©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2025; 17(12): 113198
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113198
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113198
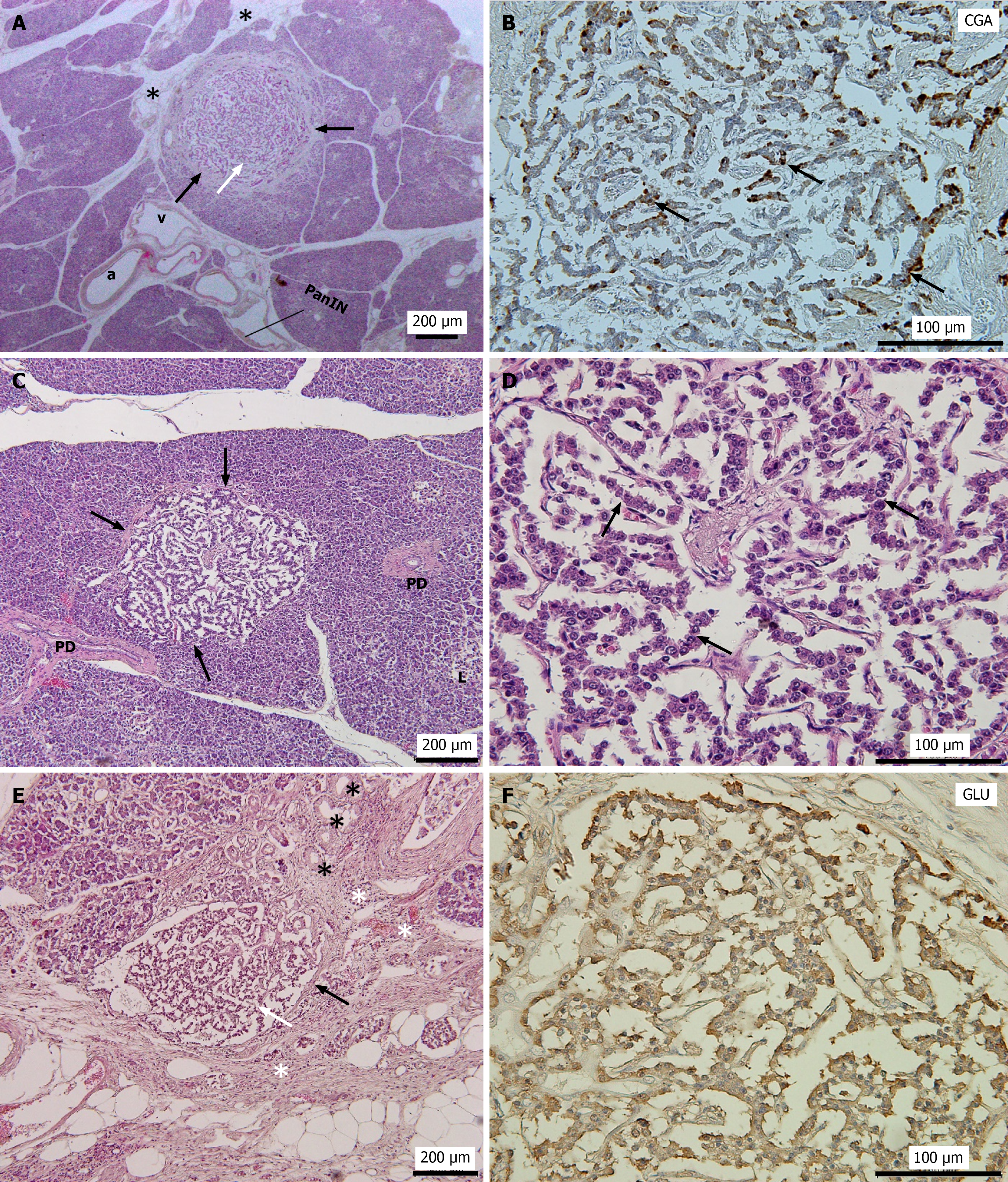
Figure 1 Histopathological changes of 3 cases of pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors (PNEMTs) of Case 1; B: Immunostaining of PNEMTs in A with chromogranin A (CGA) antibody; C: H&E staining of PNEMTs of Case 2; D: H&E staining of PNEMTs in C; E: H&E staining of PNEMTs of Case 3; F: Immunostaining of PNEMTs in E with glucagon antibody. White arrows, PNEMTs. Although PNEMTs was not found to have infiltrated into the pancreatic tissue, the black arrows (in A-C) indicated a slight membrane structure between PNEMTs and the pancreatic tissue. Black asterisk in A: Fatty degeneration; black arrows in B: CGA-positive cells; black asterisk in E: Acinar ductal metaplasia; white asterisk in E: Fibrosis with inflammation cell infiltration; black arrows in D: The tumors exhibited an organoid-like architecture, with tumor cells arranged in a trabecular pattern. a: Artery; L: Islets of Langerhans; PD: Pancreatic duct; v: Vein; CGA: Chromogranin A; GLU: Glucagon.
