©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2026; 32(8): 115077
Published online Feb 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115077
Published online Feb 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115077
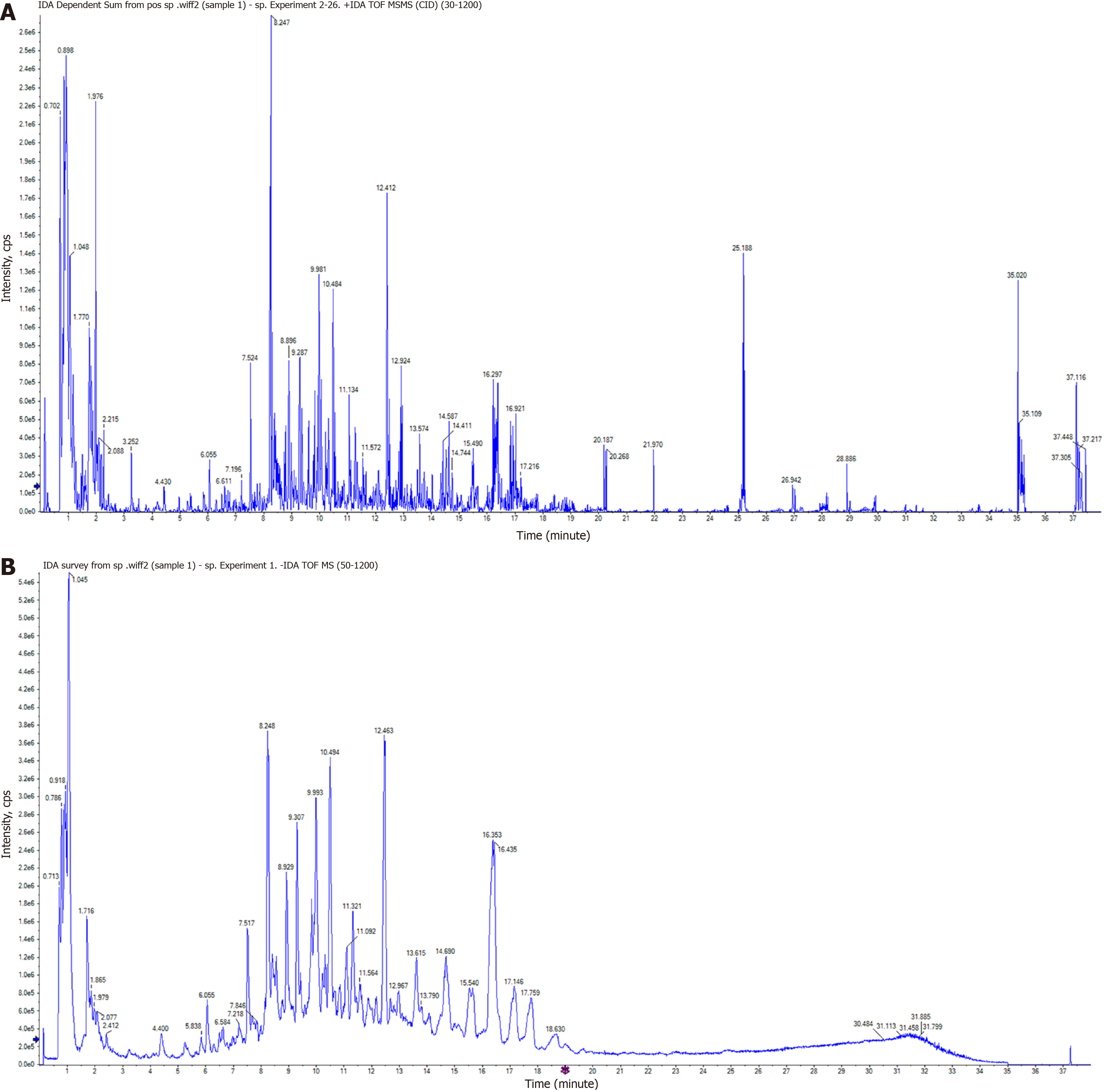
Figure 1 Characterization of ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction total ion current chromatogram obtained by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. A: Positive ion mode; B: Negative ion mode.
