Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6935
Peer-review started: May 6, 2021
First decision: June 6, 2021
Revised: June 7, 2021
Accepted: June 22, 2021
Article in press: June 22, 2021
Published online: August 16, 2021
Processing time: 91 Days and 9 Hours
Paragangliomas (PGLs) are rare catecholamine-secreting neuroendocrine tumors, which often present with secondary hypertension. The most common location is the retroperitoneal space. For the first time, we report a rare case of large retroperitoneal compound PGL, and we have innovatively applied a new surgical plan to completely remove the tumor.
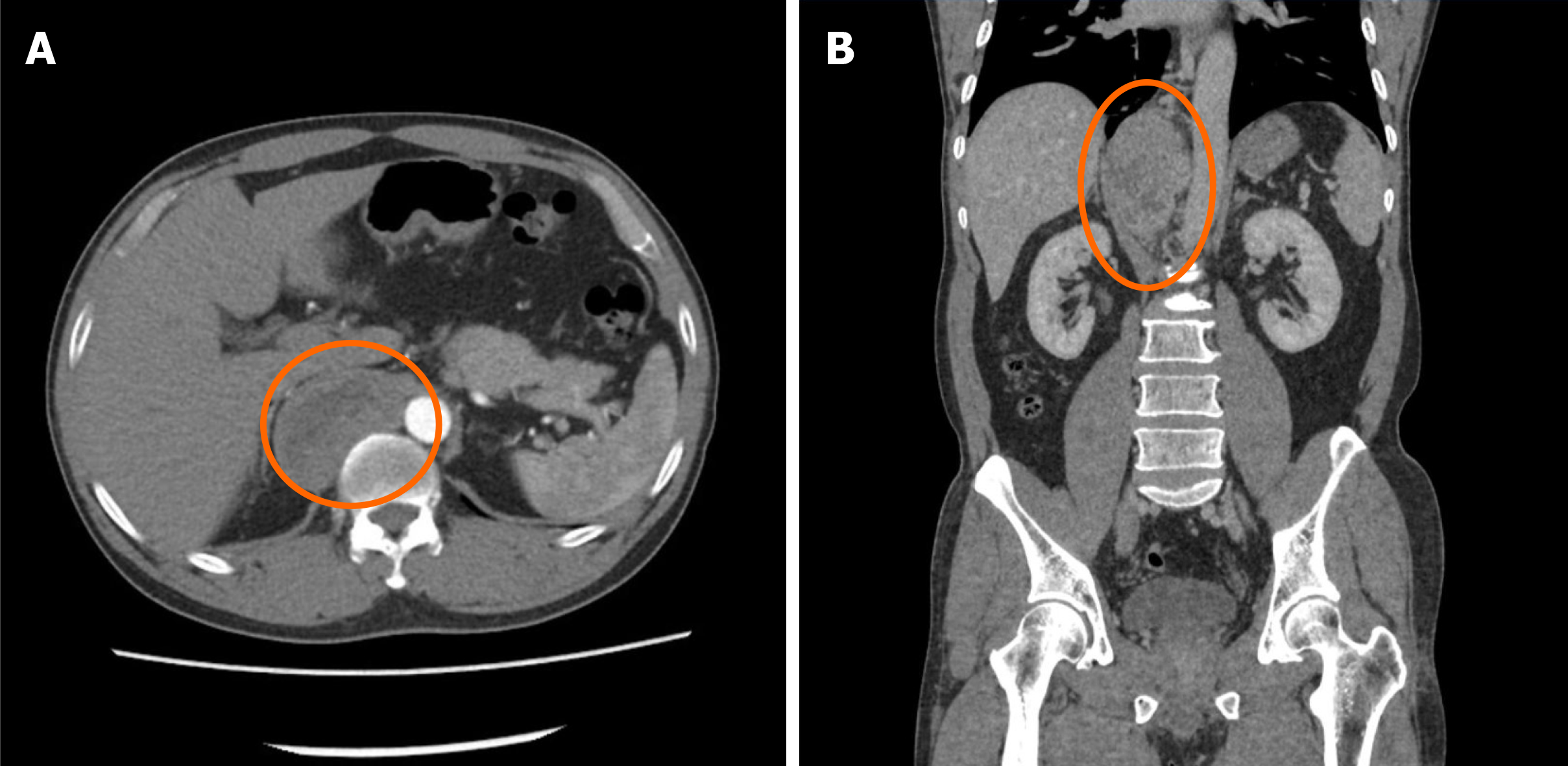
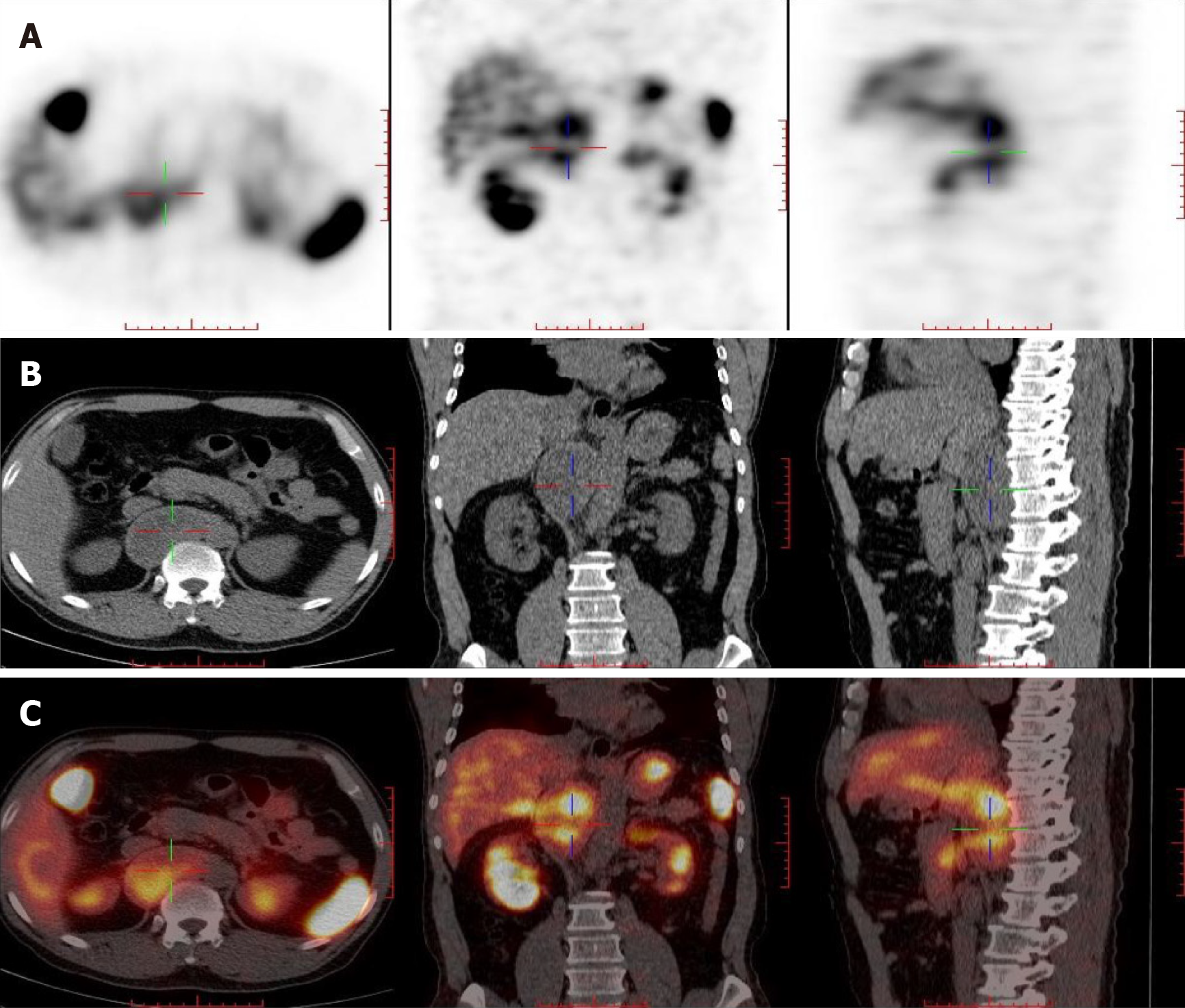
A 55-year-old middle-aged man was admitted to the hospital for fluctuating blood pressure for more than 1 year with intermittent headache. He suffered dozens of attacks every day. Blood and urine catecholamines were elevated, somatostatin receptor imaging was positive, and the diagnosis of PGL was clear. The imaging examination revealed a large tumor on the right front of the mediastinal spine at the level of T10-L1 (the posterior space of the right phrenic foot). For the first time in our department, a combined thoracoscopic and laparoscopic operation was used to detect and remove large tumors.
This is the first reported case of using a thoracoscopic and laparoscopic approach simultaneously to remove a large retroperitoneal compound PGL, which may provide a new surgical approach for similar cases.
Core Tip: We report a rare case of large retroperitoneal compound paraganglioma (PGL) for the first time, and a combined thoracoscopic and laparoscopic operation was used to detect and remove the large tumor. This is the first reported case of using a thoracoscopic and laparoscopic approach simultaneously to remove a large retroperitoneal compound PGL.
