©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2021; 9(10): 2394-2399
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2394
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2394
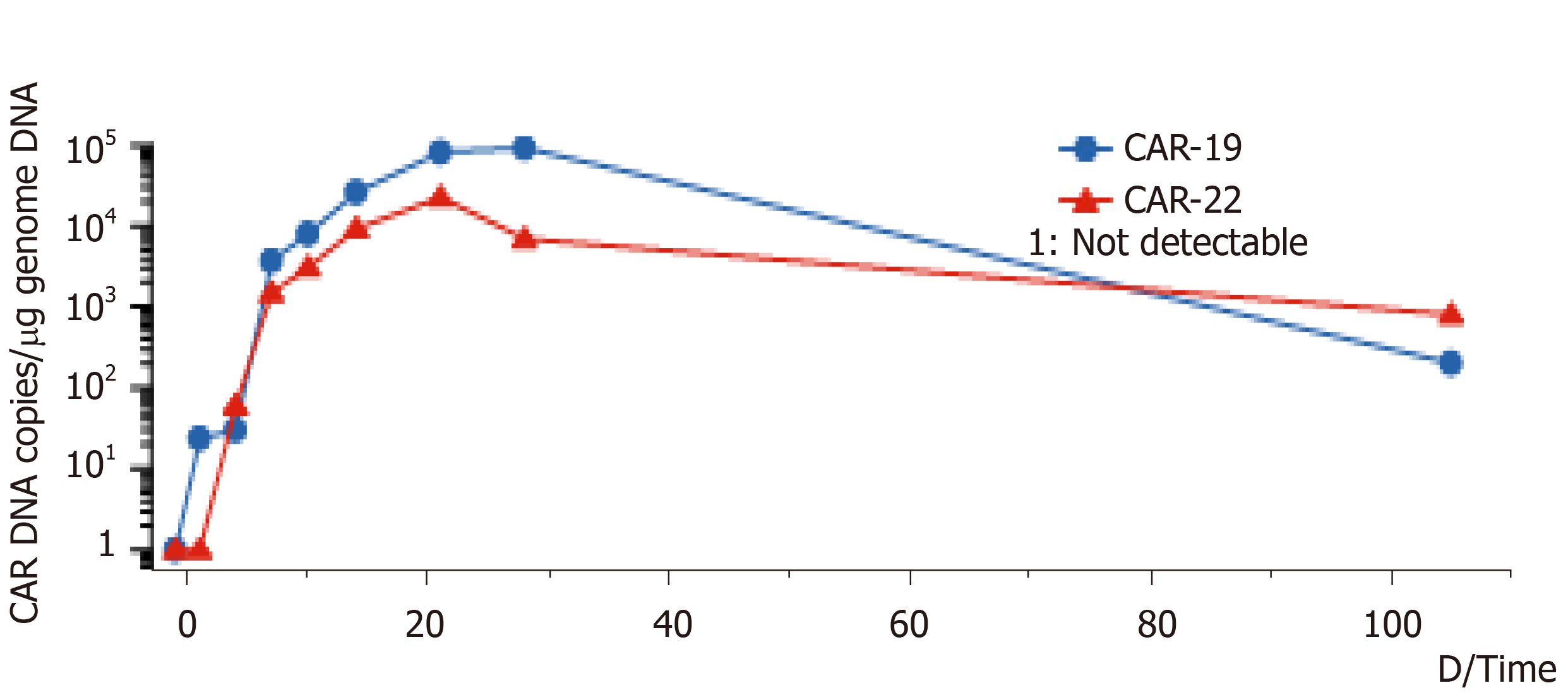
Figure 1 DNA variation trend of CD19-CAR-T cell and CD22-CAR-T cell.
Copy number of CD19-CAR-T cells and CD22-CAR-T cells DNA per μg genome in peripheral blood of the lymphoma patient at different times. CAR: Chimeric antigen receptor; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid.
