©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2025; 13(33): 112684
Published online Nov 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i33.112684
Published online Nov 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i33.112684
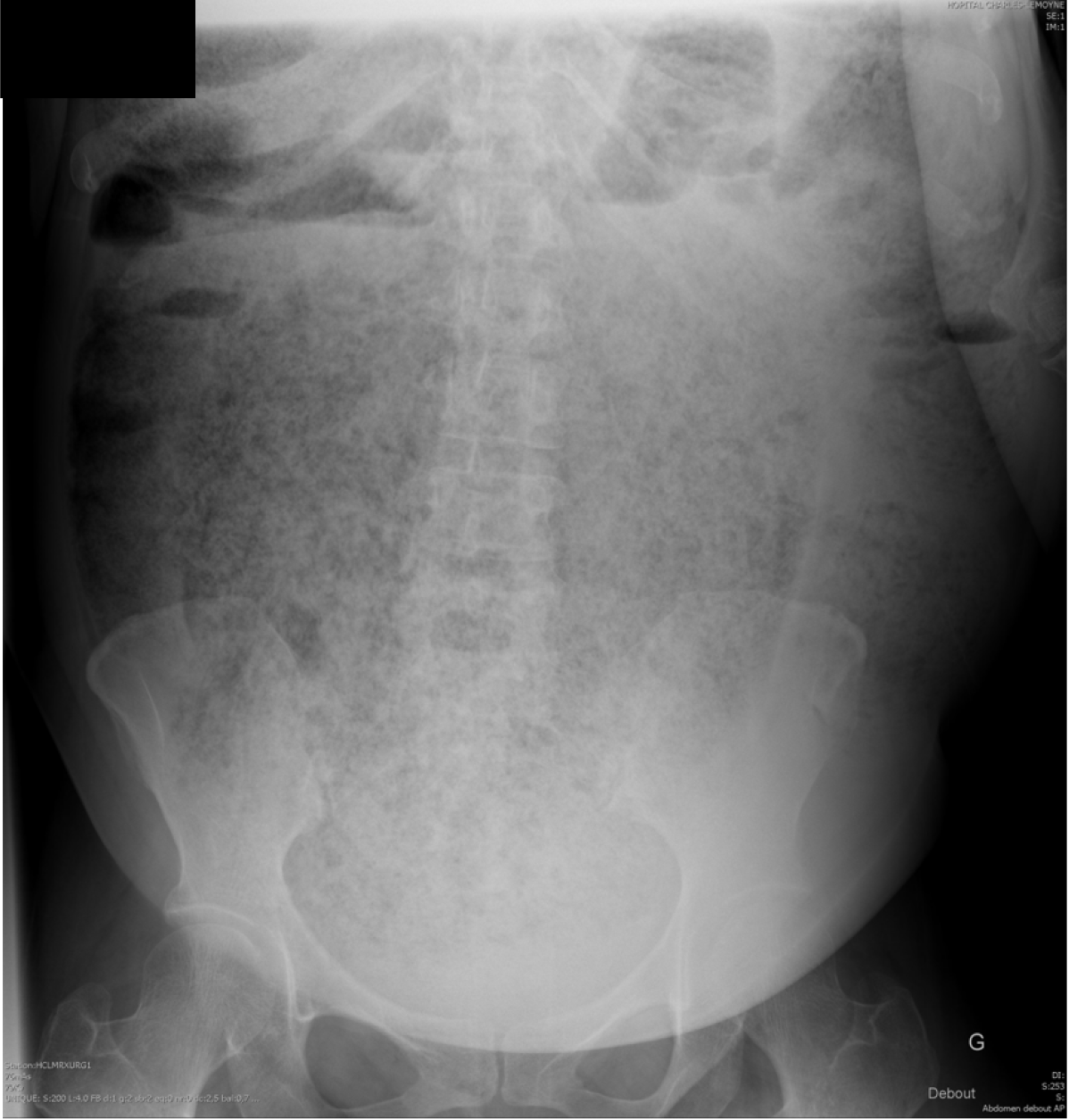
Figure 1 Plain film showing huge accumulation of stools.
