©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2025; 31(47): 113496
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.113496
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.113496
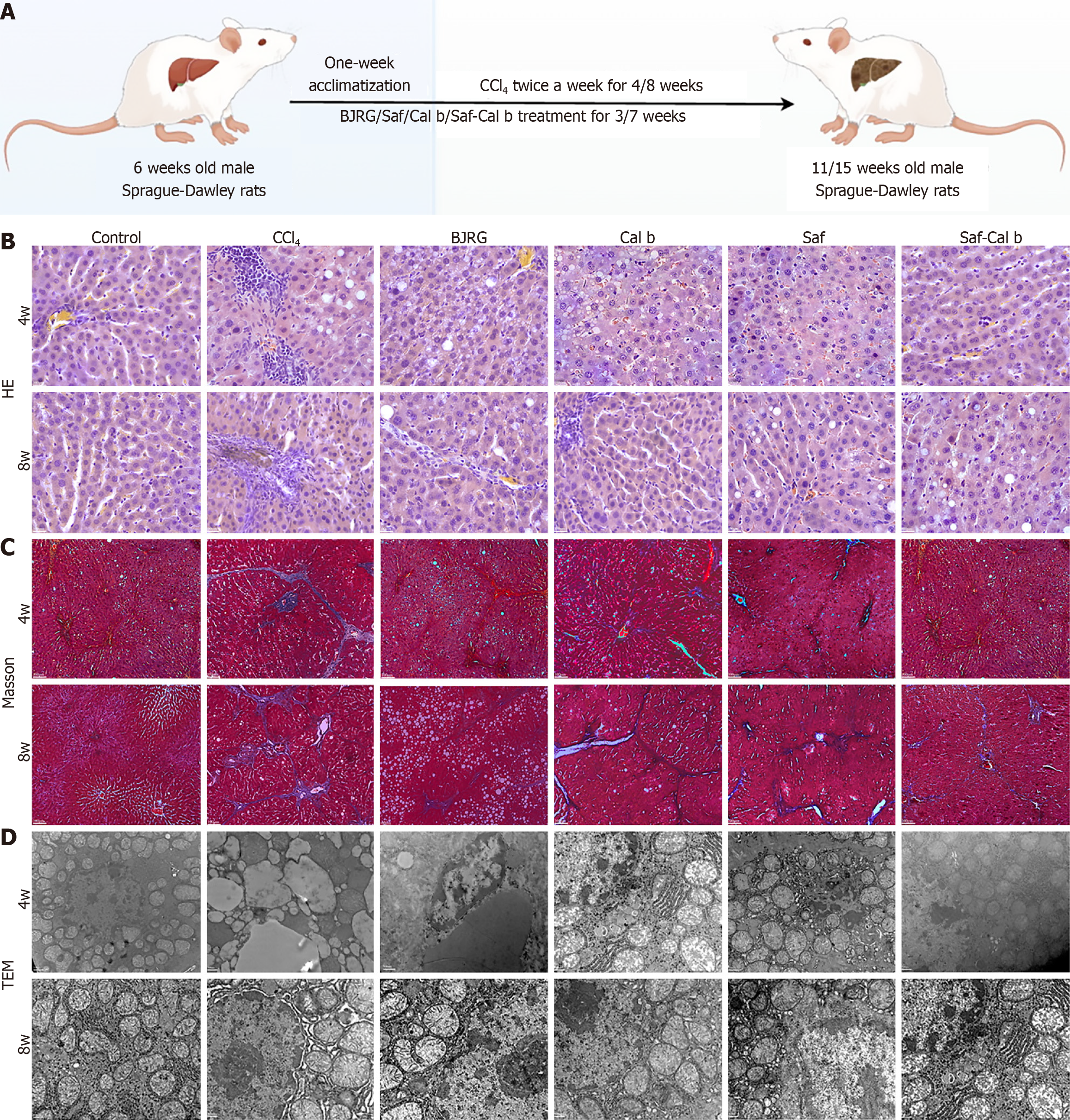
Figure 1 The saffron and Calculus bovis treatment inhibited liver fibrosis in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis rats at 4 weeks and 8 weeks.
