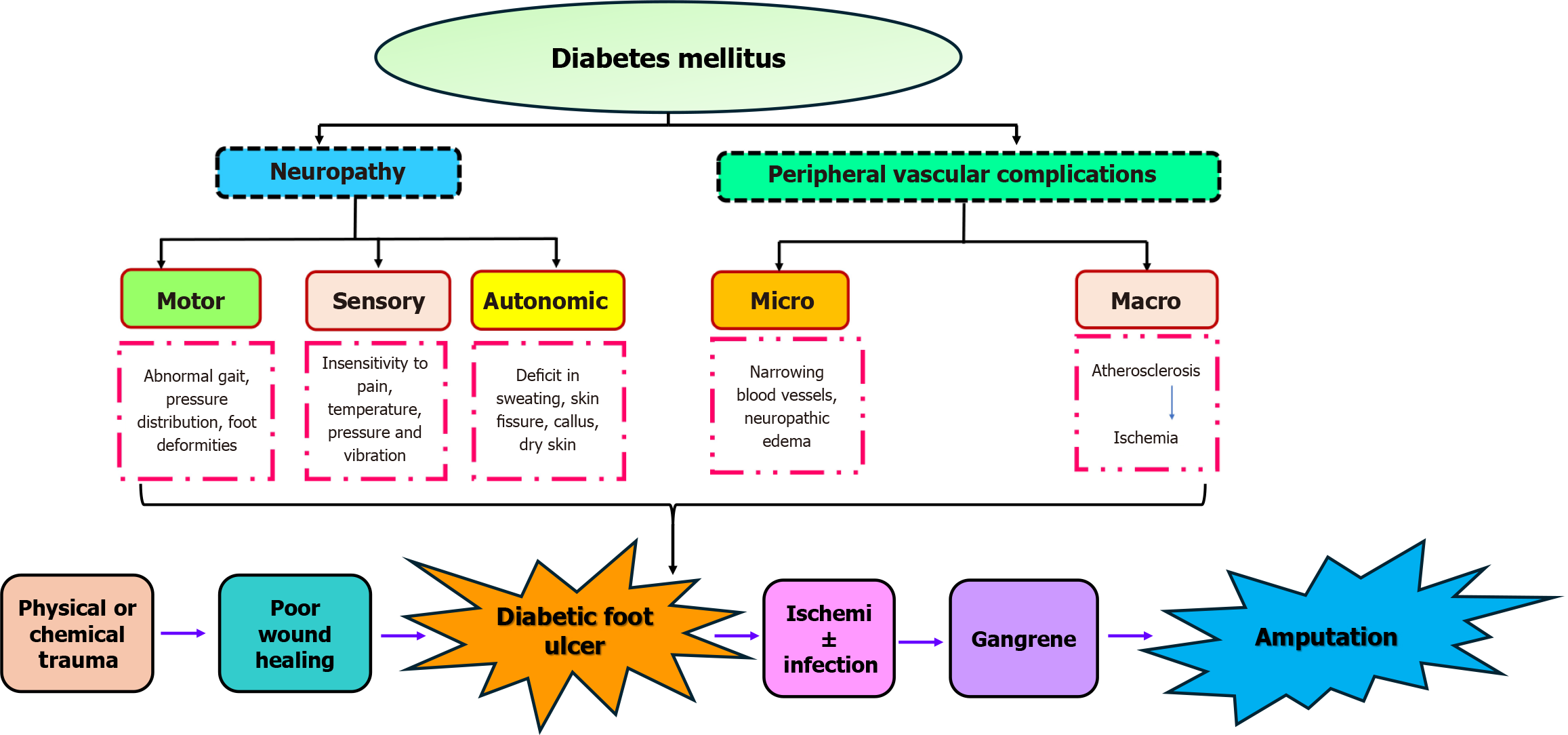
Figure 2 Pathophysiology of diabetic foot ulcer: Major factors involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic foot ulcers.