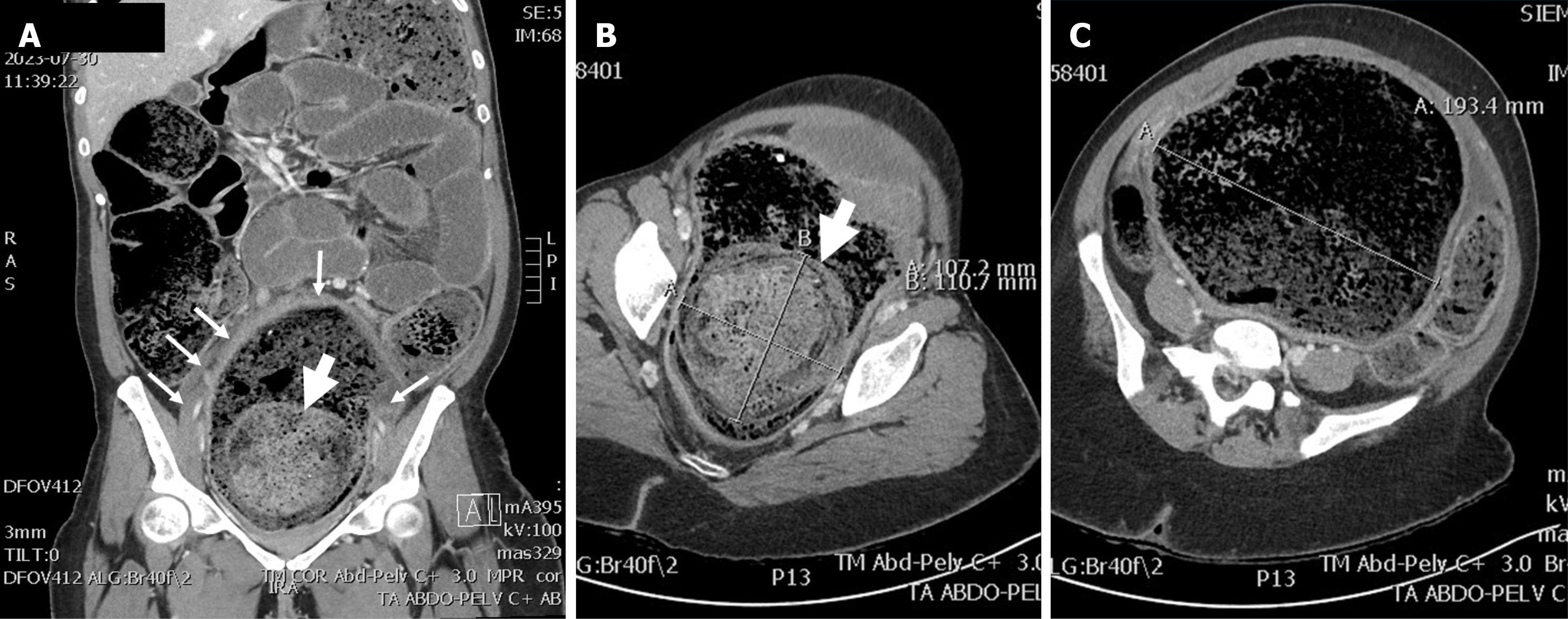
Figure 2 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: Coronal view showing diffuse colonic distension with accumulation of stools. The rectal wall is thickened (small arrows) and a large and dense fecaloma is demonstrated within the lumen (large arrow); B: Rectum