©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2025; 17(12): 113341
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113341
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113341
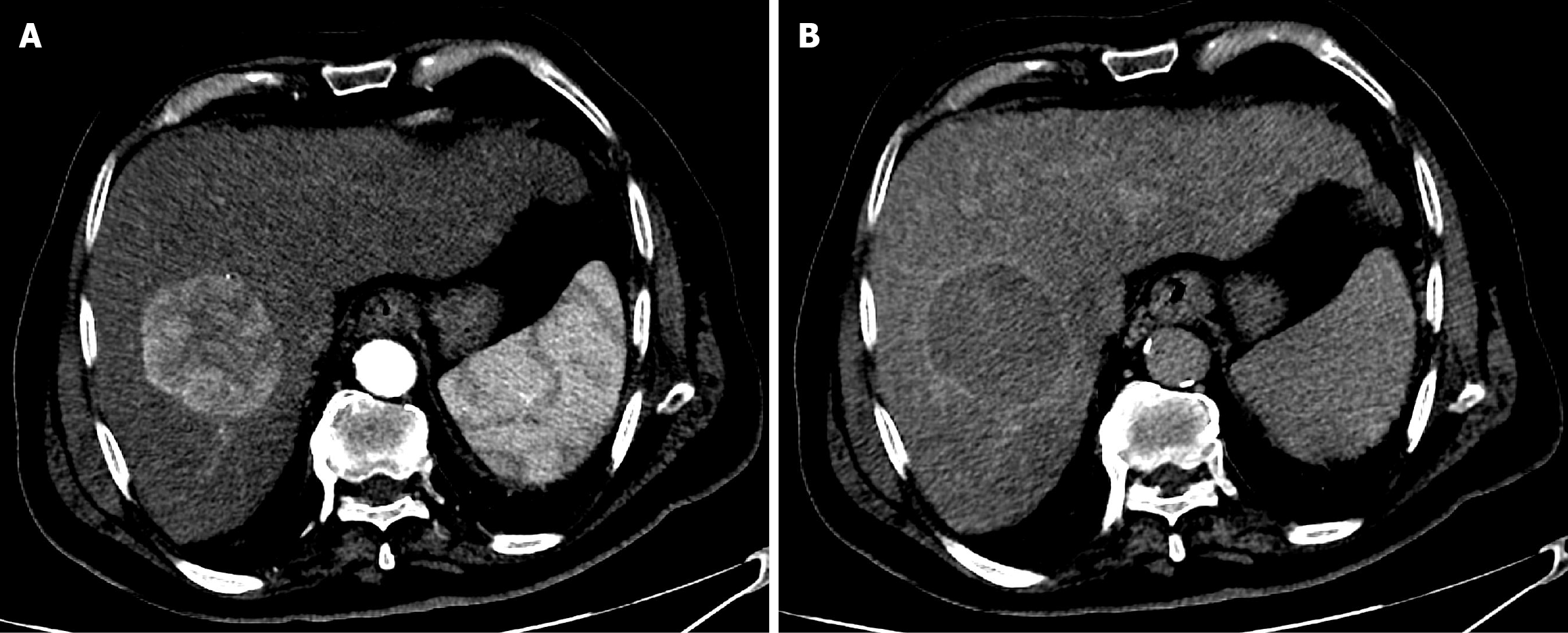
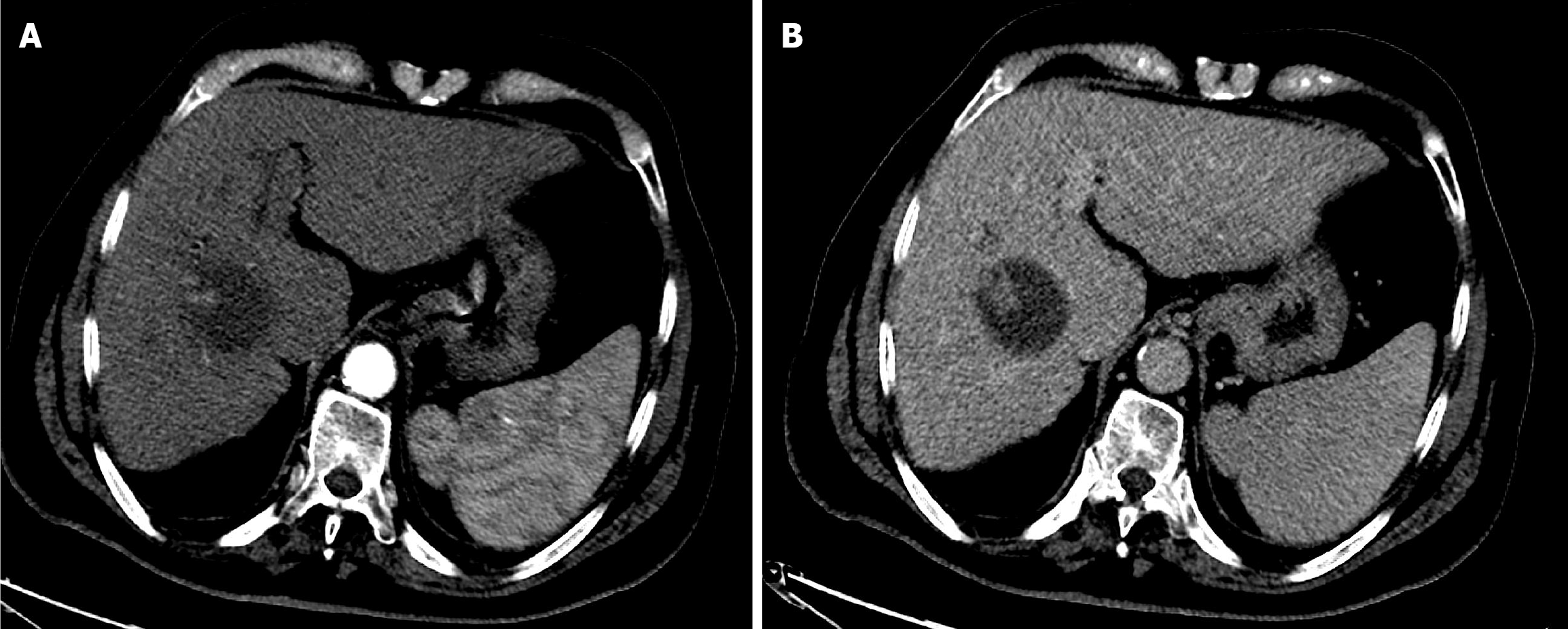
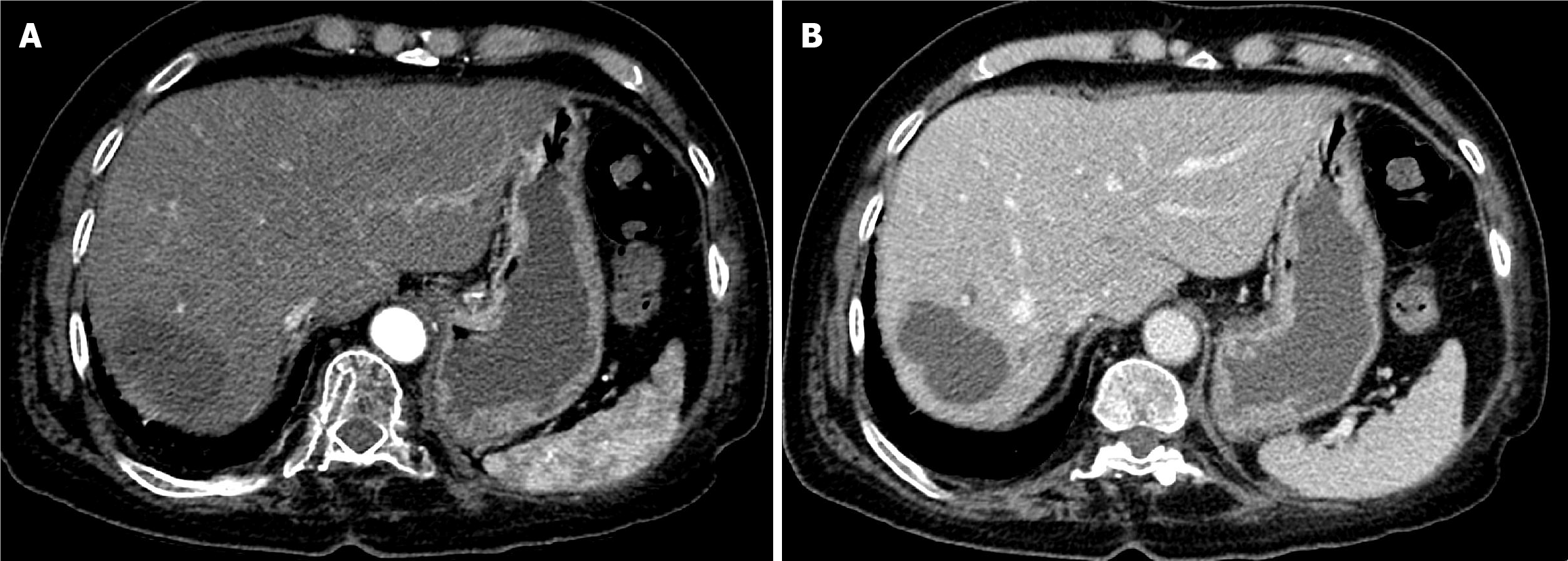
Figure 1 Baseline computed tomography of the abdomen.
