©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2019; 7(22): 3778-3783
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3778
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3778
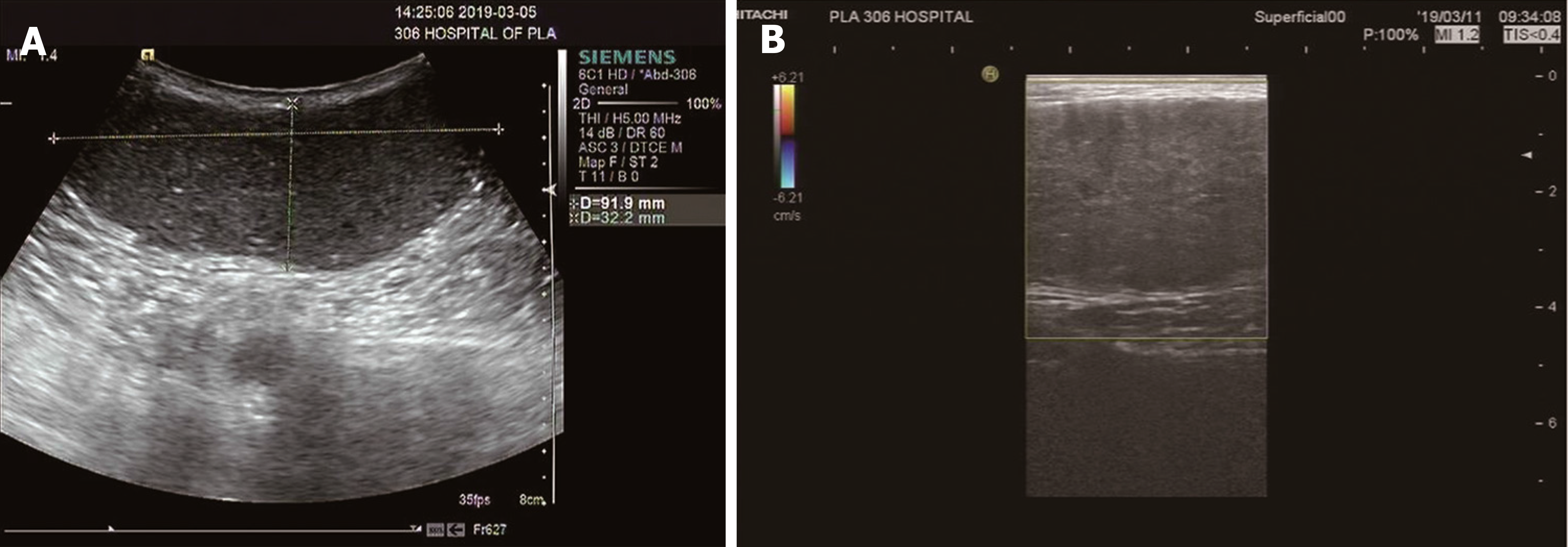
Figure 1 Ultrasound images.
A: Ultrasound image showing a hypoechoic mass, with the maximum range of 9.2 cm × 3.7 cm, clear margins, and regular morphology; B: Color Doppler flow image indicating that there was no obvious blood flow in the mass.
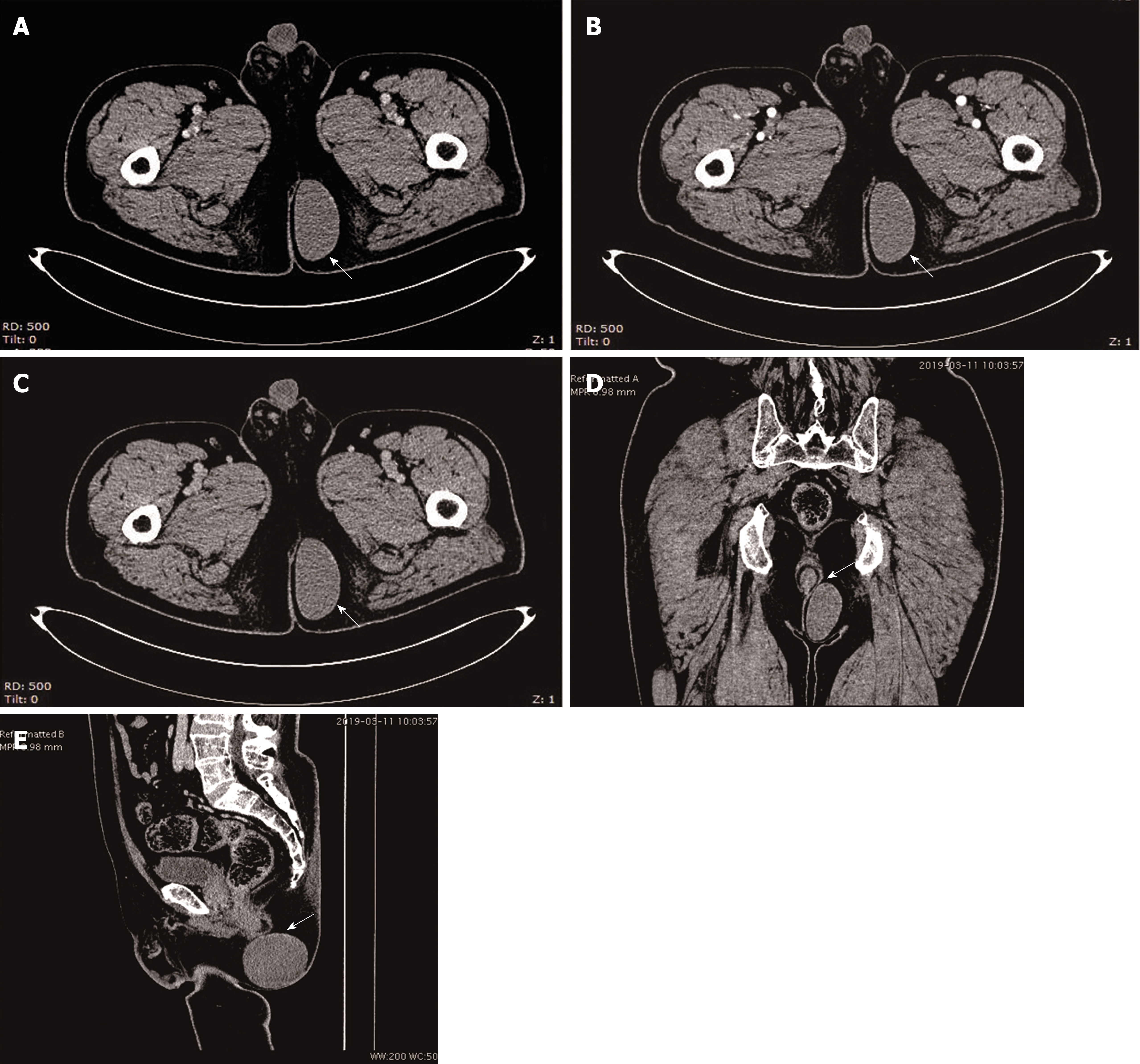
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography images.
