©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2025; 31(44): 112719
Published online Nov 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i44.112719
Published online Nov 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i44.112719
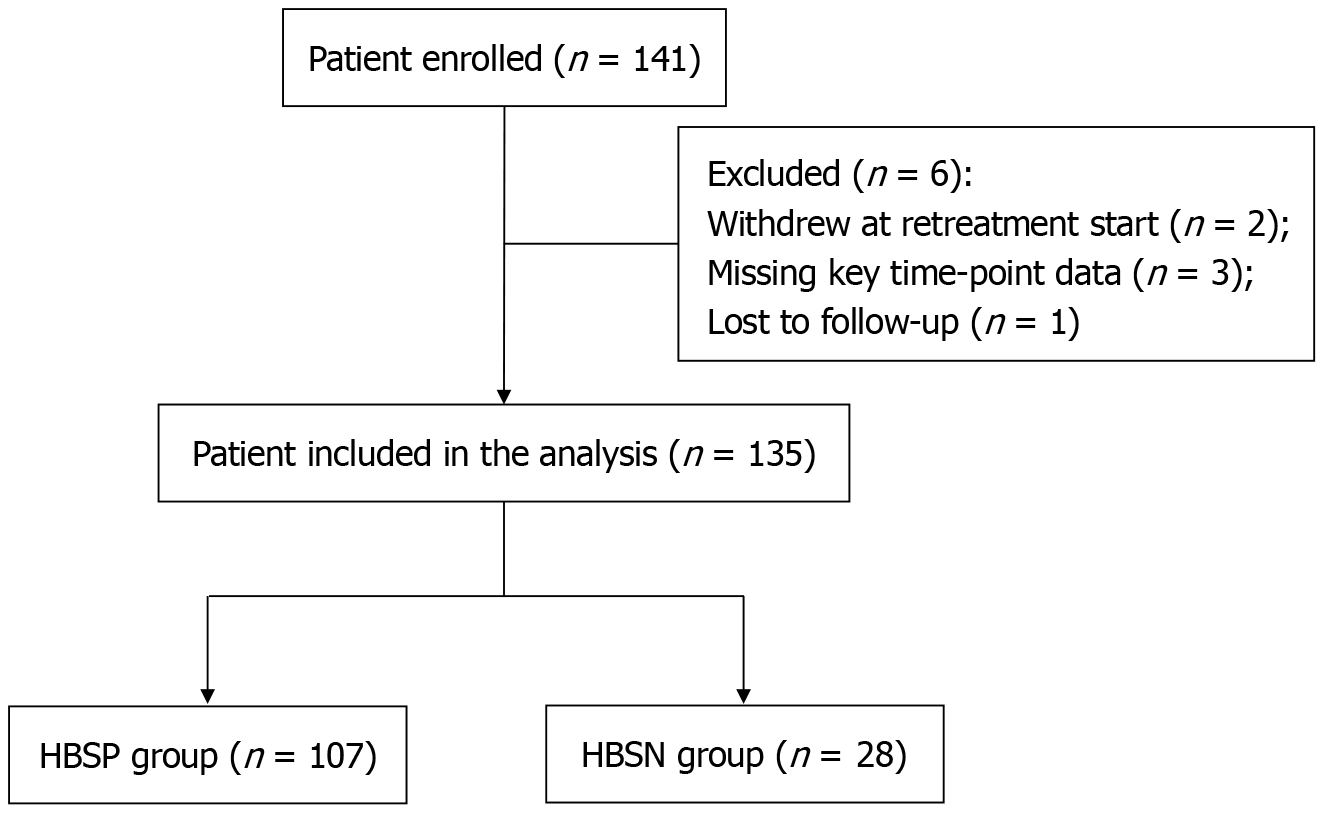
Figure 1 Flow diagram of patient enrollment and grouping.
A total of 141 patients with chronic hepatitis B and compensated liver cirrhosis meeting inclusion criteria were initially enrolled. Six patients were excluded: 2 withdrew at the start of retreatment, 3 had missing key time-point data, and 1 was lost to follow-up. The remaining 135 patients were included in the final analysis and stratified by hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) serostatus: 107 in the HBsAg-positive group and 28 in the HBsAg-negative group. Arrows indicate the progression through enrollment, exclusion, and final group allocation. HBSP: Hepatitis B surface antigen positive; HBSN: Hepatitis B surface antigen negative.