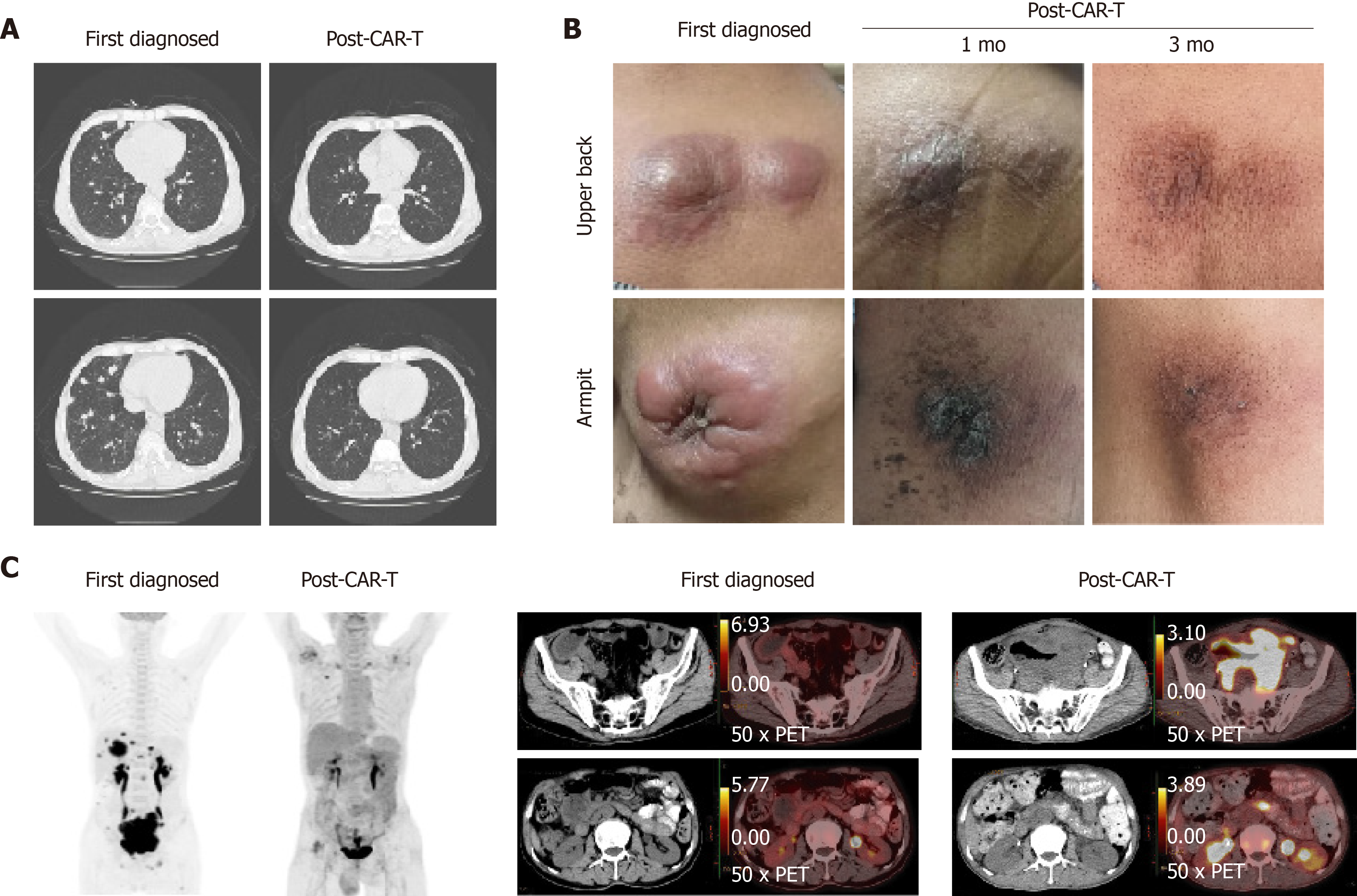
Figure 2 Changes in lung, subcutaneous mass, and abdominal mass before and after chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy.
A: The patient developed multiple pulmonary nodules after disease progression detected by computed tomography. After treatment with chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) and programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitor for 21 days, the absorption of pulmonary nodules decreased significantly; B: Changes in the subcutaneous mass before and after CAR-T cell therapy. The comparison of local mass size before and after CAR-T cell treatment in the 1st mo and 3rd mo; and C: Changes in the abdominal mass detected by positron emission tomography-computed tomography before and after CAR-T cell therapy. In early diagnosis of the disease, the maximum standardized uptake values were 22.40 and 15.60 in the abdomen and pelvis, respectively. 5 mo after the combination treatment, the maximum standardized uptake values in the abdomen and pelvis were 3.80 and 3.30, respectively.
- Citation: Niu ZY, Sun L, Wen SP, Song ZR, Xing L, Wang Y, Li JQ, Zhang XJ, Wang FX. Programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitor combined with chimeric antigen receptor T cells in the treatment of relapsed refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(10): 2394-2399
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i10/2394.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2394