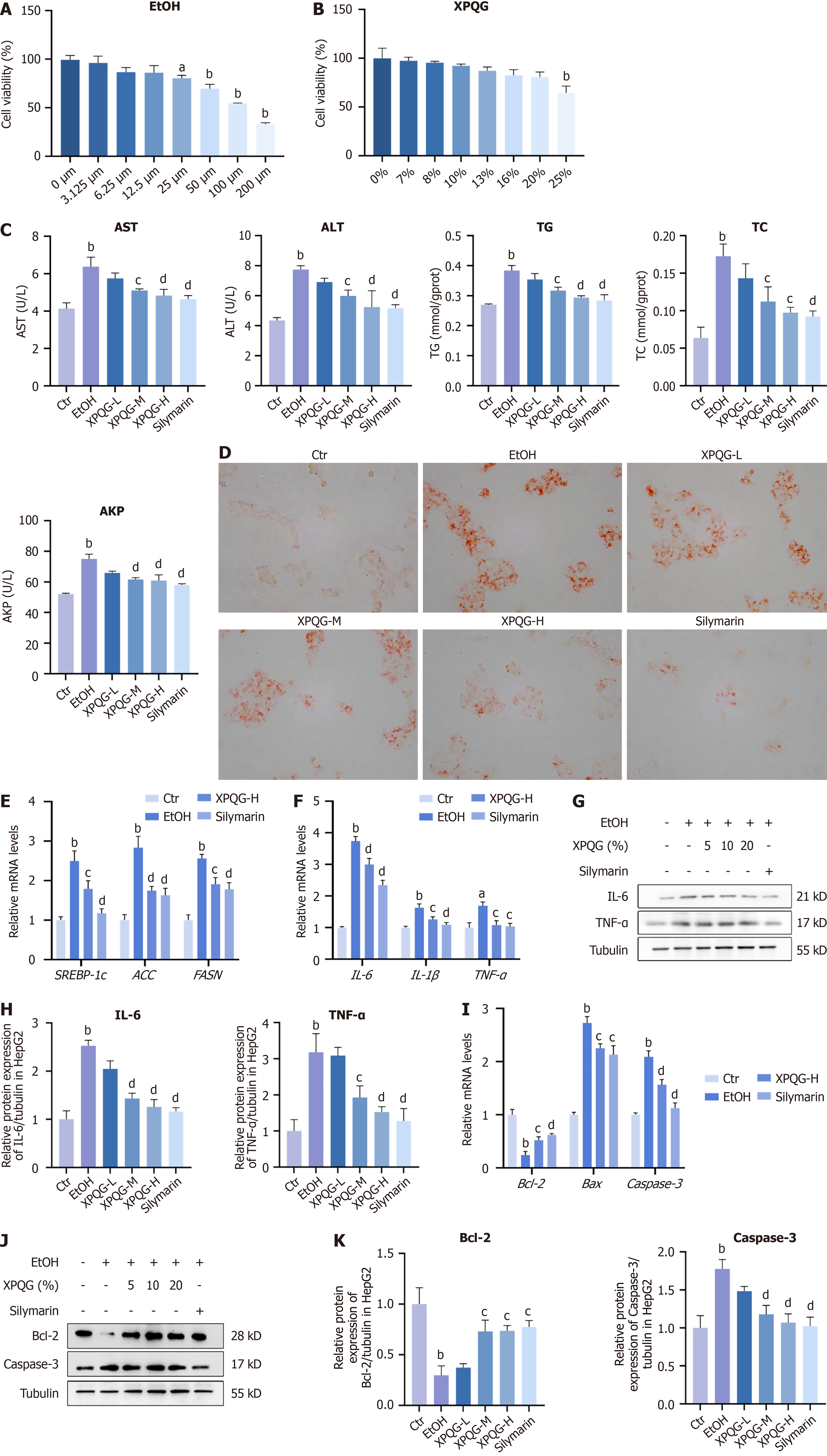
Figure 2 Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction attenuates ethanol-induced dysfunction in HepG2.
A and B: Quantitation of cell viability of HepG2 cells treated with ethanol (A) and with Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction (B) was determined by CCK-8 assay; C: HepG2 alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglyceride and alkaline phosphatase levels; D: Oil Red O staining, images were taken (40 ×); E: Relative mRNA levels of lipogenesis; F-H: Relative mRNA levels and relative protein expression of inflammation; I: Relative mRNA levels of Apoptosis; J and K: Relative protein expression of Bcl-2, Caspase-3 in HepG2 (n = 3-5). aP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05 vs the ethanol-fed group; dP < 0.01 vs the ethanol-fed group. Ctr: Control; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol; AKP: Alkaline phosphatase; XPQG-L: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-low; XPQG-M: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-medium; XPQG-H: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-high; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
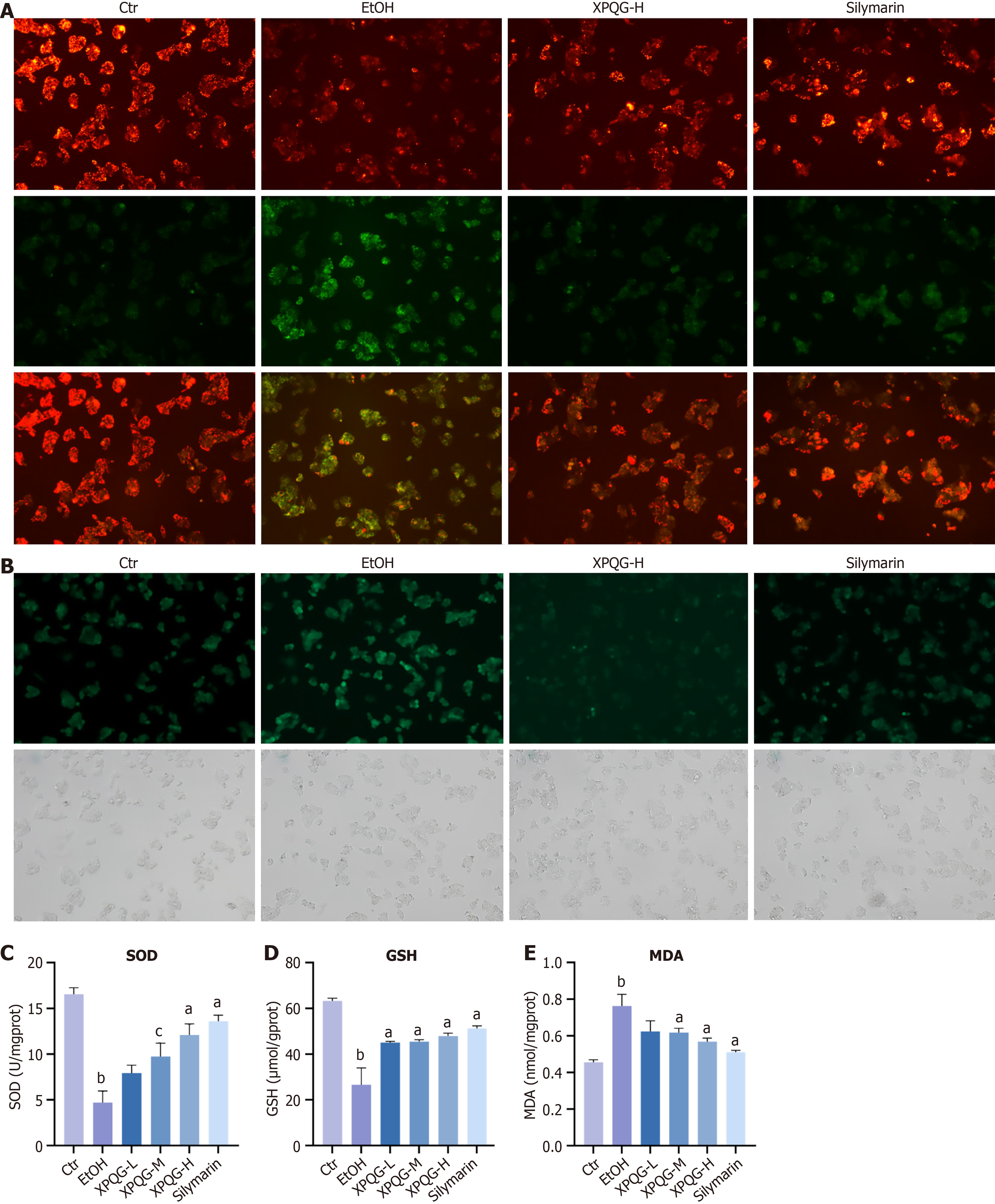
Figure 3 Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-treated serum significantly reduced the oxidative stress caused by ethanol on HepG2 cells.