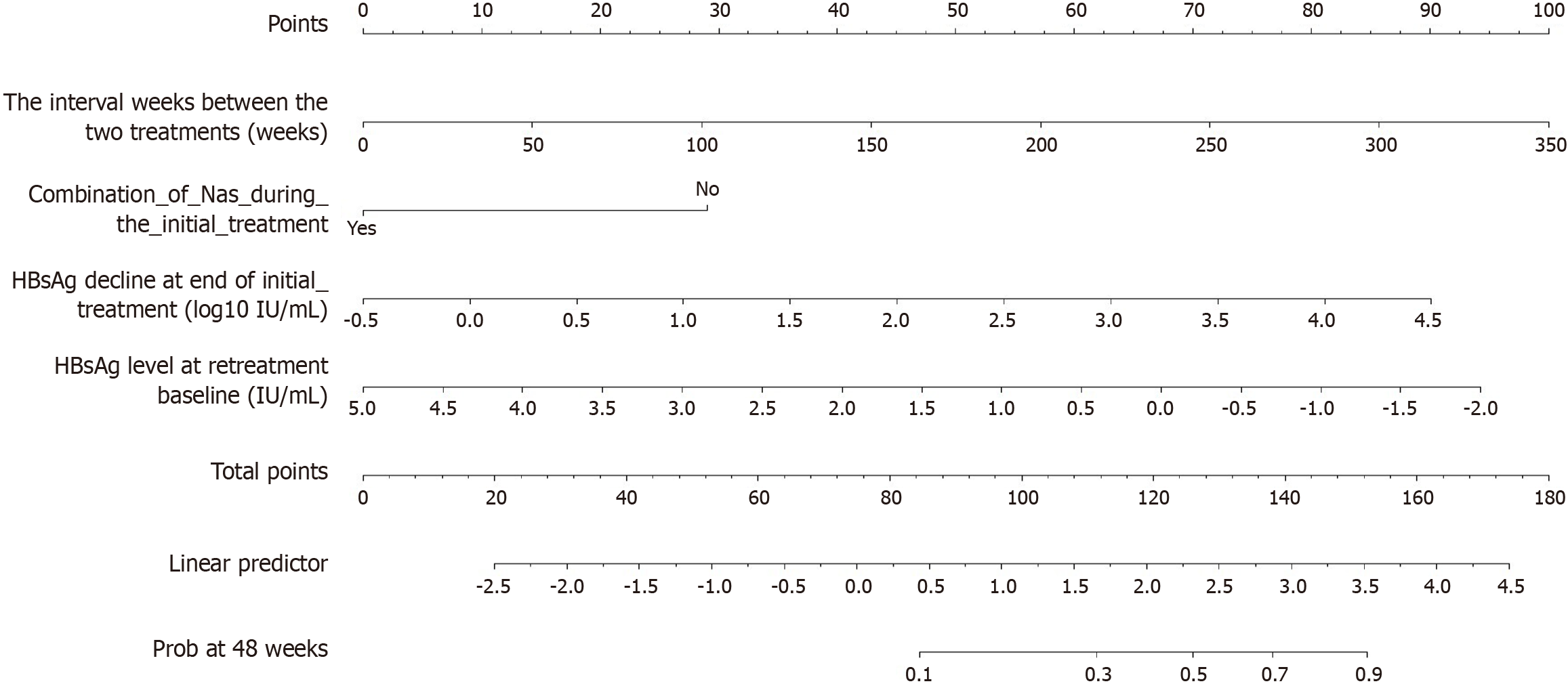
Figure 2 Nomogram for predicting hepatitis B surface antigen clearance after retreatment.
This prognostic model was constructed based on independent predictors identified through least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression and multivariable Cox analysis. The nomogram integrates four variables: Interval between treatments (weeks; range: 0-350); Combination of nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) during initial treatment (binary: Yes/no); Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) decline at end of initial treatment (log10 IU/mL; range: -0.5 to 4.5); HBsAg level at retreatment baseline (IU/mL; range: -5.0 to -2.0). Scoring procedure: (1) Locate patient values on each variable axis; (2) Draw vertical lines to the points axis to obtain individual scores; (3) Sum all scores to calculate total points; and (4) Project total points to the linear predictor and prob at 48 weeks axes for predicted clearance probability. The retreatment HBsAg clearance prediction score (RHCP-S) is derived as: RHCP-S = 18 × (HBsAg decline) - 29 × (NA combination) + 0.29 × (interval weeks) - 13.43 × (baseline HBsAg) + 105.15. Where NA combination: Yes = 1; No = 0. Linear predictor scaling factor k = 21.971. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen.
