©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2026; 14(4): 118154
Published online Feb 6, 2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v14.i4.118154
Published online Feb 6, 2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v14.i4.118154
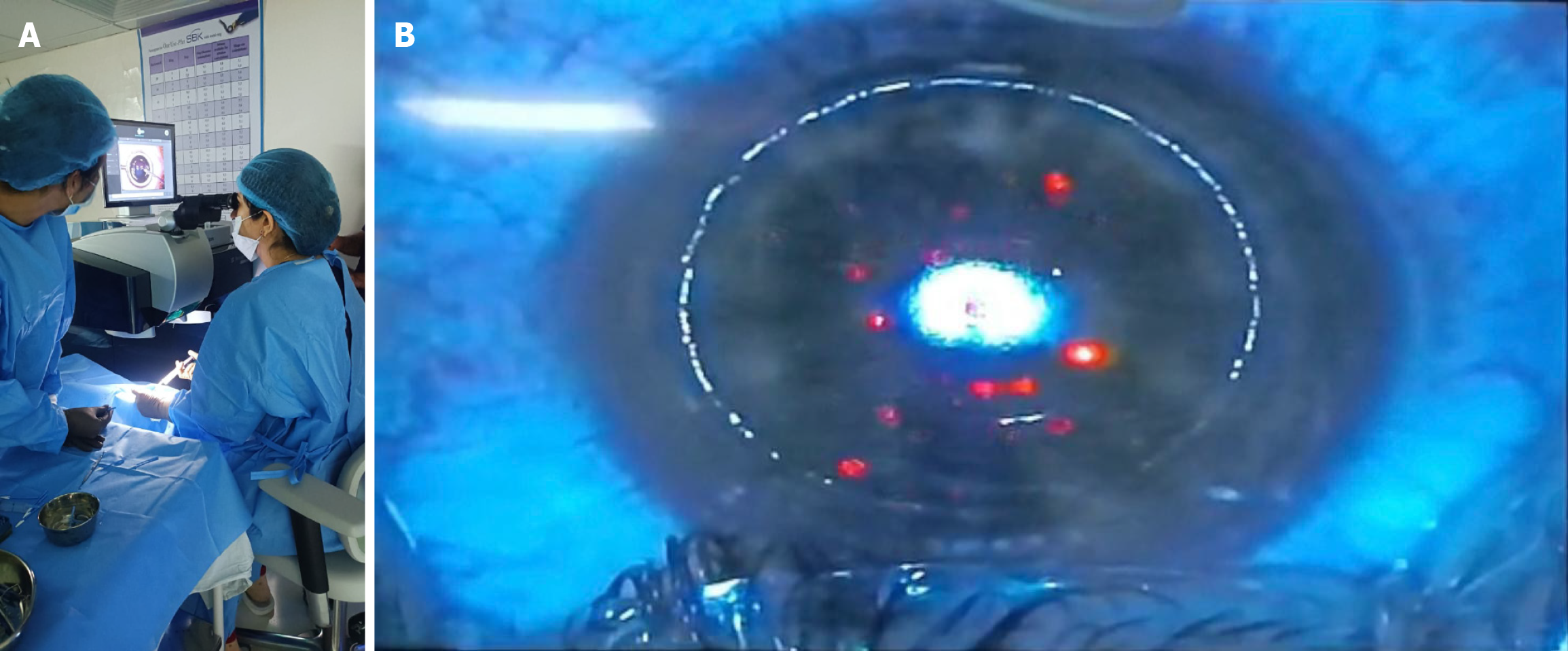
Figure 1 The photorefractive keratectomy procedure involves the removal of the epithelium, which is a primary concern in diabetics, as it may result in poor healing in the postoperative period, potentially leading to a dense stromal haze.
A: Surgeon putting alcohol in well for epithelial removal during photorefractive keratectomy; B: Laser ablation to the stromal bed post-epithelial removal during photorefractive keratectomy.
