©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2025; 17(12): 113661
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113661
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113661
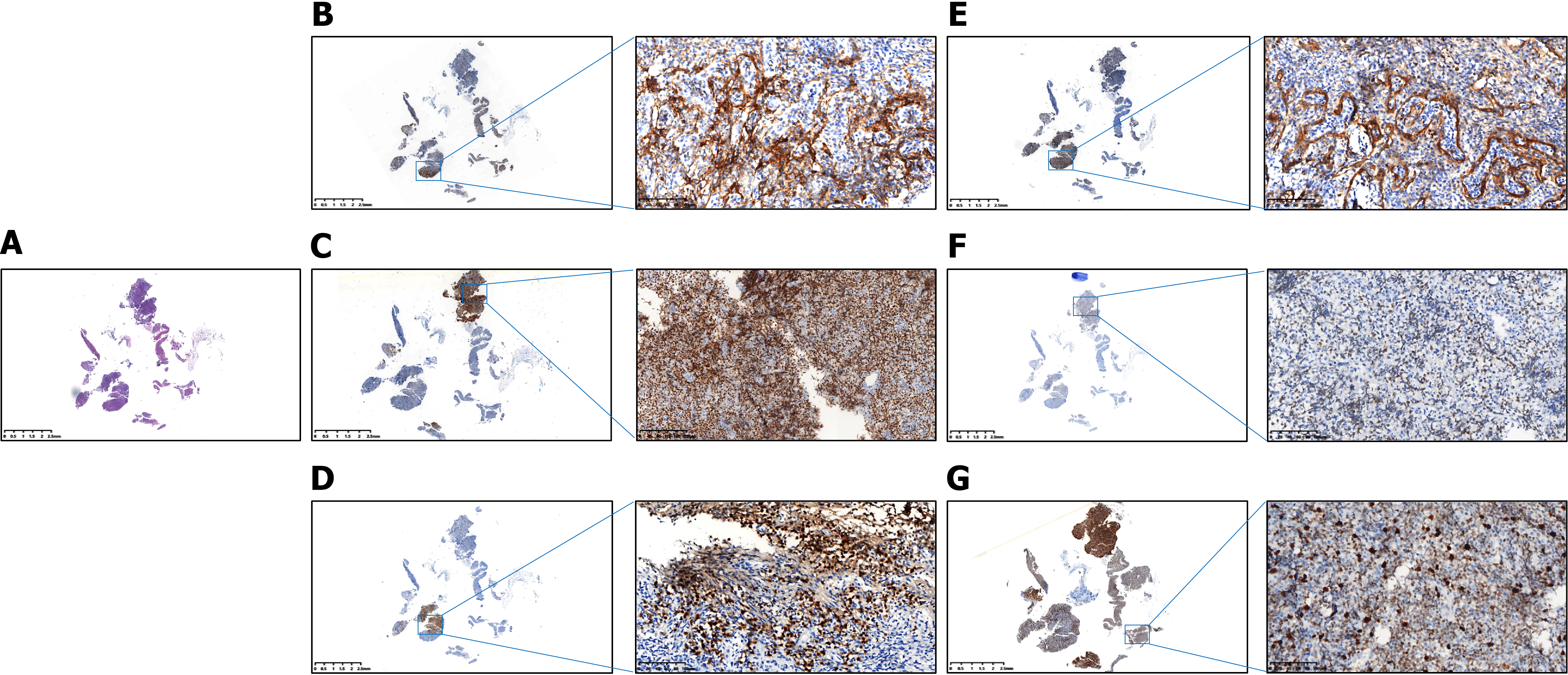
Figure 1 Stomach tissue protein expression.
A: The hematoxylin and eosin; B: CD10 expression; C: B-cell lymphoma 6 expression; D: Multiple myeloma oncogene 1 expression; E: B-cell lymphoma 2 expression; F: Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog expression; G: Ki-67 expression.