- Citation: Liu C, Wen J, Li HZ, Ji ZG. Combined thoracoscopic and laparoscopic approach to remove a large retroperitoneal compound paraganglioma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(23): 6935-6942
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i23/6935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6935
Paragangliomas (PGLs) are rare catecholamine-secreting neuroendocrine tumors, which often present with secondary hypertension[1,2]. PGLs arise from chromaffin cells at the extra-adrenal sites along the sympathetic and/or parasympathetic chain, and they have an incidence of 15%-20%[1,3]. PGLs can be found at any site in the entire body, from the skull to the pelvic floor, and the majority of these tumors occur in the abdomen. Approximately 10% of the tumors are located in the retroperitoneal space[4]. The most common location is the retroperitoneal space, which accounts for up to 77% of tumors often pictured as a mass around the corpora paraaortic[5,6]. However, PGLs that occur in the posterior space of the phrenic angle and are covered by the psoas muscle are extremely rare. After consulting the literature, we found that no similar reports have been presented earlier.
Surgical resection represents the only available curative treatment for these tumors. The close proximity to major vessels and limited accessibility make it difficult to safely remove a retroperitoneal PGL in the abdomen. The laparoscopic approach has proved to be a safe and effective technique for retroperitoneal tumor resection in experienced hands[7,8]. So far, there has been no report in the literature on a combined thoraco-laparoscopic approach to detect and remove a PGL.
We herein report a case of combined thoracoscopic and laparoscopic approach to remove a large retroperitoneal compound PGL.
A 55-year-old middle-aged man was admitted to the hospital due to hypertension for more than 1 year.
The blood pressure fluctuated between 220-230/120-130 mmHg. It was relieved when standing in a different position, accompanied by intermittent headaches, which could relieve itself in more than 10 min, and the patient experienced dozens of attacks every day. The general condition was good, and he had no other symptoms.