A: Arterial phase computed tomography (CT) showed a large, well-defined hypervascular hepatic mass; B: Delayed phase CT demonstrated washout of the mass with an enhancing peripheral rim (tumor capsule).
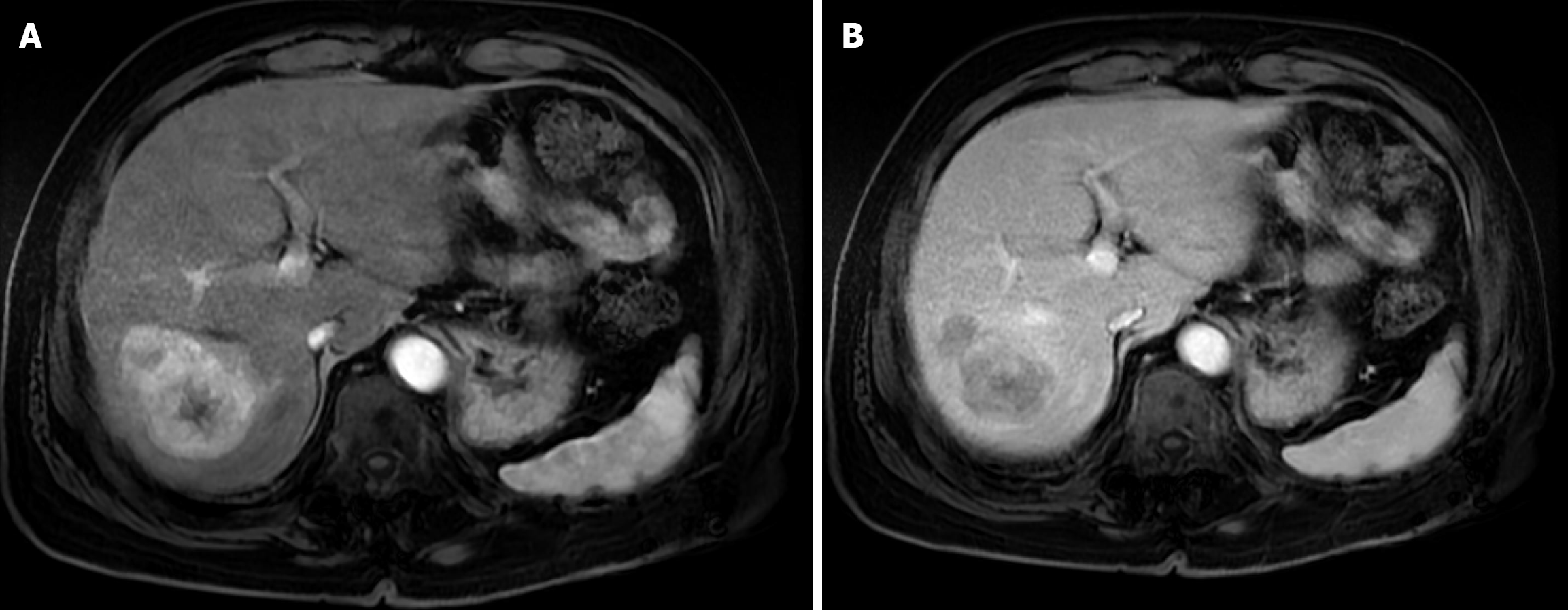
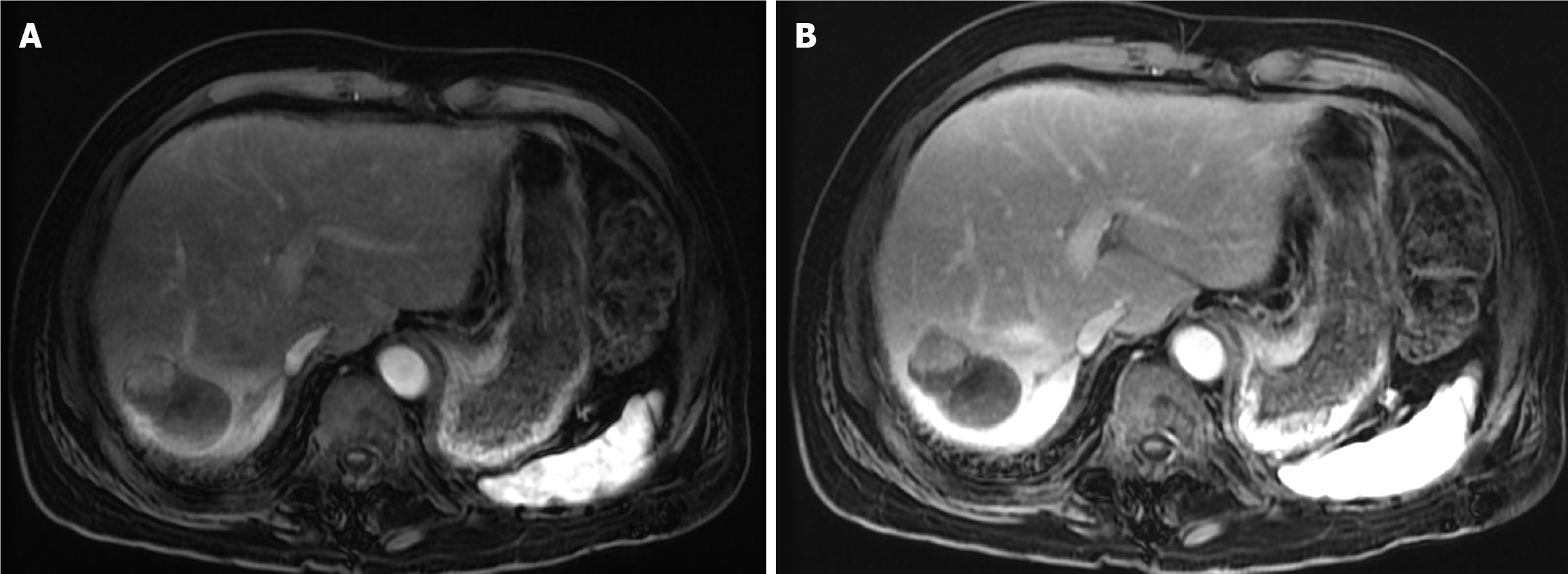
Figure 2 Baseline magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen.
