Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2020; 8(22): 5781-5789
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5781
Published online Nov 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5781
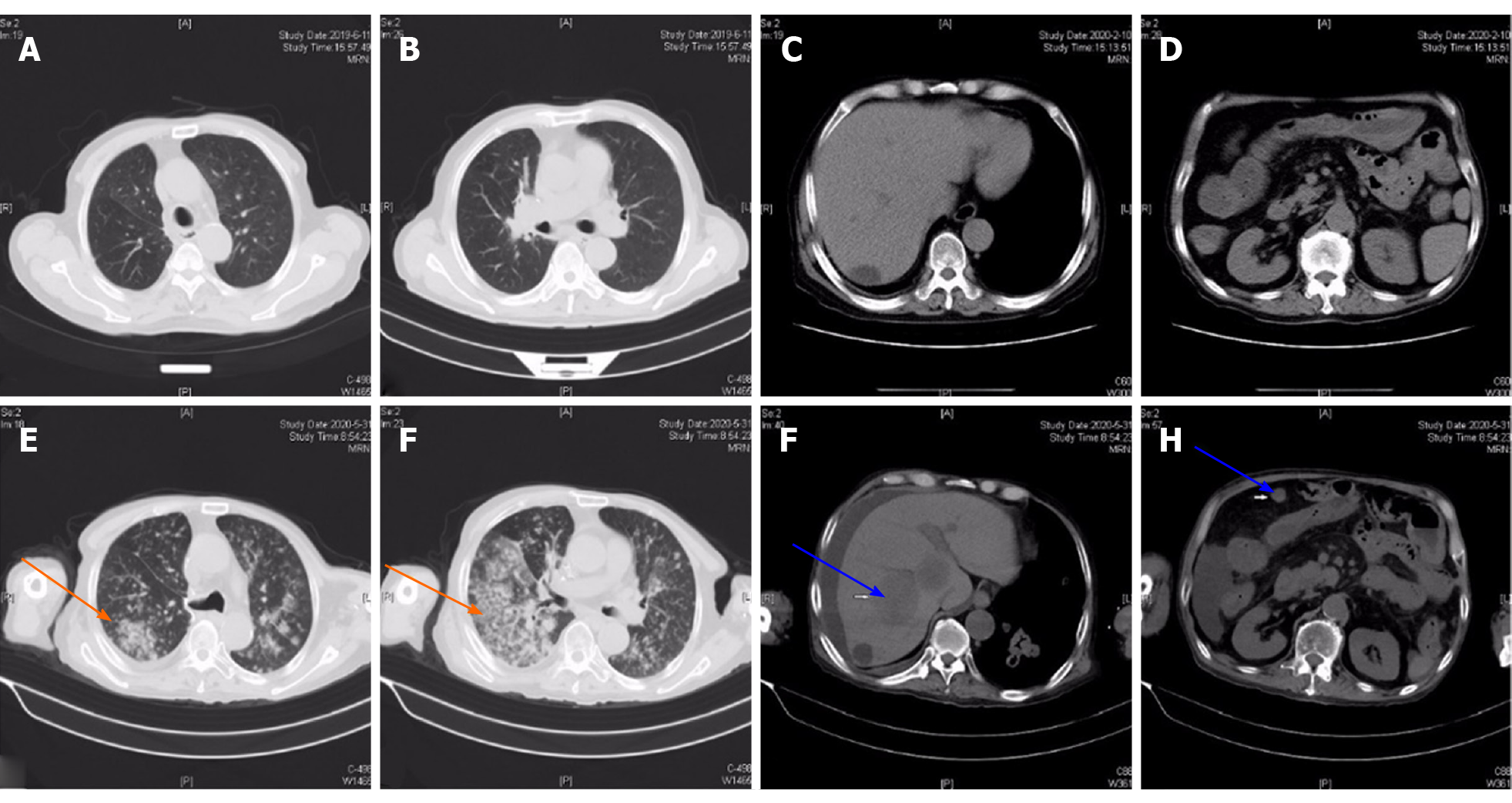
Figure 1 Chest and abdominal computed tomography showed rapid disease progression.
A and B: Chest computed tomography (CT) on June 11, 2019 showed clear lung fields on both sides; C and D: Abdominal CT on June 11, 2019 showed a liver cyst, and part of a slightly dilated small intestine; E and F: Chest CT on May 31, 2020 revealed multiple nodules and masses in both lungs, not excluding neoplastic lesions (orange arrow); G and H: Abdominal CT on May 31, 2020 showed multiple low-density lesions in the right liver and multiple soft tissue masses in the abdominal cavity, suggesting multiple metastases (blue arrow).
