Published online Feb 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i2.191
Peer-review started: July 28, 2014
First decision: September 28, 2014
Revised: November 4, 2014
Accepted: November 17, 2014
Article in press: November 19, 2014
Published online: February 16, 2015
Processing time: 192 Days and 6.1 Hours
We report the successful use of RADPLAT to treat a patient with an unresectable T4N0 sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. This patient received 4 cycles of weekly intra-arterial cisplatin together with thiosulfate infusion with concurrent radiation therapy. Radiation therapy was given in 28 daily fractions to 54 Gy using intensity-modulated radiation therapy followed by a hypofractionated stereotactic boost of 3 fractions to 13 Gy to a total dose of 67 Gy in 31 fractions to the nasal sinus and bilateral neck. Intra-arterial cisplatin was administered using a bilateral approach due to the midline site of this tumor. Within days of the first intra-arterial cisplatin, there was an obvious decrease in tumor size. She has been followed with magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography, and remains disease-free 47 mo post-treatment. Centers with expertise in intra-arterial chemotherapy could consider the RADPLAT approach for patients with unresectable sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma.
Core tip: Our patient with unresectable sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma has enjoyed nearly 4 years disease-free survival after concurrent intra-arterial cisplatin and radiation.
- Citation: Noticewala SS, Mell LK, Olson SE, Read W. Survival in unresectable sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma treated with concurrent intra-arterial cisplatin and radiation. World J Clin Cases 2015; 3(2): 191-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v3/i2/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v3.i2.191
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC) is a rare and highly aggressive neoplasm of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses[1]. Thus far, there have been less than 200 reported cases of SNUC[2]. SNUC has a poor prognosis and high mortality with one meta-analysis of 167 cases finding that the disease-free survival was only 26.3%[2]. Currently, there is not a standard treatment of care for SNUC. Treatment for SNUC typically involves a multimodal approach involving surgery (if feasible) and radiation therapy (RT) with concurrent chemotherapy[2-4]. A phase II clinical trial in inoperable stage IV head and neck cancer previously found that the RADPLAT protocol (radiation and intra-arterial cisplatin) achieved an initial tumor response in 91% of patients with 1 and 2 years locoregional control of 82% and 69%, respectively[5]. Here, we describe the successful use of RADPLAT to treat a patient with an unresectable T4N0 SNUC.
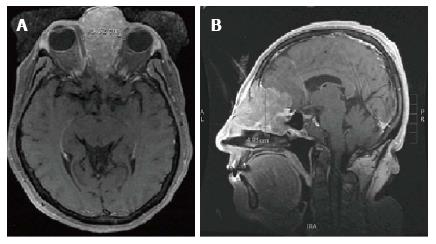
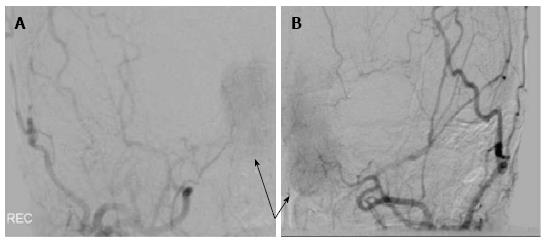
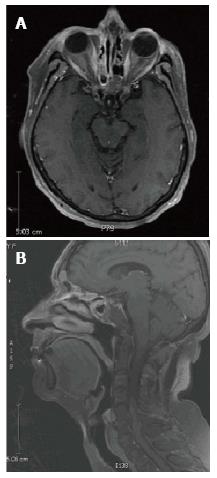
A 60-year-old woman presented with nasal cong-estion and a prominence on the left side of her nose. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a tumor arising from the ethmoid sinus extending through the cribriform plate and into the anterior cranial fossa without metastasis to the chest and neck. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the face showed edema in the left frontal lobe, interpreted as suspicious for brain invasion (Figure 1). Biopsy revealed large pleomorphic tumor cells with a high nuclear to cytoplasm ratio, prominent nucleoli and focal areas of necrosis. Immunohistochemistry was positive for pancytokeratin and CD56 and weakly positive for chromogranin. She was diagnosed with a T4N0 SNUC. Since the tumor was deemed unresectable due to brain involvement, the RADPLAT protocol was chosen in hopes of maximizing her chance for local control. She received concurrent 4 cycles of weekly intra-arterial (IA) cisplatin at 150 mg/m2, administered as a divided dose through left and right-sided feeding arteries for this midline tumor (Figure 2). With the IA cisplatin, she received intravenous (IV) thiosulfate bolus followed by thiosulfate infusion. Radiation therapy was given in 28 daily fractions to 54 Gy using intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) followed by a hypofractionated stereotactic boost of 3 fractions to 13 Gy to a total dose of 67 Gy in 31 fractions to the nasal sinus and bilateral neck. The biologically effective dose for the radiation treatment is equivalent to 82 Gy10 and 117 Gy3.
