©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2025; 17(8): 107480
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.107480
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.107480
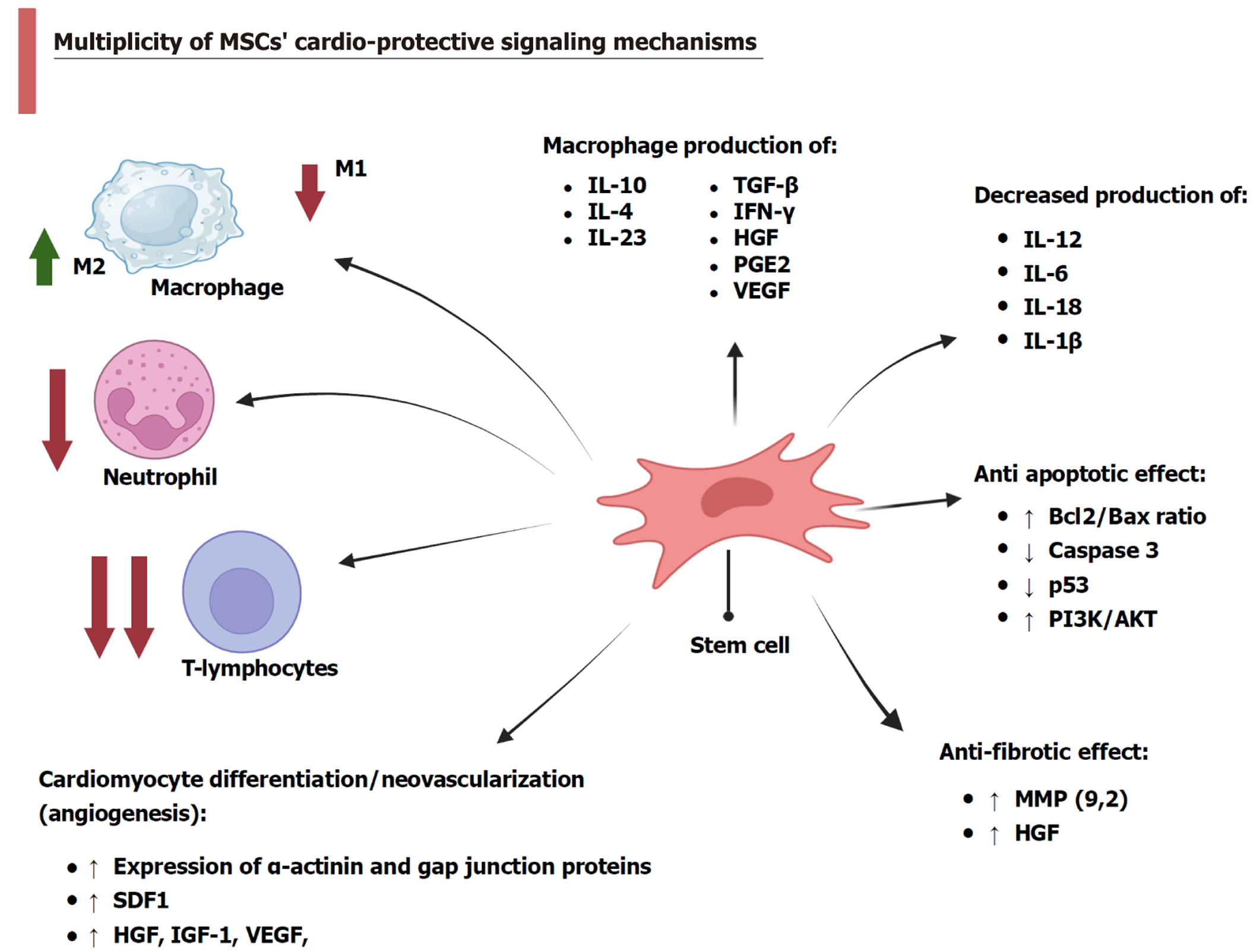
Figure 1 Multiplicity of mesenchymal stem cells’ cardio-protective signaling mechanisms.
Created in BioRender (Supplementary material). MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; IFN: Interferon; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; MMP: Matrix metalloprotease; SDF: Stromal-derived factor; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor.