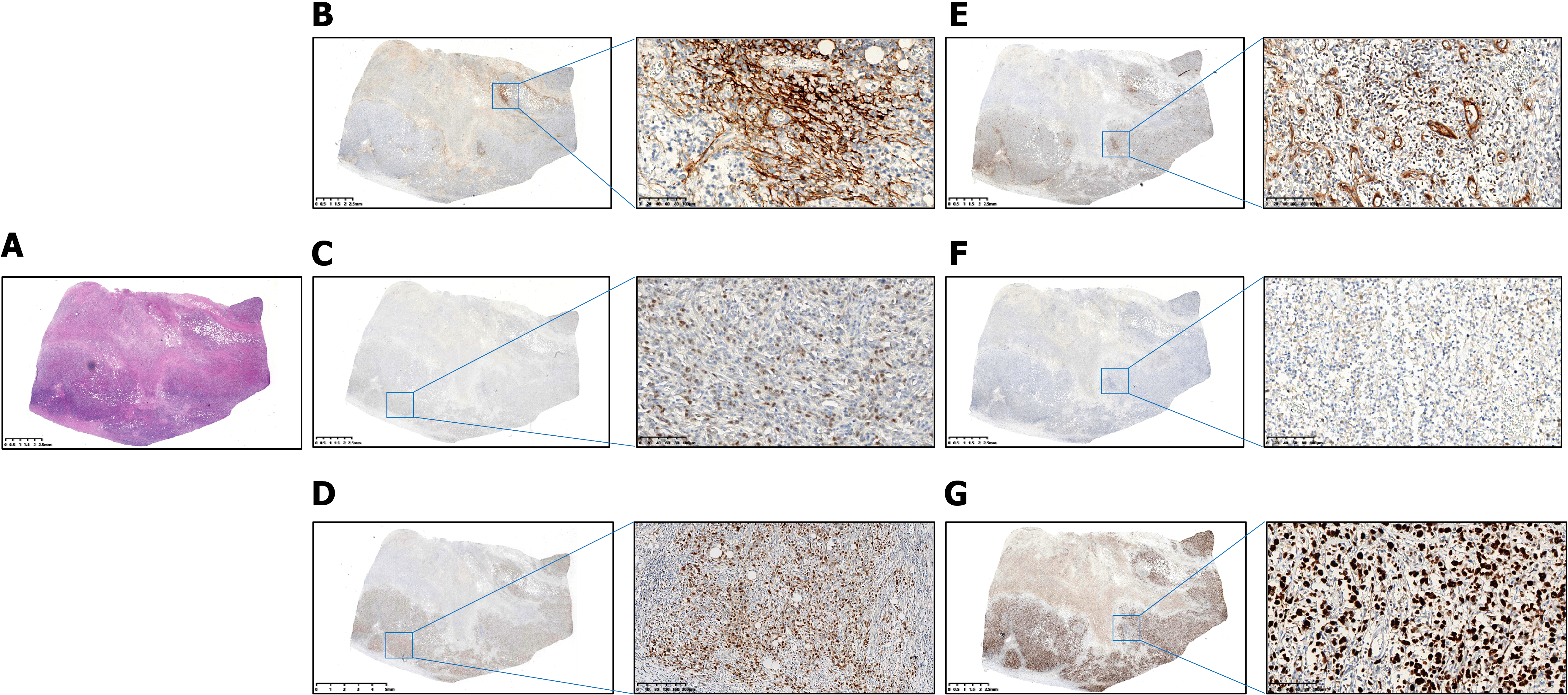
Figure 2 Intestinal tissue protein expression.
A: The hematoxylin and eosin; B: CD10 expression; C: B-cell lymphoma 6 expression; D: Multiple myeloma oncogene 1 expression; E: B-cell lymphoma 2 expression; F: Myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog expression; G: Ki-67 expression.
