©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2020; 8(11): 2181-2189
Published online Jun 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2181
Published online Jun 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2181
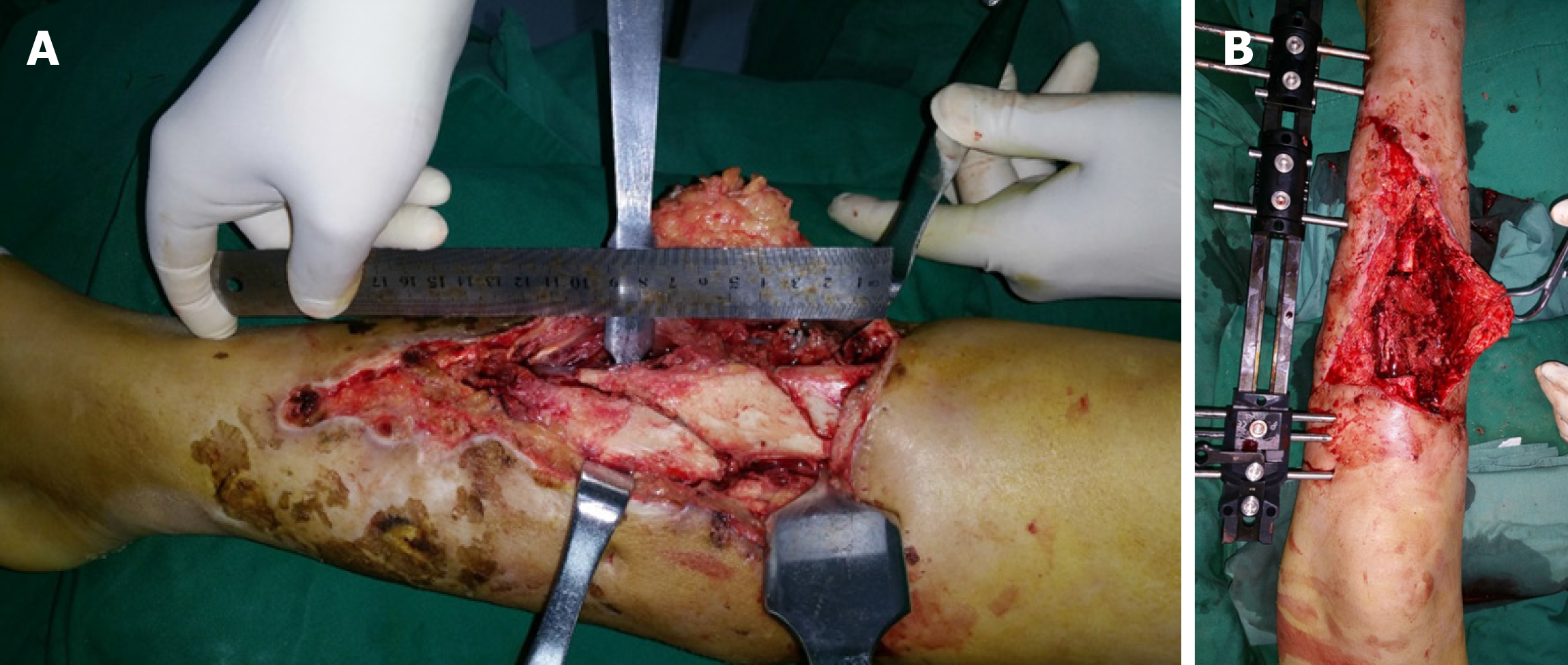
Figure 1 The length of the necrotic tibia was approximately 9 cm and the necrotic tissue was completely removed by debridement.
A: The length of tibial necrosis was approximately 9 cm in this patient with an open tibiofibular fracture caused by a traffic accident; B: The necrotic tibia was removed by complete debridement.
Figure 2 Antibiotic-polymethyl methacrylate beads were implanted intraoperatively after complete debridement.