with a dense 100-mm fecaloma (large arrow); C: Rectum reaching 193 mm in diameter.
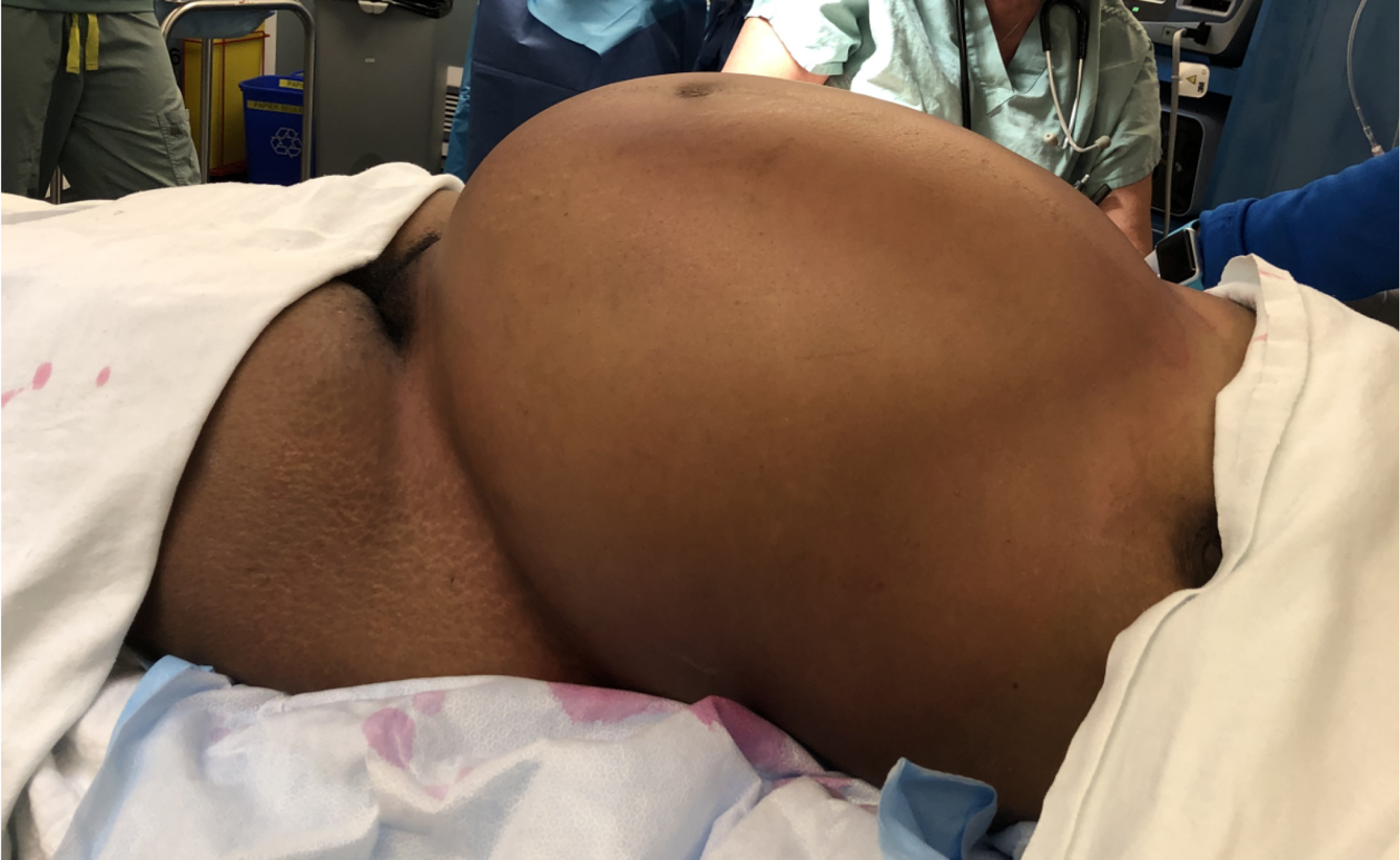
Figure 3 Patient in the operating room with overt abdominal distension.
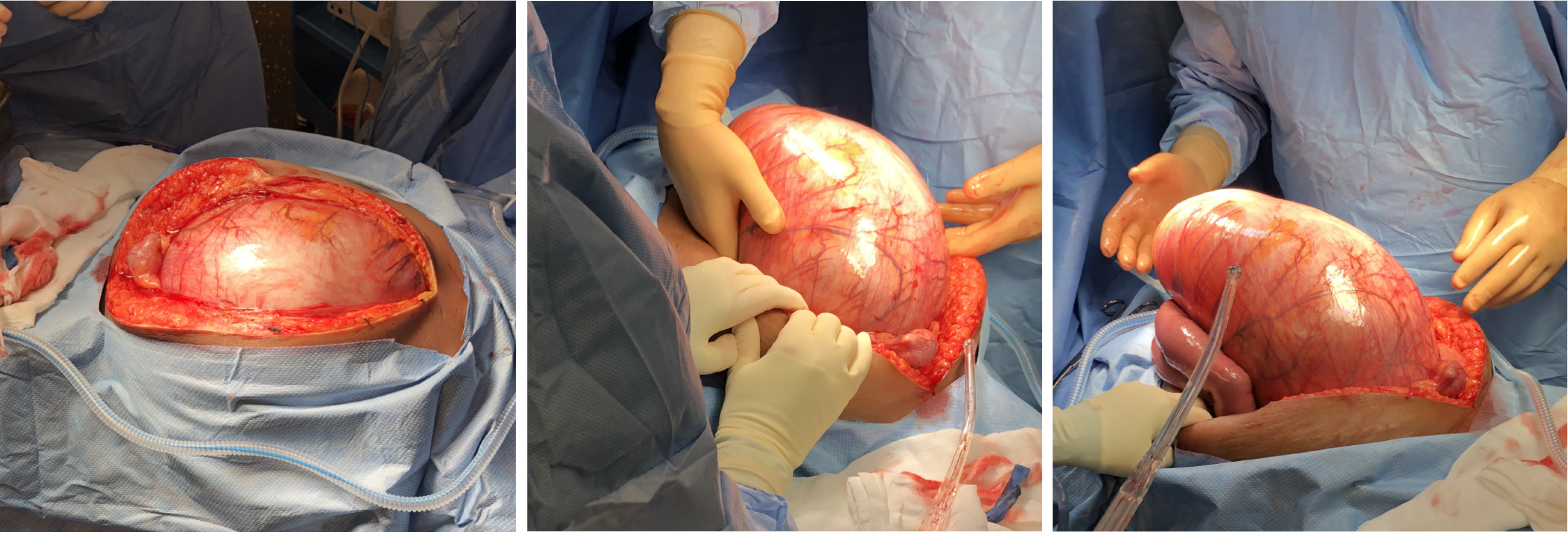
Figure 4 Xiphopubic laparotomy showing the overwhelming distended rectum.
