©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2025; 17(9): 109824
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i9.109824
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i9.109824
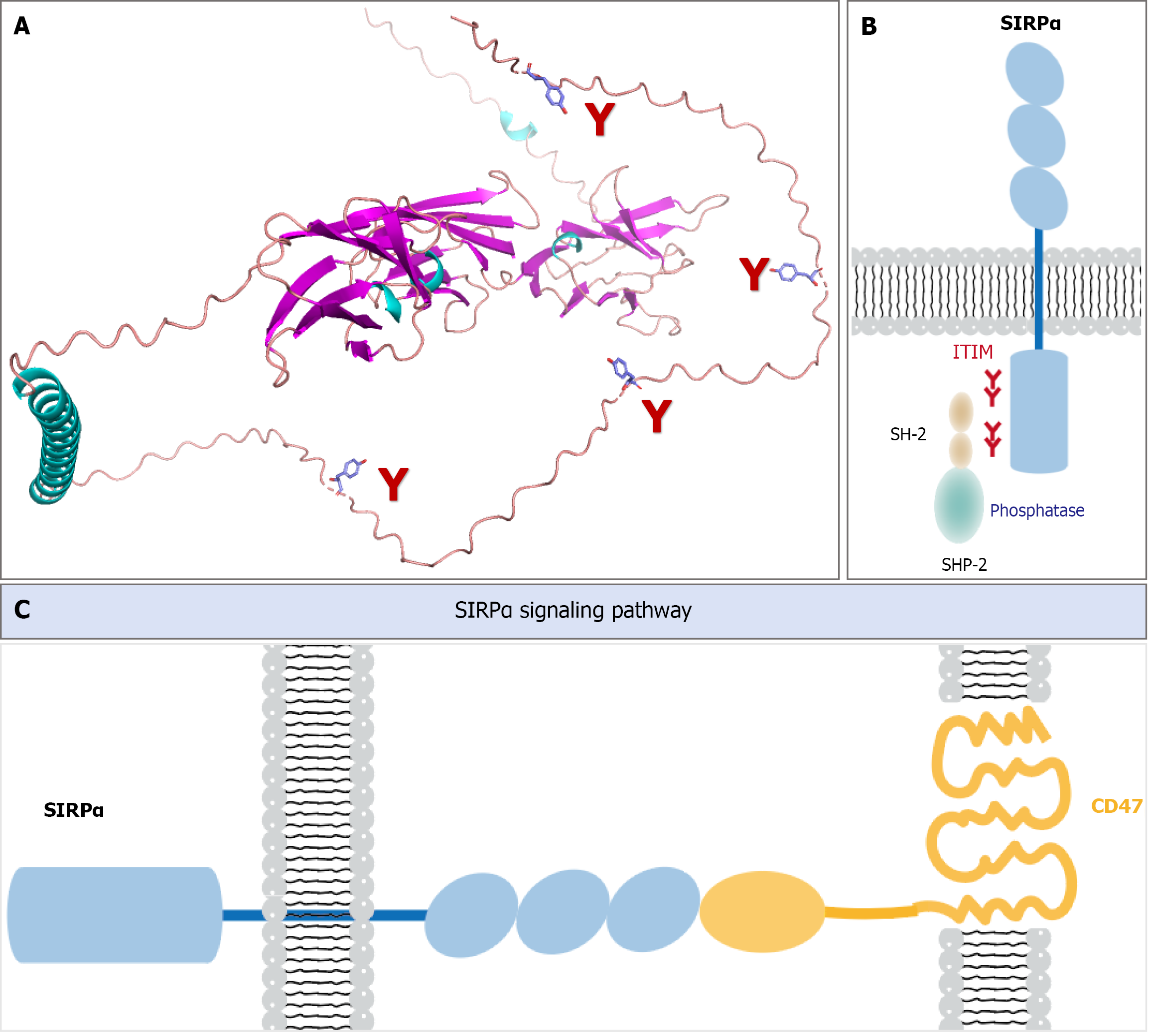
Figure 1 Structural characteristics of signal regulatory protein alpha.
A: The three-dimensional predicted structure of signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). It contains an intracellular domain, an extracellular domain, and four tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic region; B: The structure of SIRPα. It contains three immunoglobulin like domains in the extracellular domain. It contains four tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic region, forming two typical tyrosine immunosuppressive motifs; C: CD47-SIRPα signaling pathway. ITIM: Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif; SIRPα: Signal regulatory protein alpha. Parts of Figure 1 were created in pymol.