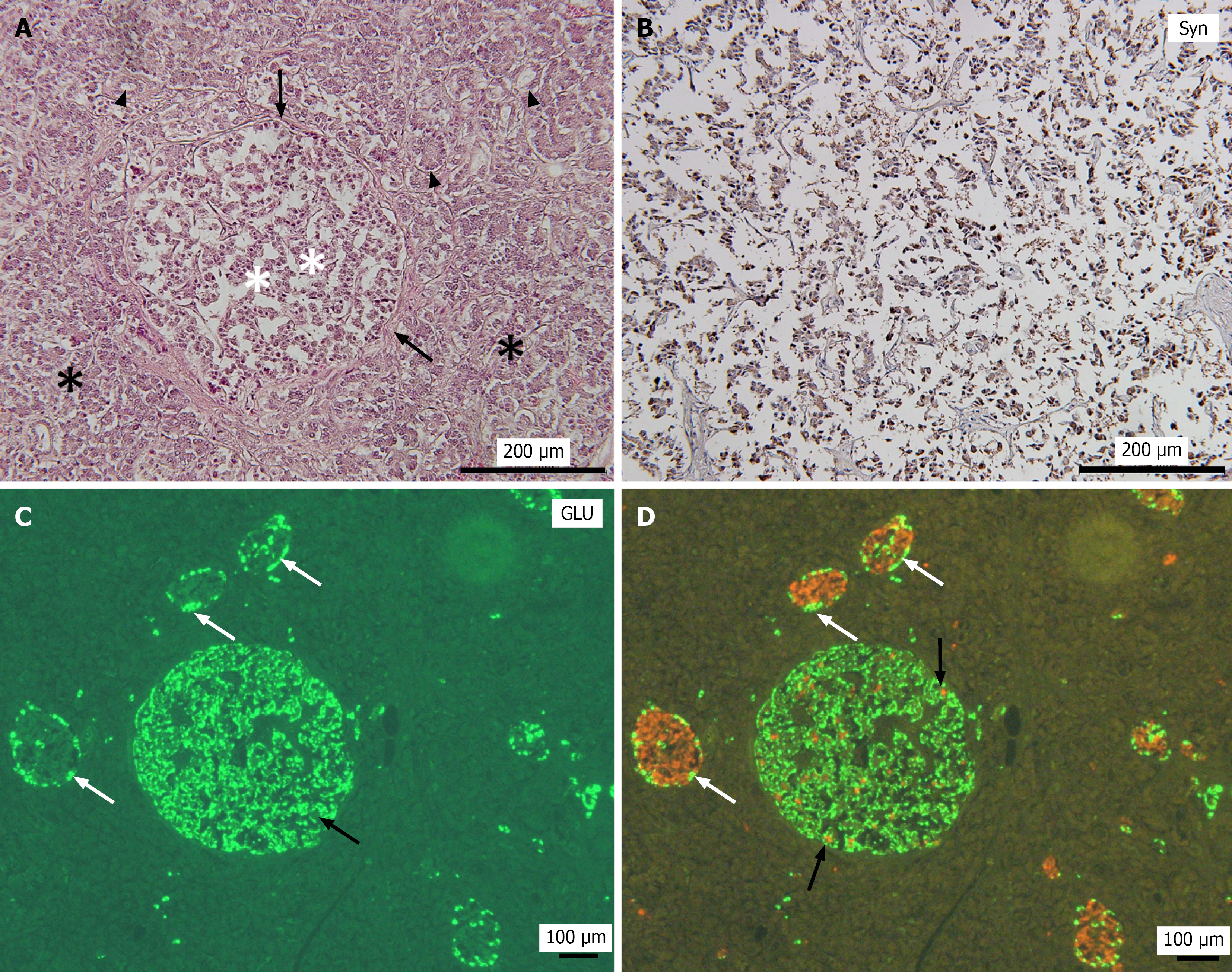
Figure 2 Histopathological changes of pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors in Case 4.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors (PNEMTs) of Case 4; B: Immunostaining of PNEMTs in A with synaptophysin (Syn) antibody; C: Immunofluorescence staining of PNEMTs with glucagon (GLU) antibody; D: GLU (green) with insulin (red) double immunofluorescence staining. White asterisk in A: The tumors exhibited an organoid-like architecture, with tumor cells arranged in a trabecular pattern; black asterisk in A: The surrounding pancreatic parenchyma appeared largely normal. Black arrows in A: Indicate a slight membrane structure between the PNEMTs and the pancreatic tissue. Black arrowheads in A: Acinar ductal metaplasia; White arrows in C: GLU-positive cells in the islets of Langerhans; Black and white arrows in D: Insulin-positive cells in PNEMTs and islets of Langerhans, respectively. GLU: Glucagon; Syn: Synaptophysin; Ins: Insulin.
