©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2025; 13(35): 115700
Published online Dec 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i35.115700
Published online Dec 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i35.115700
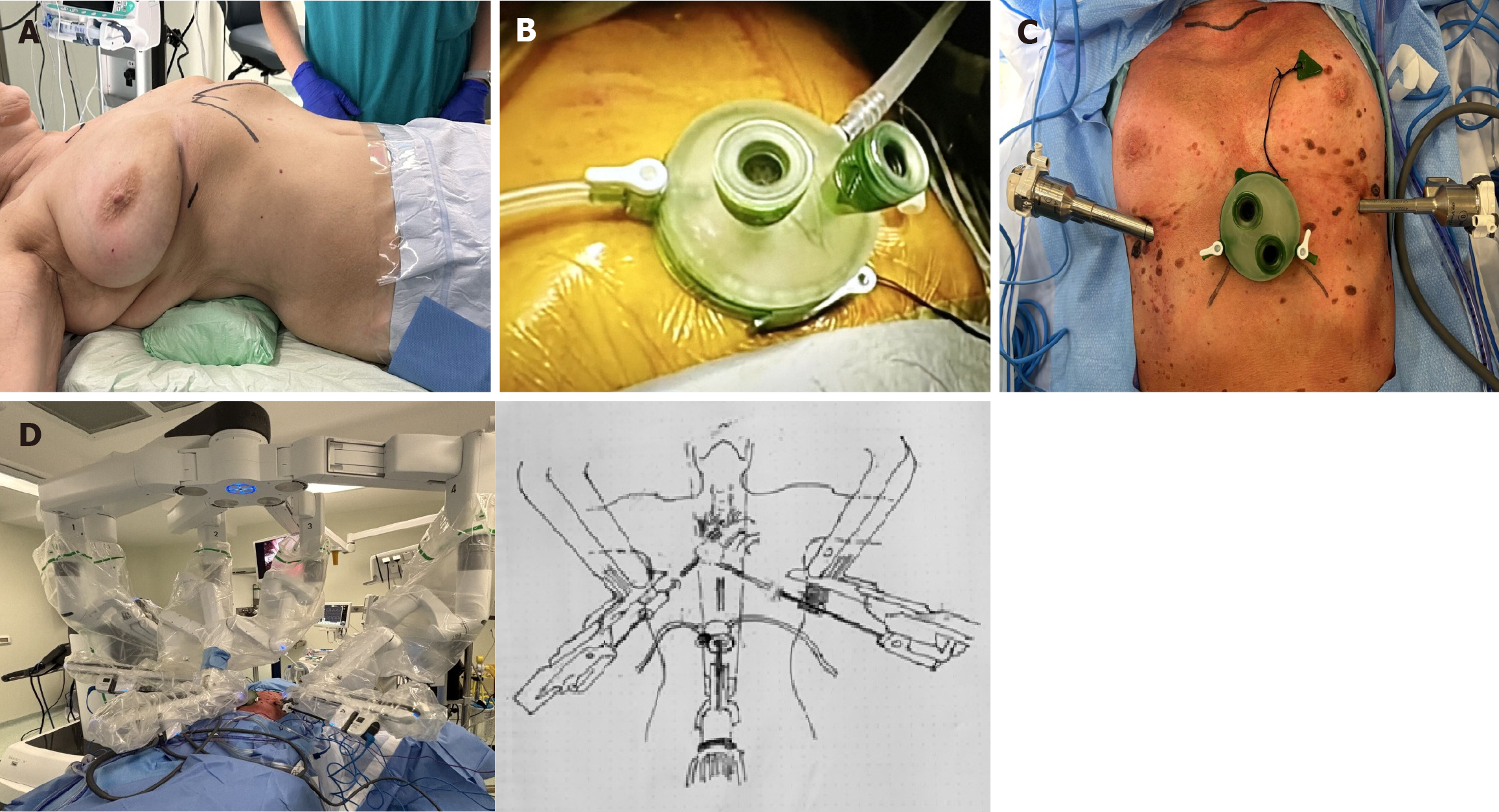
Figure 1 Stepwise illustration of the subxiphoid robotic-assisted thoracic surgery approach.
