©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2026; 14(4): 117700
Published online Feb 6, 2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v14.i4.117700
Published online Feb 6, 2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v14.i4.117700
Figure 1 SHapley Additive exPlanations analysis of best-performing models.
SHapley Additive exPlanations values were calculated for the best-performing models to investigate the effects of individual variables on predictions. The analysis demonstrates how each variable contributes to the model’s predictions for hospital-acquired functional decline. HAFD: Hospital-acquired functional decline.
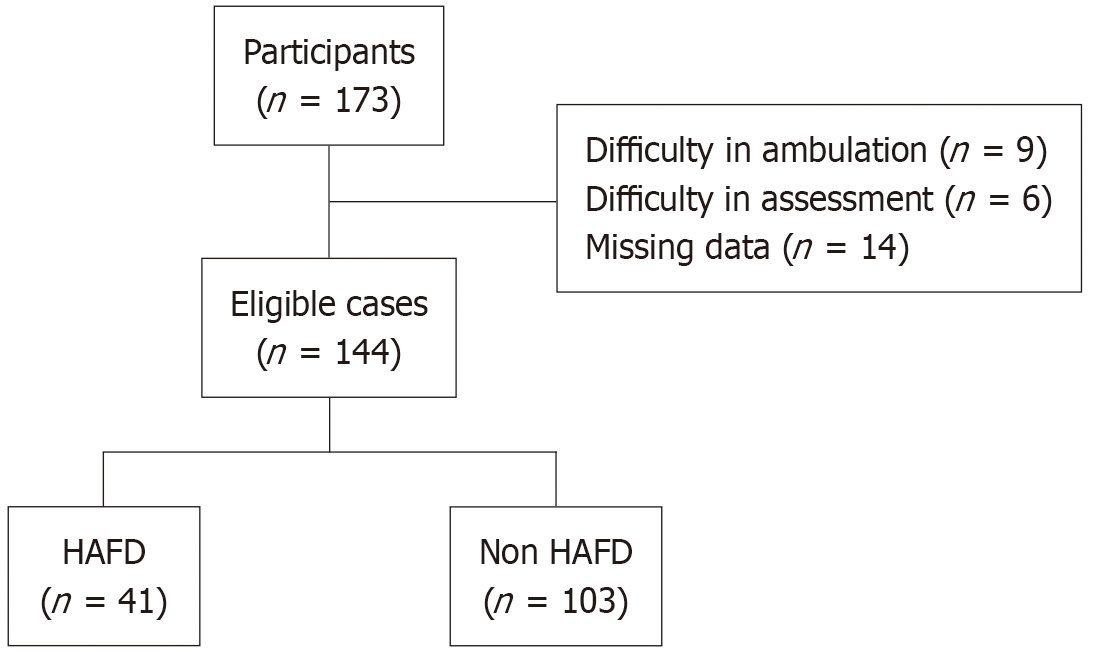
Figure 2 Study flowchart of hospital-acquired functional decline incidence among study participants.
A total of 144 patients were enrolled in the study, with 41 (28.5%) developing hospital-acquired functional decline (HAFD). The remaining 103 patients were in the non-HAFD group. AdaBoost: Adaptive boosting model; CatBoost: Category boosting model; SVM: Support vector machine model; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting model.
