©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2025; 17(10): 110248
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i10.110248
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i10.110248
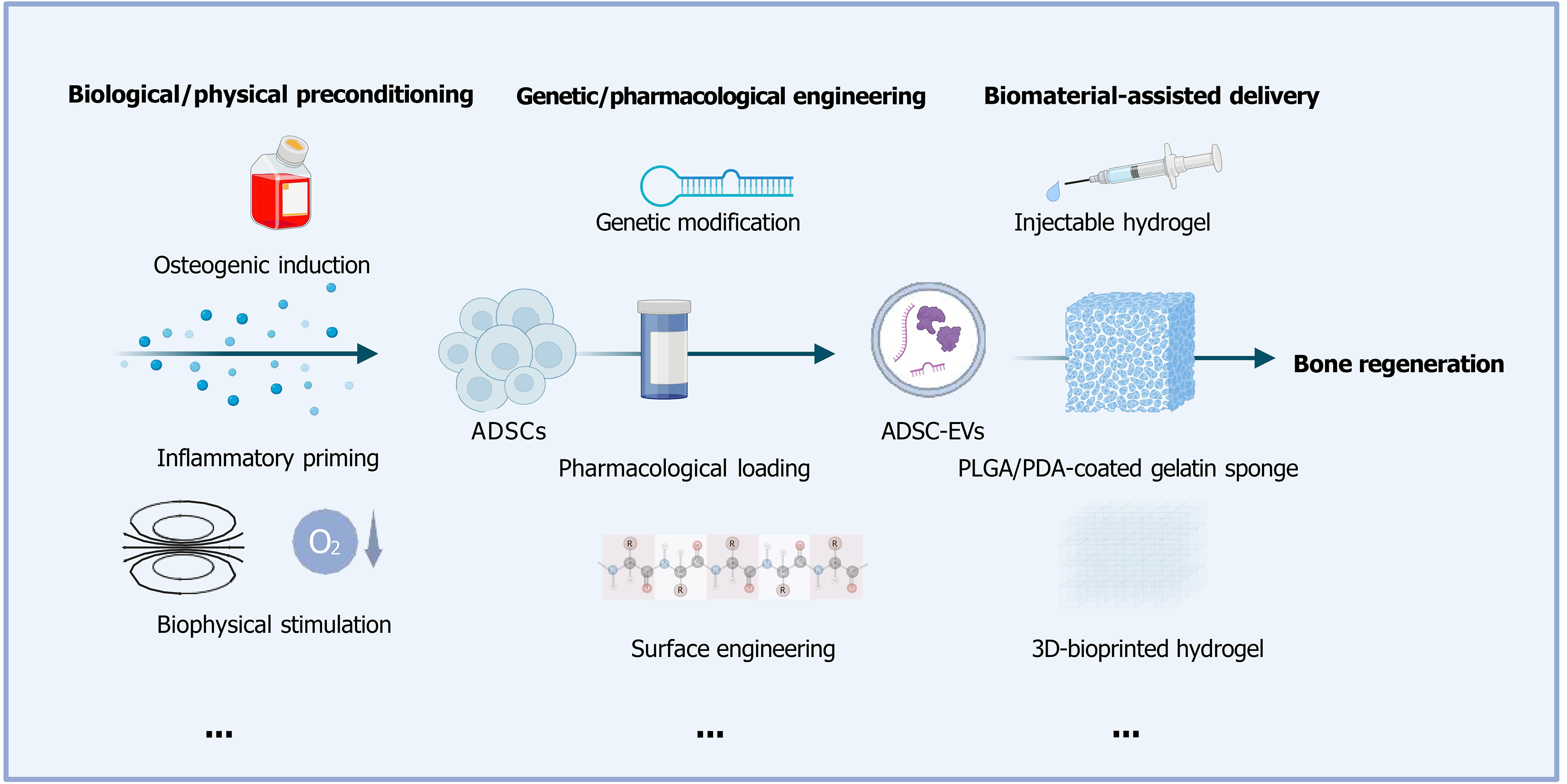
Figure 1 Translational strategies of adipose-derived stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in therapeutic use.
Adipose-derived stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) are optimized through three core strategies to enhance their therapeutic efficacy. Biological or physical preconditioning of adipose-derived stem cells, including osteogenic induction, inflammatory priming with cytokines, pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation, and others, refines the regenerative capacity of secreted EVs. Genetic and pharmacological engineering strategies, such as microRNA overexpression, curcumin loading, surface modification with Cys-Arg-Glu-Lys-Ala peptide or biotin-avidin systems, and additional approaches, modulate EV cargo and targeting ability. Biomaterial-assisted delivery, via platforms like poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid/polydopamine scaffolds, decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogels, injectable gelatin-nanoparticle hydrogels, and more, improves EV retention and release kinetics at defect sites. These optimized EVs collectively contribute to bone regeneration, supporting their application in preclinical models and potential translation to clinical settings. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material). ADSC: Adipose-derived stem cell; ADSC-EVs: Adipose-derived stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles; PLGA: Poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid; PDA: Polydopamine; 3D: Three-dimensional.
- Citation: Lin A, Yu JL, Yuan SM, Tang YF, Yang KX, Wang YH, Huo FJ, Jin ZR, Xiao Q, Yang C, Tian WD. Extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stem cells in bone regeneration: Mechanisms and therapeutic advances. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(10): 110248
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i10/110248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i10.110248