Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2021; 27(7): 592-608
Published online Feb 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.592
Published online Feb 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.592
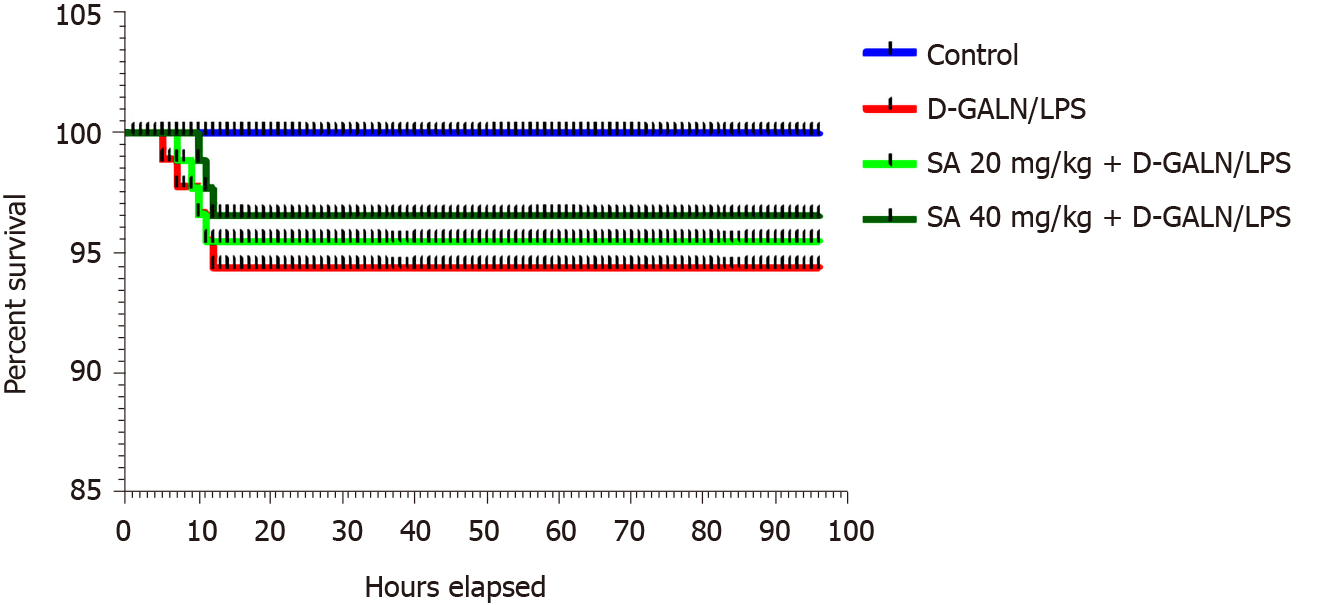
Figure 1 Effect of sinapic acid (20 and 40 mg/kg bodyweight) pretreatment on the survival rate of D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure.
SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide.
Figure 2 Effect of sinapic acid pretreatment on oxidative stress markers in hepatic tissue of D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure.
The results are presented as mean ± SE with six animals per group. aDenotes significant differences compared to the control group (P < 0.05); bDenotes significant differences compared to the D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide group (P < 0.05). MDA: Malondialdehyde; SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide.