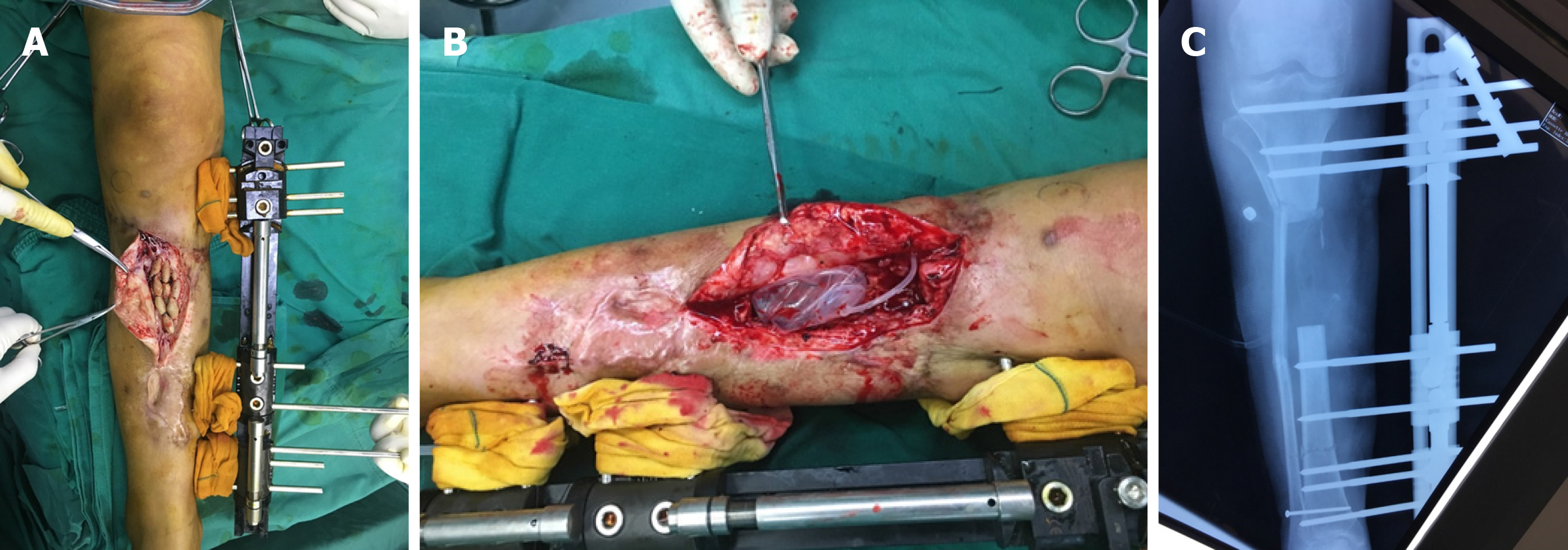
Figure 3 Three months later, the antibiotic-polymethyl methacrylate beads were removed from the lacuna, the expander was inserted and filled.
A: Antibiotic-polymethyl methacrylate beads were removed from the right leg; B: The expander was inserted and filled after the antibiotic-polymethyl methacrylate beads were removed; C: On the X-ray, the valve of the expander was intact and safely in position.