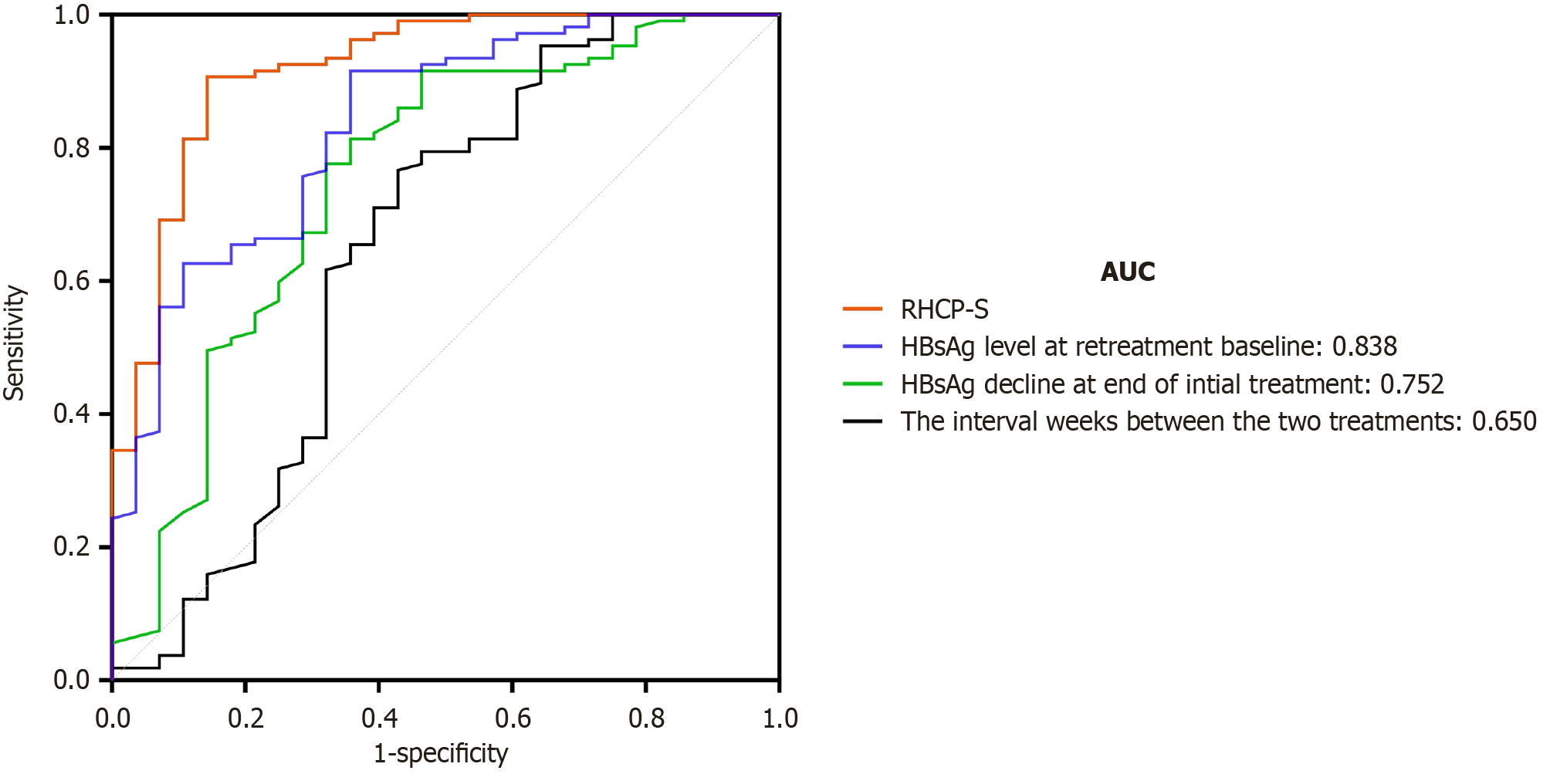
Figure 3 Time-dependent receiver operating characteristic analysis of hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction models.