The patient had a free previous medical history.
The patient had no personal and family history.
Physical examination revealed no obvious positive signs.
Laboratory examination showed elevated blood levels of meta-norepinephrine (10.76 nmo1/L) and metanephrine (3.39 nmo1/L), and 24 h urine catecholamine levels were as follows: Dopamine 341.68 μg/24 h (elevated), norepinephrine 37.03 μg/24 h, and epinephrine 4.58 μg/24 h.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) + three-dimensional (3D) re
The final diagnosis of the presented case was PGL.
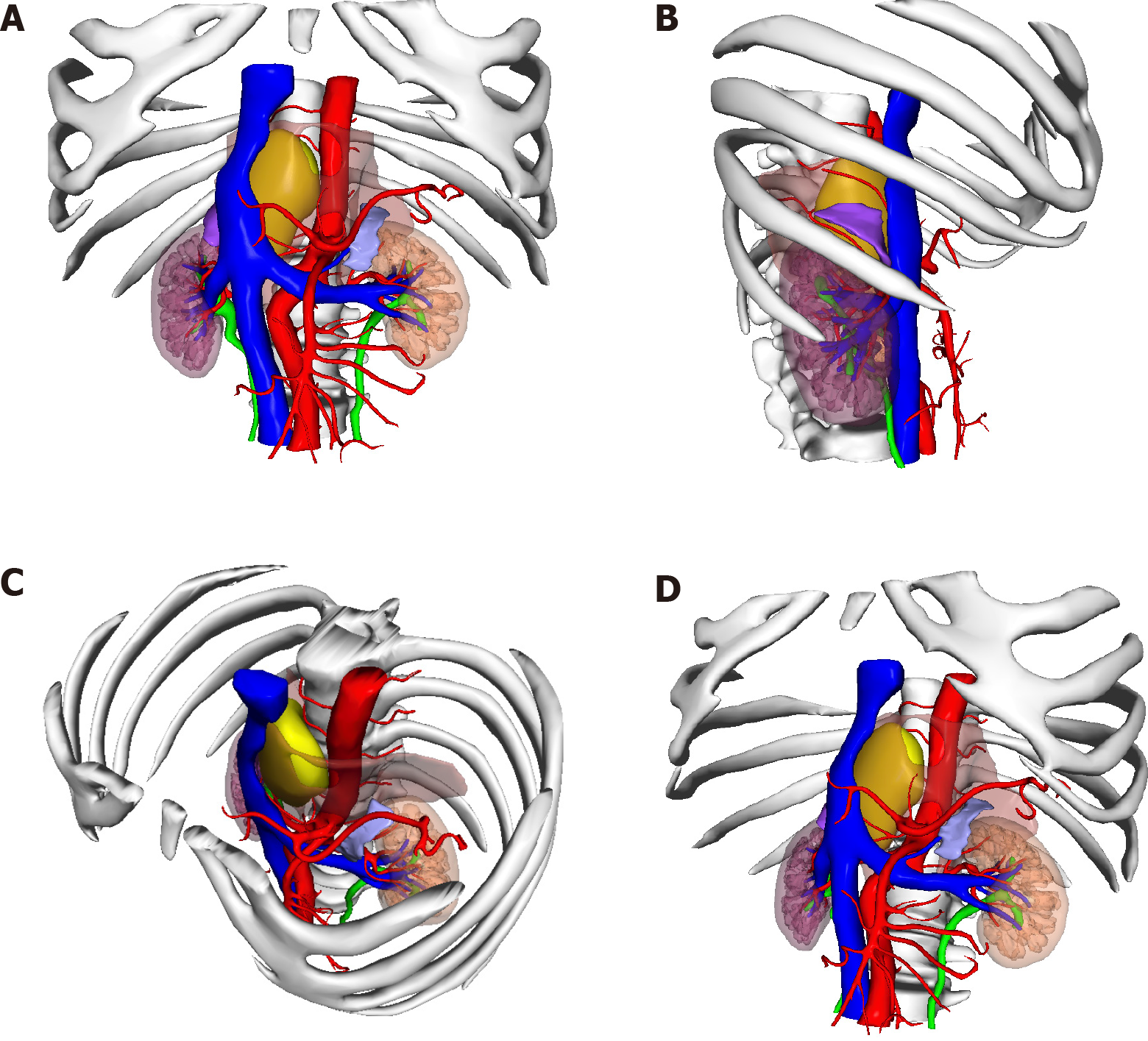
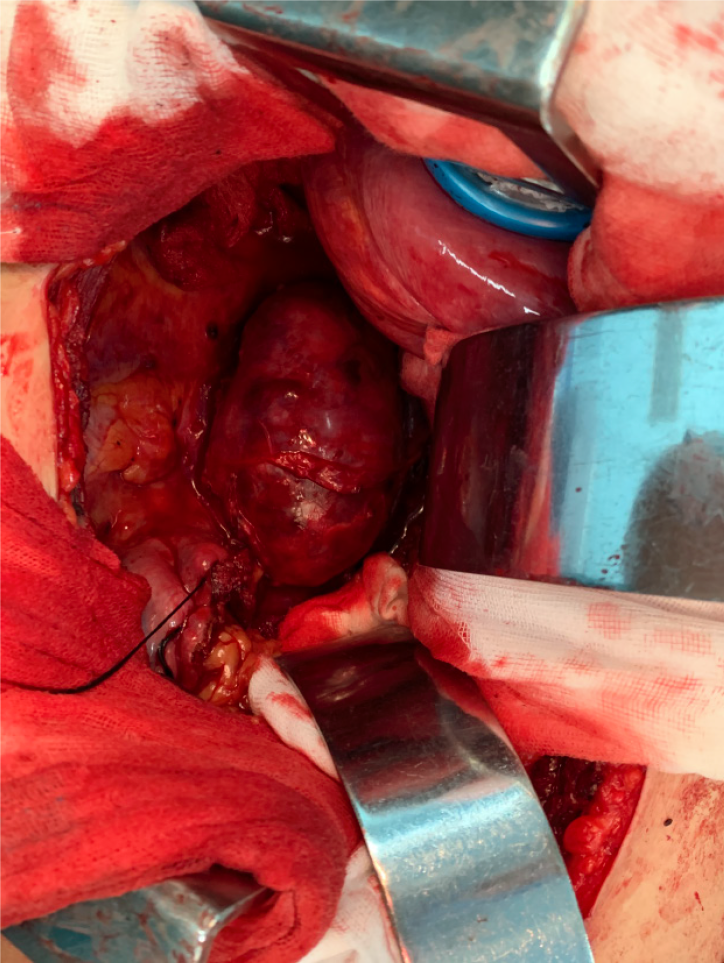
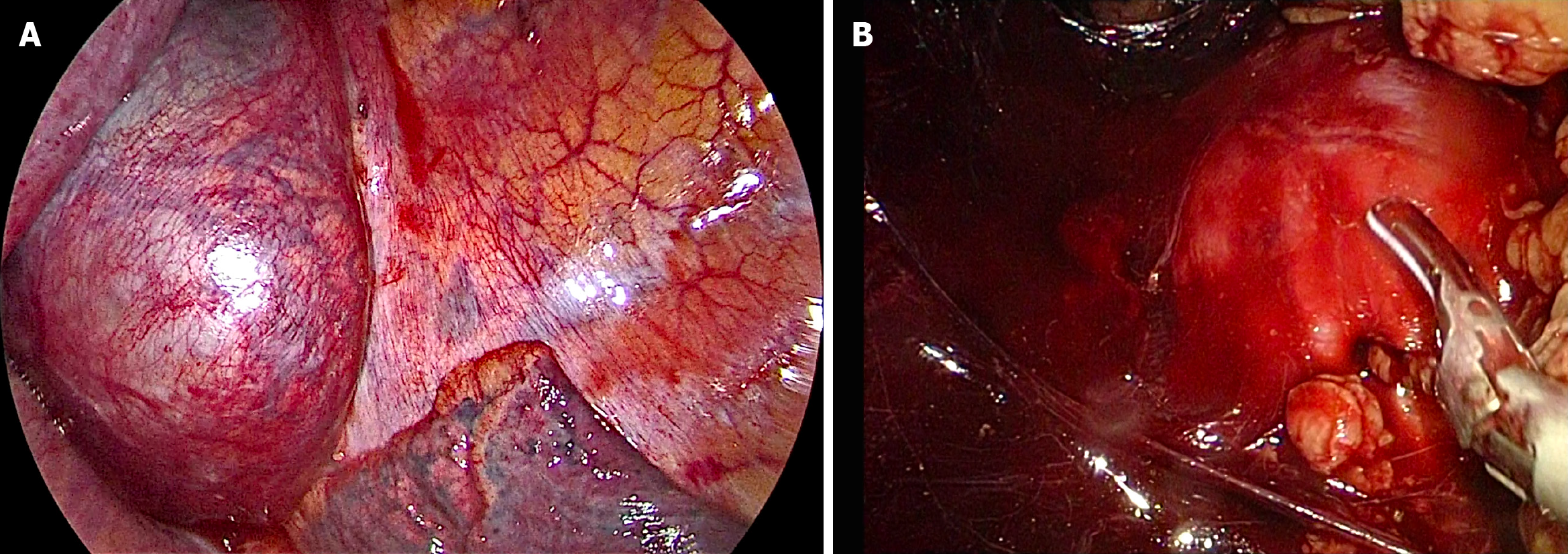
After consultations with liver surgery, vascular surgery, orthopedics, thoracic surgery, anesthesiology, and intensive care unit departments, our department and thoracic surgeons formulated a special surgical plan for this case: Thoracoscopic- and laparoscopic-assisted resection of the right retroperitoneal PGL. A double-lumen cannula was used for anesthesia. The patient was placed in the left side lying position, the lumbar bridge was raised, and a total of seven laparoscopic ports were created through the posterior abdominal cavity and thoracic cavity. The laparoscopic puncture holes were as follows: (1) The mid-axillary line 3 cm above the iliac crest; (2) The front axillary line ribs submarginal; (3) Posterior axillary line under the costal margin; and (4) Between (1) and (2). The thoracoscopic puncture holes were as follows: (1) The seventh intercostal space of the anterior axillary line; (2) The eighth intercostal space of the posterior axillary line; and (3) The mid-axillary line ninth in the intercostal area. During laparoscopic surgery, the psoas major muscle of the right phrenic angle was locally uplifted, with a range of about 5 cm × 4 cm. The size of the thoracic cavity was about 3 cm × 4 cm, a large number of tortuous blood vessels could be seen on the surface