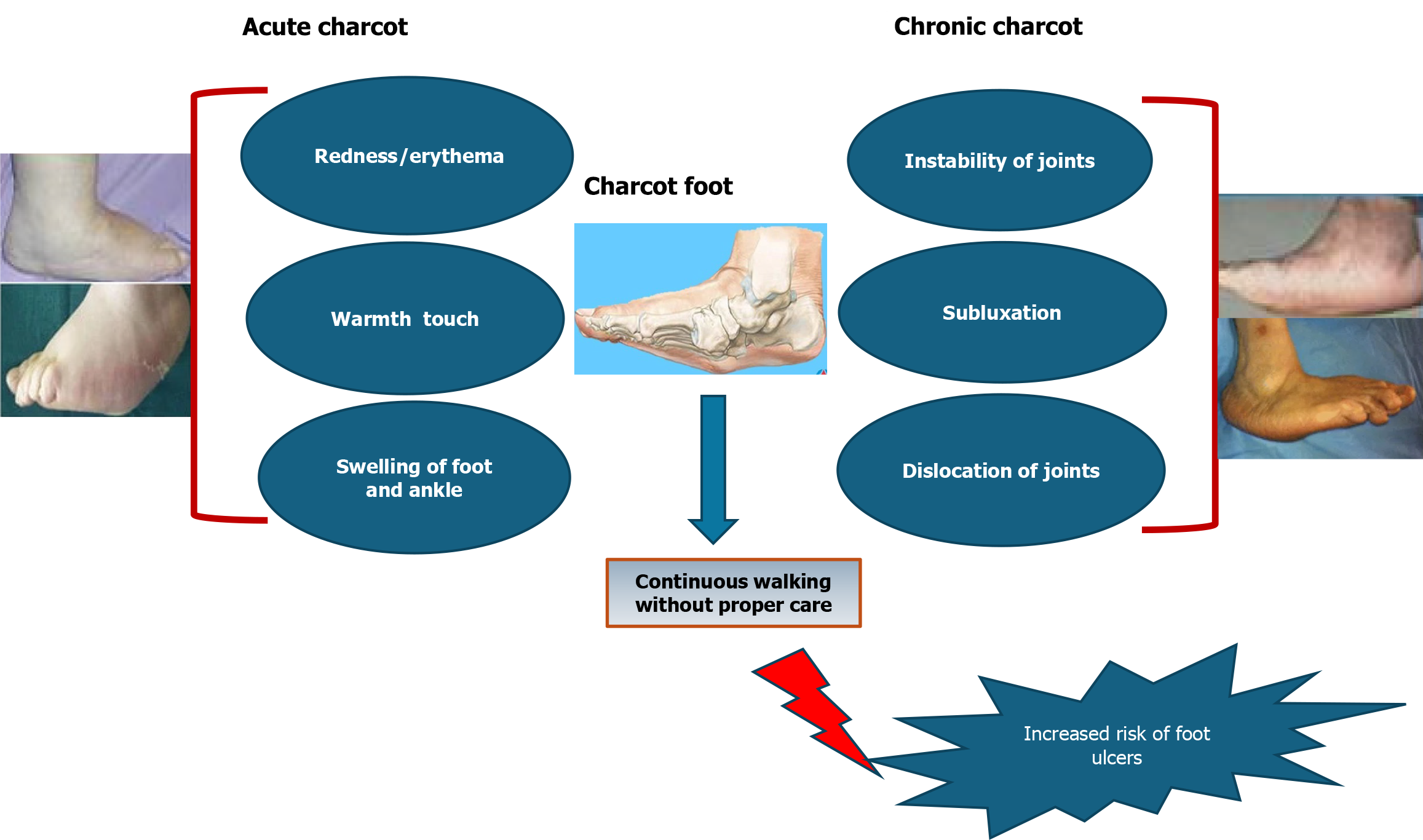
Figure 3 Representation of Charcot foot entity.