Comparison of the retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) clearance prediction score (RHCP-S) model vs individual predictors shows superior discrimination for HBsAg clearance [area under the curve (AUC) = 0.920]. Curve comparisons: RHCP-S (red solid line) > retreatment baseline HBsAg (AUC = 0.838, blue solid line) > initial HBsAg decline (AUC = 0.752, green solid line) > treatment interval (AUC = 0.650, black solid line). AUC: Area under curve; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; RHCP-S: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score.
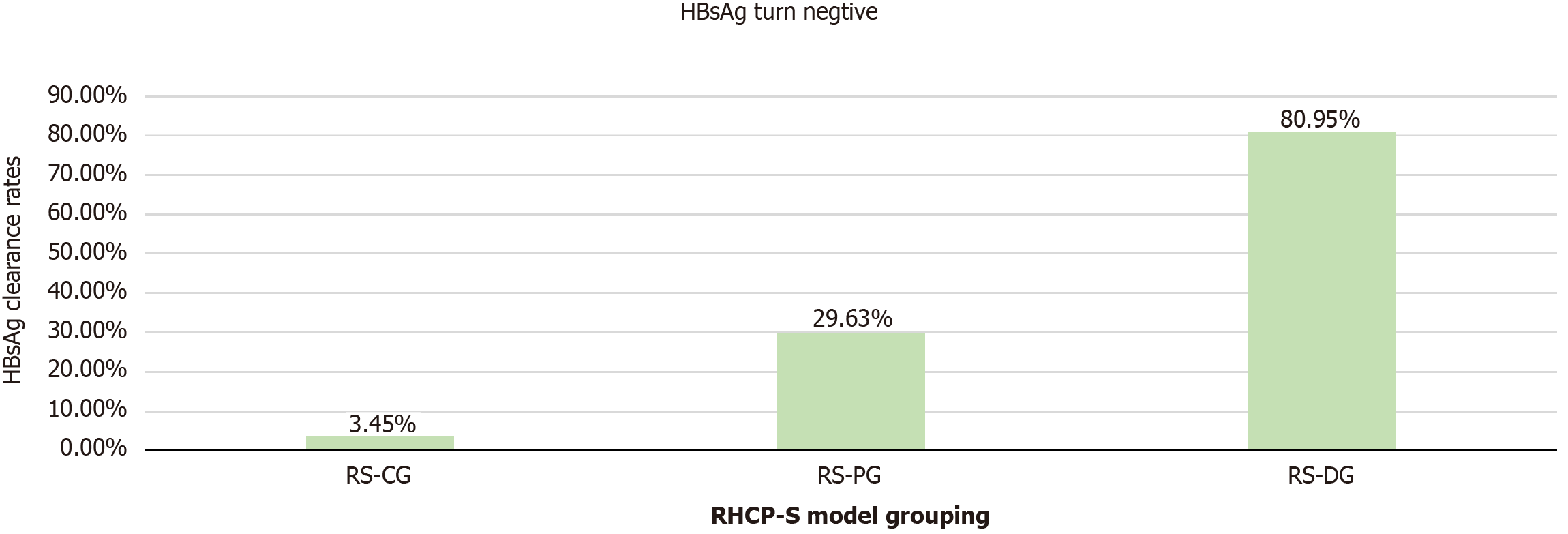
Figure 4 Stratified hepatitis B surface antigen clearance rates by retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score categories.
Patients were categorized using optimal cutoffs (74 and 110): Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score (RHCP-S) challenge group (< 74, clearance 3.45%); RHCP-S probable group (74-110, 29.63%), and RHCP-S dominant group (≥ 110, 80.95%). Bar heights represent cumulative clearance rates, demonstrating significant gradient efficacy (P < 0.001). HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; RHCP-S: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score; RS-CG: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score-challenge group; RS-PG: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score-probable group; RS-DG: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score-dominant group.