A: An overview of the experimental protocol is shown. Six-week-old rats received CCl4 gavage for 4 weeks and 8 weeks, with concurrent drug administration initiated on the second week of gavage; B: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (scale bar: 100 μm); C: Masson’s staining (scale bar: 100 μm) of liver tissue from the indicated groups; D: Transmission electron microscopy was performed to examine the ultrastructure of liver tissue (scale bar: 500 nm). Note: In this study, “4w” and “8w” are defined as the 4th and 8th week, respectively, after the initial CCl4 treatment. BJRG: Biejia Ruangan tablet; Saf: Saffron; Cal b: Calculus bovis; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; TEM: Transmission electron microscopy.
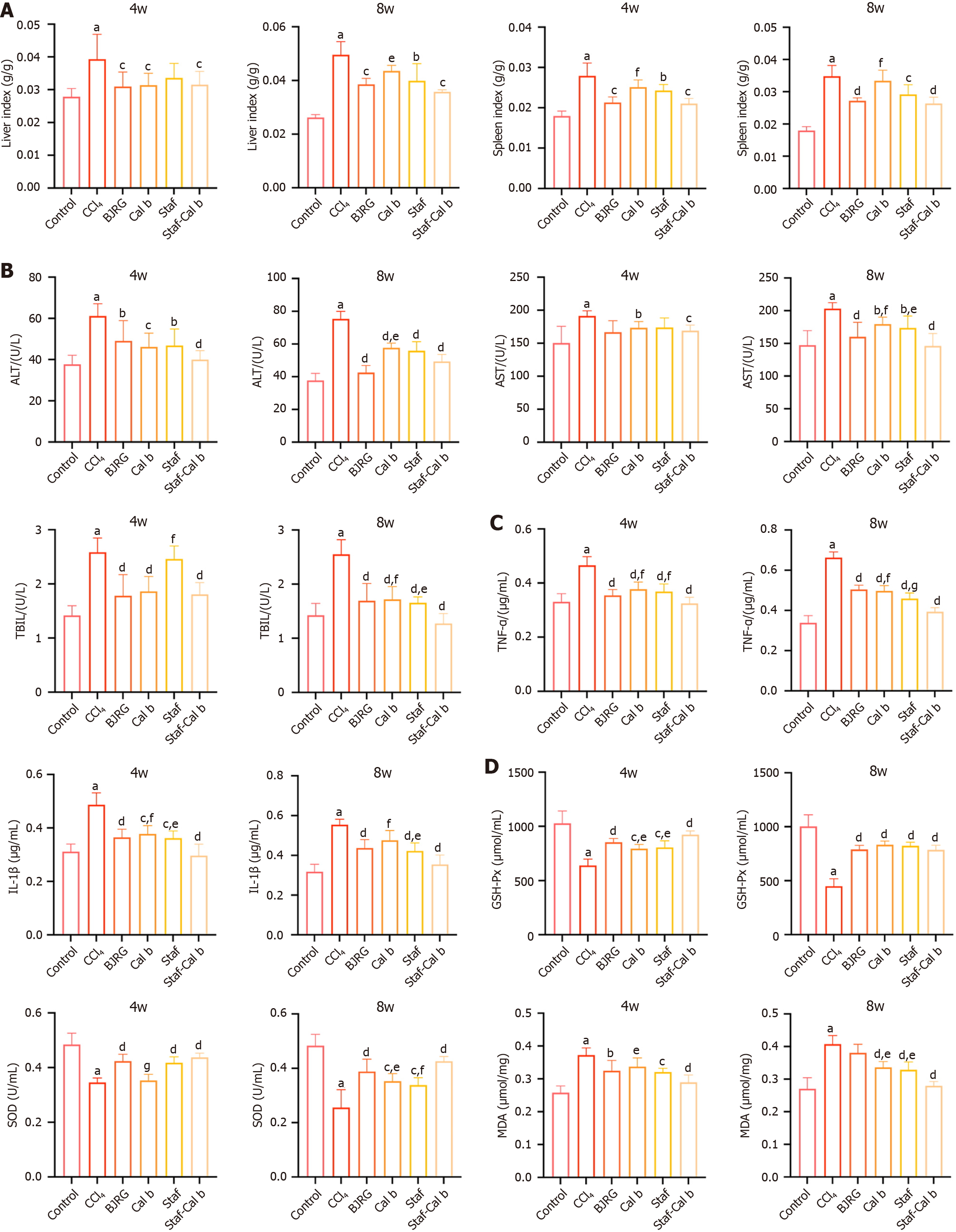
Figure 2 Effects of the saffron and Calculus bovis treatment on liver function, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress.