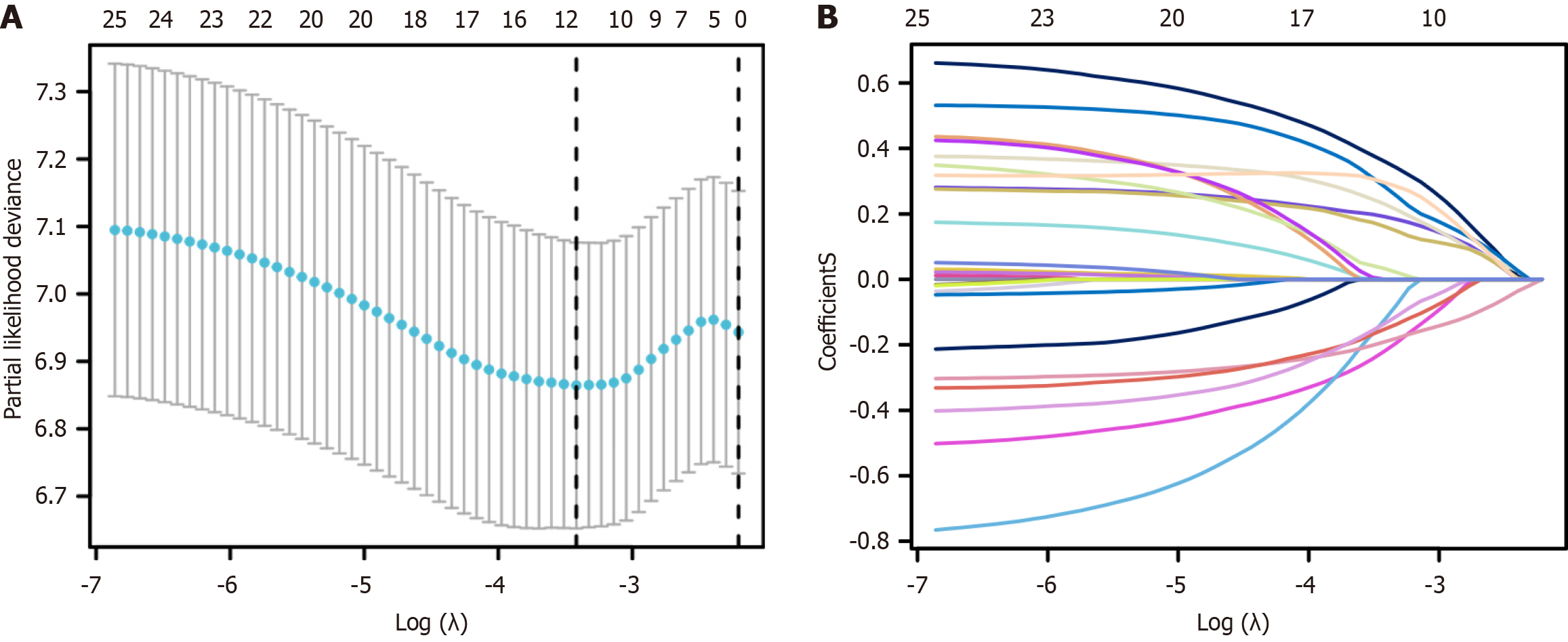
Figure 3 Identification of the influencing factors by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression.
A: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator coefficient profiles of the 13 characteristics; B: The relationship curve between the partial likelihood deviation (binomial deviation) and log(λ).
