©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2025; 31(47): 112921
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.112921
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.112921
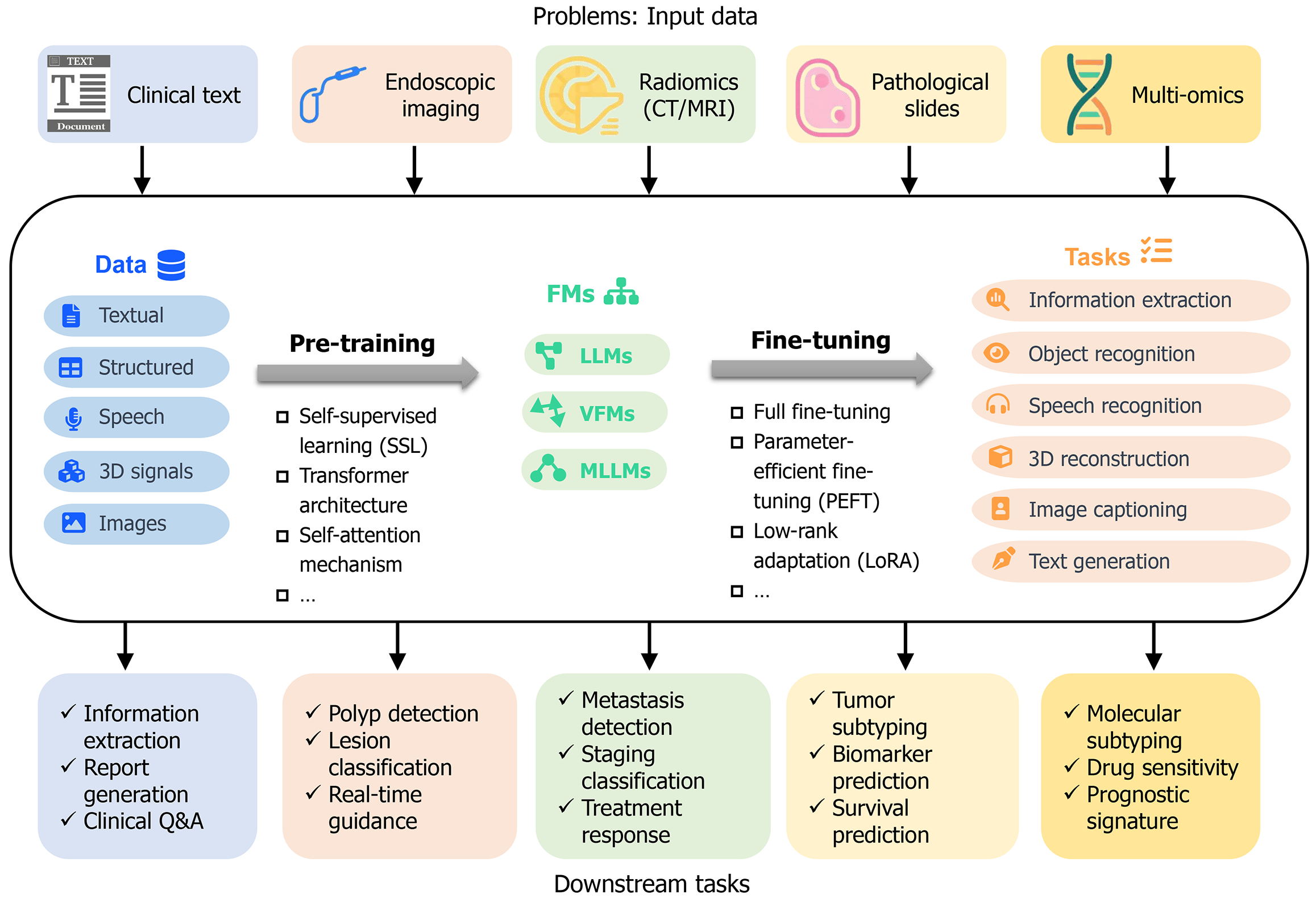
Figure 1 Application of foundation models in gastrointestinal cancer.
This figure illustrates the workflow and applications of foundation models (FMs) in addressing challenges within gastrointestinal cancer research and clinical practice. Starting with a variety of input data sources such as clinical text documents, endoscopic imaging, radiomics from computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging scans, pathological slides, and multi-omics data, these inputs are categorized into textual or image data for pre-training FMs using self-supervised learning, transformer architecture, and self-attention mechanisms to develop models like large language models, vision FMs, and multi-modal learning models. After pre-training, these models undergo fine-tuning through methods such as low-rank adaptation, enabling them to perform a wide range of downstream tasks, thereby showcasing the versatility and potential of FMs in advancing gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis, treatment, and research.
- Citation: Shi L, Huang R, Zhao LL, Guo AJ. Foundation models: Insights and implications for gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(47): 112921
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i47/112921.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.112921