©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2025; 31(44): 112481
Published online Nov 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i44.112481
Published online Nov 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i44.112481
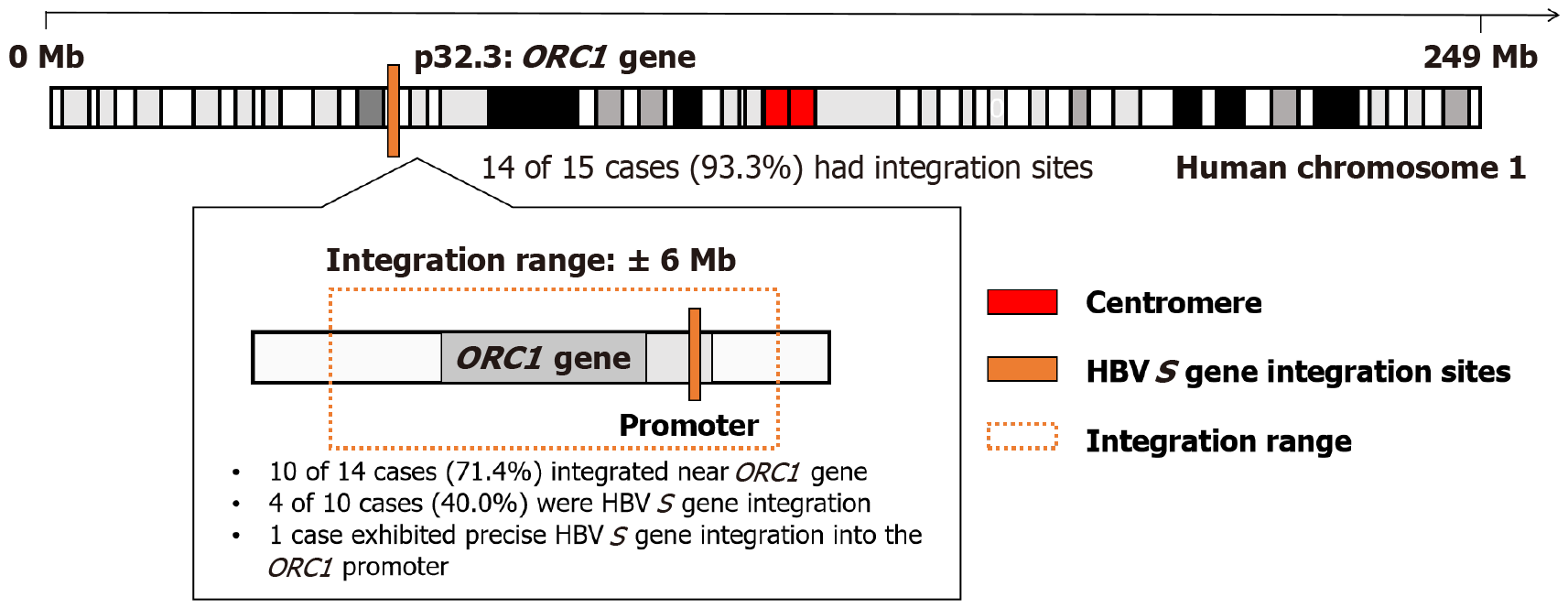
Figure 1 Hepatitis B virus S gene integration cluster near the human origin recognition complex subunit 1 gene locus on chromosome 1 (Chr1 1p32.