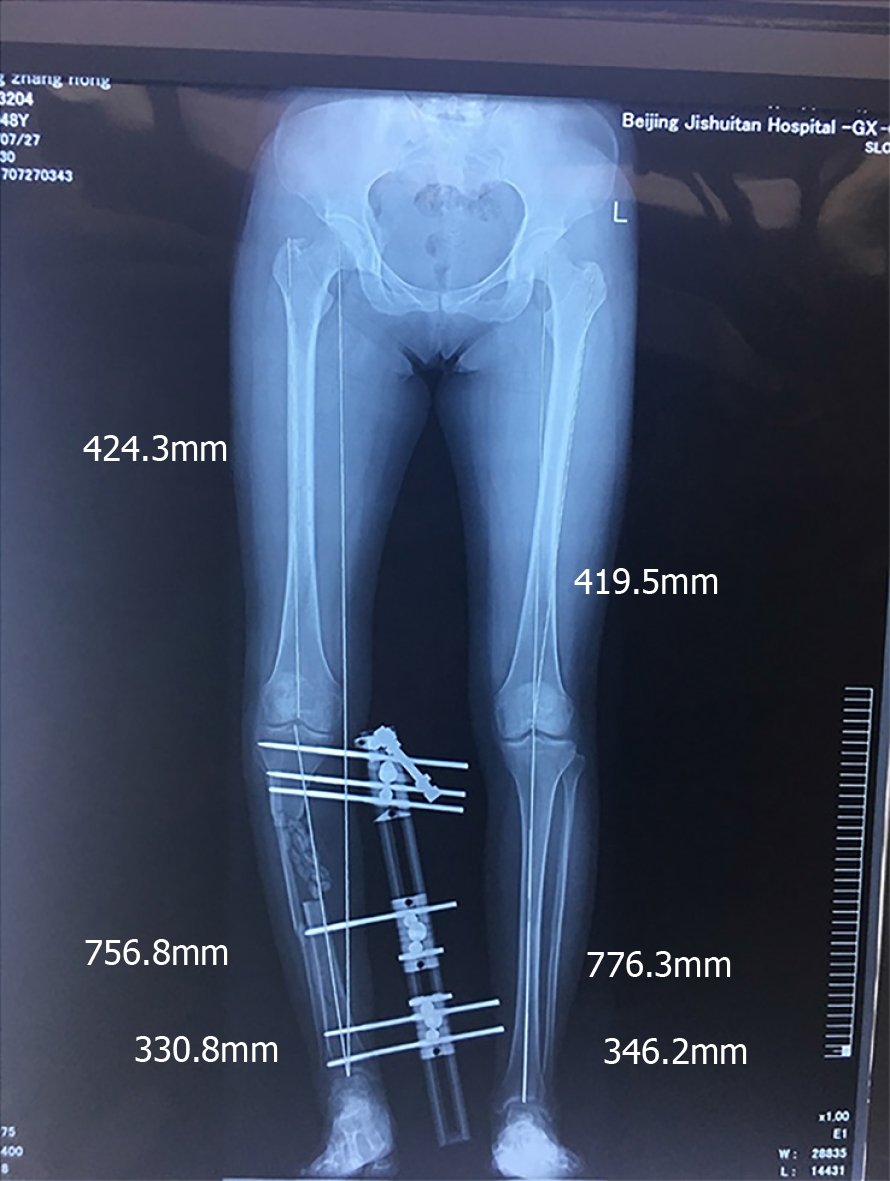
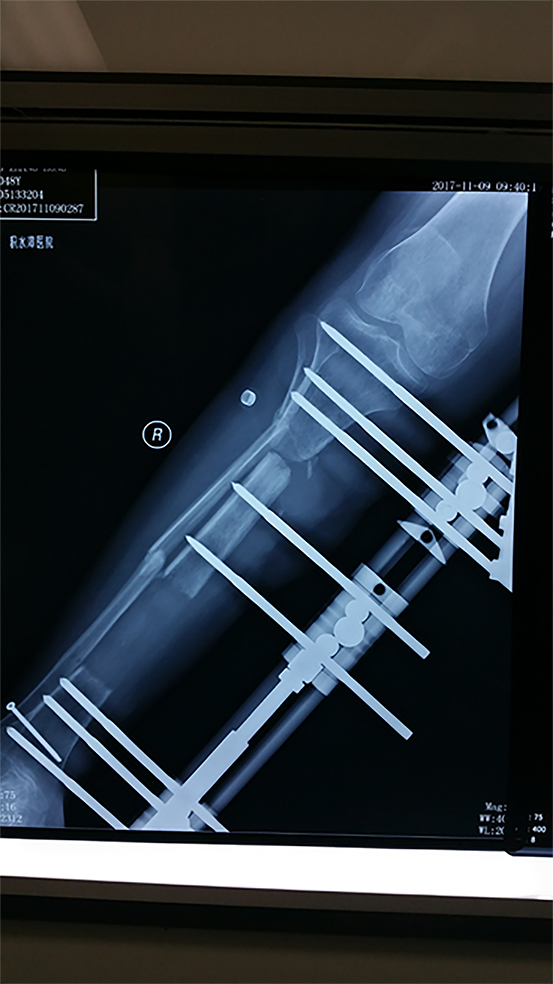
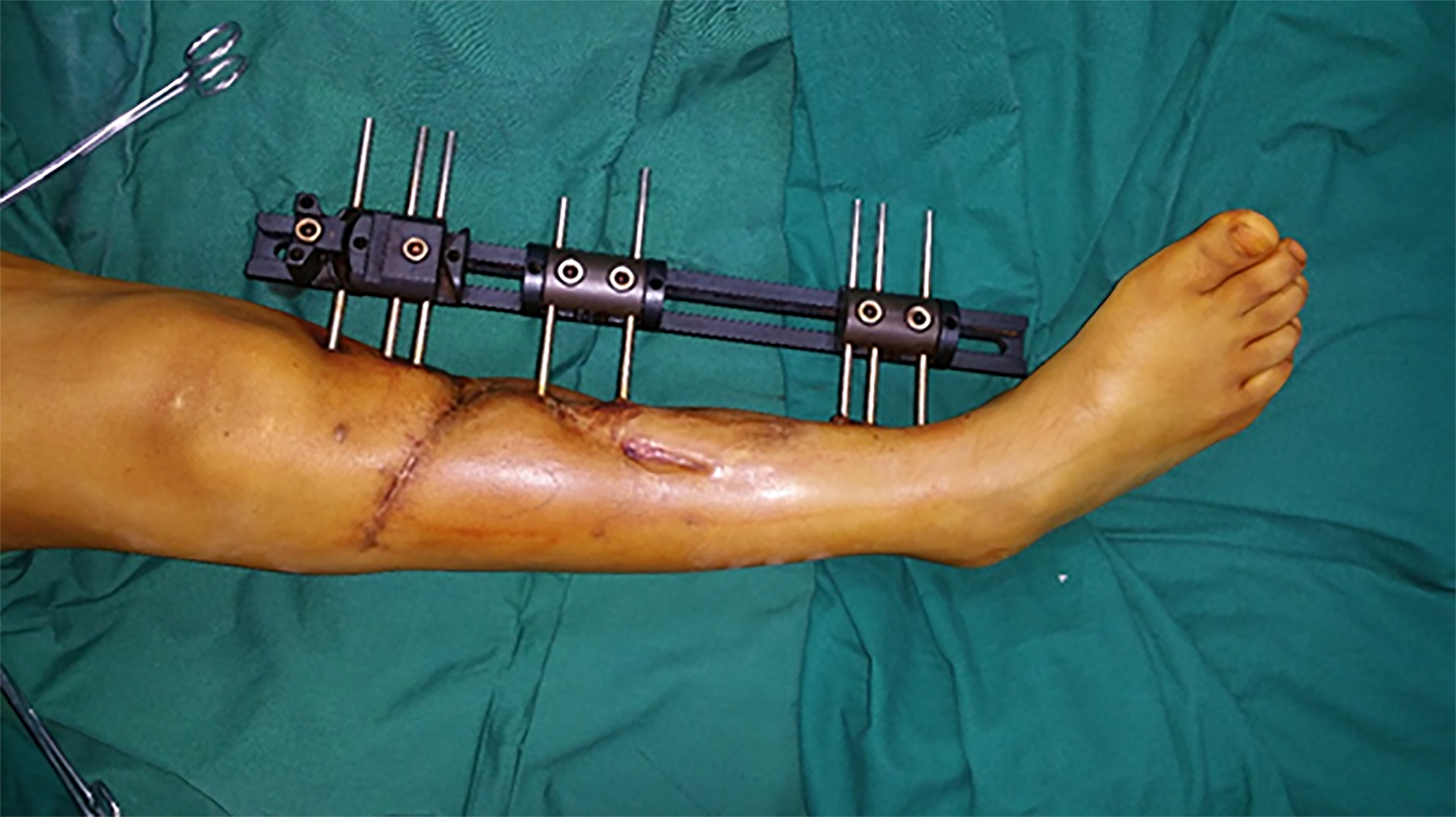
Figure 4 Distraction osteogenesis was initiated.
After 126 d, the distance between the two bone ends was less than 1 cm.
Figure 5 During the entire treatment period, tissue incarceration did not occur.