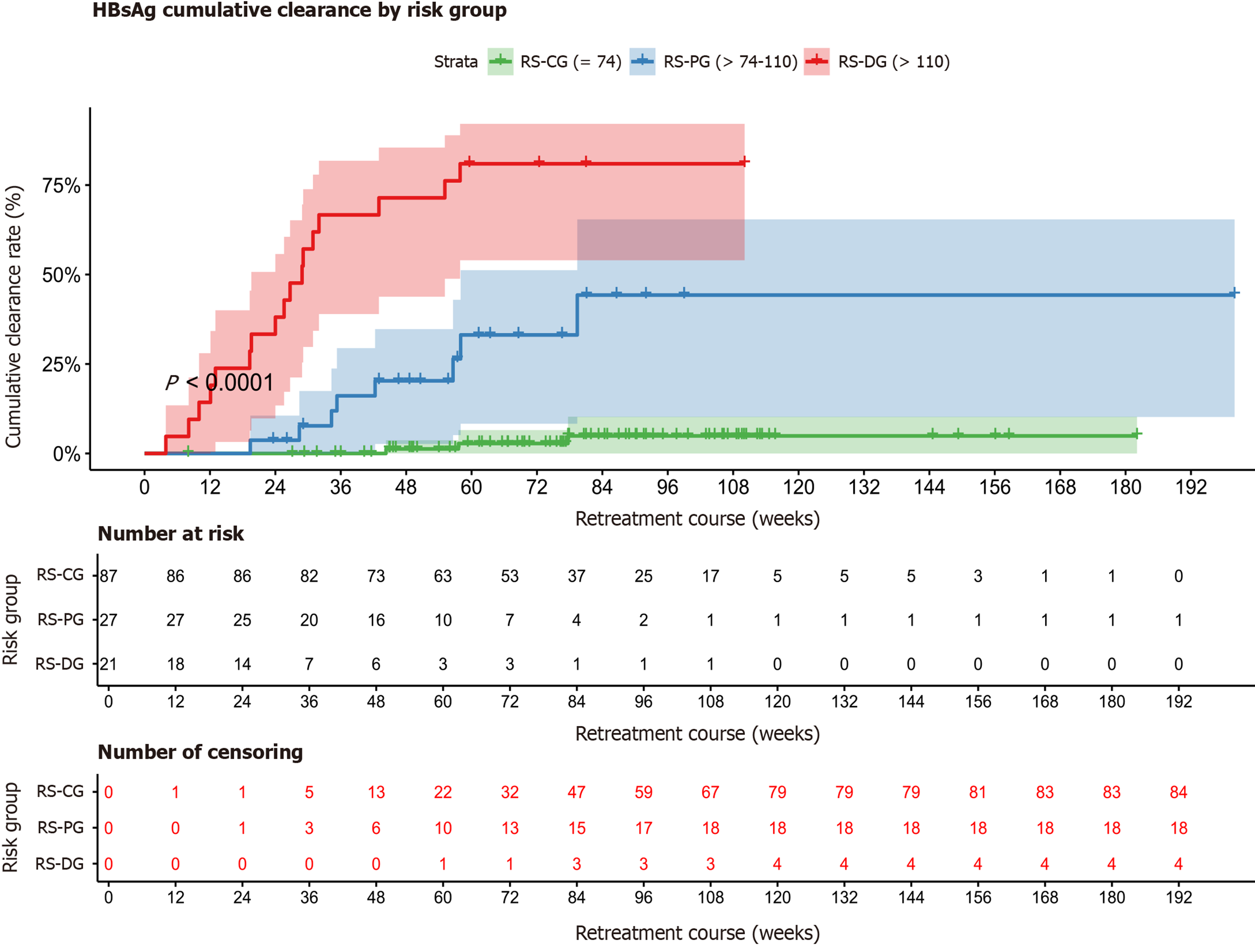
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier validation of stratified hepatitis B surface antigen clearance rates.
Significantly higher hepatitis B surface antigen clearance rates in retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score (RHCP-S)-dominant group vs RHCP-S-challenge group [hazard ratio (HR) = 56.72, 95% confidence interval (CI): 16.20-198.63; P < 0.001] and RHCP-S-probable group vs RHCP-S-challenge group (HR = 11.38, 95%CI: 3.01-43.04; P < 0.001), indicating that stratification has strong discriminatory power. All comparisons Bonferroni-corrected. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; RS-CG: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score-challenge group; RS-PG: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score-probable group; RS-DG: Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction score-dominant group.
- Citation: Fu YC, Li J, Wang JY, Zhang YW, Yan F, Chen J, Du Q, Yang C, Liang J, Ye Q, Xiang HL. Retreatment hepatitis B surface antigen clearance prediction model identifies pegylated interferon alpha candidates in chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(44): 112719
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i44/112719.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i44.112719