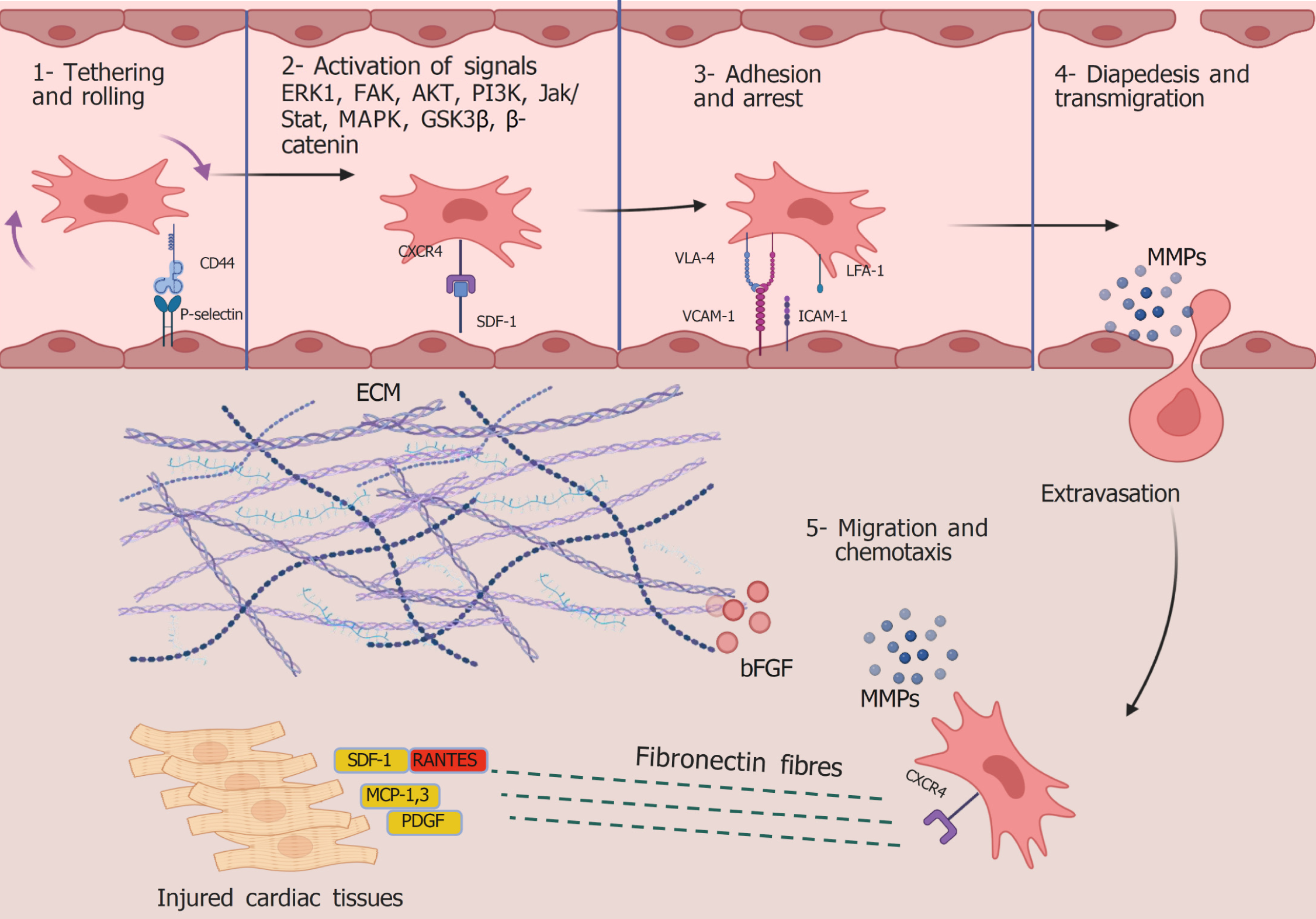
Figure 2 Steps of mesenchymal stem cell homing to injured tissues and their triggering potentials.
Created in BioRender (Supplementary material). ERK1: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; Jak: Janus kinases; Stat: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; GSK: Glycogen synthase kinase; CXCR: C-X-C chemokine receptor; SDF: Stromal-derived factor; VLA-4: Very late activating antigen-4; VCAM-1: Vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1; LFA-1: Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteases; ECM: Extracellular matrix; bGFG: Basic fibroblast growth factor; RANTES: Regulated upon activation normal T cell expressed and presumably secreted; MCP: Monocyte chemoattractant protein; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor.
