©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2026; 18(2): 113995
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.113995
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.113995
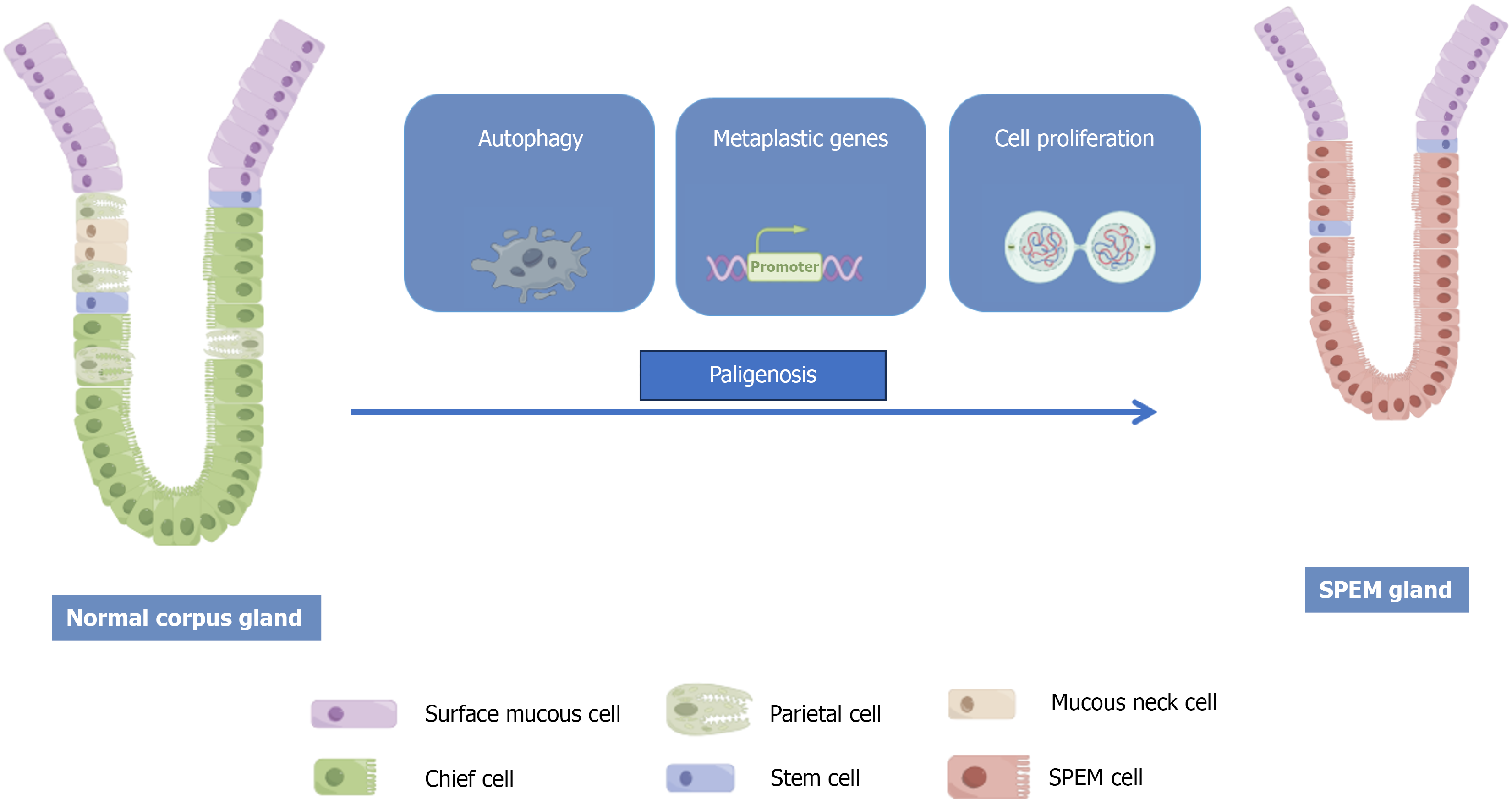
Figure 1 Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia process in “paligenosis”.
SPEM: Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia.