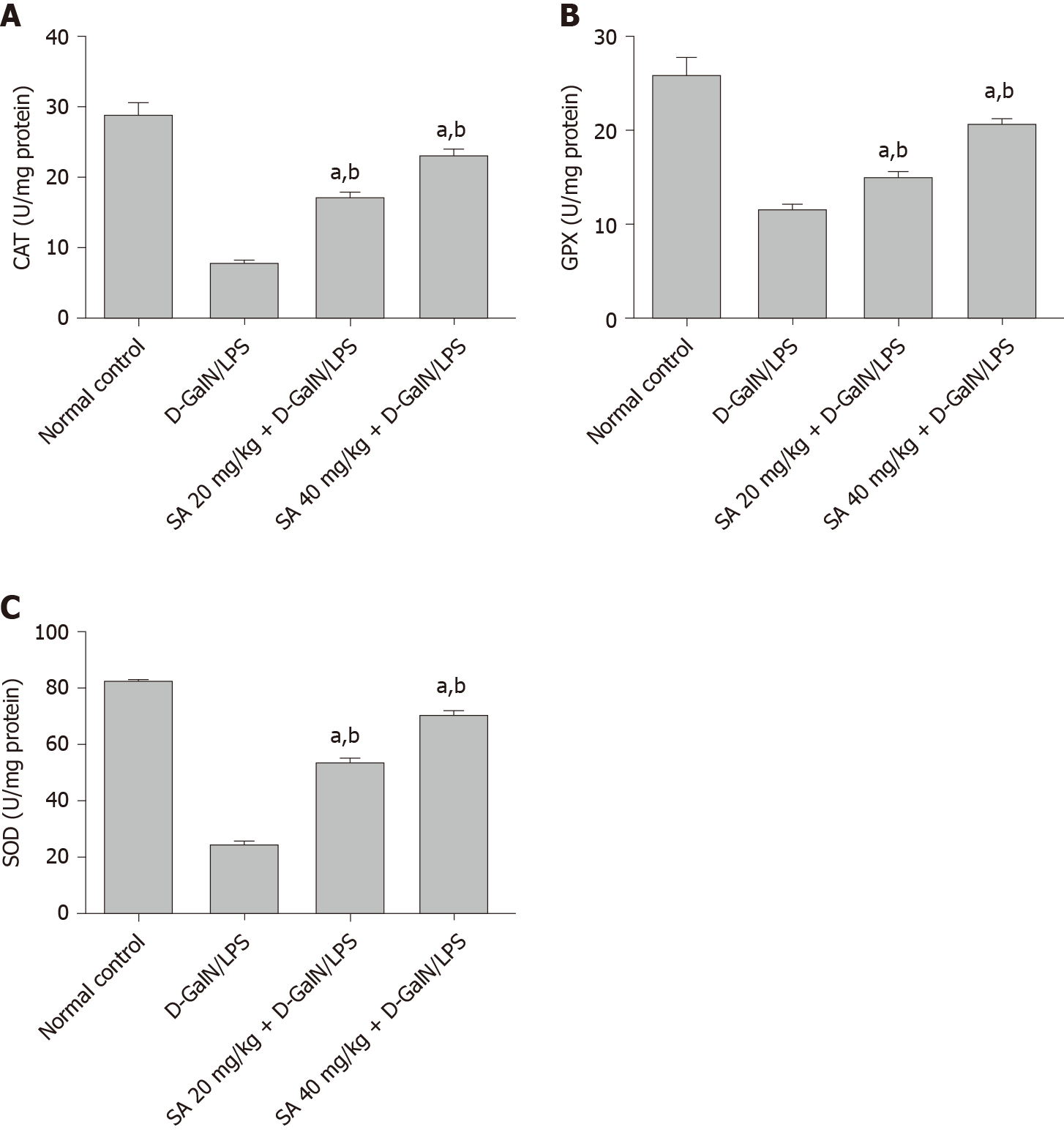
Figure 3 Effect of sinapic acid pretreatment on antioxidant enzyme activity in hepatic tissue from D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure rats.
The results are presented as mean ± SE with six animals per group. aDenotes significant differences compared to the control group (P < 0.05); bdenotes significant differences compared to the D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide group (P < 0.05). CAT: Catalase; SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide.