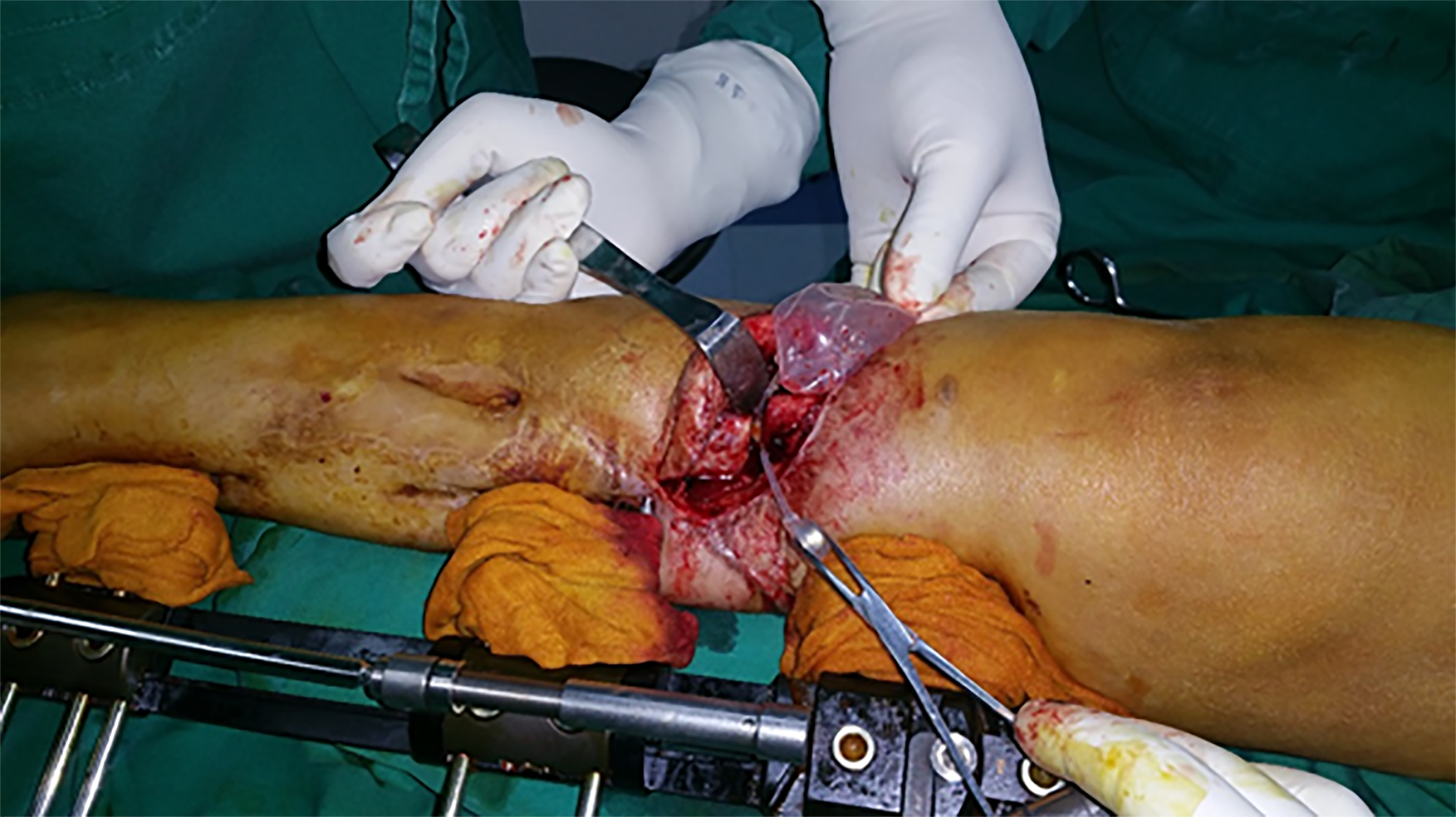
Figure 6 Expander removal and fibular osteotomy were carried out.