3). Genome-wide analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) integration in 15 HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma tumor tissues revealed 14 cases with HBV-human integration. Among these, 10 (71.4%) harbored integration events clustered within a 6 Mb region centered around the origin recognition complex subunit 1 gene (indicated by orange dashed box). A representative case showed HBV S gene integration at the origin recognition complex subunit 1 promoter region. ORC1: Origin recognition complex subunit 1; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
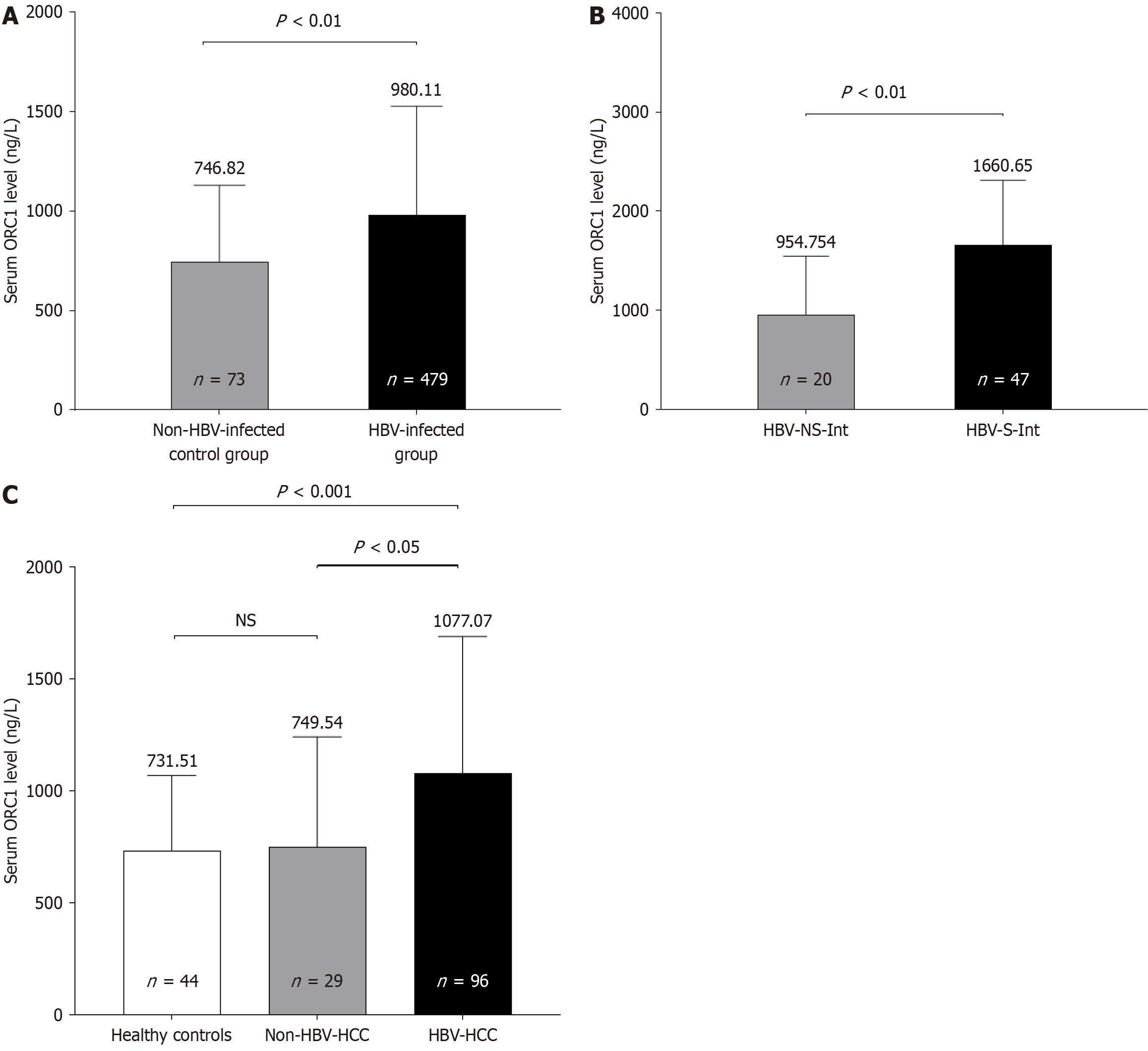
Figure 2 Comparison of serum origin recognition complex subunit 1 levels among study groups assessed by the Mann-Whitney U test.
A: Comparison between hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients (n = 479) and non-HBV-infected controls (n = 73); B: Comparison between HBV S gene integration (n = 20) and HBV non-S gene integration (n = 47) subgroups; C: Comparison between HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 96), non-HBV-hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 29), and healthy controls (n = 44). ORC1: Origin recognition complex subunit 1; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBV-S-Int: HBV S gene integration; HBV-NS-Int: HBV non-S gene integration; HBV-HCC: HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma; NS: Not significant.
