©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2025; 13(30): 109977
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i30.109977
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i30.109977
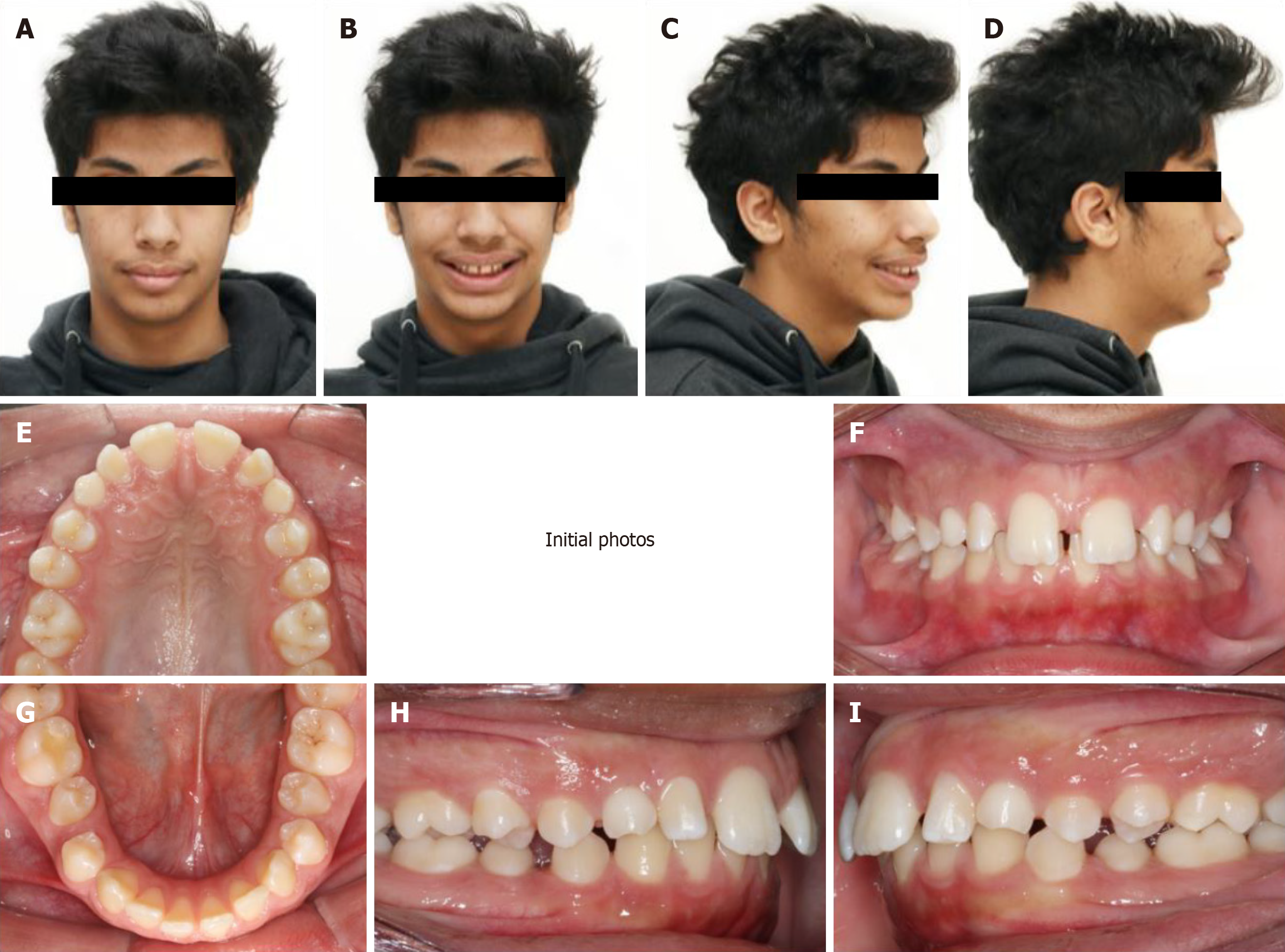
Figure 1 Extra-and intra-oral examination.
A-D: Pre-treatment facial pictures showing moderate class II skeletal pattern and retruded chin; E-I: Pre-treatment intra-oral pictures demonstrates class II division 1 malocclusion, retained maxillary primary canines and generalized spacing.