A-C: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography images revealing a cystic low density shadow with a smooth edge. The wall of the cyst was not enhanced and there were no blood vessels in and around the mass in the venous phase, arterial phase, and delayed phase; D and E: The upper right edge of the mass was very close to the anal canal.
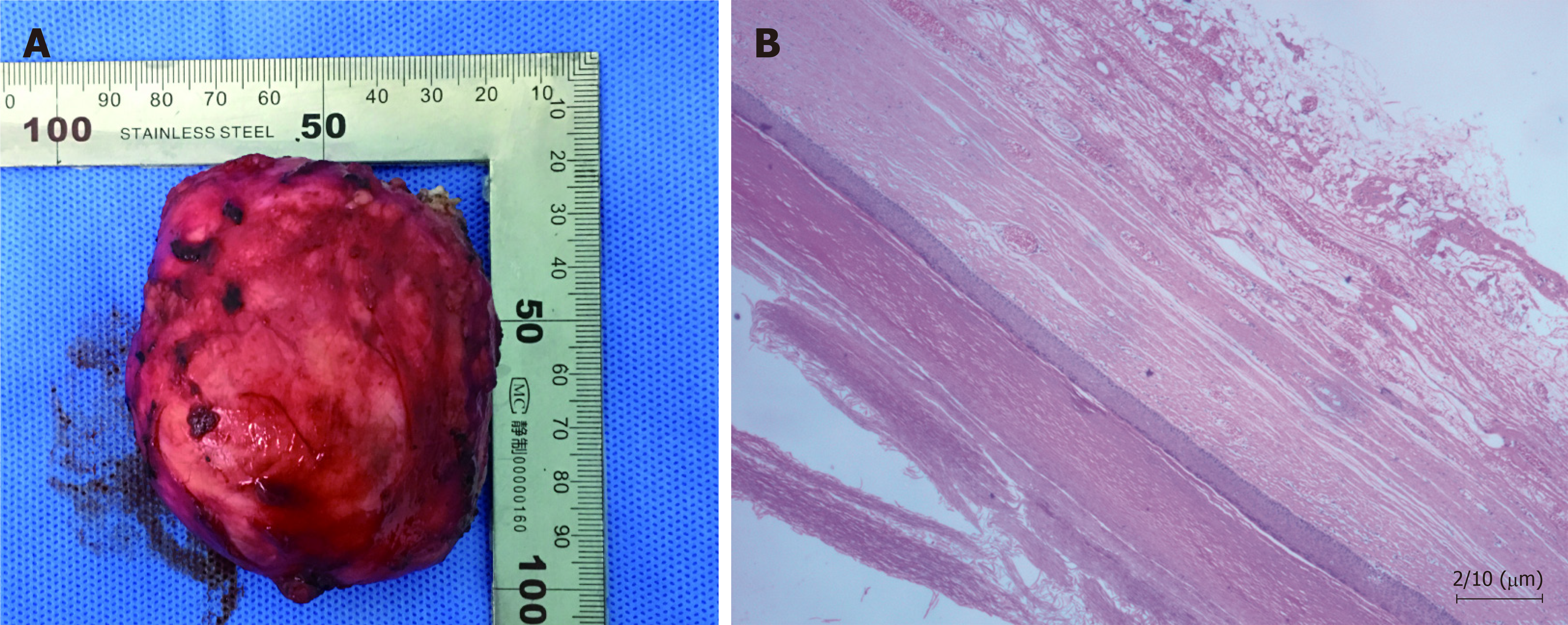
Figure 3 Histopathological findings.
A: The specimen was found to be a greyish-red cystic mass; B: The cyst wall was 40-60 μm thick and was lined with stratified squamous epithelium, which had distinct granular layers (H&E staining, ×200). The cavity of the cyst was filled with layered uniform red-stained keratin.
- Citation: Sun PM, Yang HM, Zhao Y, Yang JW, Yan HF, Liu JX, Sun HW, Cui Y. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography findings of a huge perianal epidermoid cyst: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(22): 3778-3783
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i22/3778.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3778