A: Patient position for the subxiphoid robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) approach; B: The gel port is positioned through the subxiphoid incision, with the carbon dioxide tubing connected to maintain insufflation during the robotic-assisted procedure; C: Port configuration for the subxiphoid RATS approach. The gel port is positioned through the subxiphoid incision and connected to the carbon dioxide insufflation line to maintain the operative field. Two additional trocars are placed - one on the right and one on the left side - to allow optimal access for the robotic instruments; D: The robotic system operating during the subxiphoid RATS.
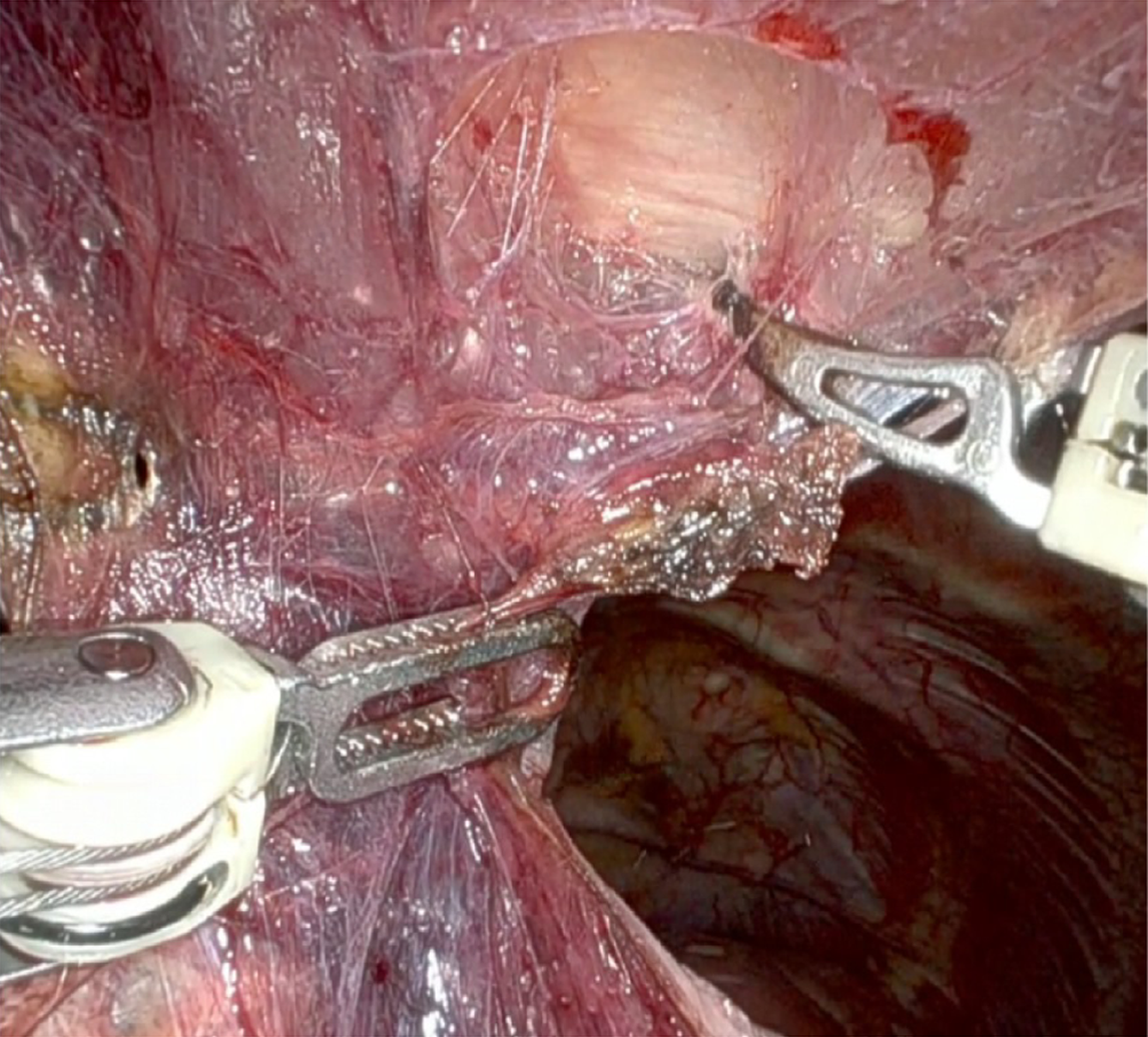
Figure 2 The procedure began with a careful blunt dissection of the tissues located beneath the sternum, starting at the lower end and proceeding upward toward the manubrium.