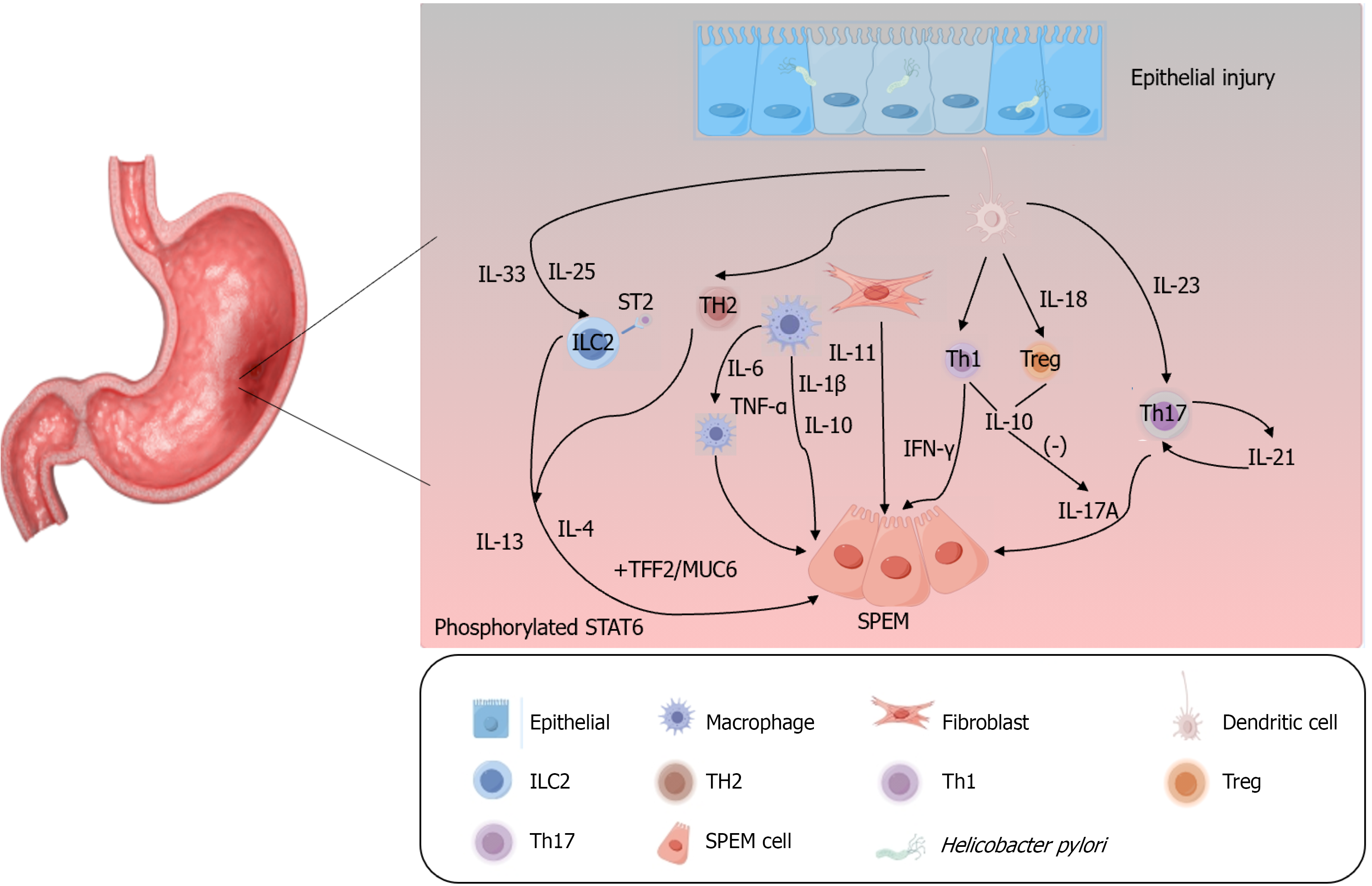
Figure 2 Cytokine-mediated induction of spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia.
Helicobacter pylori infection triggers a host immune response that can mimic autoimmunity, resulting in antigen-specific tissue damage. Following damage, interleukin (IL)-33 and IL-25 are released as early alarm signals, leading to the activation of various immune cells, including macrophages and T helper 1 (Th1), Th2, and Th17 cells. These activated cells secrete a combination of pro- and anti-inflammatory factors, collectively establishing a chronic inflammatory microenvironment conducive to metaplasia. Specifically, interleukin (IL)-33 (and, to a lesser extent, IL-25) binds to the ST2 receptor on type 2 innate lymphoid cells, prompting the secretion of type 2 cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13. IL-13 and IL-4 then signal through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 pathway in gastric epithelial cells, promoting the expression of mucous cell markers, including trefoil factor 2 and mucin 6. This process ultimately facilitated the maturation and proliferation of spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia cells. IL: Interleukin; ILC2s: Type 2 innate lymphoid cells; TFF2: Trefoil factor 2; MUC6: Mucin 6; STAT6: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IFN: Interferon; SPEM: Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia; TH2: T helper 2; Th1: T helper 1; Treg: Regulatory T.