A: Arterial phase T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed a large, well-defined, arterially enhancing hepatic mass; B: Delayed phase T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated washout of the lesion.
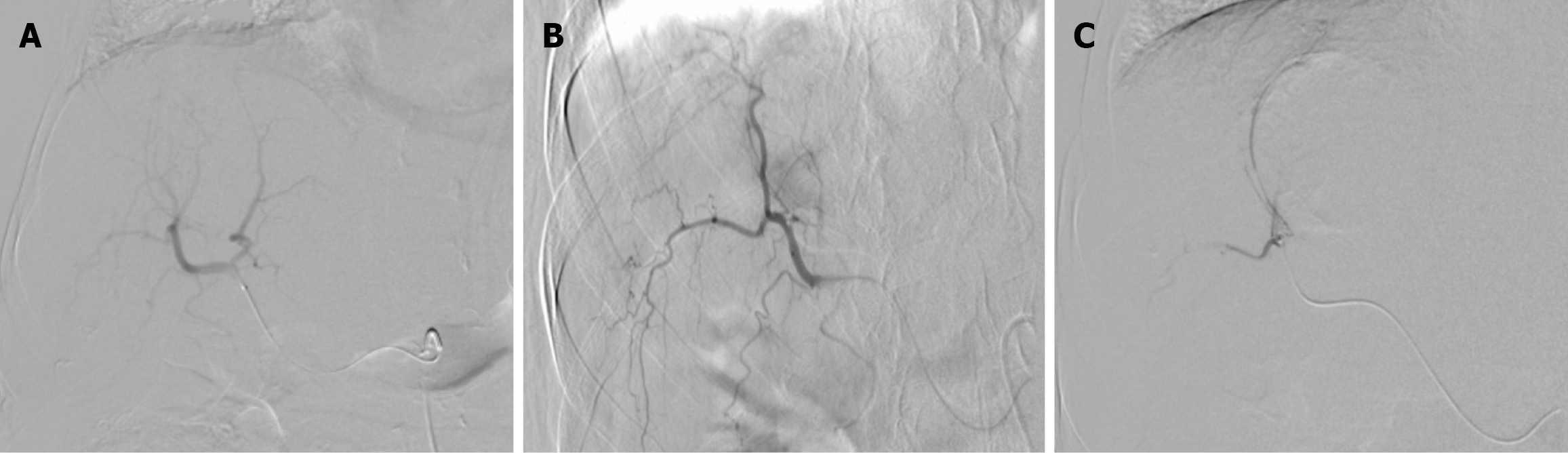
Figure 3 Digital subtraction angiography images during the first drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization session in Case 1.
A: Right hepatic artery non-selective angiogram; B: Selective hepatic angiogram showed a hypervascular mass; C: Superselective angiogram demonstrated complete stasis of the vascular supply of the tumor after embolization.