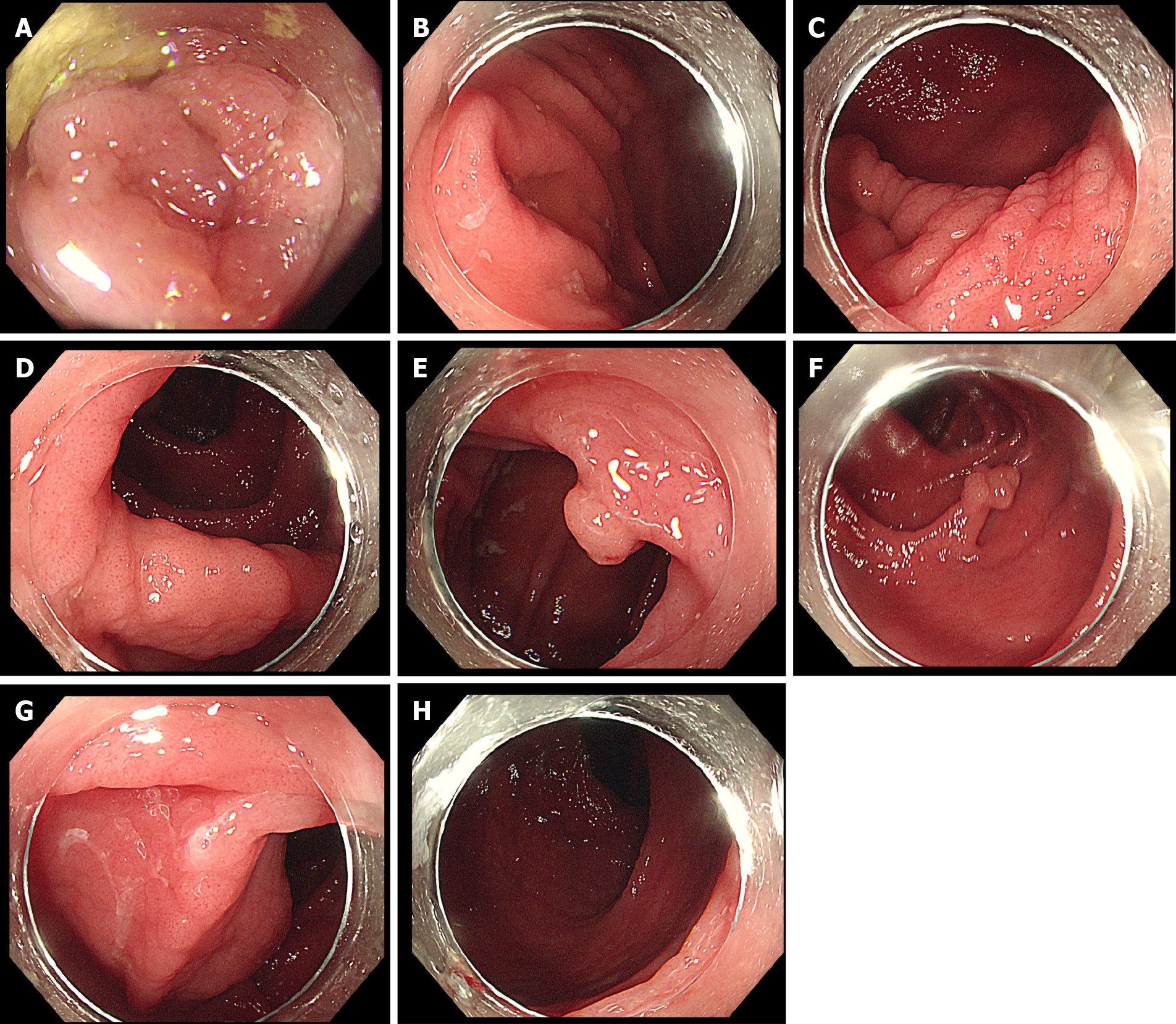
Figure 2 Diffuse swelling and finely granular appearance of the terminal ileum and entire colon mucosa.
A: The terminal ileum mucosa is swollen; B: The mucosa around the appendix opening is swollen; C: The mucosa around the ileocecal valve is finely granular; D: The mucosa of the ascending colon is diffusely finely granular; E: A polypoid lesion was observed in the liver curve of the colon, with a finely granular appearance on the surface; F: A long-pedicle polyp was found in the descending colon, with fine granular mucosal changes on the head and pedicle of the polyp; G: The sigmoid colon mucosa is finely granular; H: The rectal mucosa is swollen.