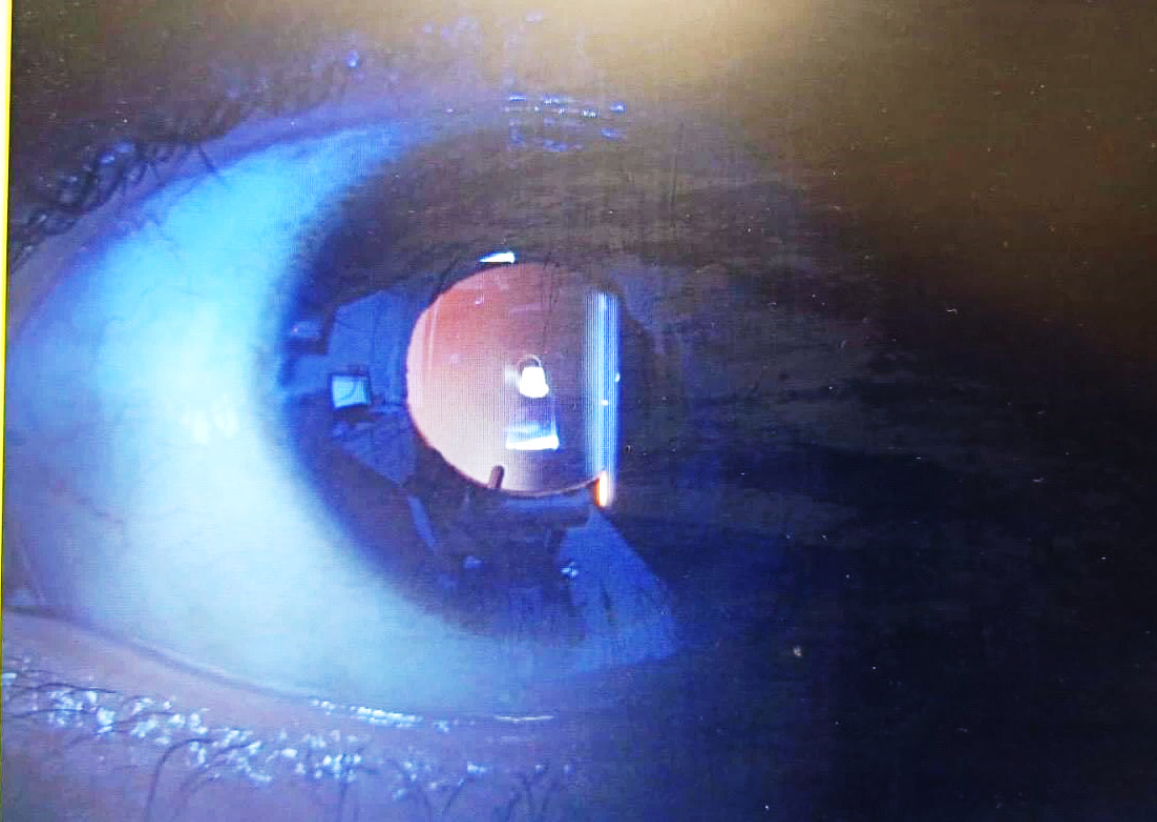
Figure 2 Cap cut in progress after completing the lenticule cut and the lenticule side cut in refractive surgery (small incision lenticule extraction).
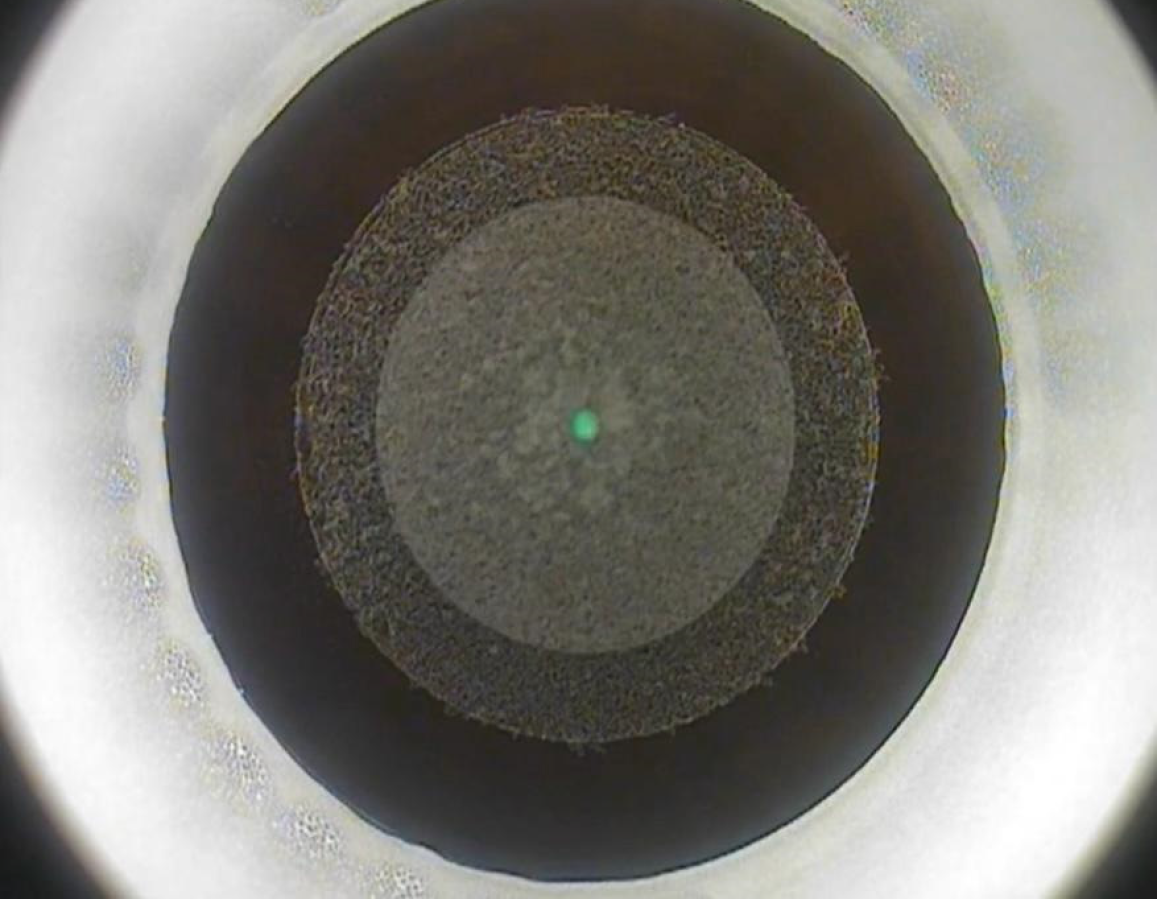
Figure 3 A toric implantable collamer lens in situ with a central hole in a high myope patient.
- Citation: Behera RK, Gupta PC, Morya AK, Khullar S. Safety and efficacy of keratorefractive surgery in diabetes mellitus: A clinical review. World J Clin Cases 2026; 14(4): 118154
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v14/i4/118154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v14.i4.118154