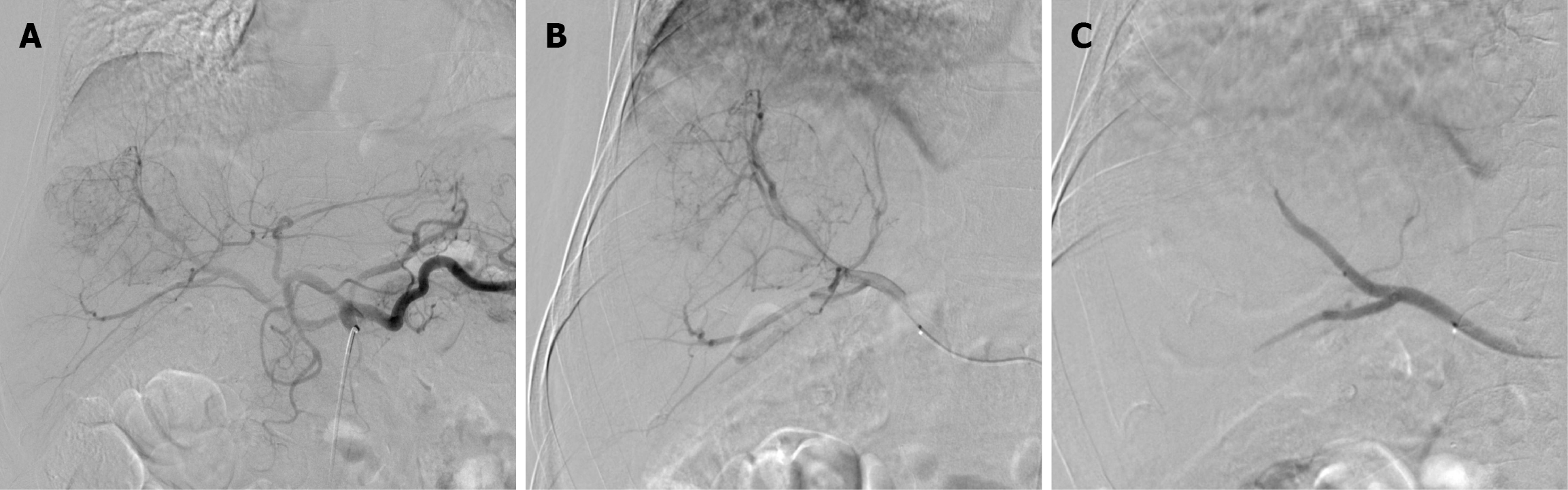
Figure 4 Digital subtraction angiography images during the first drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization session in Case 2.
A: Celiac angiogram showed a large hypervascular hepatic mass; B: Right hepatic lobar angiogram showed tumor supply by multiple right hepatic artery branches; C: Post-embolization angiogram demonstrated complete stasis of tumor supply.
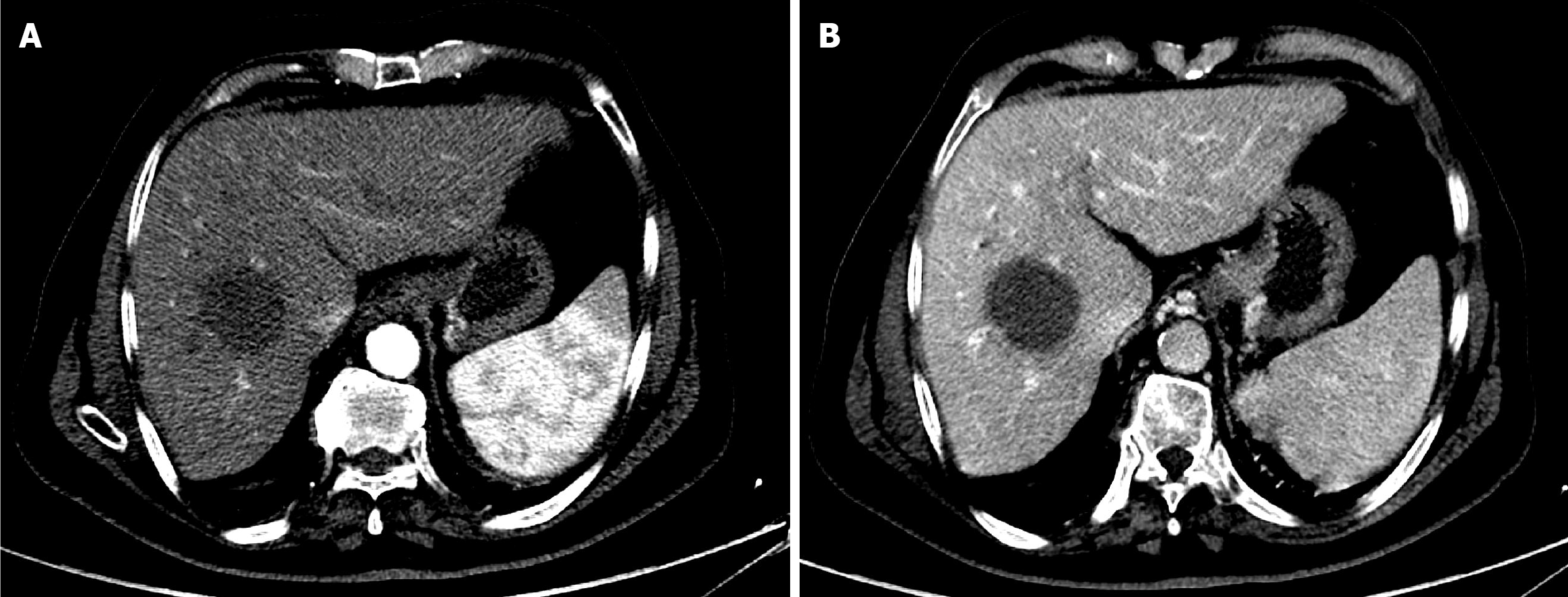