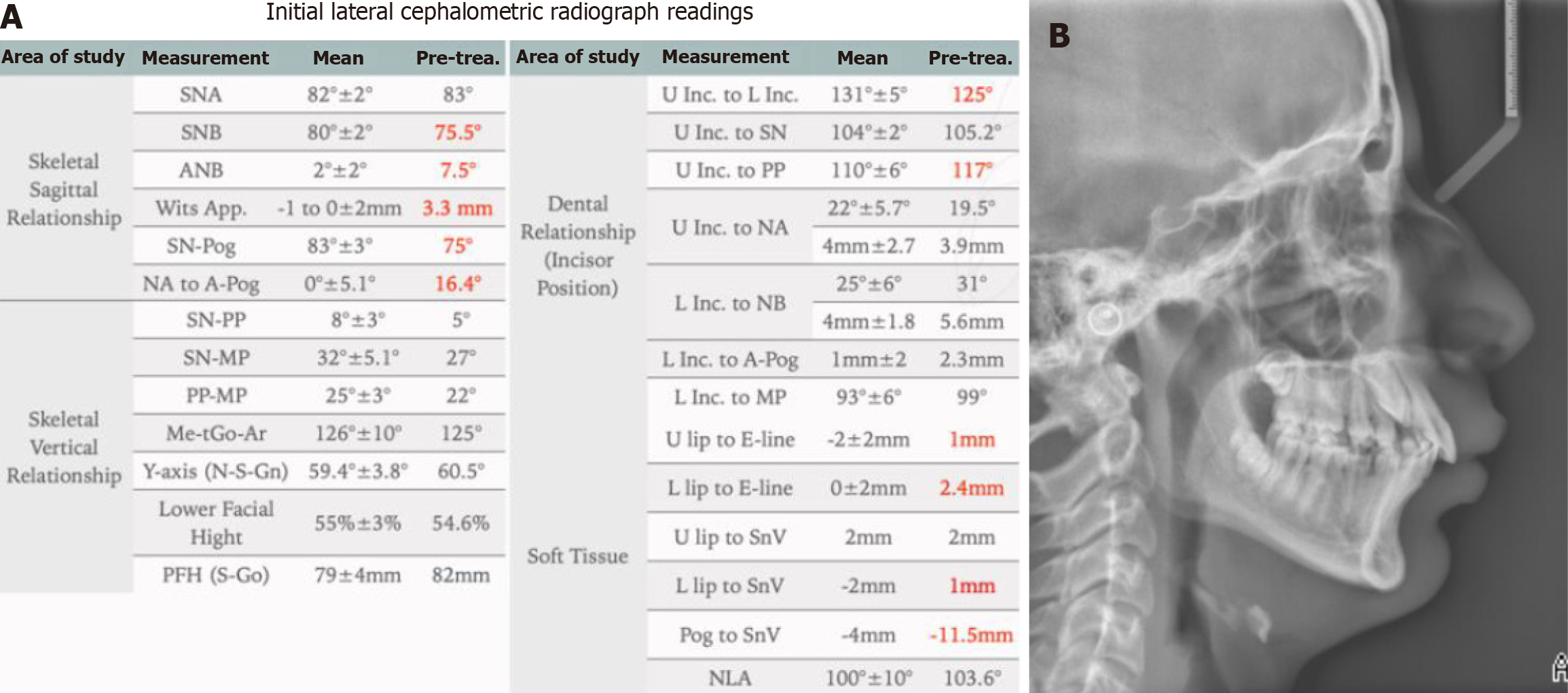
Figure 2 Pre-treatment lateral cephalometric radiograph examination.
A: Cephalometric radiograph shows cervical vertebrae maturation stage between 4 and 5; B: Cephalometric measurements confirms class II skeletal pattern due to retrognathic mandible (Note: Red color represent the abnormal values).
Figure 3 Pre-treatment panoramic radiograph examination.
A: Panoramic radiograph shows the presence of ectopic maxillary canines; B: Assessment of maxillary canines' positions shows an average to good prognosis.
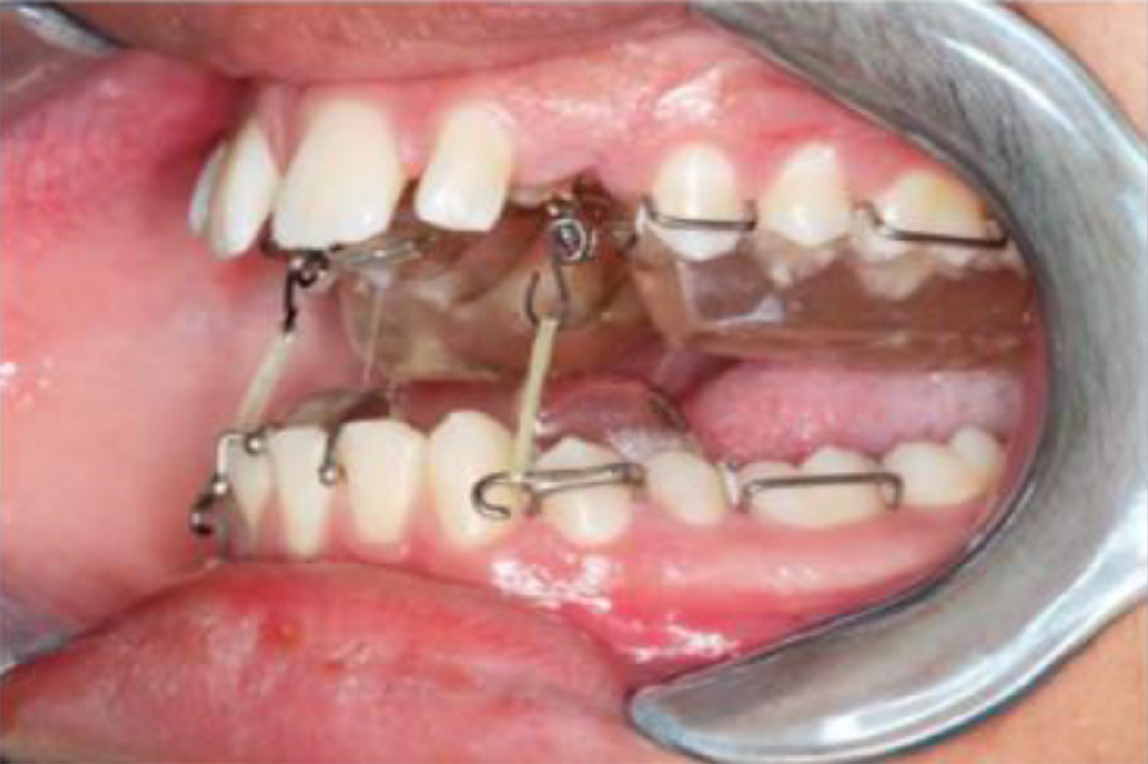
Figure 4 Modified twin block.
