©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2025; 31(47): 111900
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.111900
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.111900
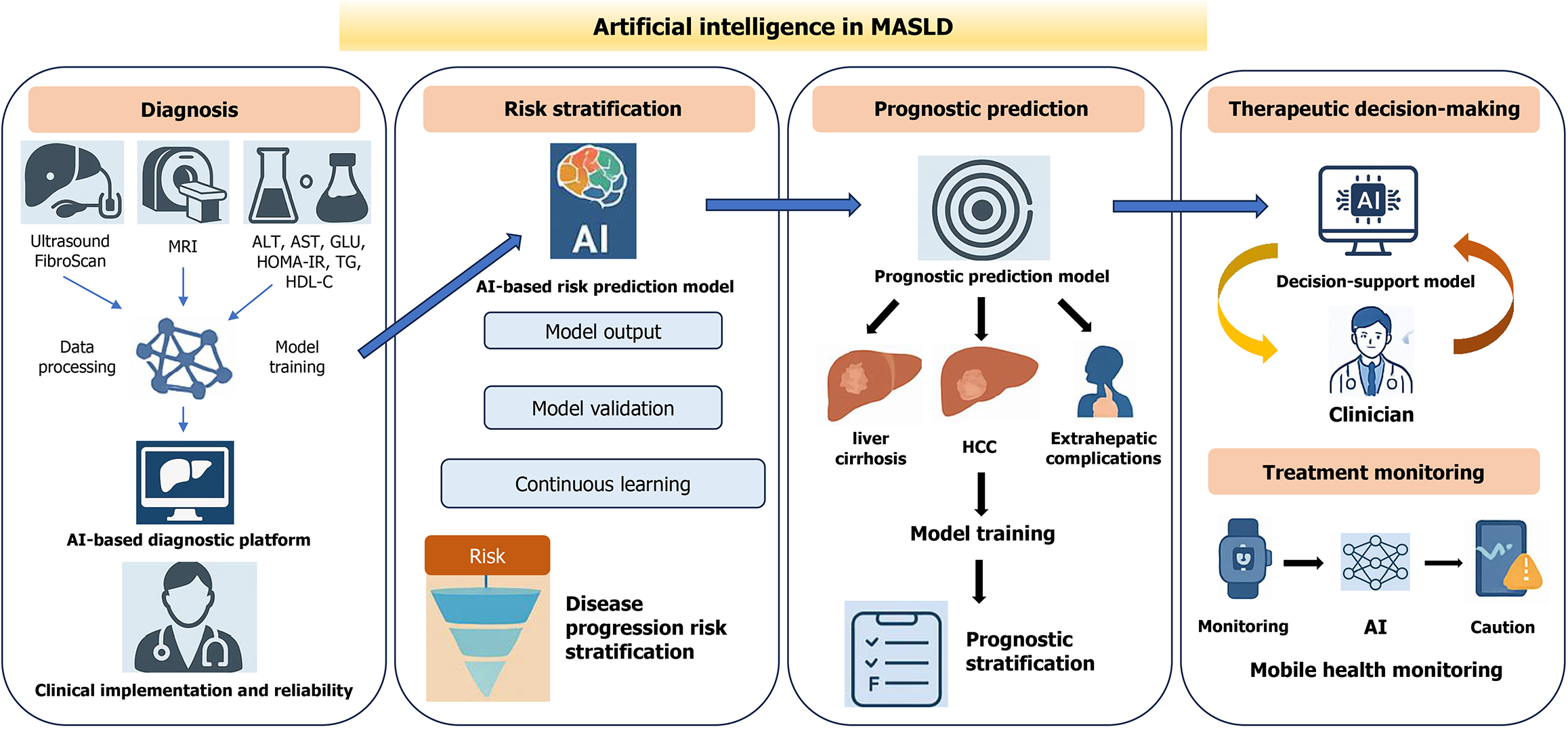
Figure 1 Artificial intelligence applications across the full management spectrum of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Diagnosis: Artificial intelligence (AI) models integrate biochemical indicators (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, glucose, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and multimodal imaging data (ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging) for automatic detection and quantification of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis. Deep learning improves diagnostic accuracy, standardization, and efficiency, enabling non-invasive and early identification of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Risk stratification: Machine-learning algorithms combine clinical, imaging, and metabolic variables to predict the probability of advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis, or extrahepatic complications. AI-based risk maps provide individualized stratification for optimized referral and management pathways. Prognostic prediction: AI fusion models integrate longitudinal clinical and lifestyle data to forecast disease trajectories and long-term outcomes. Continuous learning frameworks (e.g., recurrent or transformer networks) enable dynamic prediction of fibrosis progression, hepatocellular carcinoma, and cardiovascular events. Therapeutic decision-making and treatment monitoring: AI-assisted systems analyze treatment responses and generate personalized lifestyle or pharmacologic recommendations. By incorporating wearable-device and mobile-health data, the platform enables real-time monitoring, adaptive feedback, and closed-loop management, improving adherence and long-term efficacy. AI: Artificial intelligence; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GLU: Glucose; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR: Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TG: Triglycerides.
- Citation: Lou JJ, Zeng J. Artificial intelligence applications for managing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Current status and future prospects. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(47): 111900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i47/111900.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.111900