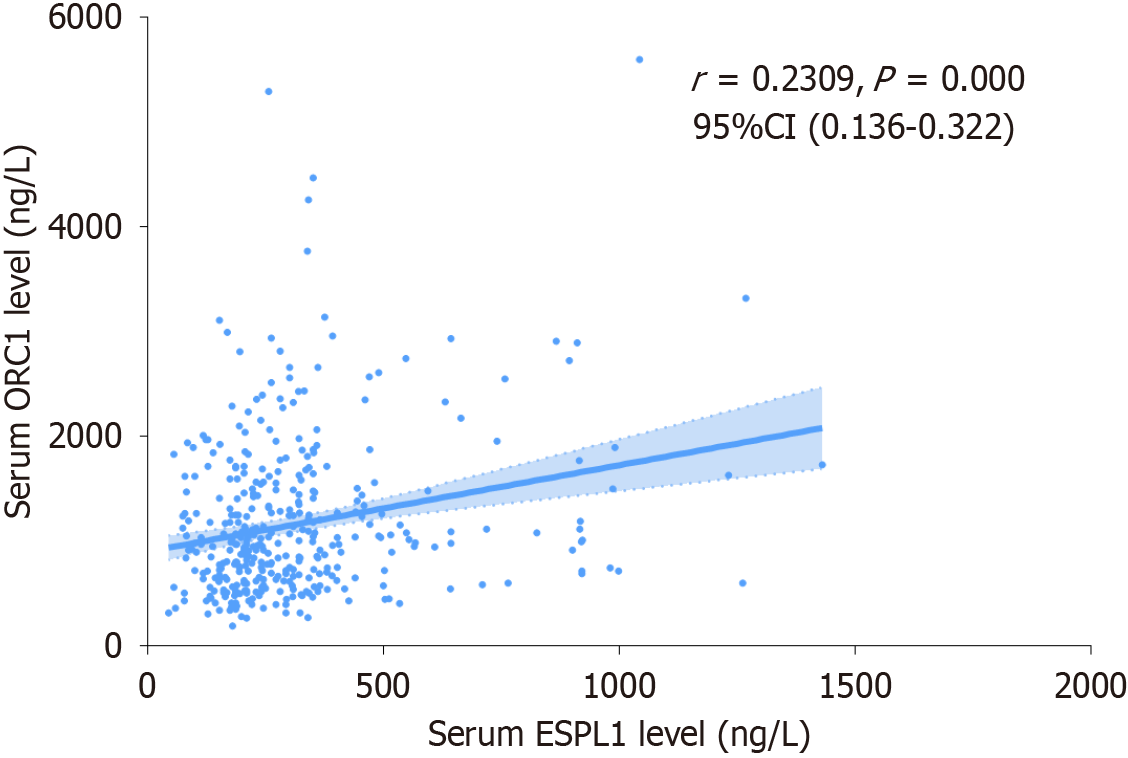
Figure 3 Correlation between serum origin recognition complex subunit 1 and extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 levels in hepatitis B virus-infected patients (n = 400).
A significant positive correlation was observed between serum origin recognition complex subunit 1 and extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 levels, suggesting functional linkage in hepatitis B virus-driven hepatocarcinogenesis. ORC1: Origin recognition complex subunit 1; ESPL1: Extra spindle pole bodies-like 1; CI: Confidence interval.