A and B: Serum aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and total bilirubin activities; C: Serum tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β levels; D: Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde concentration in the liver in the indicated groups. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 6). BJRG: Biejia Ruangan tablet; Saf: Saffron; Cal b: Calculus bovis; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; GSH-PX: Glutathione peroxidase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde. aP < 0.001 vs control group, bP < 0.05 vs CCl4 group, cP < 0.01 vs CCl4 group, dP < 0.001 vs CCl4 group, eP < 0.05 vs saffron and Calculus bovis group, fP < 0.01 vs saffron and Calculus bovis group, and gP < 0.001 vs saffron and Calculus bovis group.
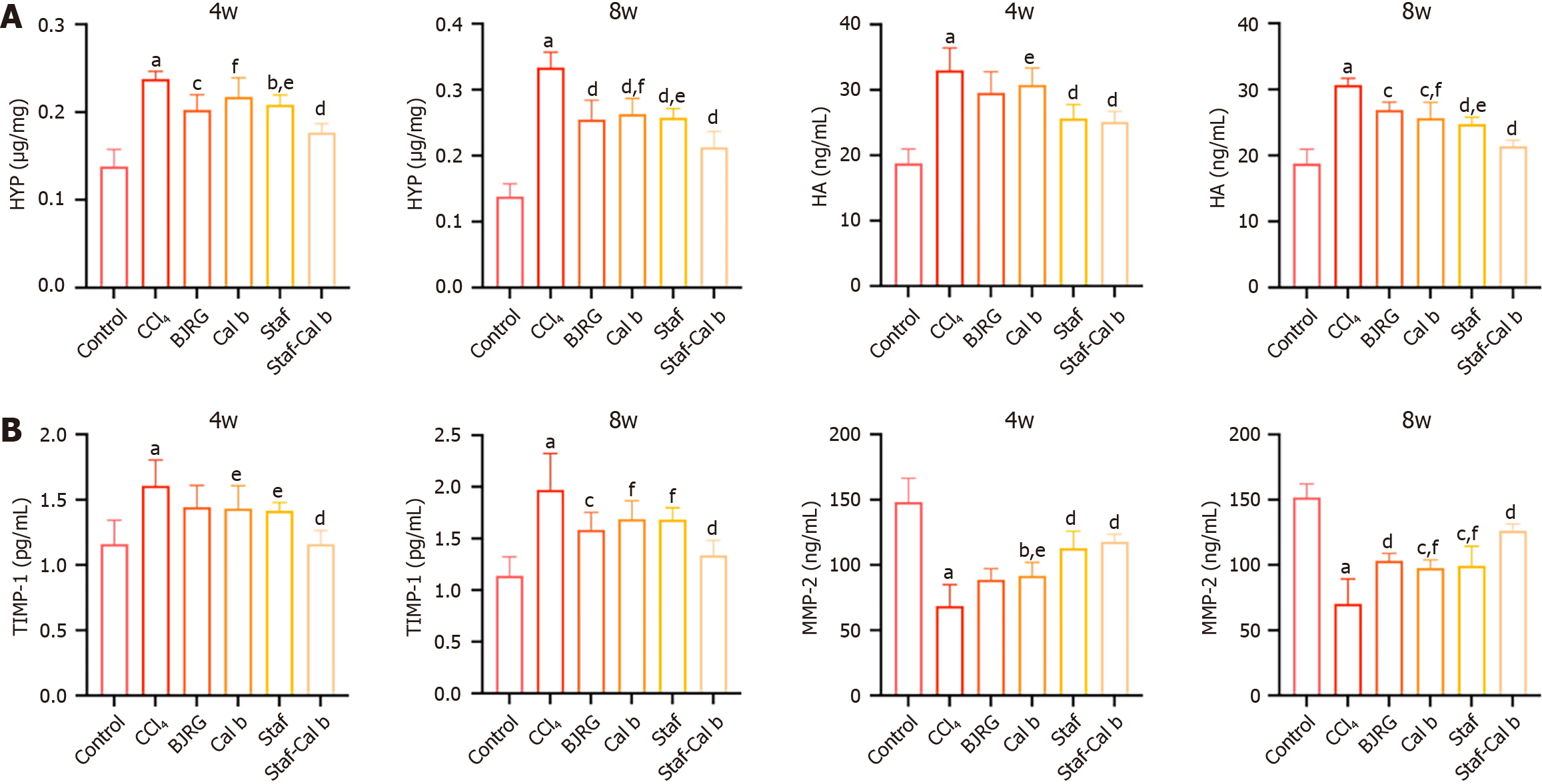
Figure 3 Effects of various drugs on hepatic fibrogenesis and degradation in rats.