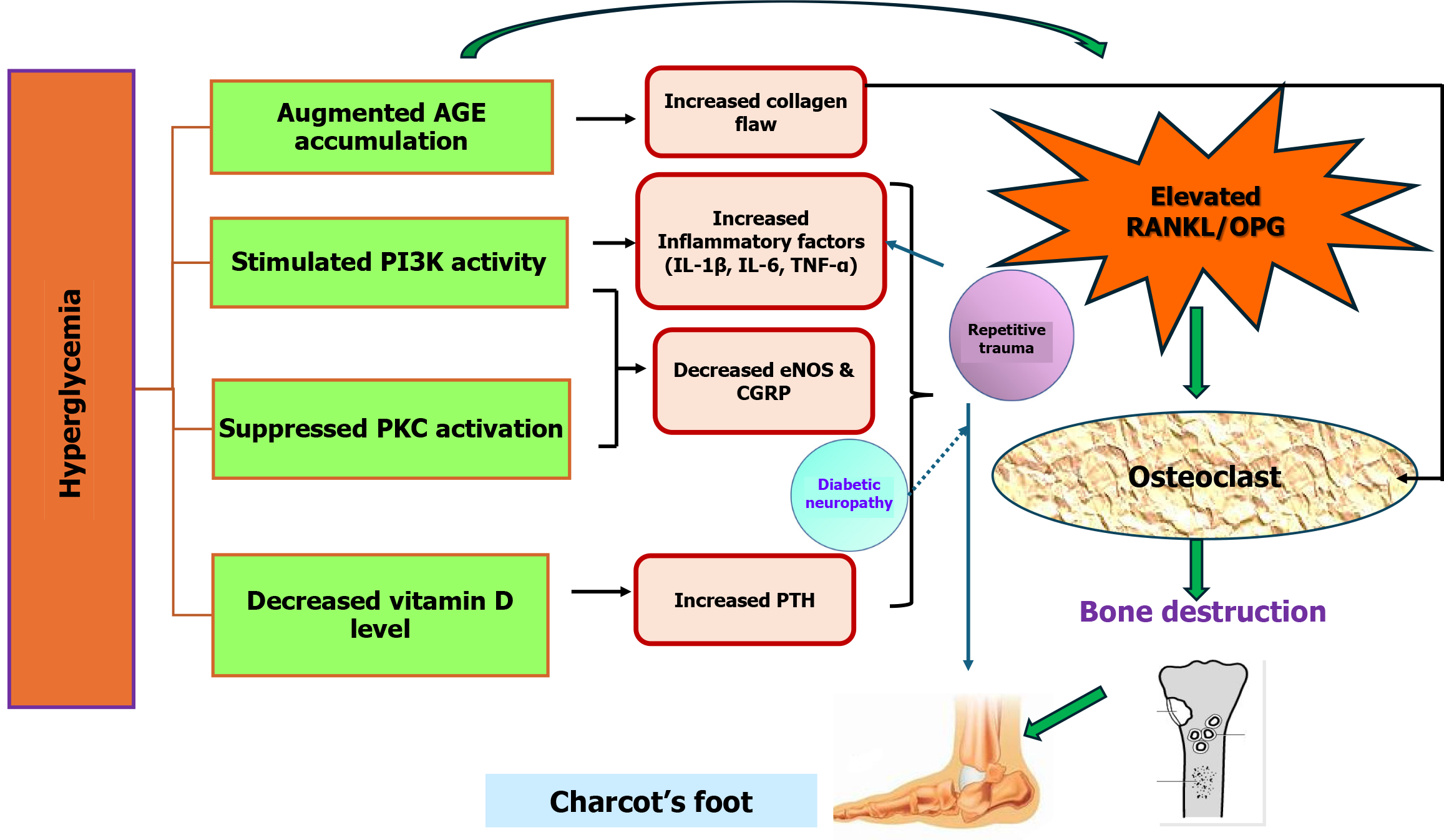
Figure 4 Underlying the pivotal function of the RANKL-OPG system in the development of deleterious bone changes is the patho
- Citation: Parveen K, Hussain MA, Anwar S, Elagib HM, Kausar MA. Comprehensive review on diabetic foot ulcers and neuropathy: Treatment, prevention and management. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(3): 100329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i3/100329.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i3.100329