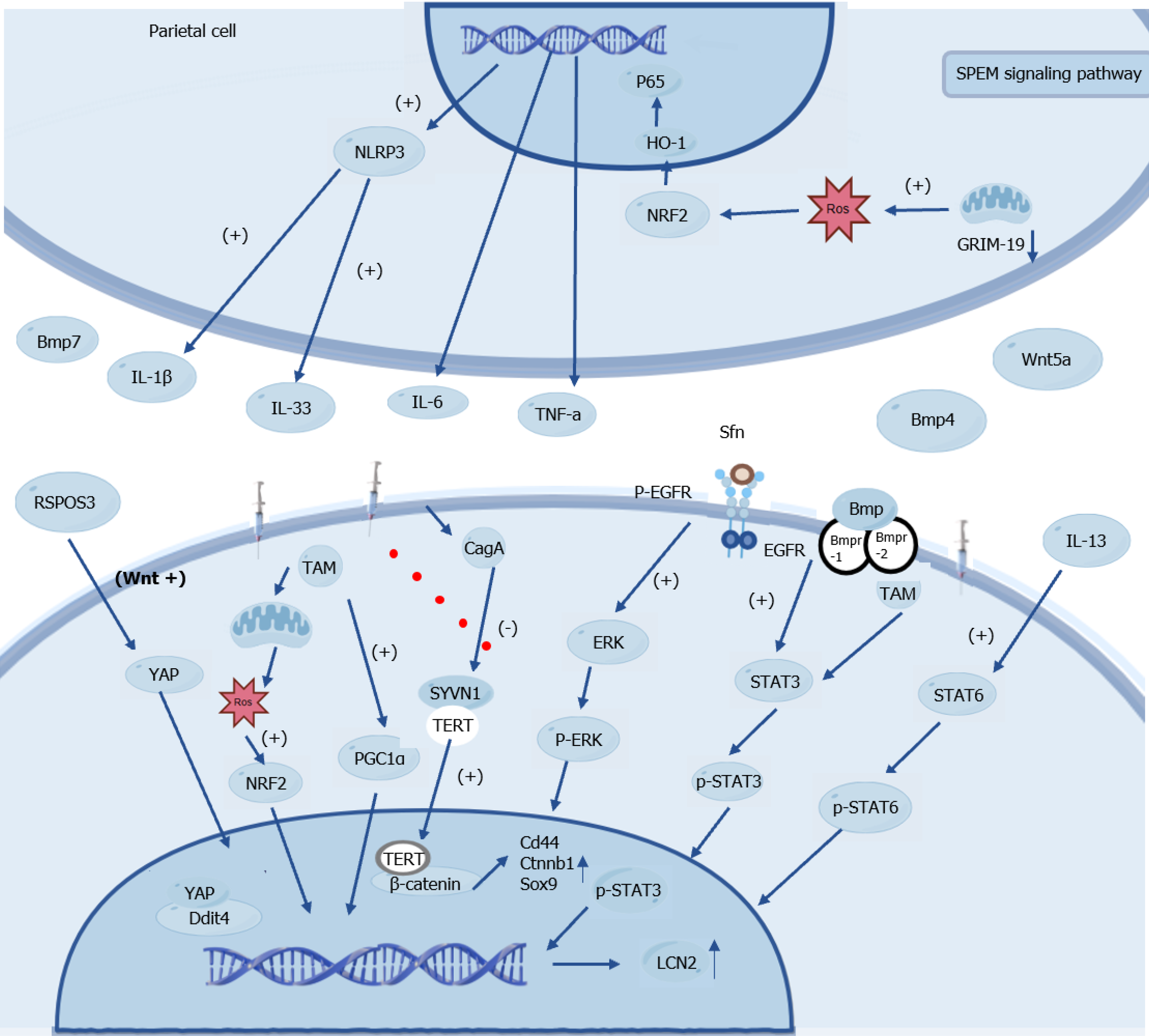
Figure 3 Interaction of key factors upstream and downstream of spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia-related signaling pathway.
The figure illustrates the molecular regulatory mechanisms associated with parietal cells and the spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia signaling pathway, as evidenced in mouse models. In parietal cells, NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 is activated by factors such as PR55, promoting the production of cytokines including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-33, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α. Concurrently, reactive oxygen species contribute to this regulation by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, which subsequently modulates downstream effectors such as heme oxygenase-1. Within the spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia signaling pathway, alterations in gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality 19 influence reactive oxygen species levels, thereby engaging in subsequent pathways, such as those involving bone morphogenetic protein. Additionally, key molecules including Yes-associated protein, telomerase reverse transcriptase, and β-catenin participate in the regulation of gene expression. For instance, lipocalin 2 expression is regulated by phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 within relevant signaling cascades, whereas the binding of sulforaphane to epidermal growth factor receptor activates a series of signal transduction events, such as the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Collectively, these interactions form a complex molecular regulatory network, as characterized by mouse studies. NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; SPEM: Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia; NRF2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GRIM-19: Gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality 19; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; Sfn: Sulforaphane; TAM: Tamoxifen; CagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; YAP: Yes-associated protein; SYVN1: E3 ubiquitin ligase synoviolin; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; stat3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Ddit4: DNA damage induced transcript 4; TERT: Telomerase reverse transcriptase; Sox9: SRY-Box transcription factor 9; LCN2: Lipocalin-2.
- Citation: Yang RR, Yan YR, Li YF. Recent advances in spasmolytic polypeptide expressing metaplasia research. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2026; 18(2): 113995
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v18/i2/113995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.113995