A: Hydroxyproline content in rat liver tissue and hyaluronic acid level in serum at 4 weeks and 8 weeks; B: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 content in rat liver tissues at 4 weeks and 8 weeks. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 6). BJRG: Biejia Ruangan tablet; Saf: Saffron; Cal b: Calculus bovis; HYP: Hydroxyproline; HA: Hyaluronic acid; TIMP: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase. aP < 0.001 vs control group, bP < 0.05 vs CCl4 group, cP < 0.01 vs CCl4 group, dP < 0.001 vs CCl4 group, eP < 0.05 vs saffron and Calculus bovis group, and fP < 0.01 vs saffron and Calculus bovis group.
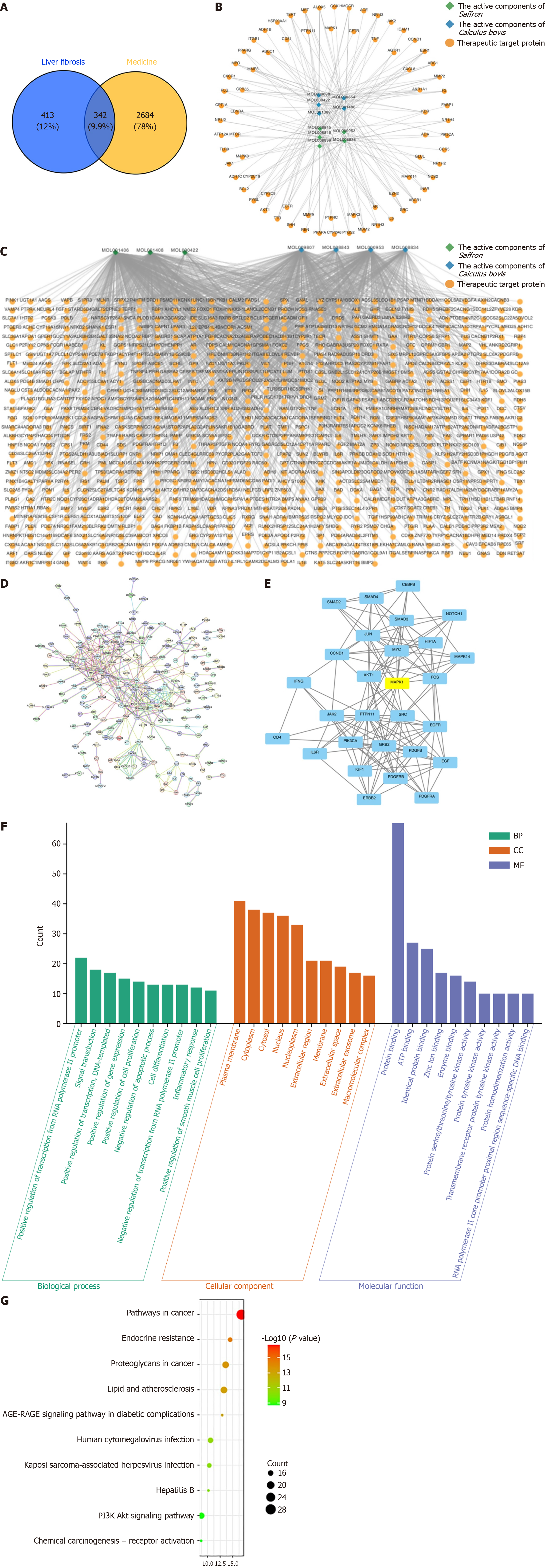
Figure 4 Mechanism of saffron and Calculus bovis against hepatic fibrosis based on network pharmacology.