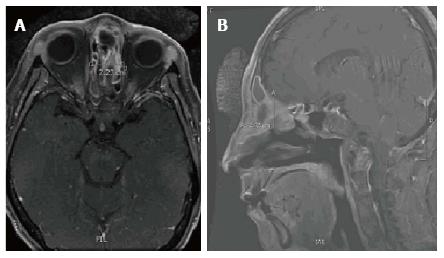
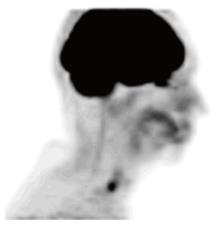
After the first administration of intra-arterial cisplatin, there was an obvious and rapid decrease in tumor size, suggesting response to the chemotherapy. There was marked tumor size reduction after the final cycle of chemotherapy (Figure 3). She tolerated treatment well, with no toxicity from chemotherapy and expected acute sequelae including grade 2 mucositis, grade 2 dermatitis, and grade 1 conjunctivitis. Collagenase and polysporin powder with Xeroform was used to treat radiation conjunctivitis. Positron emission tomography (PET)/CT four months post-treatment showed persistent soft tissue density in the anterior ethmoid sinuses, without fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake (Figure 4). Thirty months post treatment, MRI revealed no evidence of recurrent disease and a decrease in the previously noted inflammatory changes in the sinuses (Figure 5). The patient continues to be disease-free 47 mo post-treatment.
This case report presents long survival in a patient with an inoperable SNUC treated with concurrent intra-arterial cisplatin and radiation therapy.
Similar to our case, 84% to 92% of patients with SNUC present with T4 disease[4,6-9]. In many cases, the cancer can extend beyond the nasal and paranasal sinuses to involve the orbit and/or brain[5].
Currently there is no standard of care available for SNUC. Unresectable SNUC is generally treated with radiation or concurrent chemoradiation. Because the interventional radiologists and treating oncologists were familiar with RADPLAT, we opted to utilize this protocol in hopes of maximizing local control. In 213 patients with stage III-IV head and neck squamous cell cancer (SCC) treated with RADPLAT, Robbins et al[10] reported a 5 year overall survival of 38.8% and locoregional control of 74.3%[10]. Similarly, Rabbani et al[11] reported locoregional control in 78% and four year overall survival in 57% in a study of 35 patients with stage III head and neck cancer. Homma et al[12] evaluated the efficacy of RADPLAT for untreated advanced cancers (T3, T4a, and T4b) of the nasal and paranasal sinuses in 47 patients. During the median follow-up period of 4.6 years, the 5-year local progression-free survival rate was 78.4% for all patients[12]. Furthermore, the 5-year overall survival rate was 69.3% for all patients[12]. This study indicates that the RADPLAT protocol can not only effectively treat SCC of the head and neck, but also provide locoregional control and long-term survival in cancers specific to the paranasal and nasal sinuses.