of the tumor, the capsule was complete, and the tension was high. A thoracoscope and laparoscope were used simultaneously, and the blunt and sharp combination separated the tumor from the posterior chest wall, diaphragm, and psoas muscle along the surface of the tumor. It was seen that the inside of the tumor adhered tightly to the adjacent parts of the vertebral body and inferior vena cava, and multiple bundles of blood vessels penetrated the tumor from the pleural wall and paravertebral body. Much blood was oozing into the surgical field. Between the ninth to twelfth ribs, a combined thoracic-abdominal arc-shaped incision was made, and the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and muscle layers were cut sequentially. The ninth rib was broken, and the diaphragm was cut longitudinally. It could be seen that the tumor and the surrounding tissues adhered extremely, and the ninth, tenth, and eleventh left intercostal arteries passed through the tumor. Then, the tumor supplying blood vessels were separated by the thoracic surgeon one by one, ligated, and sutured (Figure 4). Attention was paid to the protection of adjacent organs and important blood vessels and nerves, and gradually, the tumor and the posterior phrenic angle tissue in the affected right diaphragm were separated and the tumor completely removed (Figure 5). Completeness of the specimen envelope was checked. The wound was rinsed with warm distilled water to fully stop bleeding. The stump of the posterior inner diaphragm was fixed to the posterior mediastinal pleura and intercostal muscles with 1-0 braided thread to reconstruct the diaphragm foot. The ninth rib was fixed end to end to completely close the diaphragm and isolate the thoracic and abdominal cavities. The thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity were drained, and the incision was closed layer by layer. The entire operation time was 310 min, and the blood loss during the operation was about 1100 mL. The patient recovered well after the operation without any serious complications and was discharged 10 d after the operation.