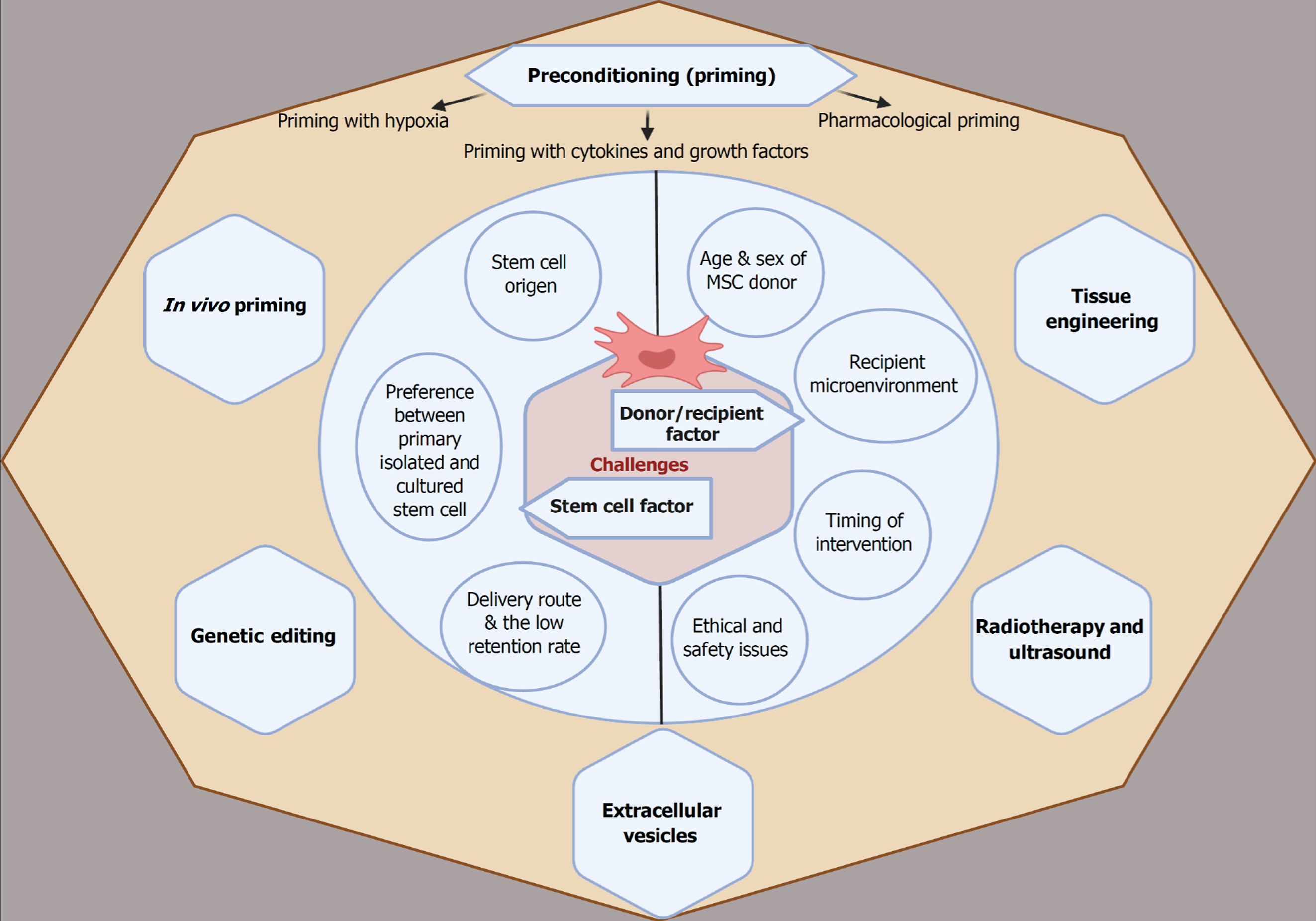
Figure 3 Summary of strategies needed to enhance mesenchymal stem cell survival and homing capacity to improve cardiac function.