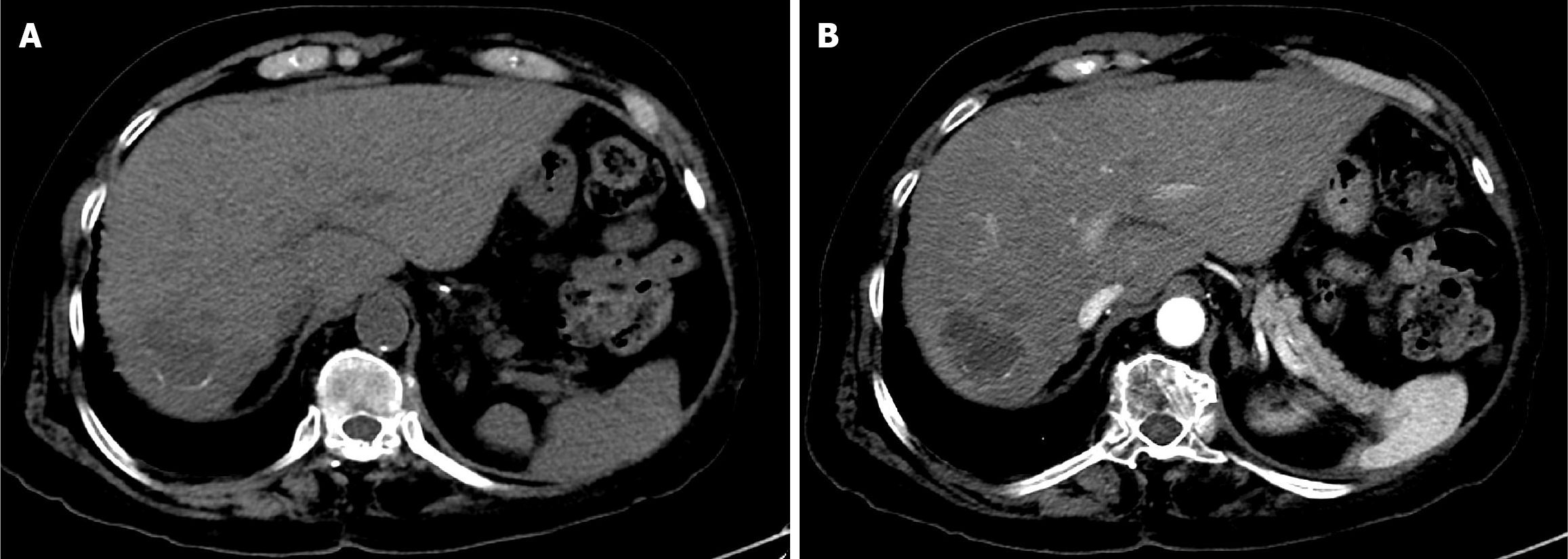
Figure 5 Six-week follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the first drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in Case 1.
A: Arterial phase computed tomography (CT) showed a residual hypervascular nodule at the periphery of the non-enhancing treated mass, indicating partial response; B: Delayed phase CT confirmed washout of the residual soft tissue nodule.