A: Venn diagram of overlapping targets of saffron and Calculus bovis (Saf-Cal b) in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis; B: Network diagram of active ingredients and targets of Saf-Cal b in the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform database; C: Network diagram of active ingredients and targets of Saf-Cal b in the Bioinformatics Annotation Database for Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine database; D: Protein-protein interaction network; E: Core clustering network; F: Bar chart of Gene Ontology functional enrichment analysis (biological processes, cellular components, molecular function) of targets of Saf-Cal b in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis; G: Bubble chart of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis of targets of Saf-Cal b in treating hepatic fibrosis. BP: Biological processes; CC: Cellular components; MF: Molecular functions; PI3K-Akt: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B.
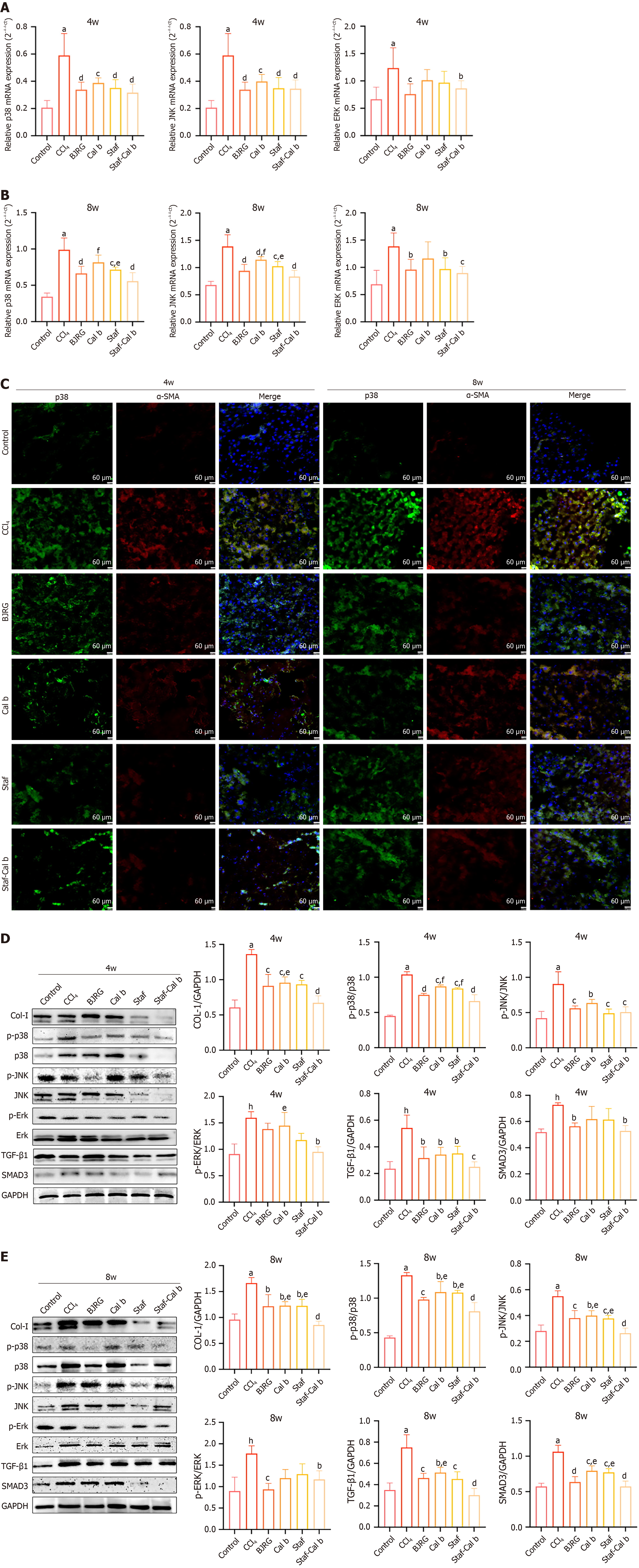
Figure 5 Potential mechanism of saffron and Calculus bovis against hepatic fibrosis.