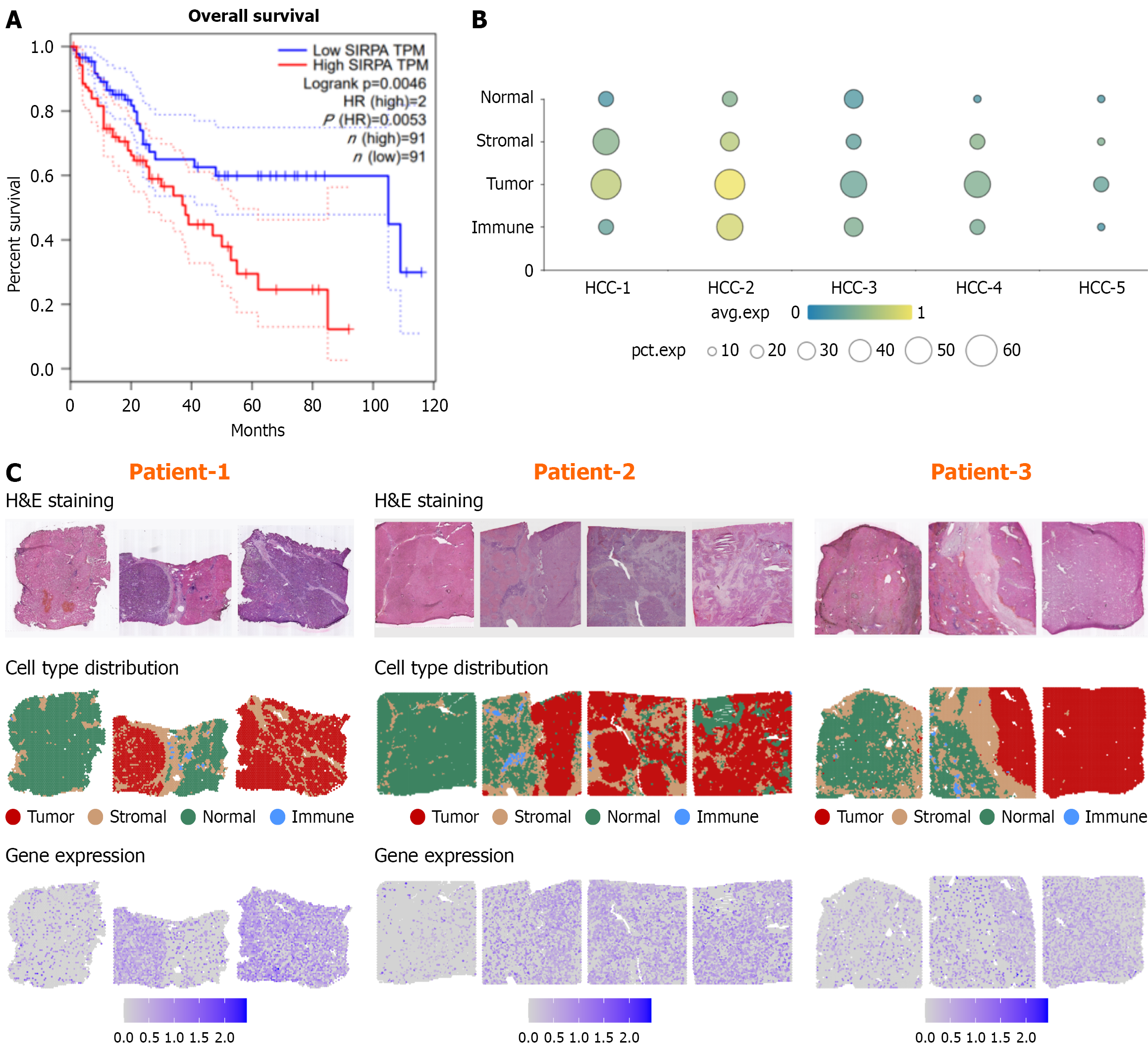
Figure 2 The expression of signal regulatory protein alpha in adjacent and tumor tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: The overall survival of signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) (The Cancer Genome Atlas, http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/). High expression of SIRPα is positively correlated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients; B and C: Expression patterns of SIRPα in tumor, stromal and normal tissues of HCC. The expression of SIRPα showed an increasing trend in normal tissues, stromal tissues, and tumor tissues of HCC (http://Lifeome.net/database/hccdb/home.html). SIRPα: Signal regulatory protein alpha.