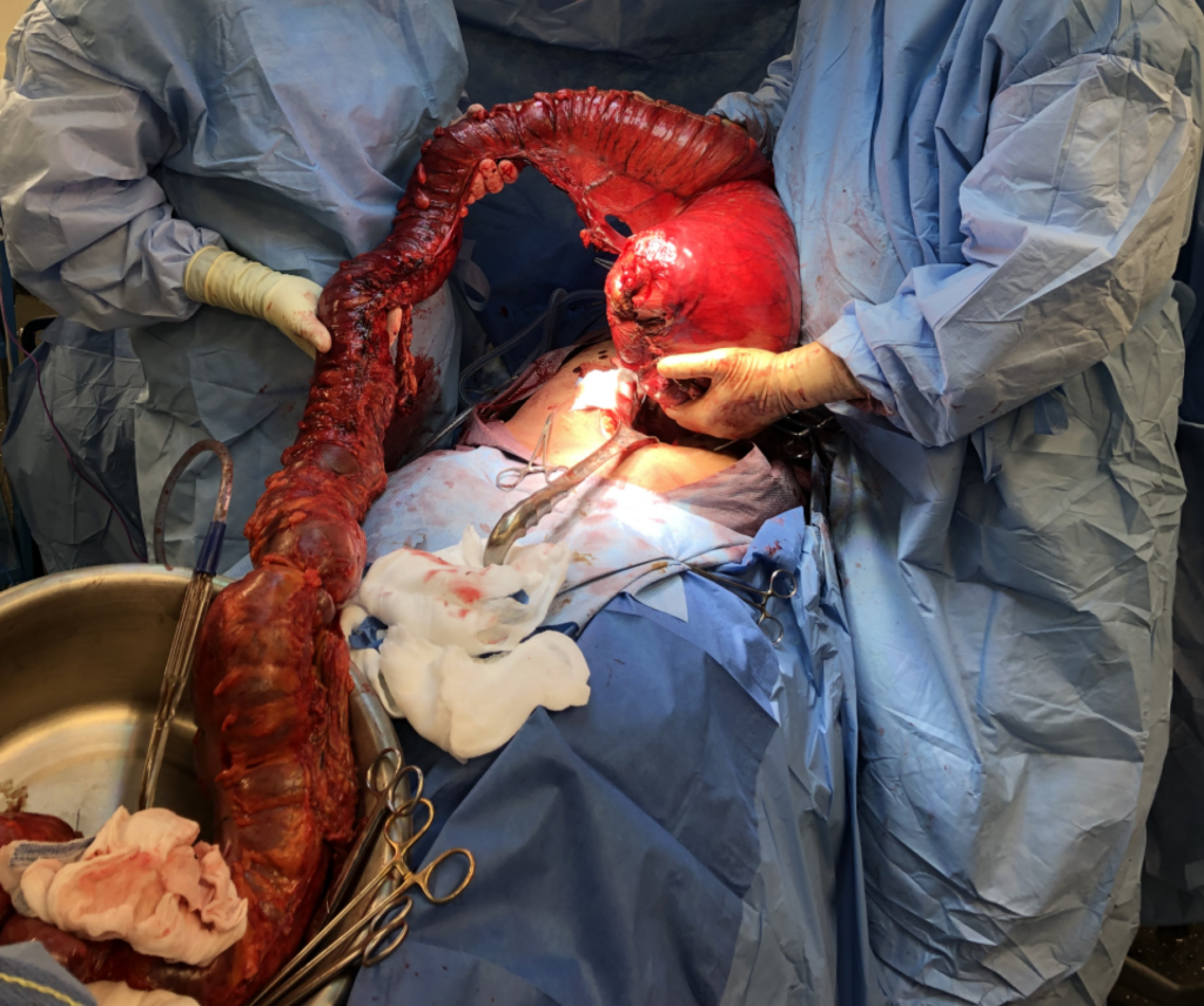
Figure 5 Total proctocolectomy completed.