A: JC-1 of HepG2 (40 ×); B: Reactive oxygen species levels of HepG2 (40 ×); C-E: Superoxide dismutase, glutathione and malondialdehyde levels of HepG2 (n = 3-5). aP < 0.01 vs the ethanol-fed group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05 vs the ethanol-fed group. Ctr: Control; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction; XPQG-L: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-low; XPQG-M: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-medium; XPQG-H: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-high; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
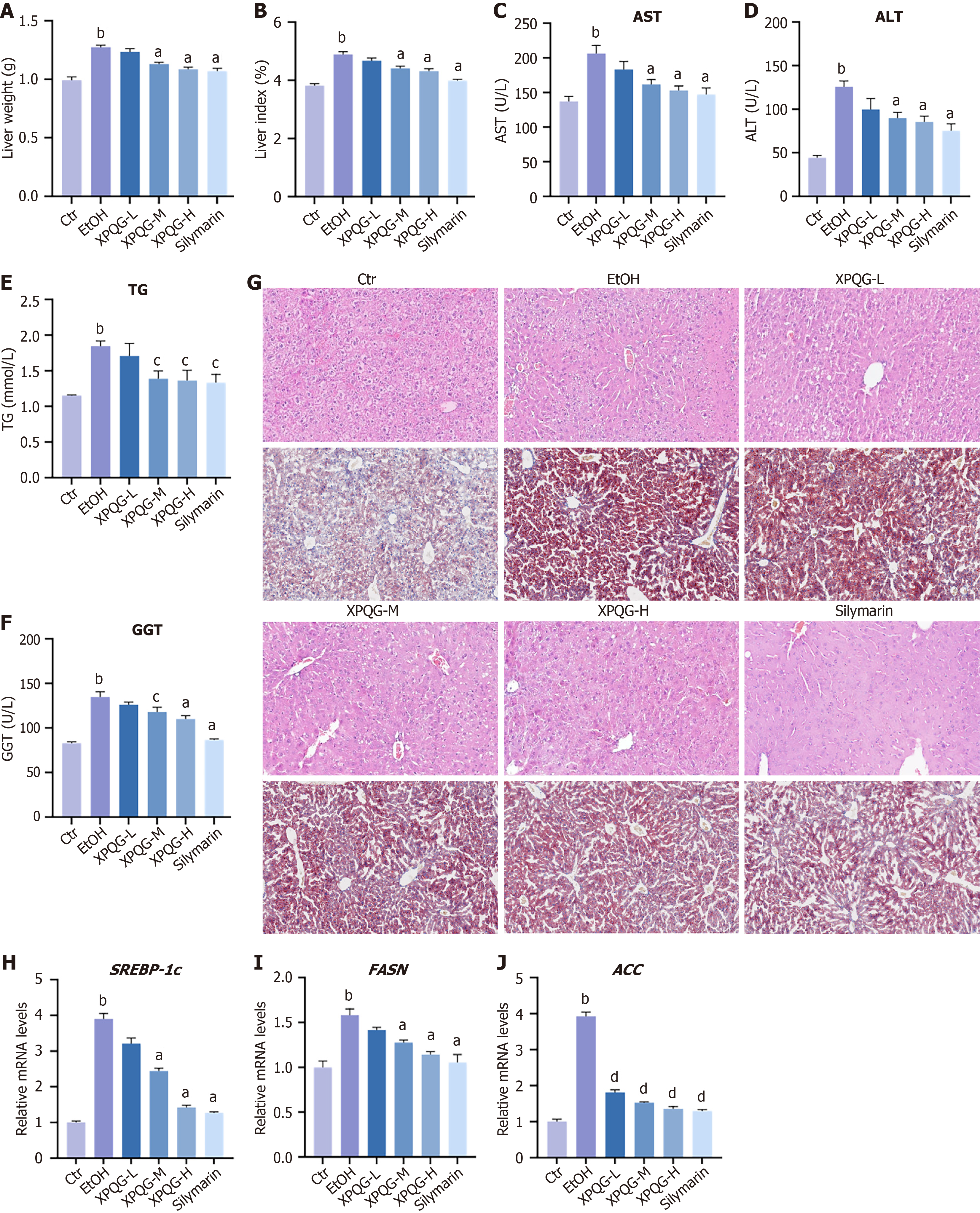
Figure 4 Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction alleviated hepatic injury in alcoholic liver injury mice.