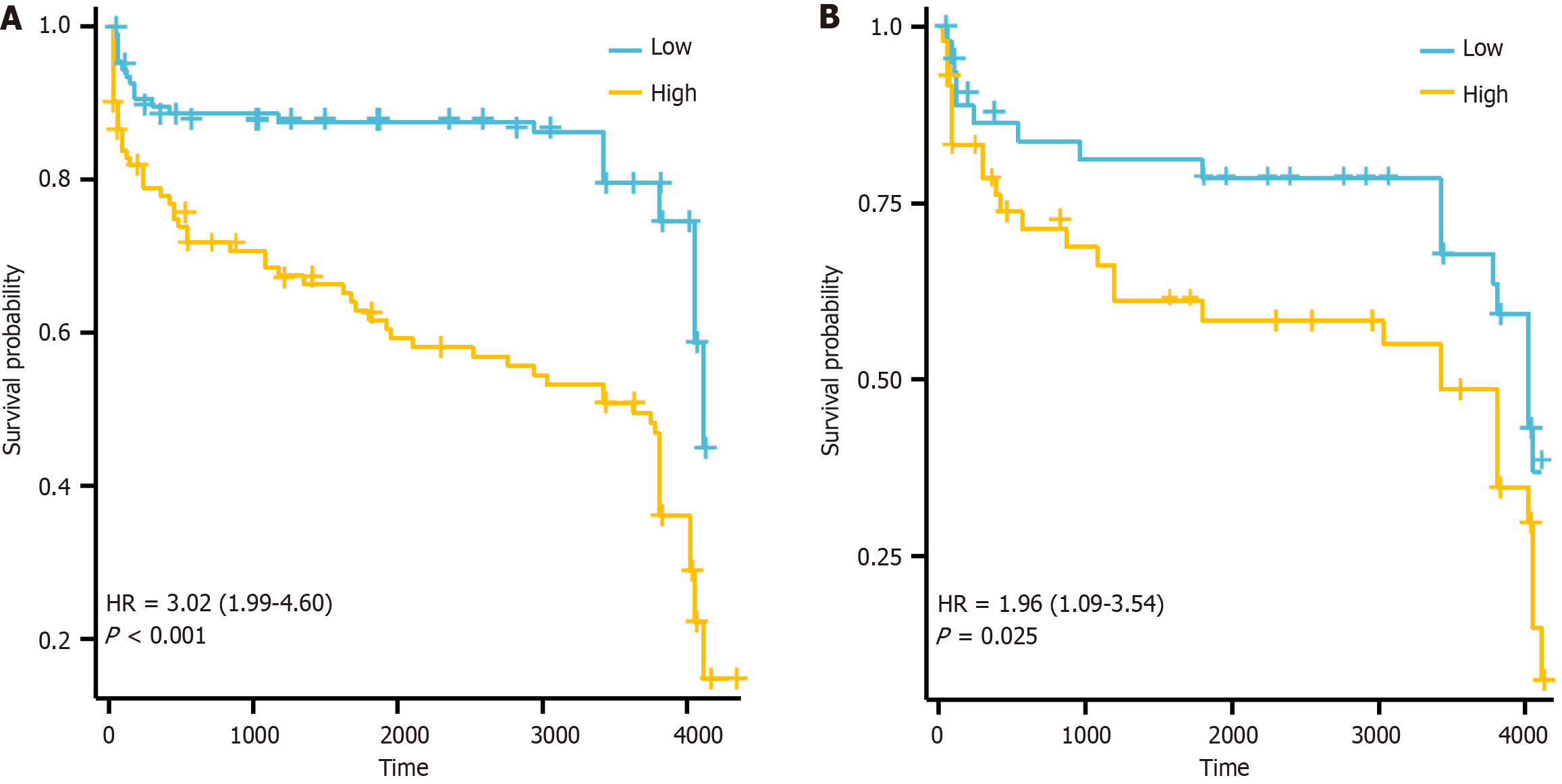
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier analysis.
A: Patients re-stratified by risk score in the training cohort; B: Validation cohort. HR: Hazard ratio.
Figure 5 Time-dependent receiver operating characteristic analyses of the risk model.
A: The training cohort; B: The validation cohort. TPR: True positive rate; FPR: False positive rate; AUC: Area under curve.