The RADPLAT protocol involves intra-arterial infusion of cisplatin with intra-venous systemic neutralization using thiosulfate. The rapid infusion of cisplatin enables high doses of the drug to directly reach the tumor bed while the thiosulfate infusion prevents the systemic toxicity of large doses of cisplatin[10,11]. The cytotoxic effects of cisplatin are potentiated by radiation[13]. This effect was first demonstrated in murine models of tumors[14]. Studies have found that tumor resistance to cisplatin can occur within 2-4 cycles[15,16]. However, resistance can be overcome by increasing doses of cisplatin as demonstrated by in vitro and in vivo studies[17,18]. Elevated doses are not well-tolerated in patients because they can lead to undesirable side-effects such as neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, mucositis, and other systemic effects[19]. To circumvent the high-dose toxicity of the cisplatin, the intra-arterial infusion of cisplatin with concomitant thiosulfate enables high doses of cisplatin to reach the tumor bed without systemic toxicity. With the RADPLAT protocol, it is possible to deliver doses 10 times higher than can be delivered intravenously[17,18].
Many studies highlight the importance of surgery in improving survival in patients with SNUC[2,6,20,21]. In our case, brain involvement of the patient’s SNUC made her a poor candidate for surgery, so she was treated with radical chemoradiotherapy to the primary site and bilateral neck. Elective neck irradiation for node negative SNUC is important for regional control[3,20]. Chemoradiation has previously been shown to be a viable treatment option for advanced SNUC. In one study, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were 43% and 64%, respectively, with three cycles of platinum and 5-fluorouracil followed by radiation with two cycles of concurrent platinum, suggesting that induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiation is effective[22]. This study found that among patients with SNUC treated to 50-60 Gy, all 4 patients treated with at least 60 Gy were alive without local progression at last follow-up[22]. Another study found that all patients that achieved cause-specific survival when treated with doses greater than 62.5 Gy[3]. Thus, doses of at least 60-70 Gy2 to the primary site are recommended, if feasible.
In conclusion, our patient was effectively treated with RADPLAT with minimal toxicity and lasting disease control for nearly 4 years. Centers with expertise in intra-arterial chemotherapy could consider this modality for patients with unresectable SNUC.
A 60-year-old woman presented with nasal congestion and a prominence on the left side of her nose is diagnosed with unresectable T4N0 sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC).
Dullness to percussion and decrease breath sounds over the upper lobe of the right lung.
Esthesioneuroblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, lymphoma, melanoma, other soft tissue sarcoma.
Labs were drawn but were found to be unremarkable.
Computed tomography revealed a tumor arising from the ethmoid sinus extending through the cribriform plate and into the anterior cranial fossa without metastasis to the chest and neck. Magnetic resonance imaging of the face showed edema in the left frontal lobe, extending back to the left lateral ventricle.
Biopsy of the mass revealed large pleomorphic tumor cells with a high nuclear to cytoplasm ratio and prominent nucleoli and focal areas of necrosis. Immunohistochemistry was positive for pancytokeratin and CD56 and weakly positive for chromogranin.
The patient was treated with RADPLAT (concurrent intra-arterial cisplatin with simultaneous thiosulfate and radiation therapy).
Sinonansal undifferentiated carcinoma is difficult to treat and there is currently no standard treatment protocol.
The RADPLAT protocol involves intra-arterial infusion of cisplatin with intra-venous systemic neutralization using thiosulfate and concurrent radiation therapy. The rapid infusion of the cisplatin enables high doses of the drug to directly reach the tumor bed while the thiosulfate infusion prevents the systemic toxicity of large doses of cisplatin.
This case report represents long survival in a patient with an unresectable T4N0 SNUC using RADPLAT. Centers with expertise in intra-arterial chemotherapy could consider this modality for patients with unresectable SNUC.