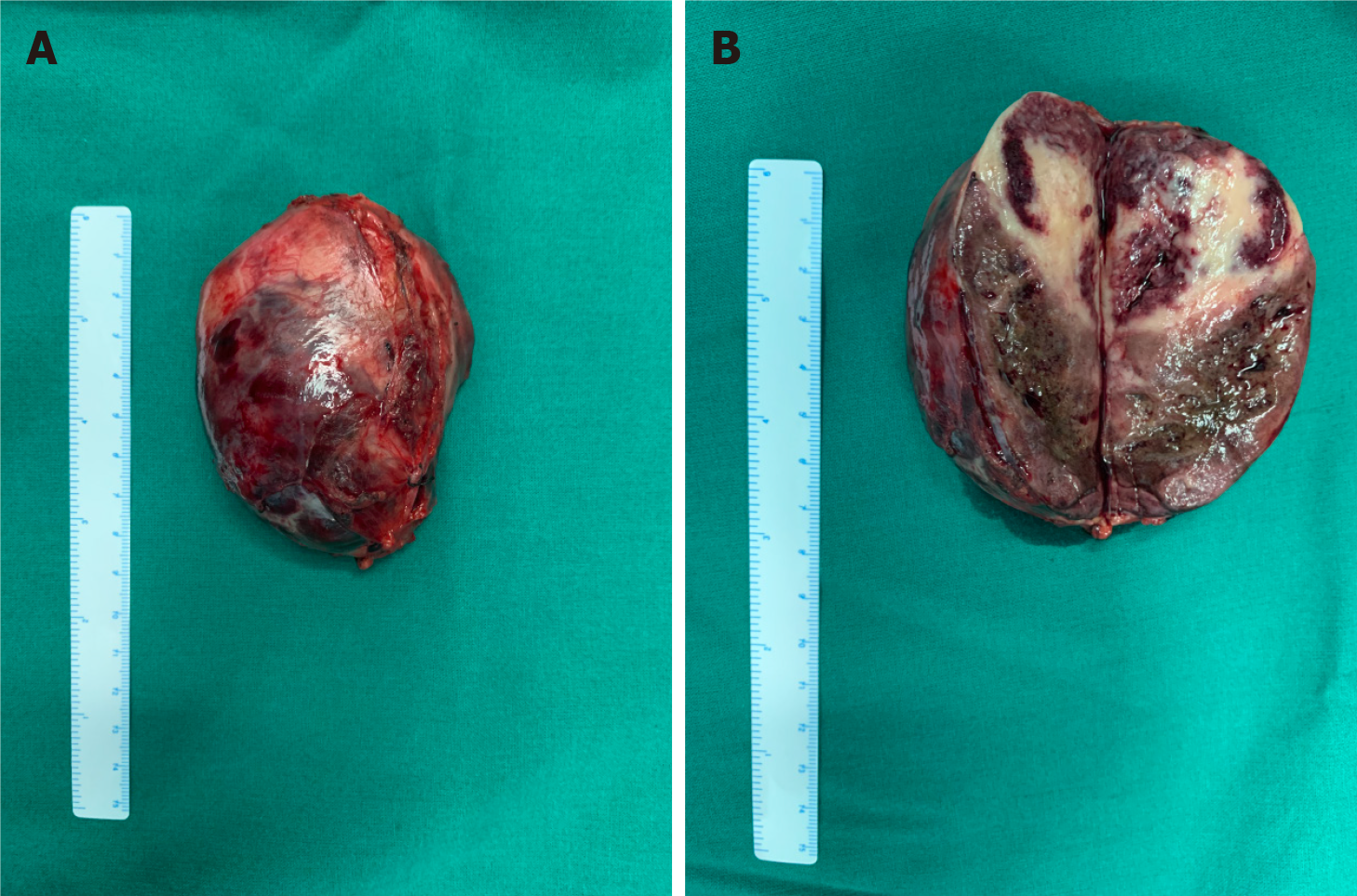
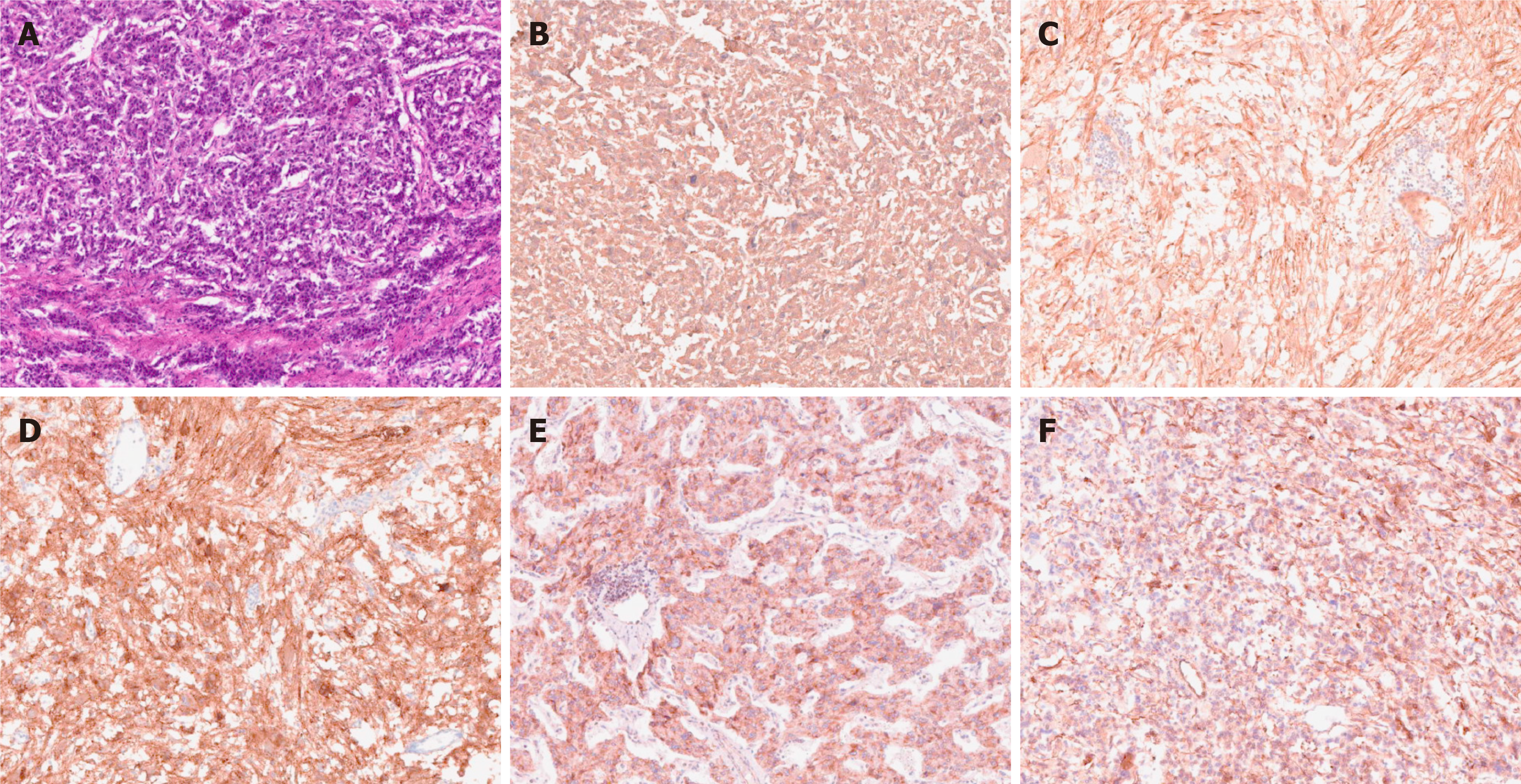
The postoperative pathological diagnosis was compound paraganglioma (paraganglioma, ganglion cell neurofibroma, and a few ganglion cell neuroblastoma components). Immunohistochemical results were as follows: Melanoma antigen (-), cytokeratin [CK (AE1/AE3)] (-), chromogranin A (+), antigen Ki-67 (index 1%), soluble protein-100 (+), α-inhibin (-), synaptophysin (+), succinate dehydrogenase B (+), neuron-specific nuclear protein (-), SOX gene family member 10 (-), neuron specific enolase (+), and nuclear factor (-) (Figure 6).
The patient was followed for 6 mo after the operation, and his general condition was good, his blood pressure returned to normal, there were no complications, and his normal life had been restored.
This unique case presented multiple challenges to surgical treatment. PGL most commonly occurs in the sympathetic or parasympathetic nerve chain, and only 10% of these tumors occur in the retroperitoneum. The postoperative pathological diagnosis of this patient was a compound PGL, including PGL and ganglion cells neuro
Surgical resection is the first choice for the treatment of PGL, and laparoscopic resection is often suitable for smaller (< 7 cm) tumors[9,10]. In recent years, laparoscopic techniques have been used to successfully remove large retroperitoneal tumors one after another[11-13]. How to design the surgical plan was another great challenge in this case. The tumor grew on the right side of the abdominal aorta at the level of the T10-L1 vertebral body and was located behind the inferior vena cava. Compared with most PGLs, this tumor was located higher, with a maximum length of 10 cm, and it spanned the thoracic cavity and abdomen. The tumor could not be completely removed with a thoracoscope or laparoscope alone. It was close to the spinal nerves, large blood vessels, and liver, and the blood supply was extremely rich.