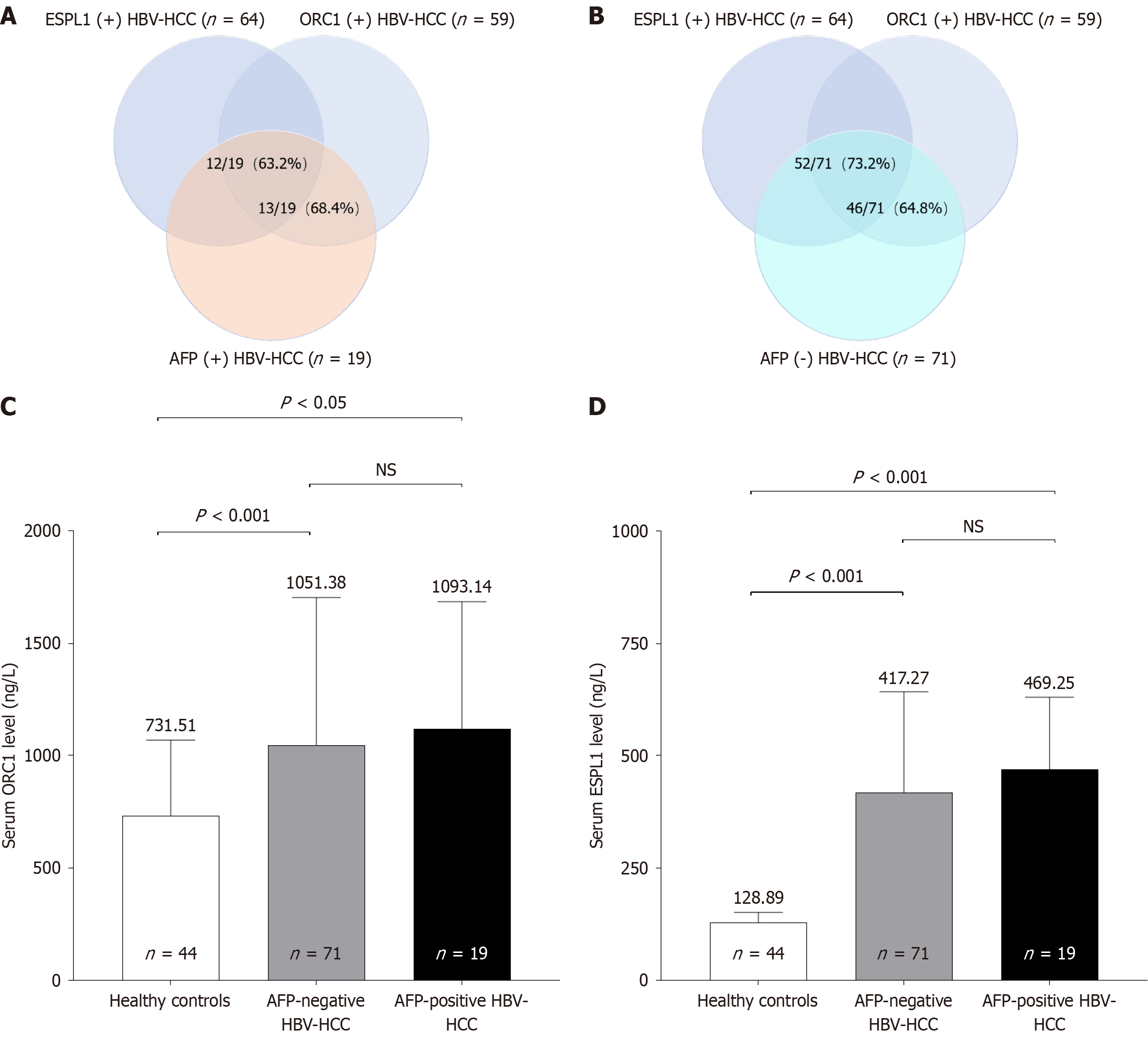
Figure 4 Detection of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma cases by alpha-fetoprotein, origin recognition complex subunit 1, and extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 among alpha-fetoprotein-negative patients.
A: Among 90 hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinomas (HBV-HCC) cases, 71 (78.9%) were alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)-negative; B: Among these AFP-negative cases, serum extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 and origin recognition complex subunit 1 identified 52 (73.2%) and 46 (64.8%) cases, respectively; C: Serum origin recognition complex subunit 1 levels were significantly elevated in both AFP-negative and AFP-positive HBV-HCC patients compared to healthy controls (P < 0.05); D: Serum extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 levels were significantly higher in AFP-negative and AFP-positive HBV-HCC patients than in healthy controls (P < 0.001). ESPL1: Extra spindle pole bodies-like 1; HBV-HCC: Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma; ORC1: Origin recognition complex subunit 1; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; NS: Not significant.
