©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2025; 17(10): 109807
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.109807
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.109807
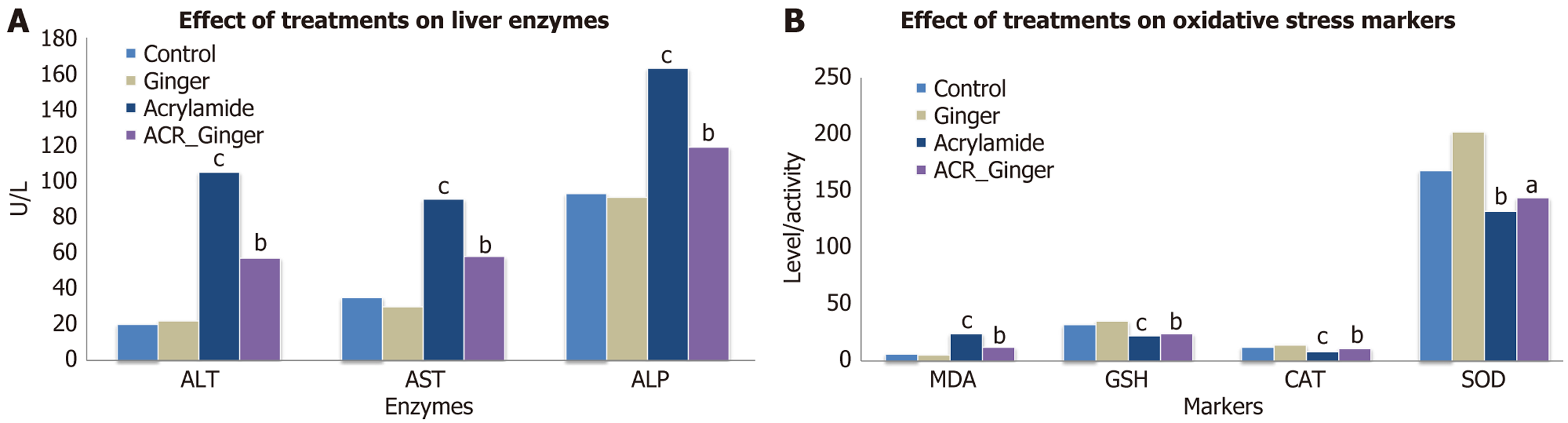
Figure 1 Effect of treatments.
A: Liver enzymes [alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP)]. The graph shows a marked elevation in liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP) in the acrylamide (ACR)-treated group, indicating hepatocellular damage. Co-treatment with ginger significantly reduced enzyme levels, suggesting a protective effect. No significant difference was found between ginger alone and control groups; B: Oxidative stress markers [malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione, catalase, superoxide dismutase]. Oxidative stress markers reveal increased lipid peroxidation and reduced antioxidant activity in the ACR group. Ginger significantly restored antioxidant levels and reduced MDA, indicating its antioxidant and protective potential. aP < 0.05 vs control, bP < 0.01 vs control, cP < 0.05 vs ACR group. ACR: Acrylamide; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; CAT: Catalase; GSH: Glutathione; MDA: Malondialdehyde; SOD: Superoxide dismutase.