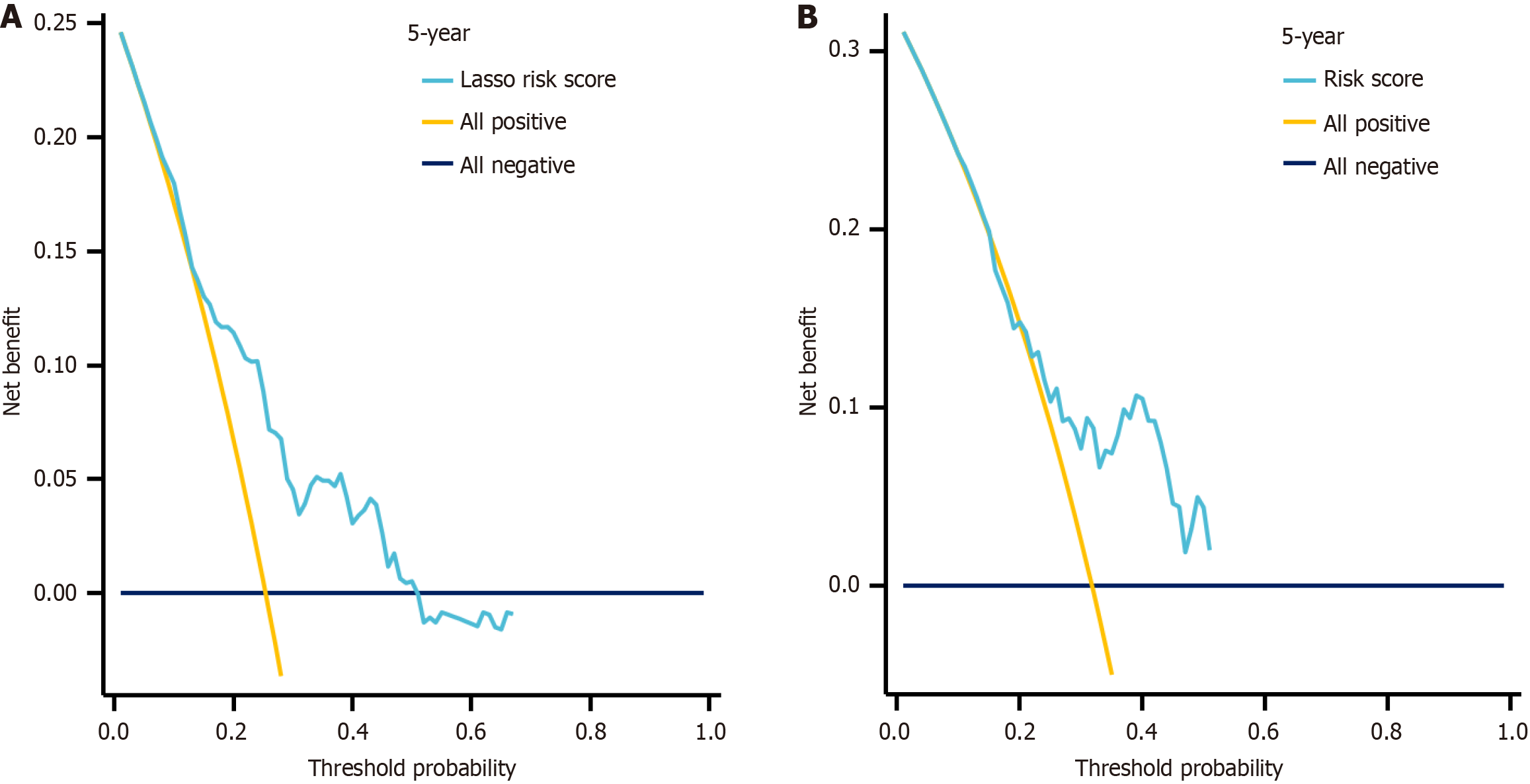
Figure 6 Decision curve analysis of the model performance.
A: The training cohort; B: The validation cohort.
- Citation: Ma JJ, Zhang H, Wang CC, Ji WL, Zhao Y, Li XX. Clinical characteristics and prognostic analysis of three hundred and nineteen cases of primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(12): 113661
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i12/113661.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113661