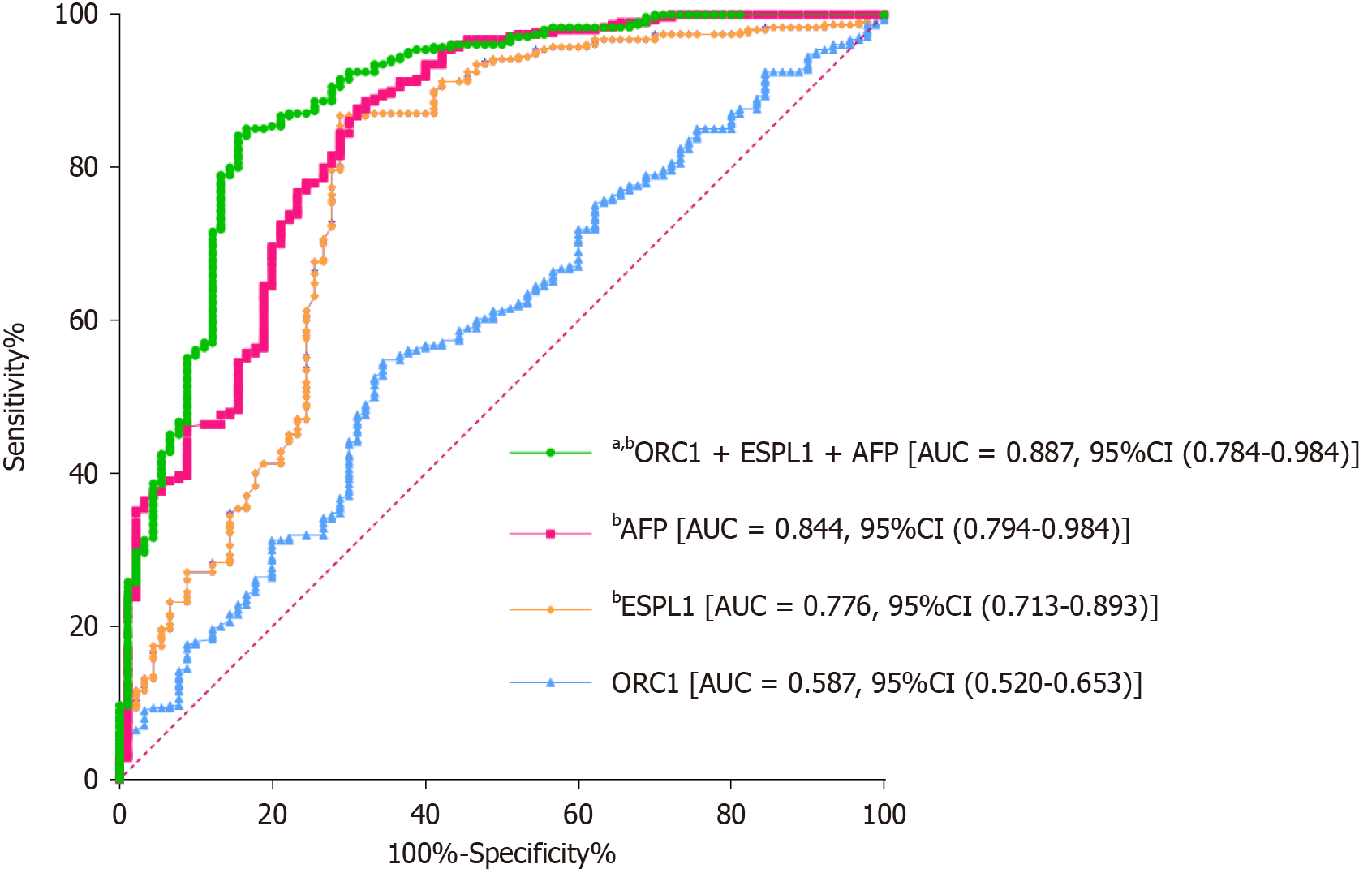
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for serum biomarkers in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular diagnosis.
aP < 0.05 vs ESPL1; bP < 0.05 vs ORC1. ORC1: Origin recognition complex subunit 1; ESPL1: Extra spindle pole bodies-like 1; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CI: Confidence interval.