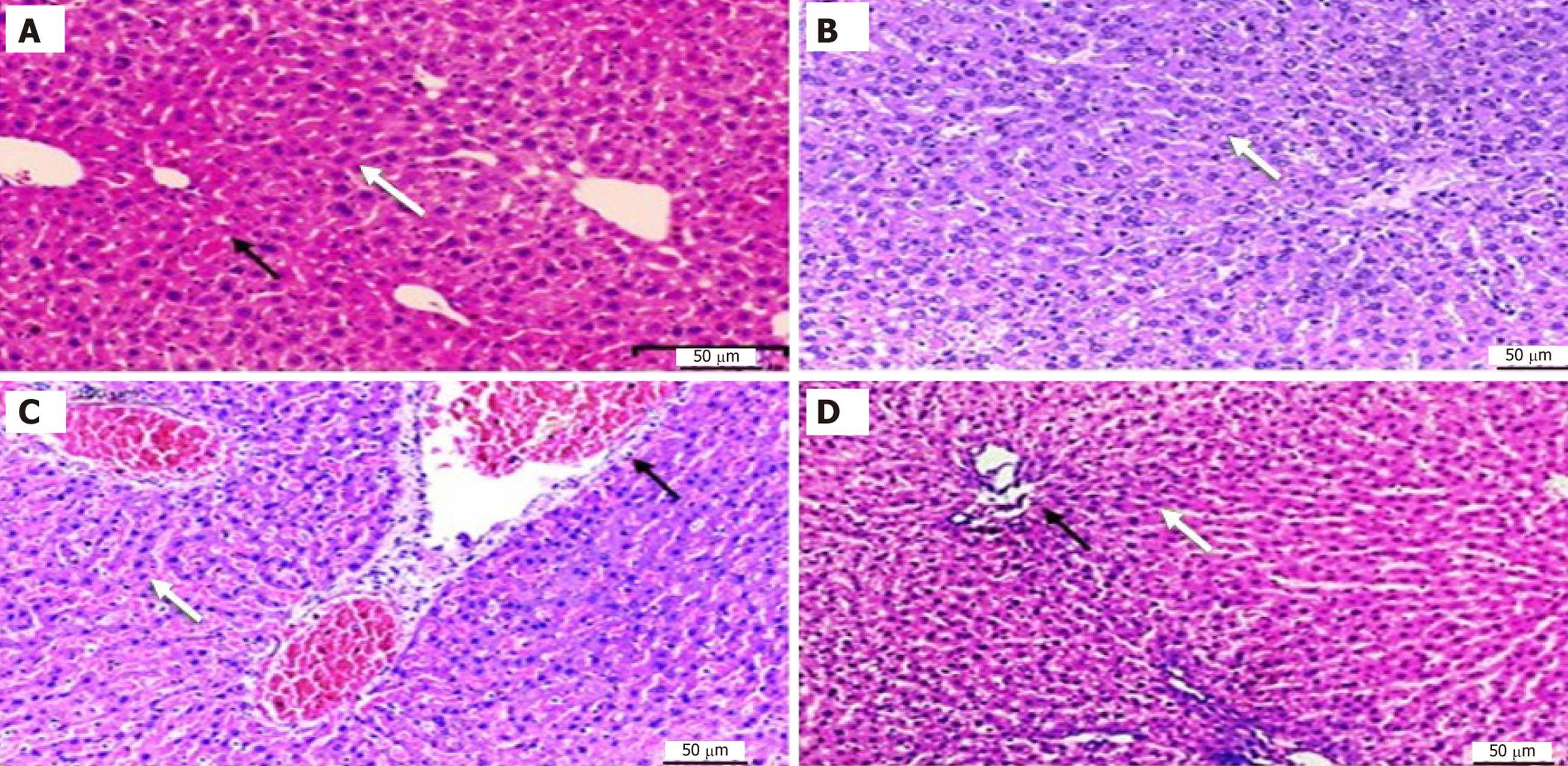
Figure 2 Histopathological examination of liver tissue in control and experimental groups.
A: Control group showing normal central vein (black arrow) and normal hepatocytes (white arrow). The liver tissue shows no significant pathological alterations; B: Ginger treated group showing normal hepatocytes (white arrow), blood sinusoids between hepatocyte cords (black arrow); C: Acrylamide (ACR) treated group showing dilated and congested portal veins (black arrow) and blood sinusoids (white arrow), and hepatocytes with dark nucleus and vacuolated cytoplasm; D: ACR + ginger treated group showing moderate damage with mild dilated central veins (black arrow) (hematoxylin and eosin 200 ×).
- Citation: Nour El Deen AES, Rashed F, Osman A, Khalil Farag O, Abdel Ghany AF, Elsayed AM, Mansour SMA, Mohammed MAA, Taha RS, Basha SAZ, Mohamed MMY, Taha A. Ginger mitigates acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in rats. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(10): 109807
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i10/109807.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.109807