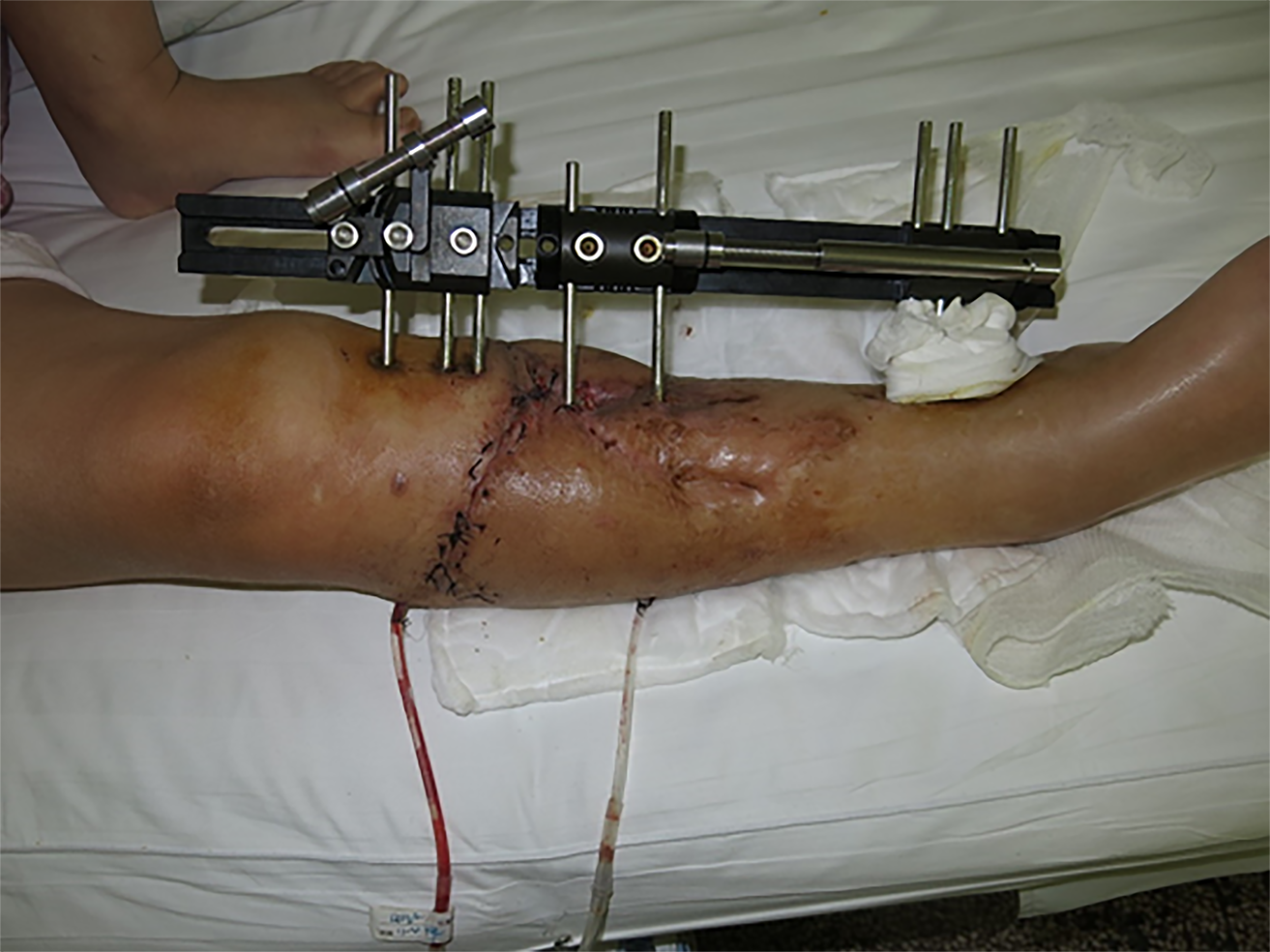
Figure 7 Good incision healing was achieved postoperatively.
- Citation: Chen H, Teng X, Hu XH, Cheng L, Du WL, Shen YM. Application of a pre-filled tissue expander for preventing soft tissue incarceration during tibial distraction osteogenesis. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(11): 2181-2189
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i11/2181.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2181