A and B: Effects of Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction (XPQG) on body weight gain: Liver weight (A) and liver weight/body weight ratio values (B); C-F: Serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglyceride and the levels of γ-glutamyl transferase in liver; G: The images of representative hematoxylin and eosin or Oil Red O stained liver sections (40 ×); H-J: Effects of XPQG on the expression of relative mRNA expression in liver in lipid synthesis, including SREBP-1c, ACC, FASN (n = 6-8). aP < 0.01 vs the ethanol-fed group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05 vs the ethanol-fed group. Ctr: Control; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TG: Triglyceride; GGT: γ-glutamyl transferase; XPQG-L: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-low; XPQG-M: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-medium; XPQG-H: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-high.
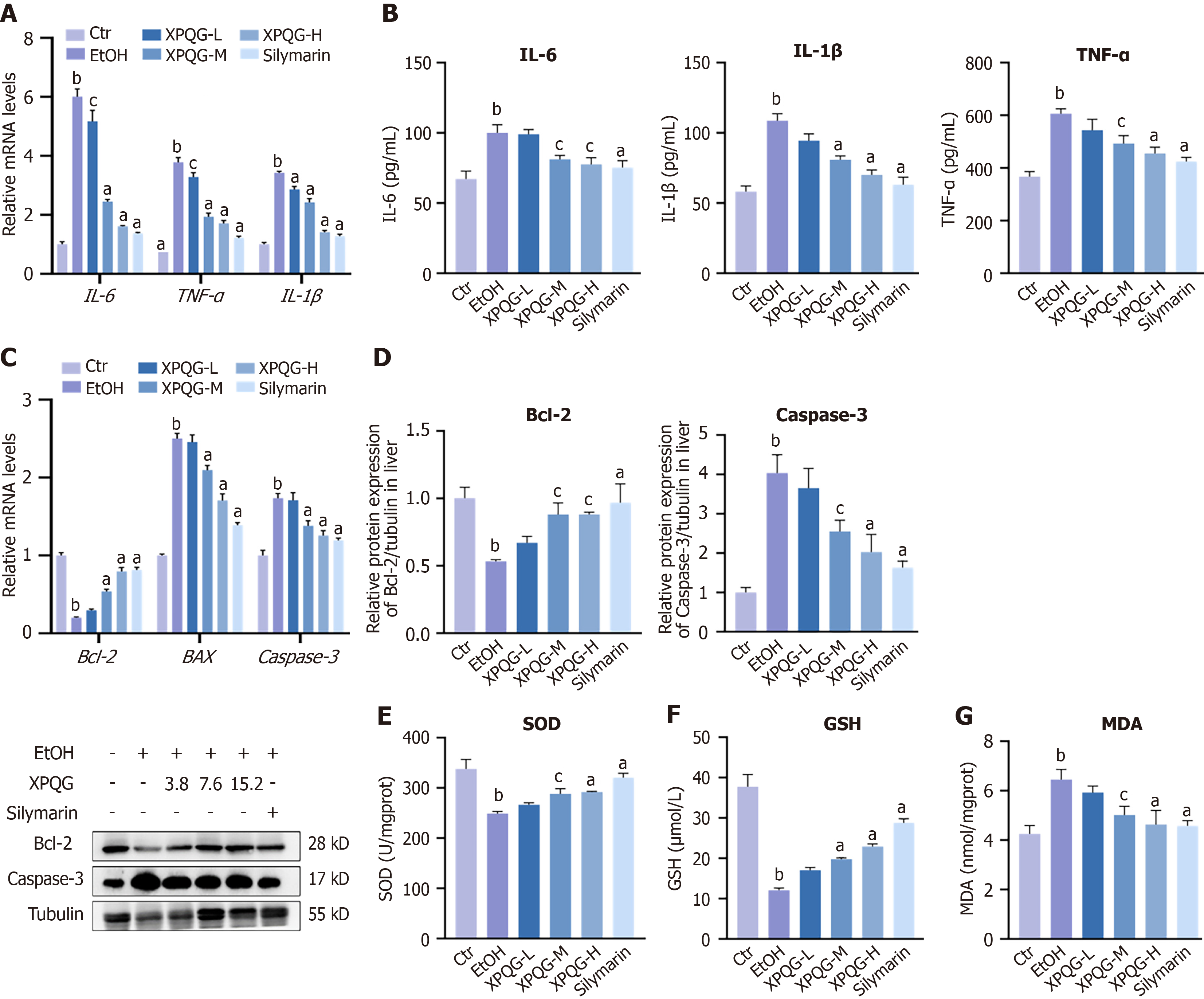
Figure 5 Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction inhibited alcohol-induced liver injury inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress.