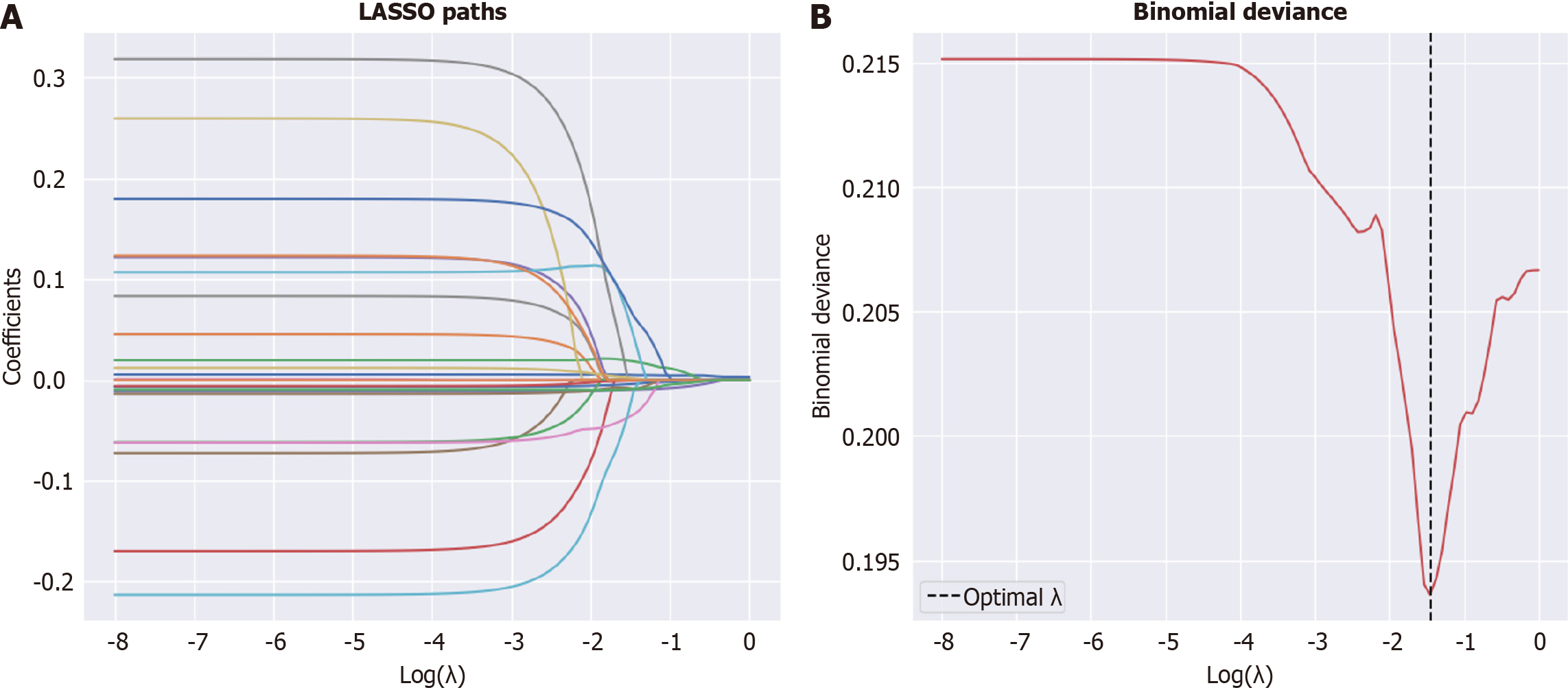
Figure 3 Variables screened using LASSO regression for hospital-acquired functional decline.
A and B: Seven variables with high coefficients are screened using LASSO regression (A), and binomial deviance (B). LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator.