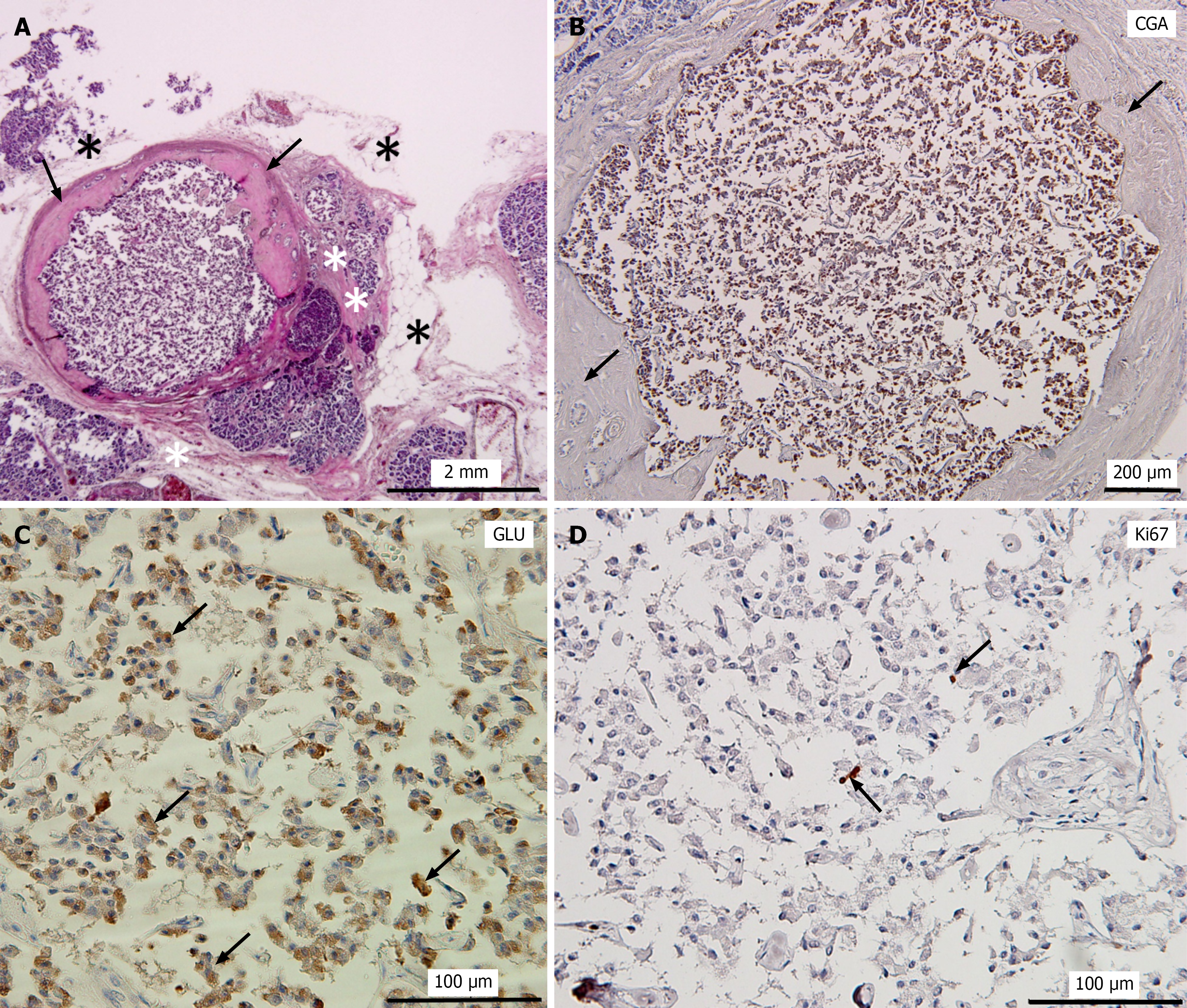
Figure 3 Histopathological changes of pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors in Case 5.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors (PNEMTs) of Case 5; B: Immunostaining of PNEMTs in A with chromogranin A antibody; C: Immunostaining of PNEMTs with glucagon (GLU) antibody; D: Immunostaining of PNEMTs with Ki-67 antibody. Black arrows in A and B: Indicate that the outer layer of the tumor was surrounded by a thick fibrotic wall; Black asterisk in A: Fatty degeneration; white two asterisks in A: Fibrosis; Black arrows in C: GLU-positive PNEMTs cells; Black arrows in D: A small number of Ki-67-positive PNEMTs cells. CGA: Chromogranin A; GLU: Glucagon.
- Citation: Yang T, Ren K, Chen XQ, Toriumi T, Natsuyama Y, Li J, Sukeda A, Nagao T, Yi SQ. Pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors in the elderly: A retrospective study using cadaveric pancreatic tissue. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(12): 113198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i12/113198.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i12.113198