A: The relative mRNA expression of inflammation in mice; B: Serum inflammatory factor levels were determined, respectively, by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; C: Effects of Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction on the expression of relative mRNA expression in apoptosis , including Bcl-2, BAX, and Caspase-3; D: Protein expression of Bcl-2 and Caspase-3; E-G: Superoxide dismutase, glutathione and malondialdehyde levels in livers (n = 6-8). aP < 0.01 vs the ethanol-fed group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05 vs the ethanol-fed group. IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
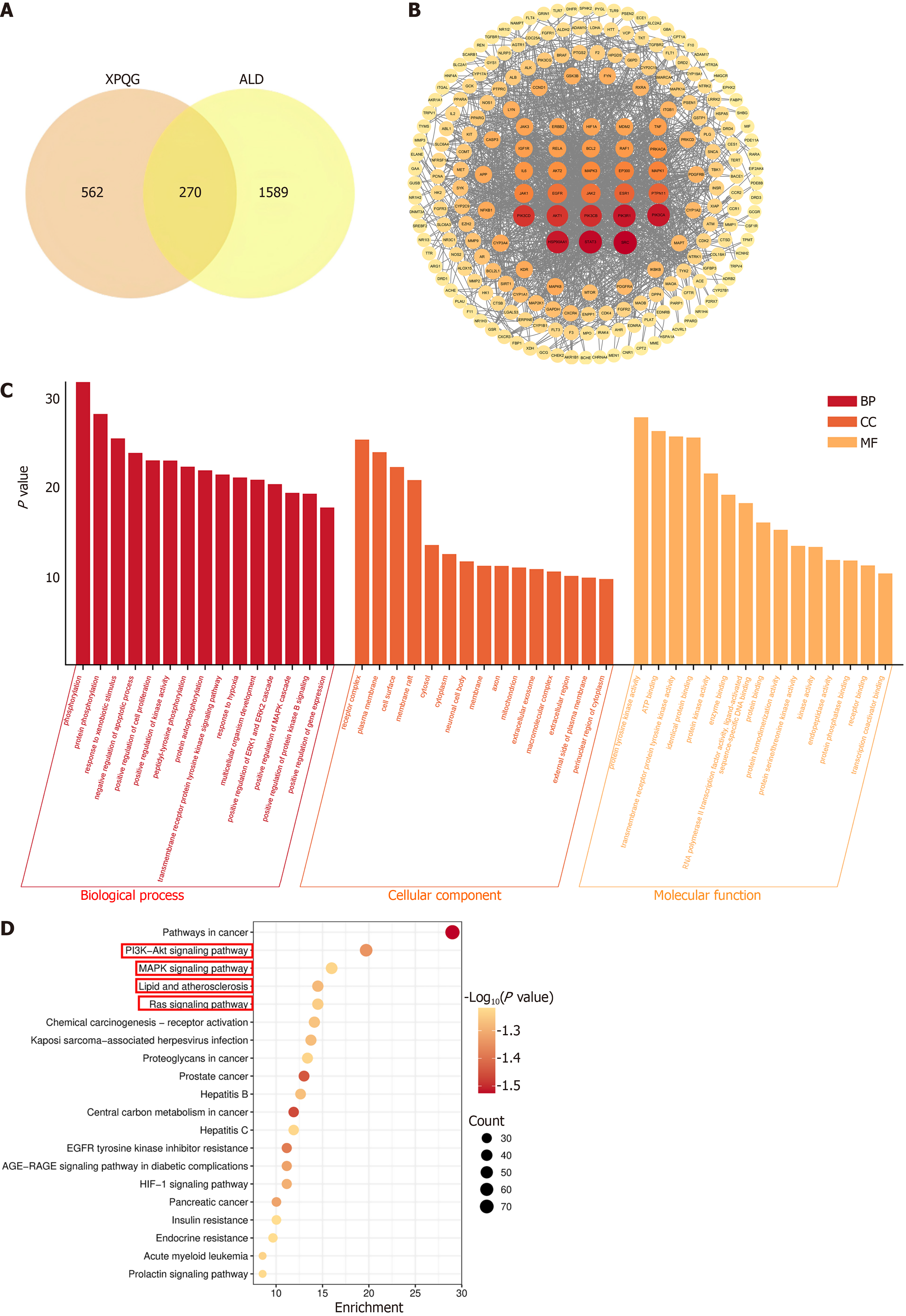
Figure 6 Network pharmacology and RNA sequencing Highlights MAPK/CHOP/Nrf2 may be important targets.
A: Intersection of “compound targets” and “disease targets”; B: Protein-Protein Interaction network; C: Gene Ontology enrichment analysis; D: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis. XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction; ALD: Alcoholic liver disease; BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
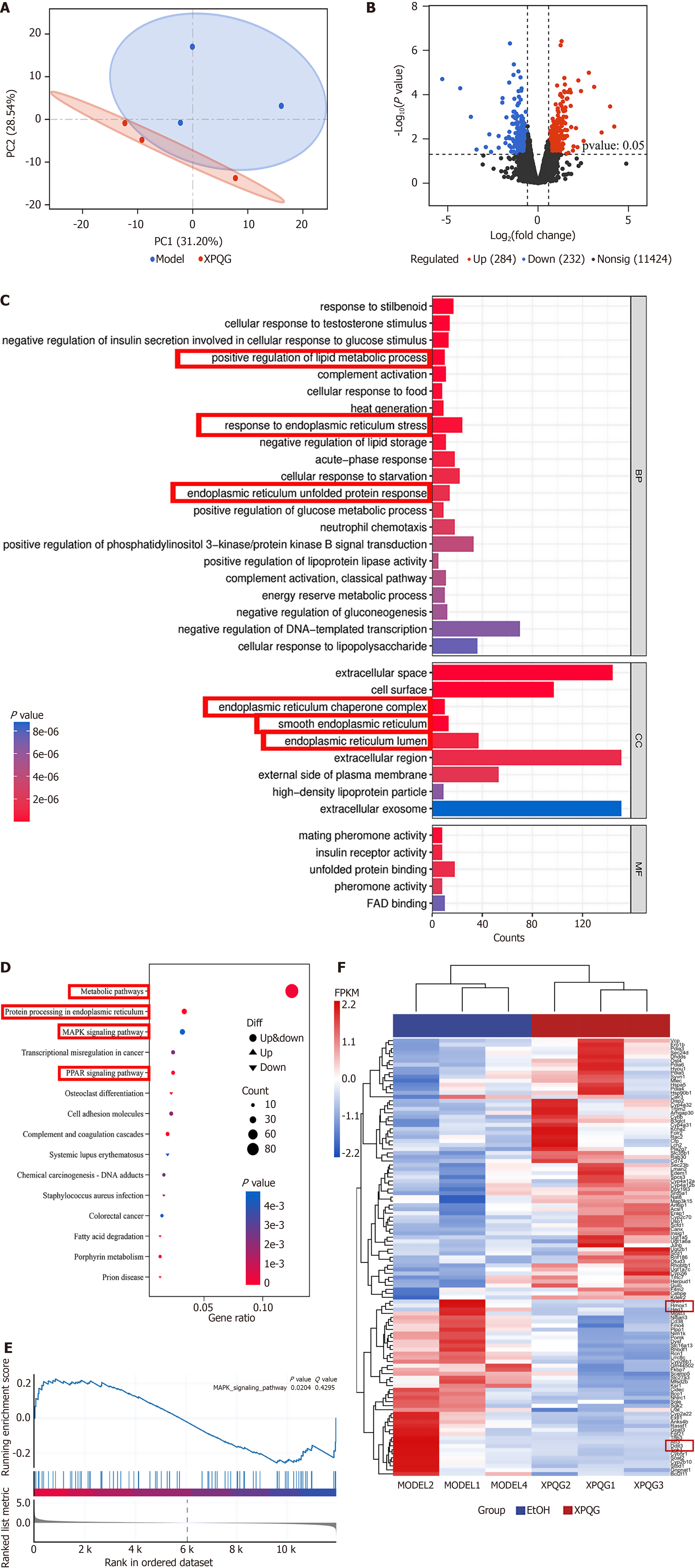
Figure 7 Network pharmacology and RNA sequencing Highlights MAPK/CHOP/Nrf2 may be important targets.