A: Effects of each drug on mRNA levels of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinases, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase at 4 weeks; B: Effects of each drug on mRNA levels of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinases, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase at 8 weeks; C: Immunofluorescence results of p38 and α-smooth muscle actin in rat liver tissues at 4 weeks and 8 weeks; D: Protein expression of type I collagen, phosphorylated-p38, phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinases, phospho
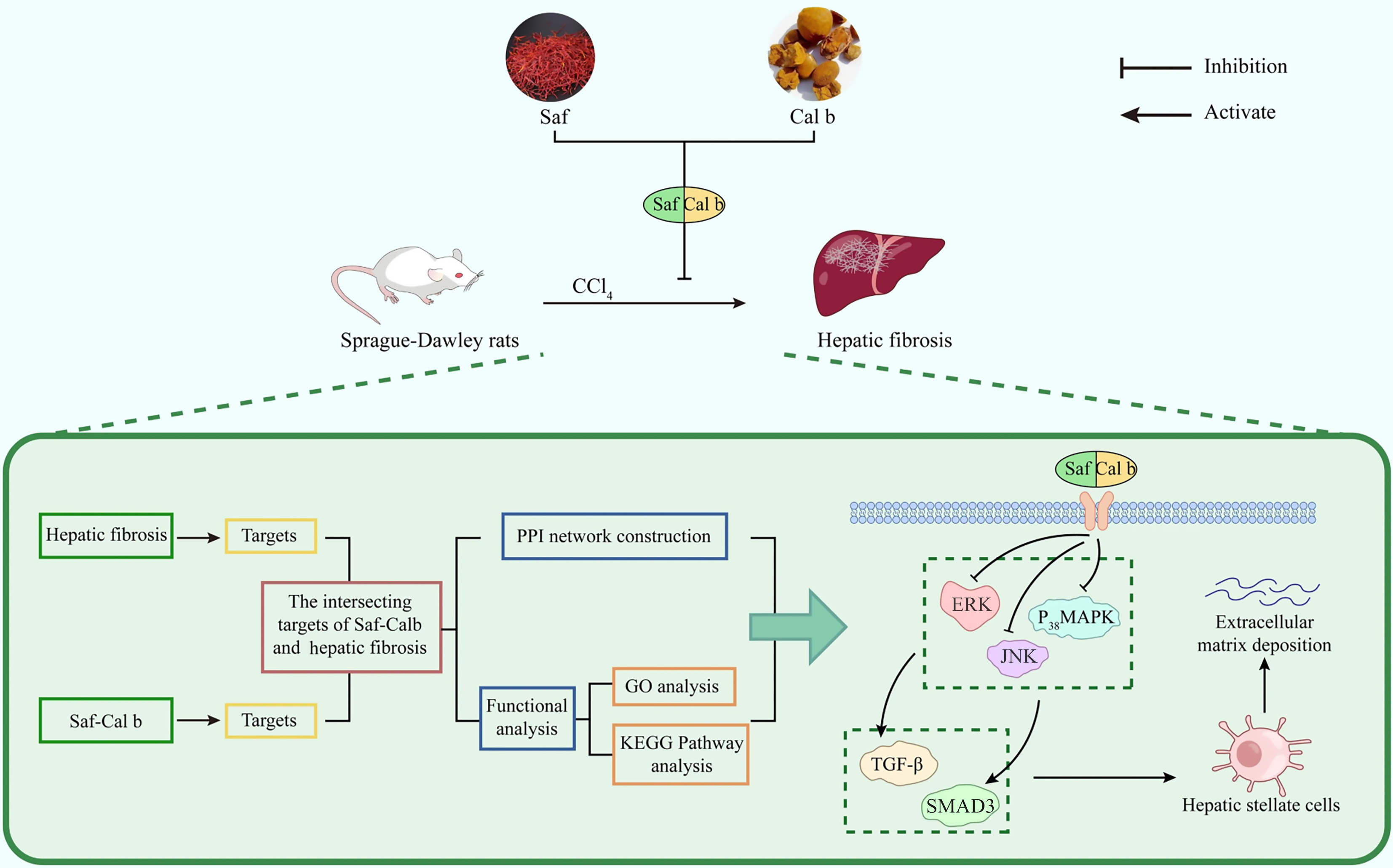
Figure 6 Graphical abstract.
Saf: Saffron; Cal b: Calculus bovis; PPI: Protein-protein interactions; GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinases; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; SMAD3: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3.
- Citation: Sun SN, Wang K, Xu Y, Ye F, Xia WN, Wang ZW, Liu F, He ZX, Chen M, Du QH. Saffron and Calculus bovis combination exerts anti-hepatic fibrotic effect in liver fibrosis rats via the mitogen-activated protein kinases pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(47): 113496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i47/113496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.113496