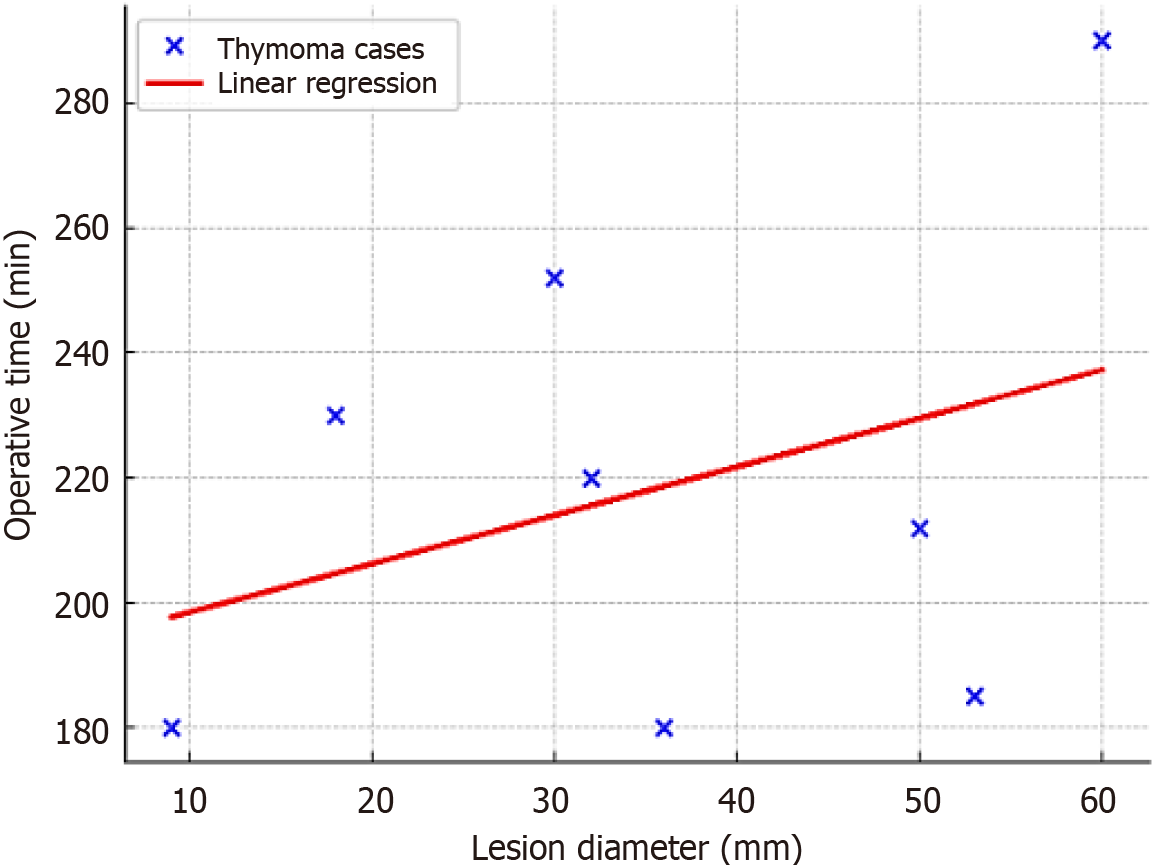
Figure 3 Scatter plot of operative time vs lesion diameter.
- Citation: Pardolesi A, Ferrari M, Leuzzi G, Cioffi U, Cioffi G, Solli P. Robotic subxiphoid surgical approach for mediastinal lesions: One-year experience. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(35): 115700
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i35/115700.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i35.115700