A: Principal component analysis; B: Volcano plot of differentially expressed mRNAs in alcoholic liver disease mice after Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction intervention; C: Gene Ontology enrichment analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs; D: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed genes from liver RNA-seq data. The top 15 significantly enriched pathways are shown; E: Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs in MAPK significant pathways; F: Heatmap shows endoplasmic reticulum-related differentially expressed genes. XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction.
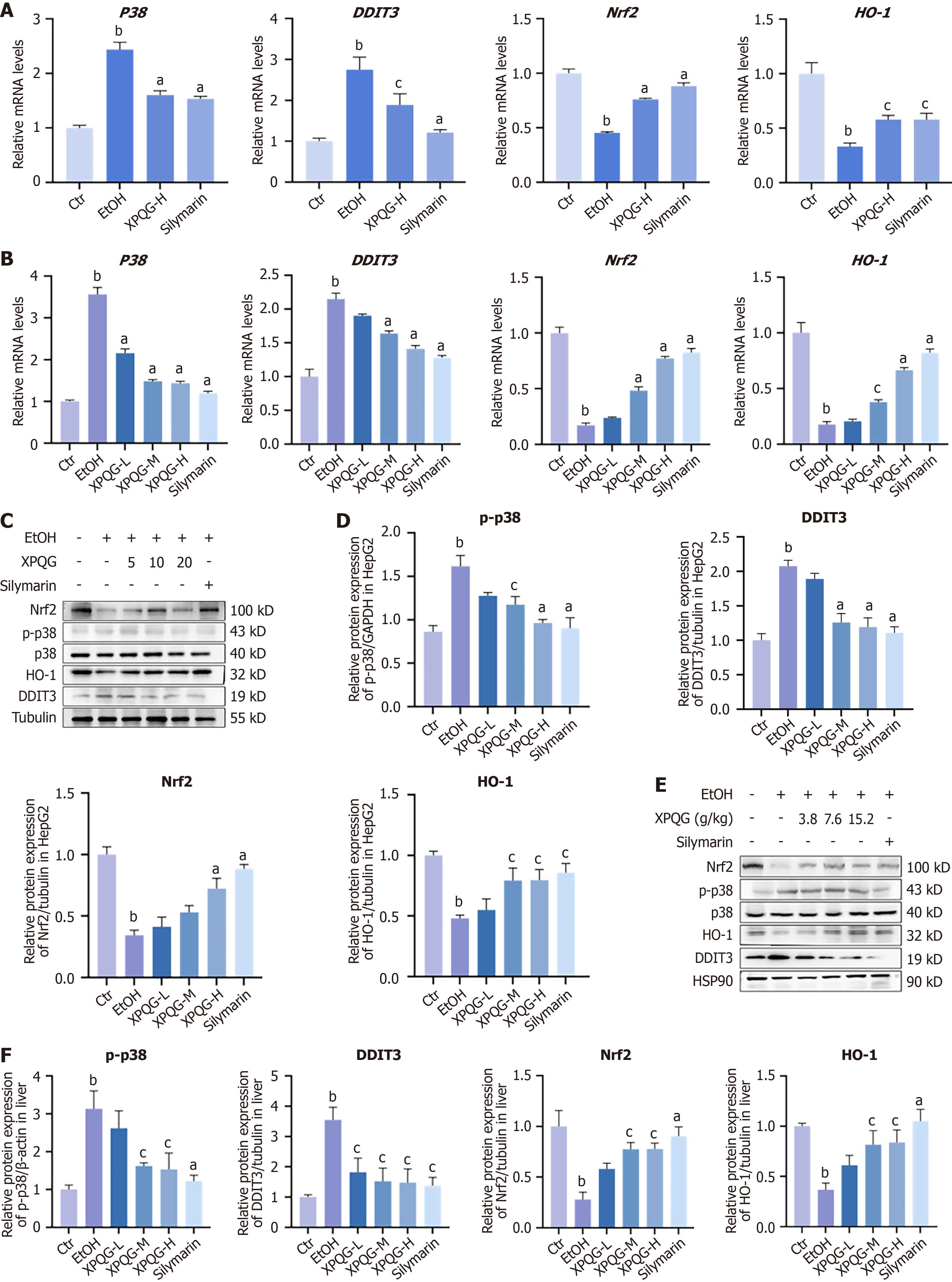
Figure 8 Effect of Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction on the expression of pp38, DDIT3, Nrf2 and HO-1.