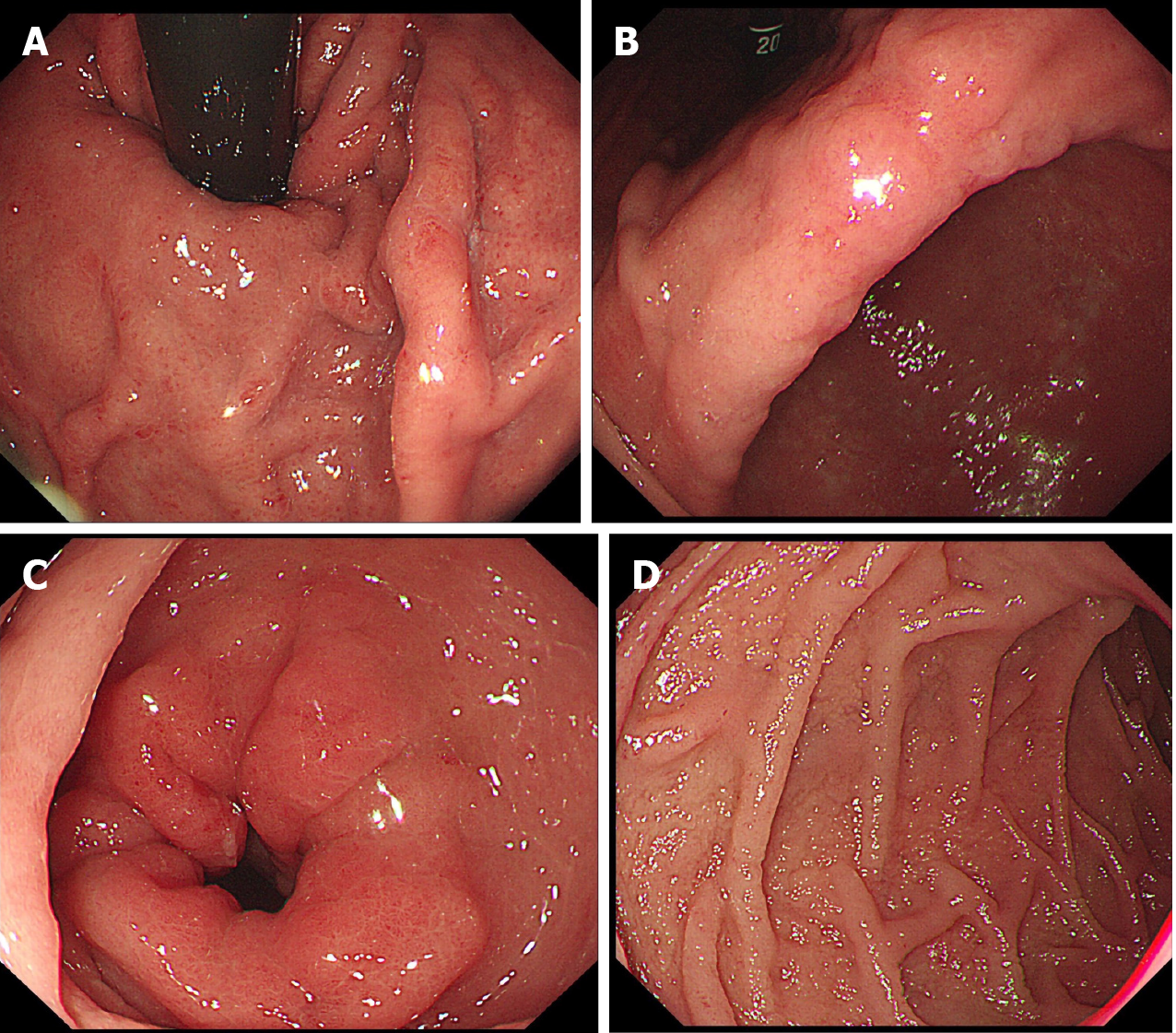
Figure 3 The whole gastric mucosa is swollen with flaky erosions in the angle and antrum of the stomach, and the mucosa of the stomach and descending duodenum is finely granular.
A: The fundus mucosa is swollen; B: The angle of the stomach is rough and swollen; C: Flaky mucosal erythema in the gastric antrum; D: The mucosa of the duodenum is finely granular.