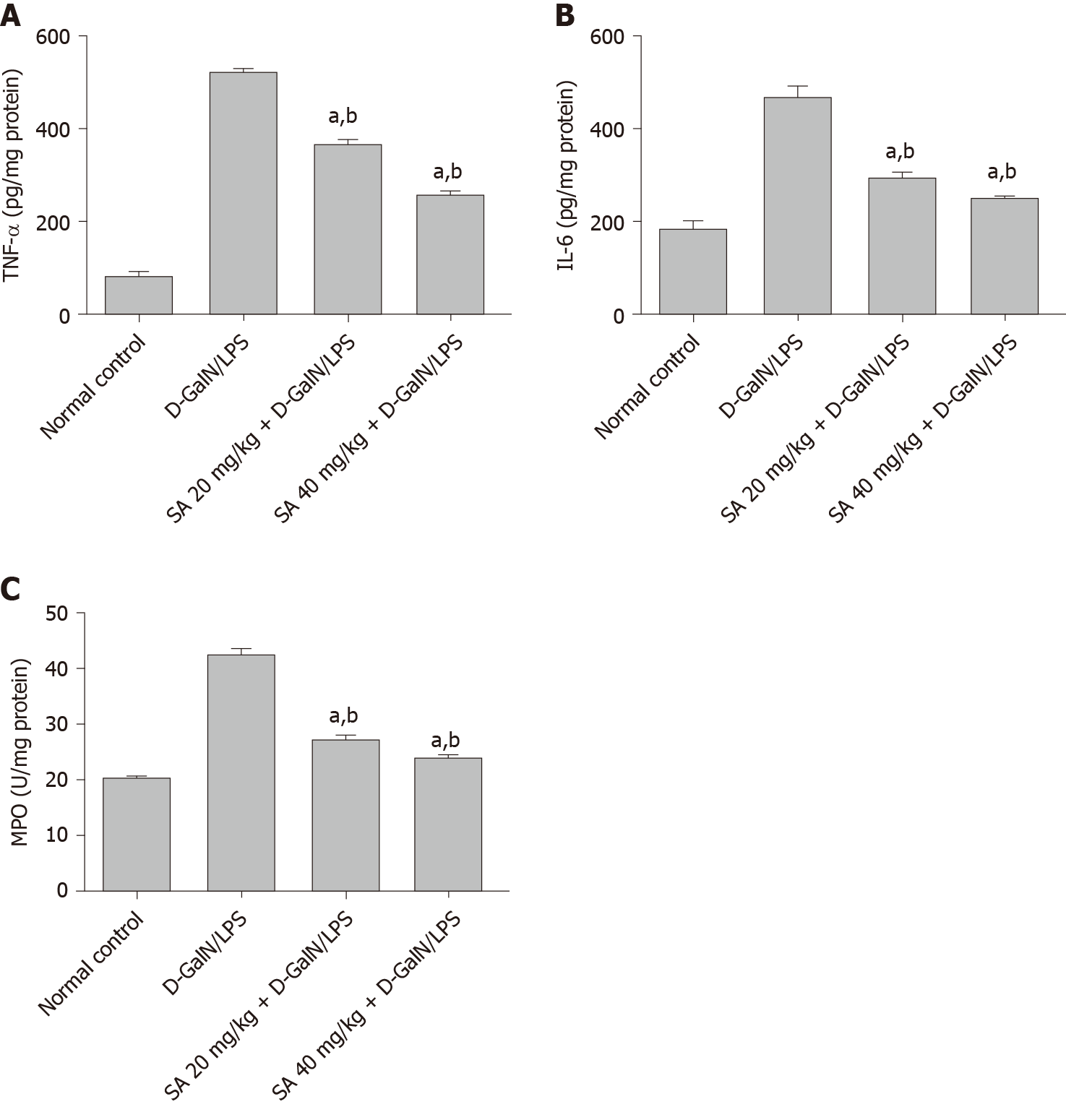
Figure 4 Effect of sinapic acid pretreatment on cytokines and inflammatory markers in hepatic tissue of D-galactosamine /lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure.
The results are presented as mean ± SE with six animals per group. aDenotes significant differences compared to the control group (P < 0.05); bdenotes significant differences compared to the D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide group (P < 0.05). TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin 6; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide.