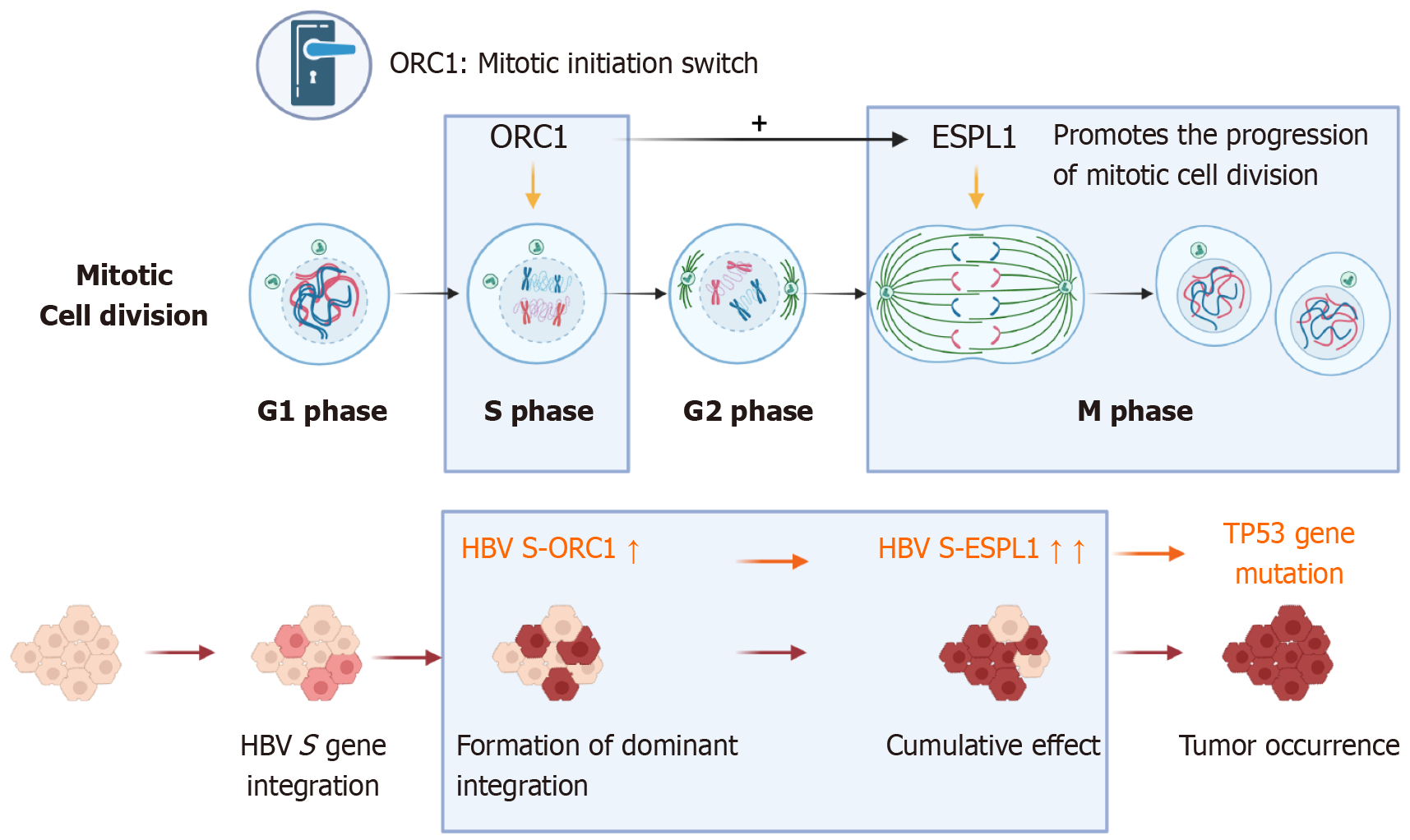
Figure 6 Schematic model illustrating the molecular mechanism and diagnostic workflow of hepatitis B virus integration near origin recognition complex subunit 1 and extra spindle pole bodies-like 1.
The hepatitis B virus S gene integrates near the origin recognition complex subunit 1 and extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 loci, promoting their overexpression. These genes may be co-regulated in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Since origin recognition complex subunit 1 controls the S phase while extra spindle pole bodies-like 1 regulates the M phase, their concurrent dysregulation could drive aberrant cell cycle progression, leading to hepatocyte aneuploidy and malignant transformation. ORC1: Origin recognition complex subunit 1; ESPL1: Extra spindle pole bodies-like 1; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Feng YF, Su TM, Hu BB, Wang H, Li QM, Yin QB, Huang L, Liang HQ, Ren AL, Su MH, Jiang JN. Diagnostic performance of serum origin recognition complex subunit 1 protein for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(44): 112481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i44/112481.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i44.112481