A: The relative mRNA expression of p38, DDIT3, Nrf2, HO-1 in HepG2; B: The relative mRNA expression of p38, DDIT3, Nrf2, HO-1 in mice; C and D: Representative protein expression of Nrf2, p-p38, p38, HO-1 and DDIT3 in HepG2; E and F: Representative protein expression of Nrf2, p-p38, p38, HO-1 and DDIT3 in mice (n = 3-5). aP < 0.01 vs the ethanol-fed group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05 vs the ethanol-fed group. Ctr: Control; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction; XPQG-L: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-low; XPQG-M: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-medium; XPQG-H: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction-high.
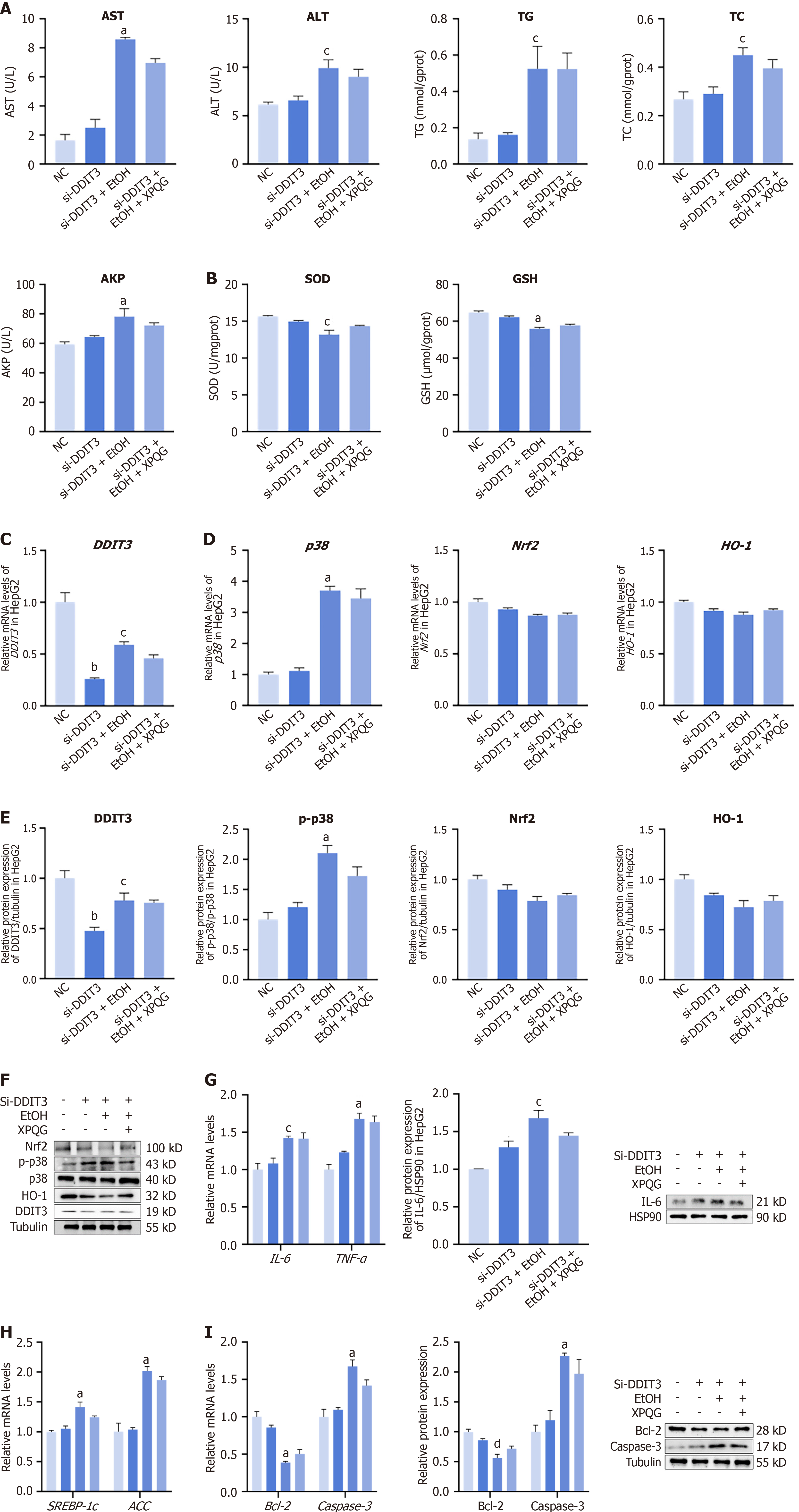
Figure 9 DDIT3 knocked-down confirms its role in Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction -mediated protection.
A: The effects of Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction (XPQG) on alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglyceride, total cholesterol, and alkaline phosphatase expression in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA; B: After transfected with DDIT3 siRNA, XPQG had no obvious effect on the expression of superoxide dismutase and glutathione; C: Transcript levels of DDIT3 were measured by quantitative RT-PCR in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA; D: Relative mRNA levels of p38, Nrf2 and HO-1 in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA; E and F: Relative protein expression of DDIT3, p38, Nrf2 and HO-1 in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA; G: Effects of XPQG on the expression of inflammatory factors in HepG2 in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA; H: Relative mRNA levels of SREBP1-c and ACC in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA; I: Effects of XPQG on the expression of Apoptosis in HepG2 cells as transfected with DDIT3 siRNA (n = 3-5). aP < 0.01 vs si-DDIT3 group; bP < 0.01 vs negative control group; cP < 0.05 vs the si-DDIT3 group. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol; AKP: Alkaline phosphatase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; NC: Negative control; IL-6: Interleukin-6; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction.