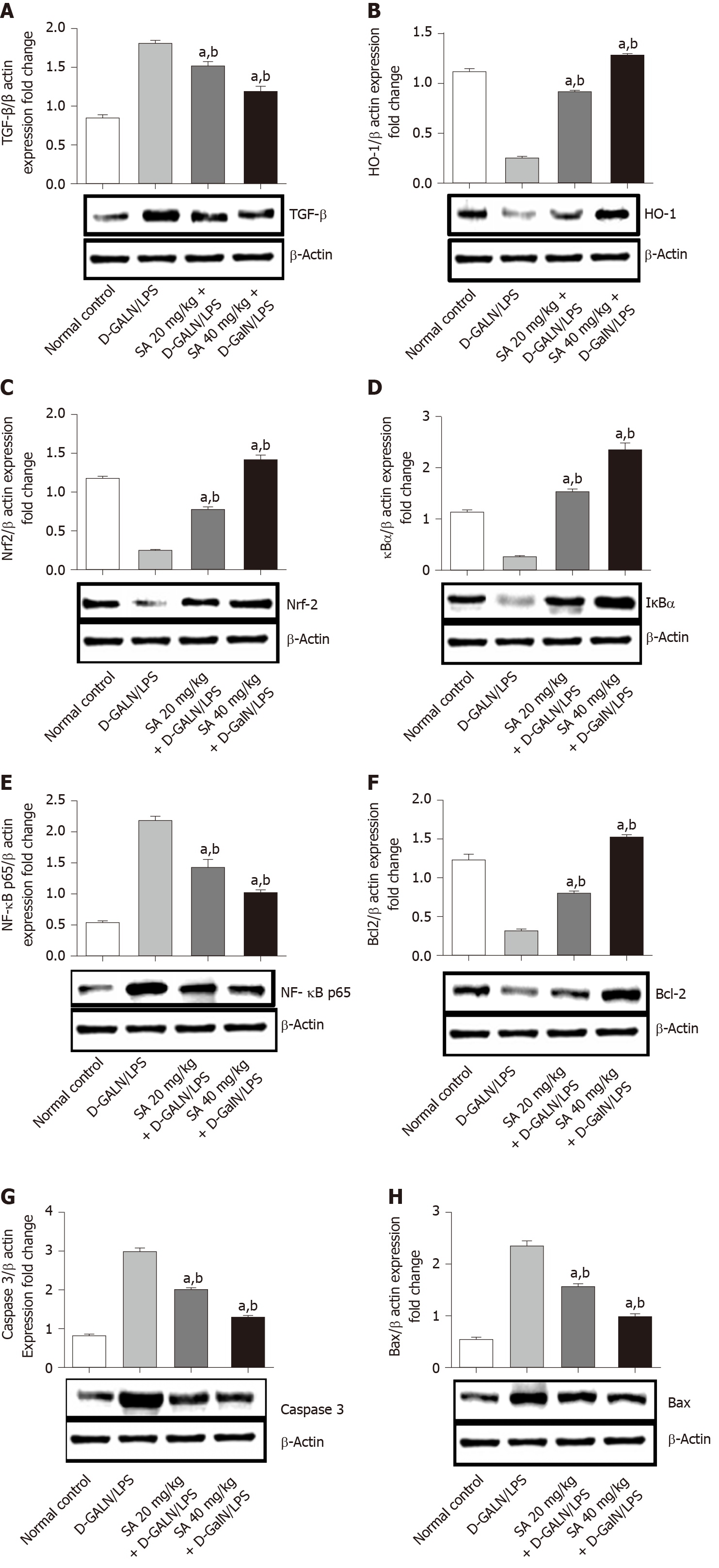
Figure 5 Sinapic acid downregulates nuclear factor kappa B in acute liver failure.