These data are thorough and convincing.
| 1. | Franchi A, Moroni M, Massi D, Paglierani M, Santucci M. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, nasopharyngeal-type undifferentiated carcinoma, and keratinizing and nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma express different cytokeratin patterns. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:1597-1604. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Reiersen DA, Pahilan ME, Devaiah AK. Meta-analysis of treatment outcomes for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;147:7-14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Christopherson K, Werning JW, Malyapa RS, Morris CG, Mendenhall WM. Radiotherapy for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. Am J Otolaryngol. 2014;35:141-146. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Lin EM, Sparano A, Spalding A, Eisbruch A, Worden FP, Heth J, Sullivan SE, Thompson BG, Marentette LJ. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: a 13-year experience at a single institution. Skull Base. 2010;20:61-67. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Balm AJ, Rasch CR, Schornagel JH, Hilgers FJ, Keus RB, Schultze-Kool L, Ackerstaff AH, Busschers W, Tan IB. High-dose superselective intra-arterial cisplatin and concomitant radiation (RADPLAT) for advanced head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 2004;26:485-493. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Jeng YM, Sung MT, Fang CL, Huang HY, Mao TL, Cheng W, Hsiao CH. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma and nasopharyngeal-type undifferentiated carcinoma: two clinically, biologically, and histopathologically distinct entities. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:371-376. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Mourad WF, Hauerstock D, Shourbaji RA, Hu KS, Culliney B, Li Z, Jacobson A, Tran T, Manolidis S, Schantz S. Trimodality management of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma and review of the literature. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:584-588. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Tanzler ED, Morris CG, Orlando CA, Werning JW, Mendenhall WM. Management of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. Head Neck. 2008;30:595-599. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Revenaugh PC, Seth R, Pavlovich JB, Knott PD, Batra PS. Minimally invasive endoscopic resection of sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011;32:464-469. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Robbins KT, Kumar P, Wong FS, Hartsell WF, Flick P, Palmer R, Weir AB, Neill HB, Murry T, Ferguson R. Targeted chemoradiation for advanced head and neck cancer: analysis of 213 patients. Head Neck. 2000;22:687-693. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Rabbani A, Hinerman RW, Schmalfuss IM, Amdur RJ, Morris CG, Peters KR, Robbins KT, Mendenhall WM. Radiotherapy and concomitant intraarterial cisplatin (RADPLAT) for advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007;30:283-286. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Homma A, Sakashita T, Yoshida D, Onimaru R, Tsuchiya K, Suzuki F, Yasuda K, Hatakeyama H, Furusawa J, Mizumachi T. Superselective intra-arterial cisplatin infusion and concomitant radiotherapy for maxillary sinus cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2980-2986. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Alkureishi LW, de Bree R, Ross GL. RADPLAT: an alternative to surgery? Oncologist. 2006;11:469-480. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Zák M, Drobník J. Effect of cis-dichlorodiamine platinum (II) on the post-irradiation lethality in mice after irradiation with X-rays. Strahlentherapie. 1971;142:112-115. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Andrews PA, Jones JA, Varki NM, Howell SB. Rapid emergence of acquired cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) resistance in an in vivo model of human ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 1990;2:93-100. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Andrews PA, Murphy MP, Howell SB. Characterization of cisplatin-resistant COLO 316 human ovarian carcinoma cells. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1989;25:619-625. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Robbins KT, Storniolo AM, Hryniuk WM, Howell SB. “Decadose” effects of cisplatin on squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. II. Clinical studies. Laryngoscope. 1996;106:37-42. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Robbins KT, Hoffman RM. “Decadose” effects of cisplatin on squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. I. Histoculture experiments. Laryngoscope. 1996;106:32-36. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Vokes EE, Weichselbaum RR. Concomitant chemoradiotherapy: rationale and clinical experience in patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:911-934. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Musy PY, Reibel JF, Levine PA. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: the search for a better outcome. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:1450-1455. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 100] [Cited by in RCA: 99] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Chen AM, Daly ME, El-Sayed I, Garcia J, Lee NY, Bucci MK, Kaplan MJ. Patterns of failure after combined-modality approaches incorporating radiotherapy for sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma of the head and neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:338-343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Rischin D, Porceddu S, Peters L, Martin J, Corry J, Weih L. Promising results with chemoradiation in patients with sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. Head Neck. 2004;26:435-441. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
P- Reviewer: Xiao Q S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Lu YJ
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/