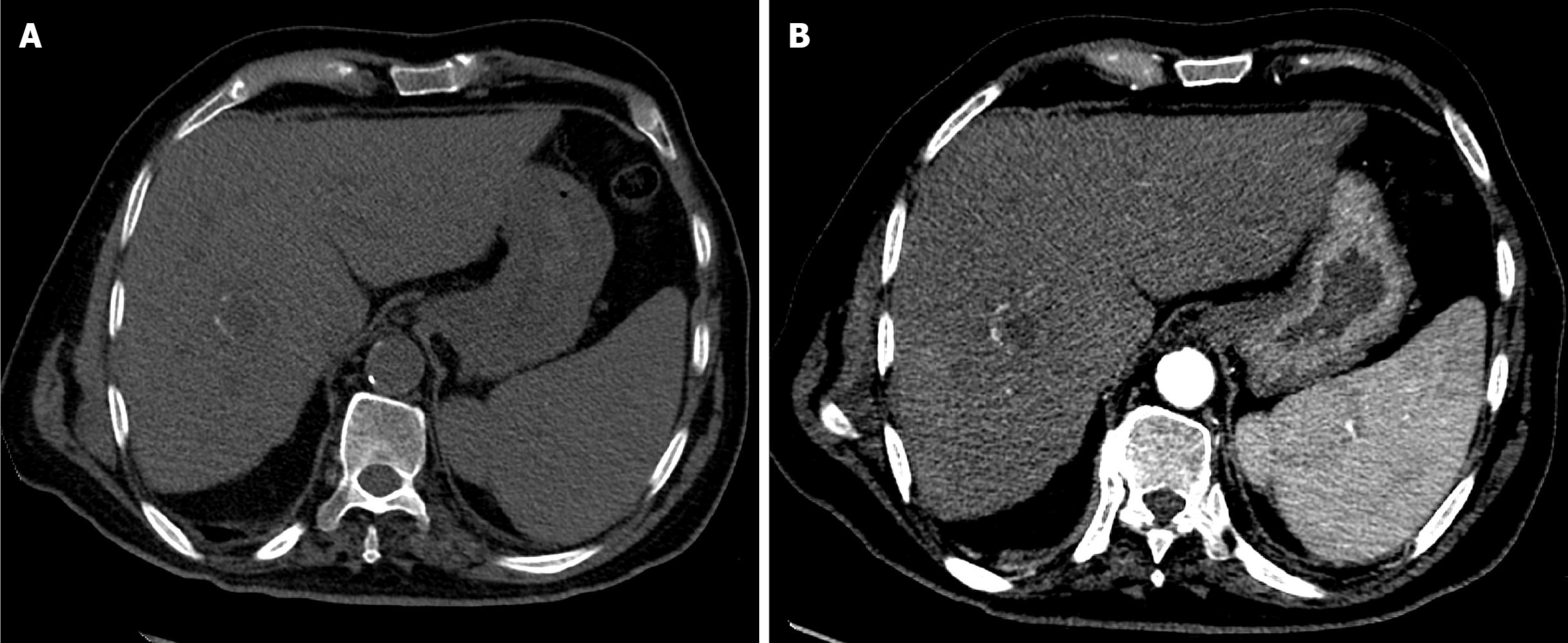
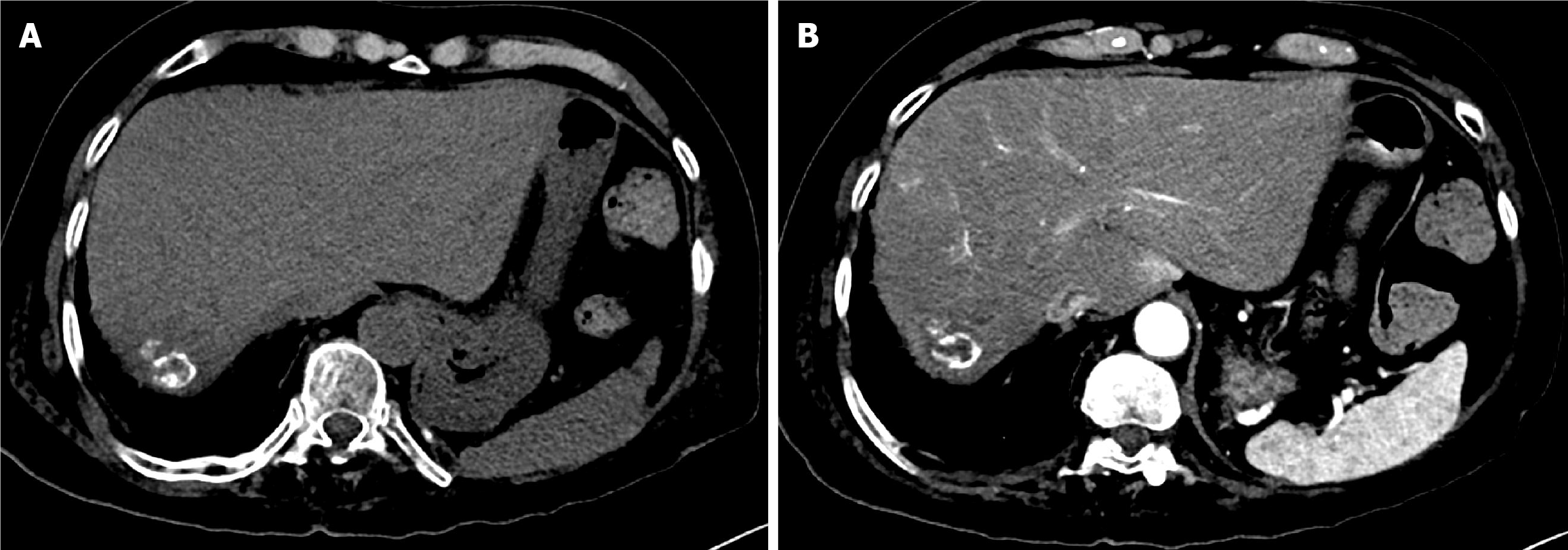
Figure 6 Four-week follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the second drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in Case 1.