A-H: Effect of sinapic acid on the protein expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (A), heme oxygenase-1 (B), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (C), nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha protein (D), nuclear factor kappa B (E), anti-apoptotic protein BCl2 (F), caspase 3 (G), and Bax in D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide (D-GalN/LPS)-induced acute liver failure (ALF) (H). The results are presented as the mean ± SE of six animals per group. aDenotes significant differences to the D-GalN/LPS-induced ALF group (P < 0.05); bdenotes significant differences compared to the normal control. TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; IkBα: Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha; NF-κb: Nuclear factor kappa B; SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide.
Figure 6 Light photomicrographs of hepatic tissues.
Hematoxylin and eosin stains, magnification 100 ×. A: Hepatic section of normal control rat exhibits normal architecture of hepatic cord of cells; B: Hepatic section of D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide (D-GalN/LPS) treated rats exhibiting massive fatty changes, focal central vein congestion, ballooning formation, necrosis with inflammation, and loss of cellular boundaries, massive cellular infiltration; C: Hepatic section of rats treated D-GalN/LPS and 20 mg/kg of sinapic acid (SA) showing mild central vein congestion, mild fatty changes, ballooning, necrosis with sinusoidal dilatation, mild cellular infiltration; D: Hepatic section of rats treated D-GalN/LPS and 40 mg/kg of SA exhibiting the absence of ballooning, inflammatory cells, and regeneration of hepatocytes around central vein toward near-normal liver architecture but slight congestion in the central vein.
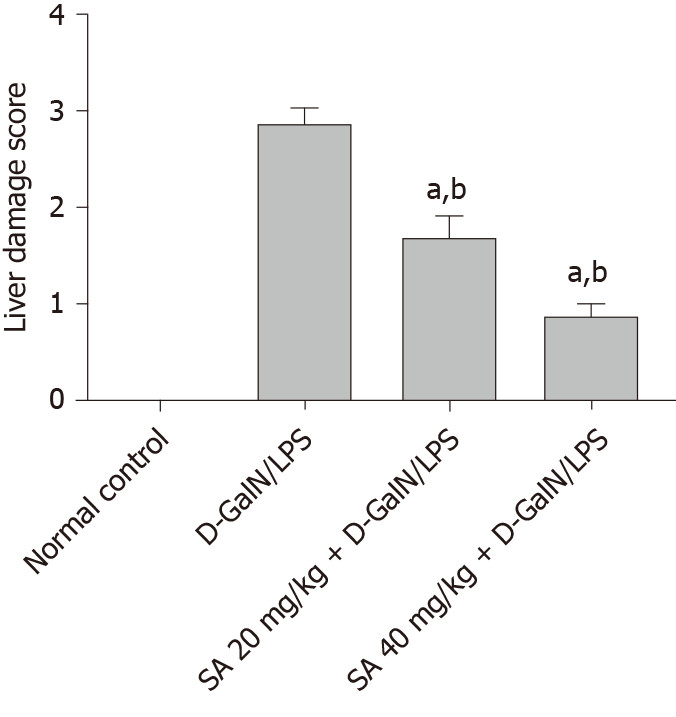
Figure 7 The liver damage score was examned using four-point scale from 0 to 3.
0, l, 2, and 3 represent no damage, mild damage, moderate damage, and very severe damage, scoring system in 20 random fields at 400 × magnification per animal (n = 6 per group). aDenotes significant differences compared to the control group (P < 0.05); cDenotes significant differences compared to the D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide group (P < 0.05). SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide.