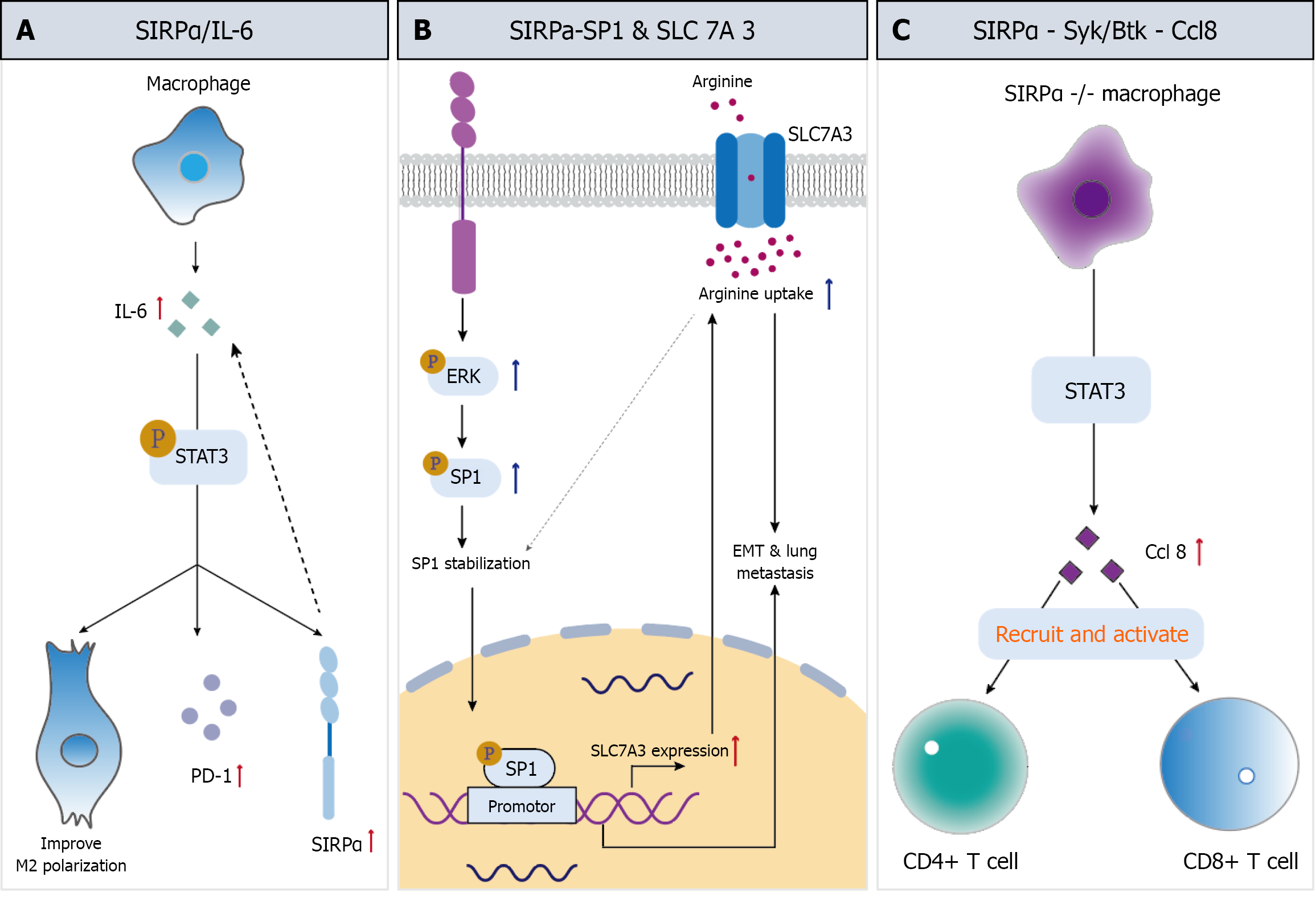
Figure 3 The mechanism of signal regulatory protein alpha.
A: The signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα)/interleukin-6 axis may promote lung cancer development; B: Upregulation of SIRPα promotes osteosarcoma metastasis through the "SP1 stable loop" and SLC 7A3 mediated arginine uptake; C: SIRPα (-/-) macrophages promote T cell recruitment into tumors through Syk/Btk dependent Ccl8 secretion.
- Citation: Zhang X, Chen DB, Zhang R, Chen P, She SP, Yang Y, Ren LY, Chen HS. Immune checkpoint molecules signal regulatory protein alpha in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(9): 109824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i9/109824.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i9.109824