Created in BioRender (Supplementary material). MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
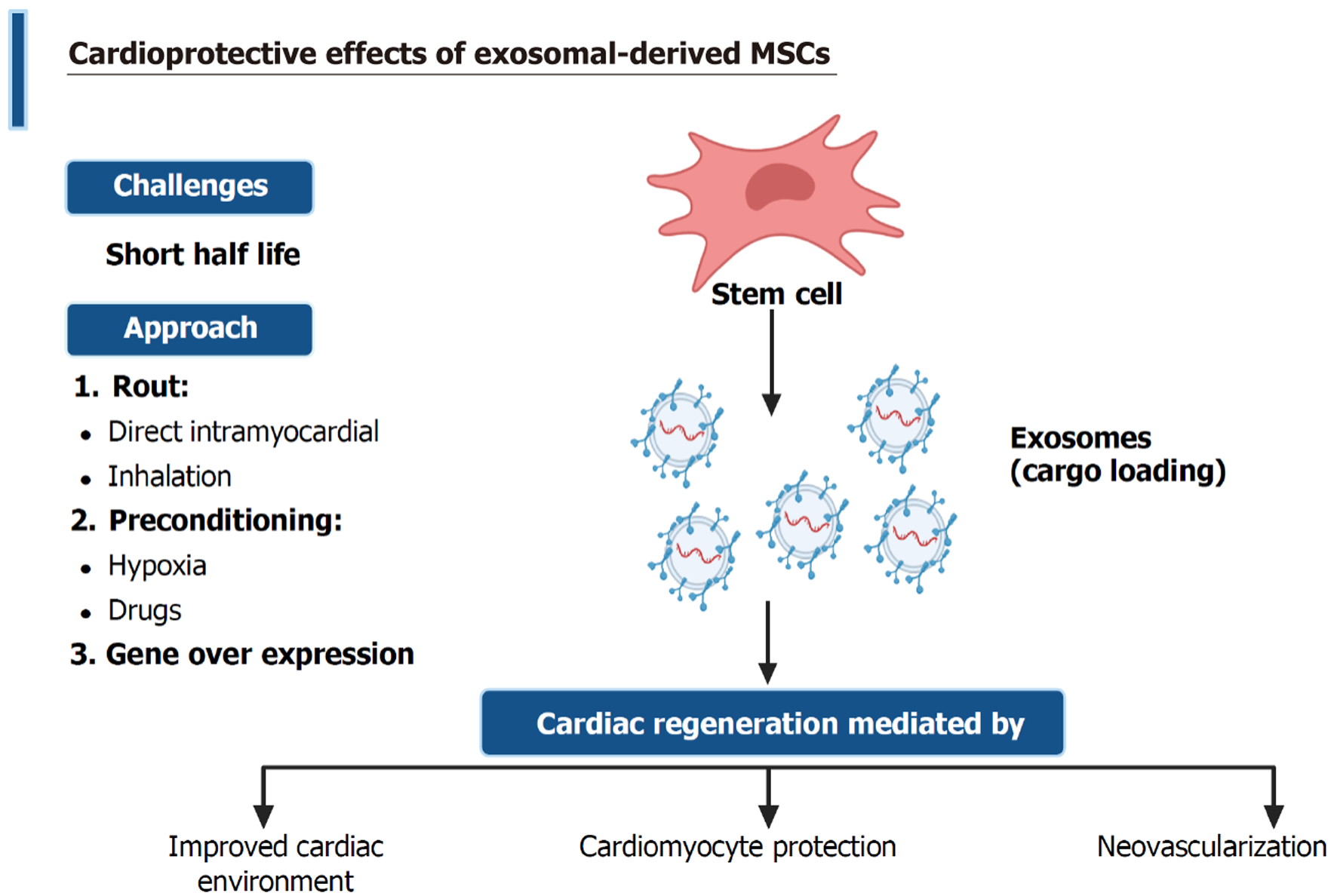
Figure 4 Cardioprotective effects of exosomal-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
Created in BioRender (Supplementary material). MSC: Mesen
- Citation: ShamsEldeen AM, Hosny SA, Maghib K, Ashour H. Current perspectives on regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells in alleviating cardiac injuries: Molecular pathways and therapeutic enhancement. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(8): 107480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i8/107480.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i8.107480