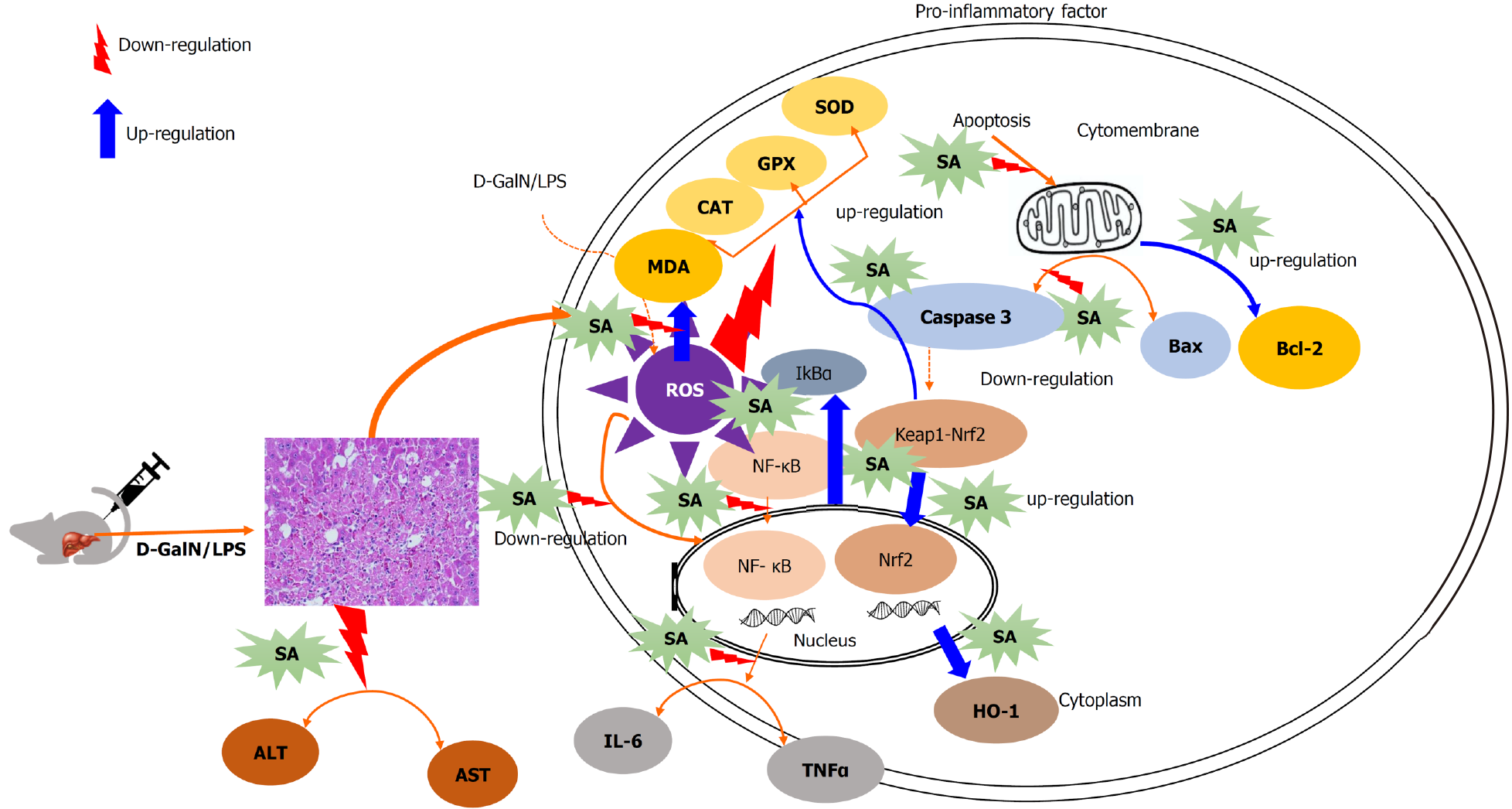
Figure 8 Graphical abstract.
SA: Sinapic acid; D-GalN/LPS: D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: Interleukin 6; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; IkBα: Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha; NF-κb: Nuclear factor kappa B; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; CAT: Catalase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase.
- Citation: Ansari MA, Raish M, Bin Jardan YA, Ahmad A, Shahid M, Ahmad SF, Haq N, Khan MR, Bakheet SA. Sinapic acid ameliorates D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatitis in rats: Role of nuclear factor erythroid-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(7): 592-608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i7/592.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i7.592