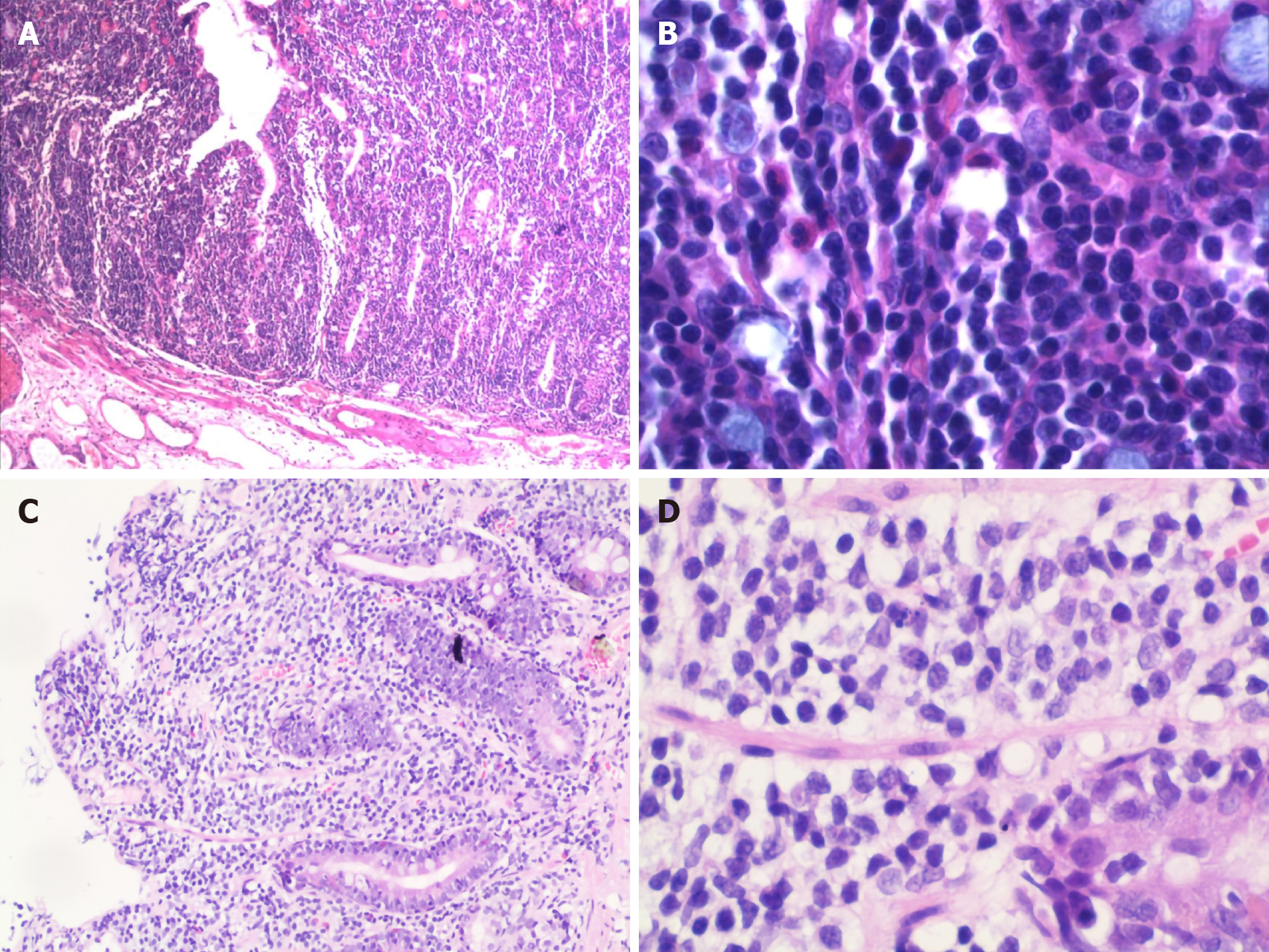
Figure 4 Pathology of the colon and duodenum A: Descending colon.
Villous adenoma with focal carcinogenesis (moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma), limited to the mucosal layer, was observed (× 100); B: Descending colon. There was diffuse atypical lymphocyte proliferation with a single form mainly infiltrated in the mucosal epithelium and lamina propria, partly invading the submucosa (× 400); C: Duodenum. Several lymphocytes infiltrated in the mucosal layer (× 100); D: Duodenum. Atypical lymphocytes accumulated in the mucosal layer with medium-sized cell bodies consisting of few cytoplasm and large oval or irregular nucleus containing coarse chromatin (× 400).
- Citation: Zhang MY, Min CC, Fu WW, Liu H, Yin XY, Zhang CP, Tian ZB, Li XY. Early colon cancer with enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma involving the whole gastrointestinal tract: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(22): 5781-5789
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i22/5781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5781