A: Arterial phase computed tomography (CT) showed a non-enhancing mass, consistent with complete response; B: Portal venous phase CT demonstrated normal hepatic parenchymal enhancement with a necrotic treated mass.
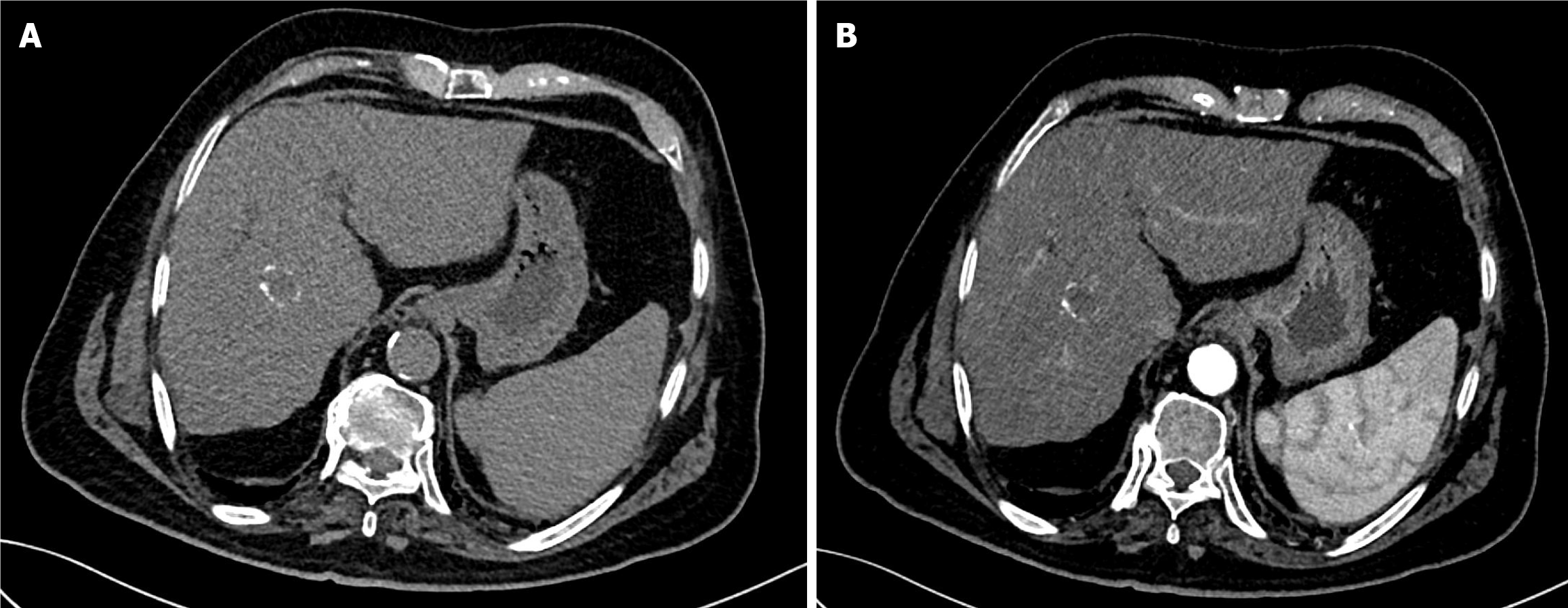
Figure 7 One-year follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the second drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in Case 1.
A: Pre-contrast computed tomography (CT) demonstrated faint linear peripheral calcification of the treated hepatic mass; B: Arterial phase CT showed a non-enhancing mass, consistent with complete response.
Figure 8 Six-year follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the second drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in Case 1.
A: Pre-contrast computed tomography (CT) demonstrated progressive peripheral concentric calcification encircling the treated hepatic mass; B: Arterial phase CT showed a non-enhancing mass, consistent with sustained complete response.
Figure 9 Eight-week follow-up magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen after the first drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoem
Figure 10 Six-week follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the second drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in Case 2.
A: Arterial phase computed tomography (CT) showed a non-enhancing treated mass, consistent with complete response; B: Portal venous phase CT demonstrated normal hepatic parenchymal enhancement with a necrotic treated mass.
Figure 11 One-year follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the second drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoemboli
Figure 12 Six-year follow-up computed tomography of the abdomen after the second drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in Case 2.
A: Pre-contrast computed tomography (CT) demonstrated dense, progressive peripheral concentric calcification surrounding the treated hepatic mass; B: Arterial phase CT showed a non-enhancing mass, consistent with sustained complete response.
- Citation: Alharbi SR. Tumor calcification and sustained complete response after chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: Two case reports and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(12): 113341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i12/113341.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113341