©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2025; 17(8): 109106
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.109106
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.109106
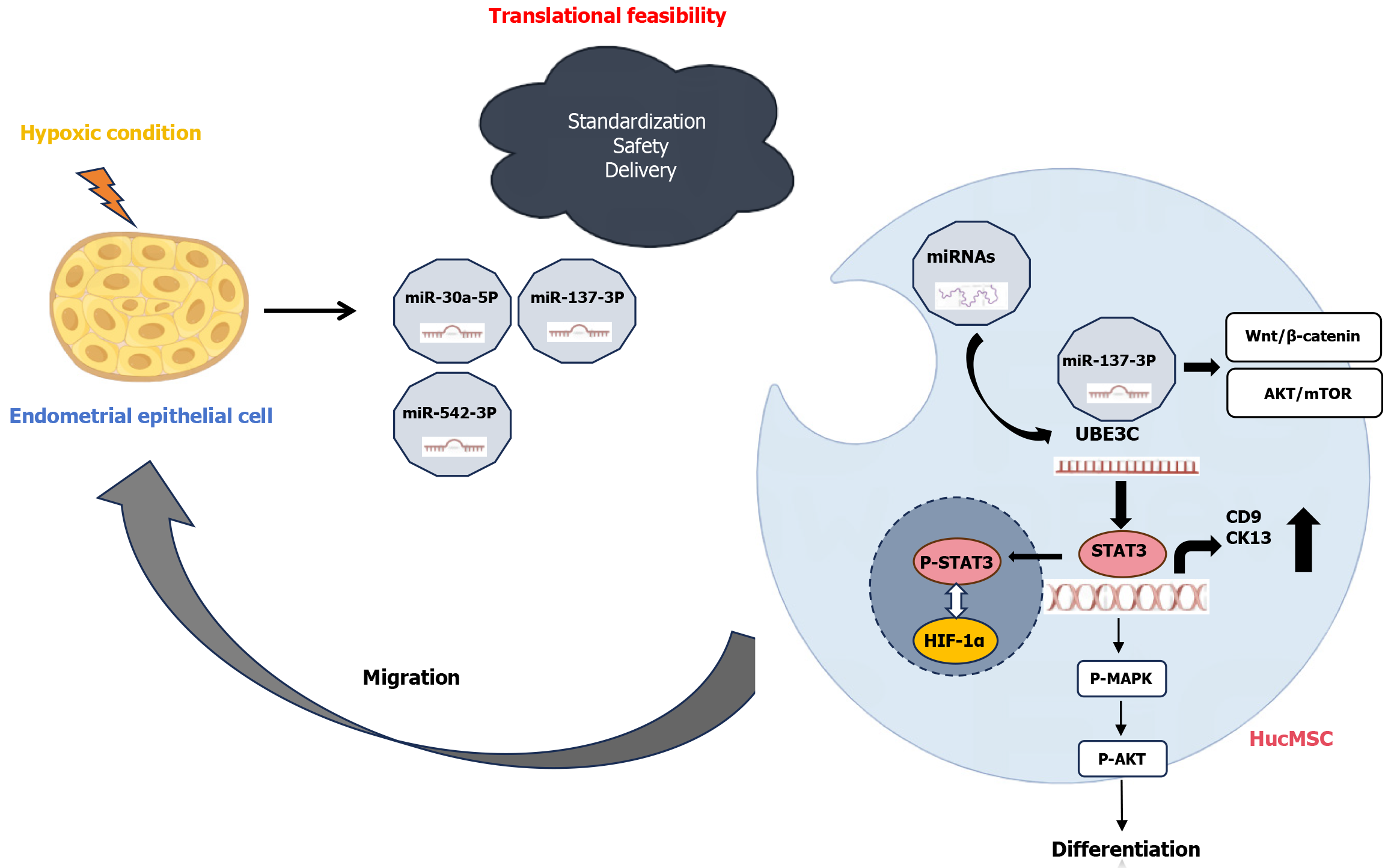
Figure 1 Advancing mechanistic insights and clinical translation of exosomal miR-137-3p in endometrial regeneration.
Elucidating the mechanisms underlying microRNA regulatory networks, multiple signaling pathways, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-hypoxia-inducible factor-1α crosstalk will further enhance our understanding of the functional roles of exosomal miR-137-3p. Additionally, optimizing exosome delivery protocols, safety profiles, and tissue-targeting strategies will be instrumental in promoting the clinical translation of endometrial regeneration therapies. miRNAs: MicroRNAs; UBE3C: Ubiquitin protein ligase E3C; Wnt: Wingless; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; HucMSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Han LF, Fu GK, Wen YQ, Bian XL. Advancing mechanistic insights and clinical translation of exosomal miR-137-3p in endometrial regeneration. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(8): 109106
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i8/109106.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.109106