©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2026; 18(1): 114312
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i1.114312
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i1.114312
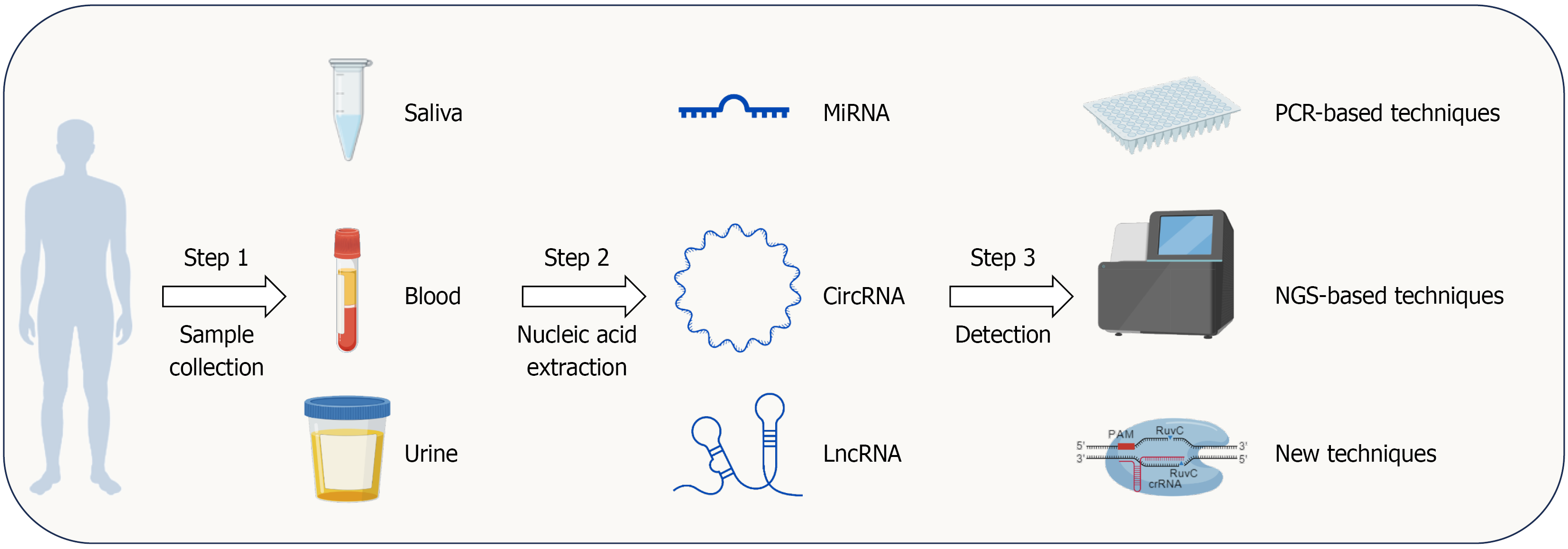
Figure 1 The workflow for non-coding RNA-based liquid biopsy in clinical screening.
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) from blood, saliva, and urine have been reported as potential biomarkers for Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric cancer (GC). Clinically, blood, saliva, and urine can be collected from patients, followed by nucleic acid extraction in the lab. After that, PCR, next-generation sequencing, or other techniques can be used to detect GC-associated ncRNAs. This figure was created with BioGDP.com[46]. LncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; MiRNA: MicroRNA; CircRNA: Circular RNA; NGS: Next-generation sequencing.
- Citation: Lv ZP, Sultan MH, Wang YG. Helicobacter pylori-related non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer screening: Emerging evidence and translational challenges. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2026; 18(1): 114312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v18/i1/114312.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v18.i1.114312