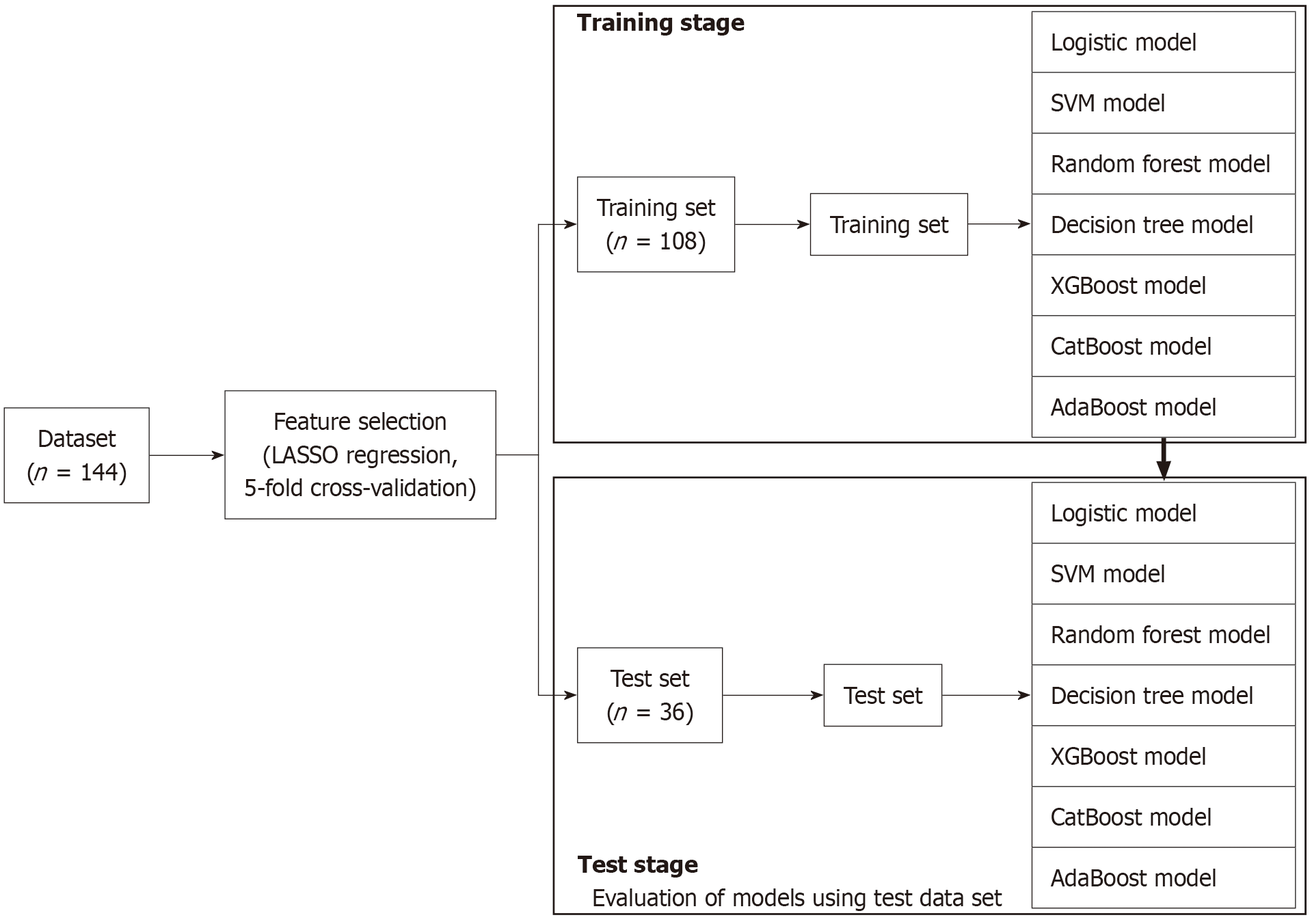
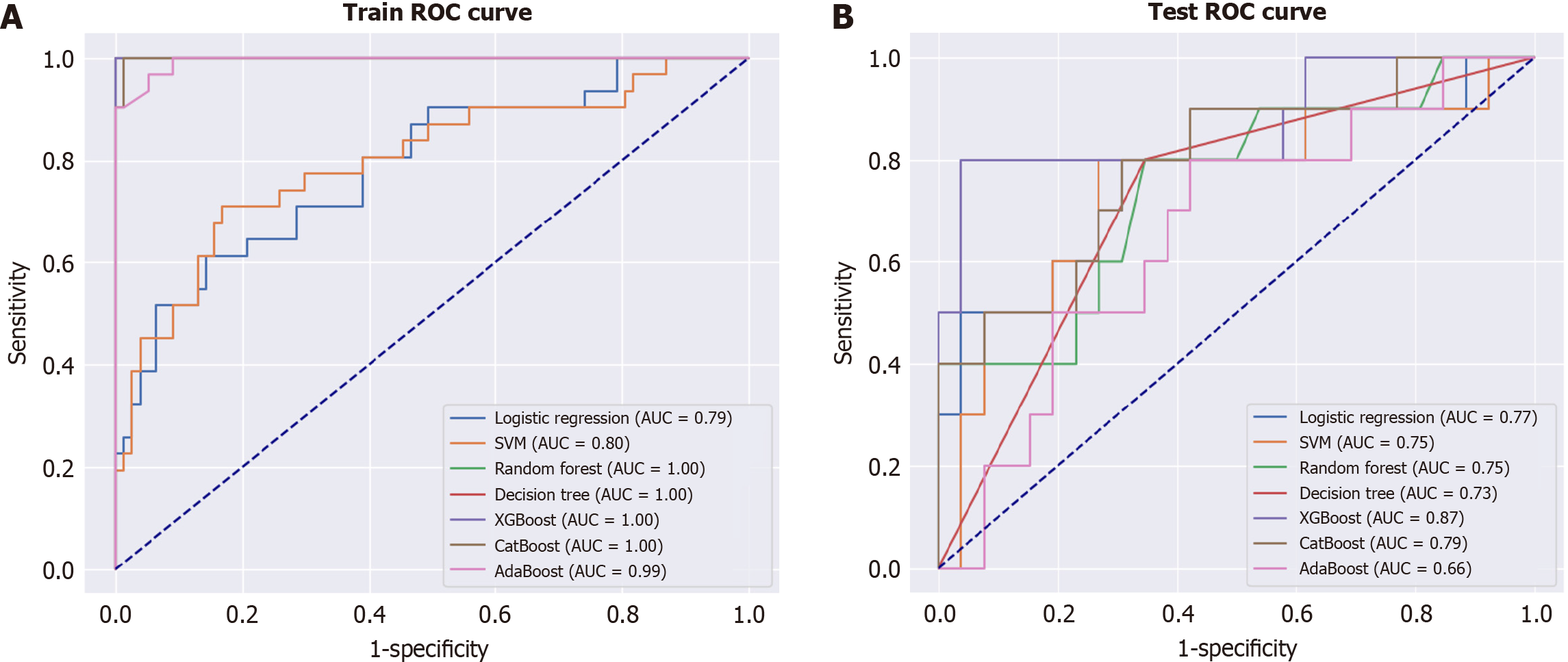
Figure 4 Predictive performance of the extreme gradient boosting model assessed using a receiver operating characteristic curve.
A: SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) dependence plot; B: SHAP beeswarm plot. The extreme gradient boosting model (XGBoost) model performed the best for predicting hospital-acquired functional decline, achieving an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve value of 0.87. The XGBoost model is compared with other models. SPPB: Short physical performance battery; BMI: Body mass index.