The specimen measured 500 cm in length.
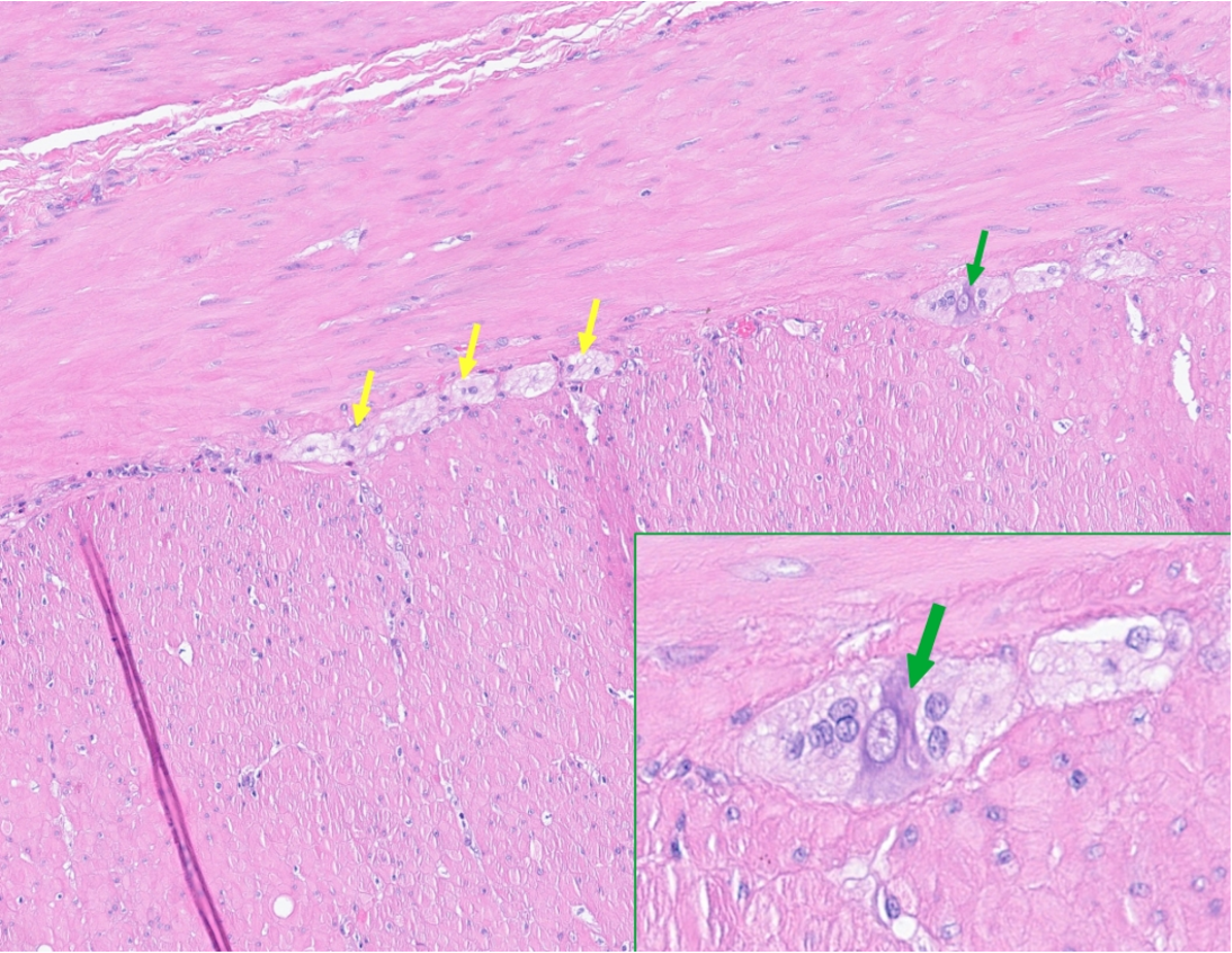
Figure 6 Section of the muscle layer of the distal bowel, from the area showing thickened wall and stenosis.
A ganglion with a single ganglion cell is demonstrated (green arrows) while in other places only Schwann cells are demonstrated (yellow arrows). The insert: An enlarged view showing the single ganglion cell.
- Citation: Bergeron E, Gologan A. Abdominal compartment syndrome with colonic hypoganglionosis and massive colonic distension in a young adult: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(33): 112684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i33/112684.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i33.112684