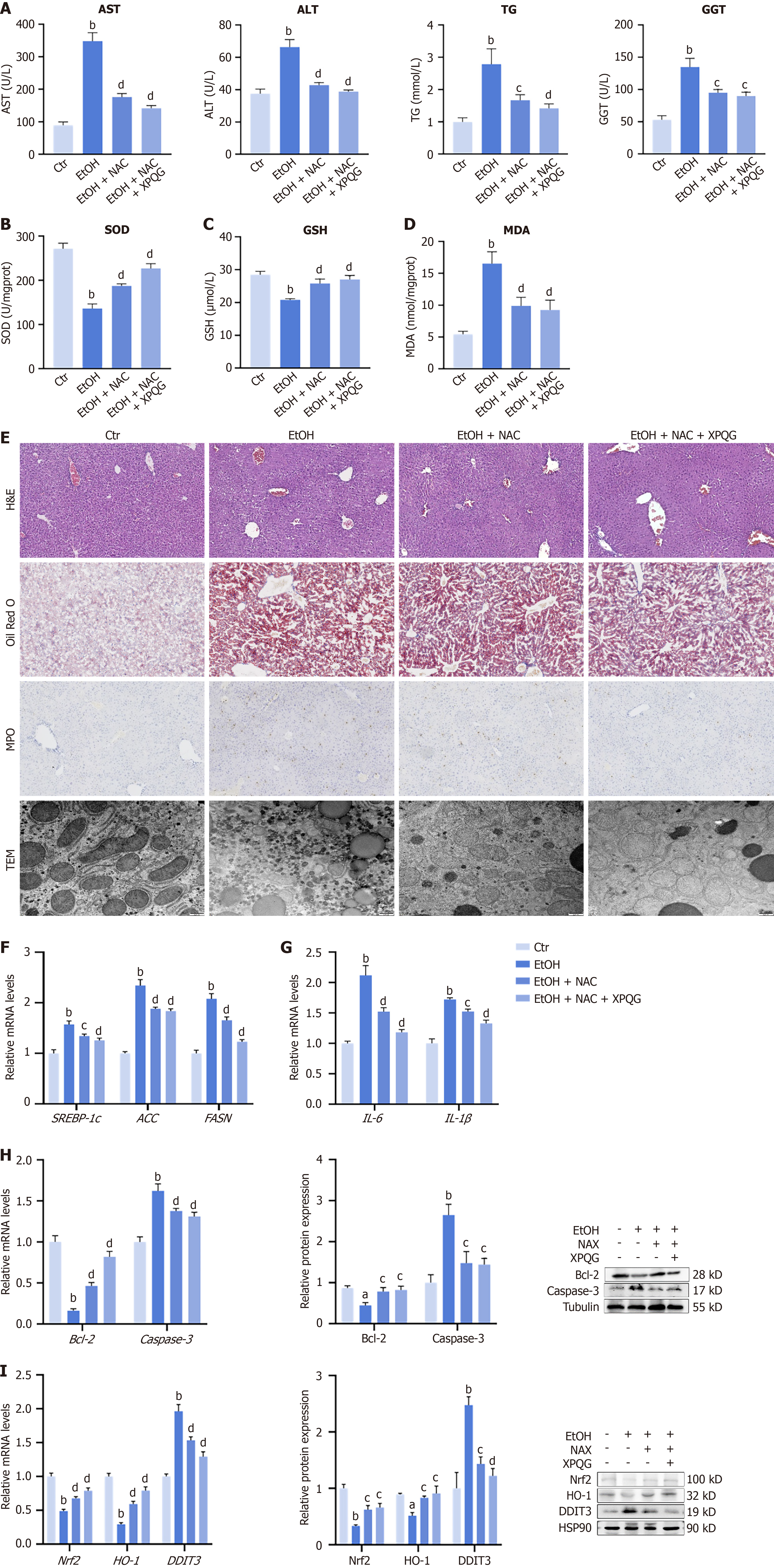
Figure 10 By regulating oxidative stress Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction alleviated hepatic injury in alcoholic liver disease mice.
A: Hepatic parameters including alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglyceride and alkaline phosphatase (n = 6-8); B-D: Oxidative stress levels include liver glutathione, malondialdehyde, and superoxide dismutase in each group (n = 6-8); E: Pathomorphological changes in liver evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin (40 ×), Oil Red O staining (40 ×), immunohistochemistry staining of MPO (40 ×) and transmission electron microscopy analysis (25000 ×) in liver tissues of mice (n = 3); F: Relative mRNA levels of lipid metabolism, including SREBP1-c, ACC, FASN (n = 6-8); G: Relative mRNA levels of inflammation (n = 6-8); H: Effects of N-acetylcysteine and Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction on the expression of Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 (n = 3-5); I: Relative mRNA levels and protein expression levels of Nrf2, HO-1, DDIT3 (n = 3-5). aP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group; cP < 0.05 vs the ethanol-fed group; dP < 0.01 vs the ethanol-fed group. AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TG: Triglyceride; GGT: γ-glutamyl transferase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; MDA: Malondialdehyde; Ctr: Control; EtOH: Ethanol-fed; NAC: N-acetylcysteine; XPQG: Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction.
- Citation: Huang NF, Ling P, Xu YJ, Feng XF, Zheng Y, Sun T. Xing-Pi-Qing-Gan decoction alleviates alcoholic liver disease by down-regulating DDIT3 and restoring Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant signaling: Multi-omics and experimental evidence. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(8): 115077
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i8/115077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115077