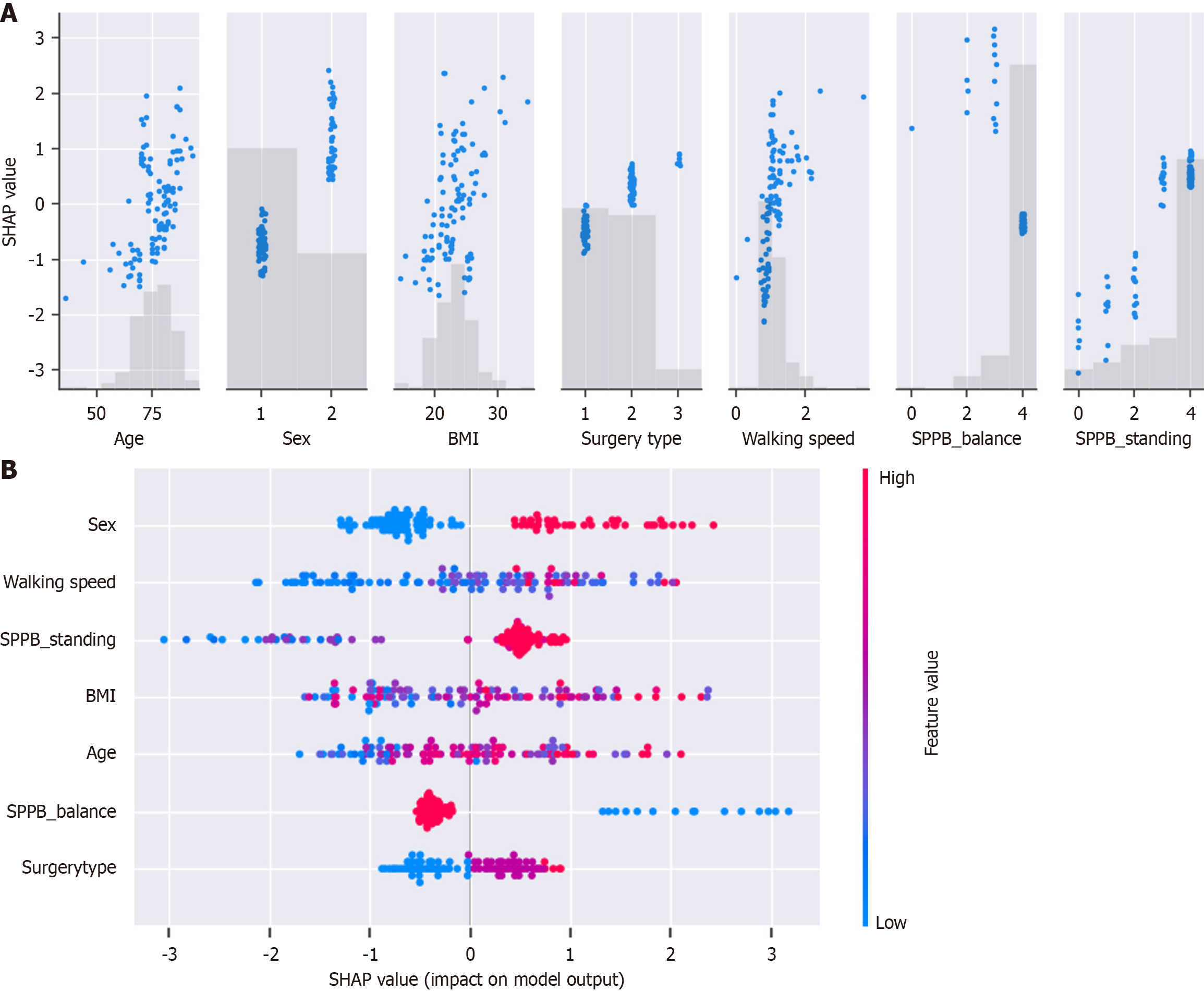
Figure 5 SHapley Additive exPlanations analysis of the extreme gradient boosting model.
A and B: SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) values were calculated for the extreme gradient boosting model model to reveal the influence of individual variables on predictions from the SHAP dependence plot (A), and SHAP beeswarm plot (B). Being female and having a slower preoperative walking speed were key factors affecting the model’s predictions of hospital-acquired functional decline. XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting model; CatBoost: Category boosting model; AdaBoost: Adaptive boosting model; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; SVM: Support vector machine model; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
- Citation: Hiramatsu R, Imaoka S, Minata S, Sako H, Sato N. Machine learning model for predicting hospital-acquired functional decline in older patients with postoperative cardiovascular surgery. World J Clin Cases 2026; 14(4): 117700
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v14/i4/117700.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v14.i4.117700