How to completely remove this large PGL without damaging the spinal nerves and causing paralysis, and avoiding massive bleeding is the focus of our surgery. By combining the successful experience of laparoscopic technology, our department innovatively designed the surgical method: Thoracoscopic and laparoscopic assisted resection of a right retroperitoneal PGL. According to a review of the literature, this is the first time that the thoracoscopic and laparoscopic techniques have been used simultaneously to remove large retroperitoneal tumors. After several case discussions between our department and thoracic surgeons, it was finally decided to adopt the left side decubitus position to obtain the most adequate operating space. During the operation, two sets of endoscopic instruments were used, and they were placed in two different directions. The thoracic surgeon and our surgeon stood, respectively, on the left and right sides of the patient to perform the operation. At the same time, the large tumor was explored and freed from the head and tail ends. With the diaphragm as the boundary in the middle, the two operating spaces were independent (Figure 7). During the operation, the inner side of the tumor was adherent closely to the adjacent parts of the vertebral body and inferior vena cava. It was seen that the blood supply of the tumor was very rich, and the surgical field showed more bleeding. Thus, the operation was converted to open surgery, and the diaphragm was cut longitudinally and gradually separated until the tumor was completely removed. Because the tumor is too large, in the peeling process thoracoscopy or laparoscopy cannot reveal the back of the tumor very well, if adhering to use this combination surgery method, it will greatly prolong the operation time, resulting in unnecessary large amounts of blood loss, so we consider that open surgery could have been safer, better, and lesser time consuming in such a vascular and adherent tumor, compared to the attempts to remove the tumor through thoracoscopic and laparoscopic approaches.
In short, so far, this is the first reported case of a large compound PGL in the posterior space of the right phrenic foot and wrapped by the psoas muscle. It is also the first case in which thoraco-laparoscopic combined exploration was used to remove the tumor. A clear diagnosis, a detailed surgical plan, adequate drug preparation, and satisfactory cooperation among multiple departments are necessary conditions for successful surgery. This case report may provide a new surgical approach for similar cases in the future.
| 1. | Silva I, Santos MJ, Cardoso R, Carvalho S, Vilaça V, Vasconcelos M. Retroperitoneal Paraganglioma - a rare cause of arterial hypertension. Galicia Clin. 2017;78:38-41. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Pappachan JM, Tun NN, Arunagirinathan G, Sodi R, Hanna FWF. Pheochromocytomas and Hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018;20:3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Lam AK. Update on Adrenal Tumours in 2017 World Health Organization (WHO) of Endocrine Tumours. Endocr Pathol. 2017;28:213-227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 350] [Cited by in RCA: 316] [Article Influence: 35.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Erickson D, Kudva YC, Ebersold MJ, Thompson GB, Grant CS, van Heerden JA, Young WF Jr. Benign paragangliomas: clinical presentation and treatment outcomes in 236 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5210-5216. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 302] [Cited by in RCA: 329] [Article Influence: 13.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Vikas V, Ahmed Z, Singh O, Pal SS, Songra MC. Primary Retroperitoneal Inter-aorto-Caval Paraganglioma of the Organ of Zuckerkandl. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:ND06-ND07. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Purnell S, Sidana A, Maruf M, Grant C, Agarwal PK. Genitourinary paraganglioma: Demographic, pathologic, and clinical characteristics in the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database (2000-2012). Urol Oncol. 2017;35:457.e9-457.e14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Abe T, Sazawa A, Harabayashi T, Oishi Y, Miyajima N, Tsuchiya K, Maruyama S, Okada H, Shinohara N. Laparoscopic resection of paraaortic/paracaval neurogenic tumors: surgical outcomes and technical tips. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:4640-4645. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Ping W, HongZhou M, Jie Q, TaiLe J, Hao P, Dan X, Jun C, Shuo W. Laparoscopic Resection of Retroperitoneal Paragangliomas: A Comparison with Conventional Open Surgical Procedures. J Endourol. 2016;30:69-74. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Barfield R, Hill DA, Hoffer FA, Tekautz T, Spunt SL. Retroperitoneal paraganglioma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002;39:120-124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Edström Elder E, Hjelm Skog AL, Höög A, Hamberger B. The management of benign and malignant pheochromocytoma and abdominal paraganglioma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003;29:278-283. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Radfar MH, Shakiba B, Afyouni A, Hoshyar H. Laparoscopic management of paraganglioma in a pregnant woman: a case report. Int Braz J Urol. 2018;44:1032-1035. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Ren X, Shang J, Ren R, Zhang H, Yao X. Laparoscopic resection of a large clinically silent paraganglioma at the organ of Zuckerkandl: a rare case report and review of the literature. BMC Urol. 2020;20:156. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Chung HS, Kim MS, Yu HS, Hwang EC, Kim SO, Oh KJ, Jung SI, Kang TW, Park K, Kwon DD. Laparoscopic adrenalectomy using the lateral retroperitoneal approach: Is it a safe and feasible treatment option for pheochromocytomas larger than 6 cm? Int J Urol. 2018;25:414-419. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Urology and nephrology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Marickar F S-Editor: Wu YXJ L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Wang LYT