Extended hooks on the lower block for traction of maxillary canines and beta titanium hooks bonded to the exposed canines.
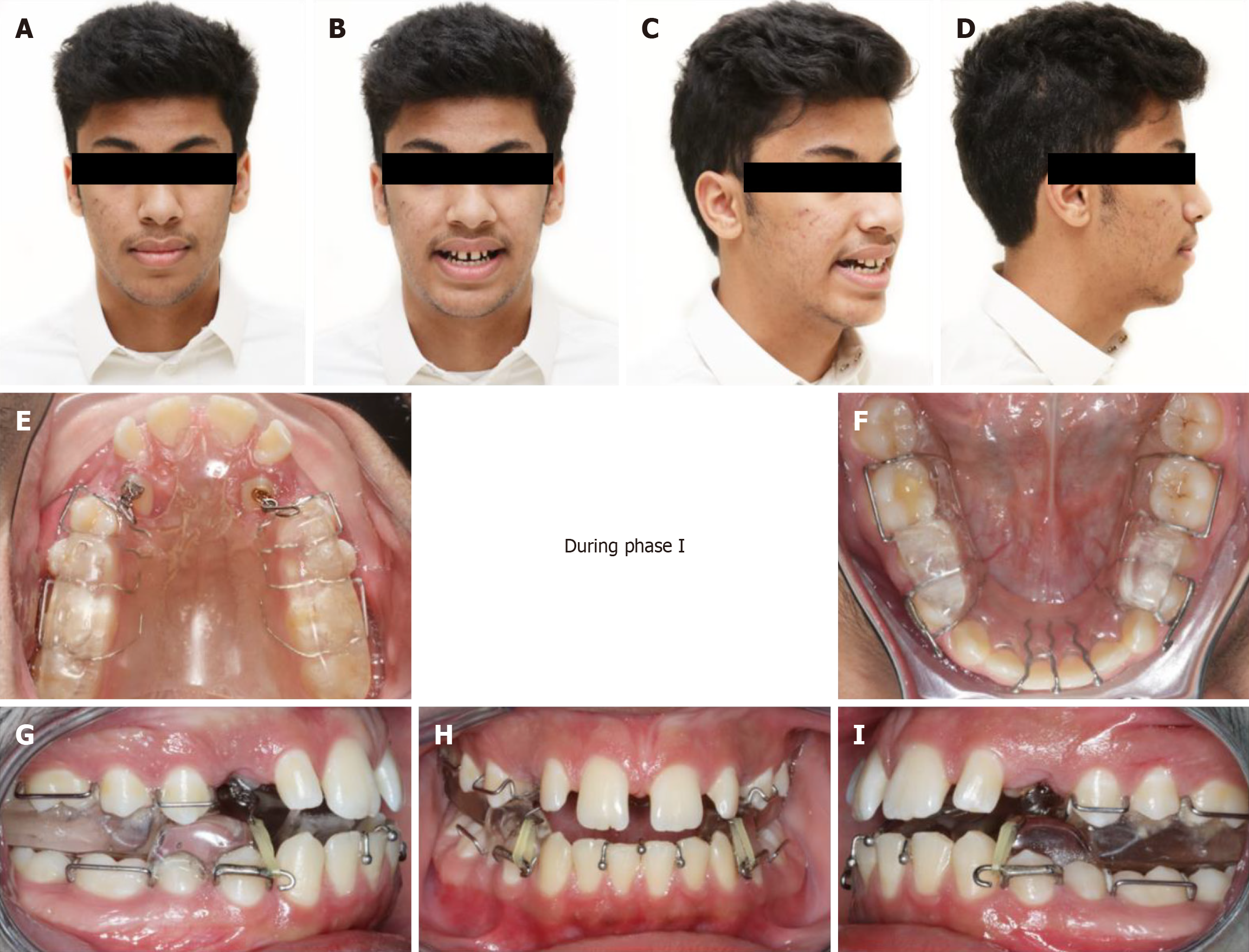
Figure 5 In progress photos.
A-D: Facial pictures of the patient during treatment wearing the twin block (TB); E-I: Intra-oral photos showing the design of the modified TB and the use of inter-arch elastics.
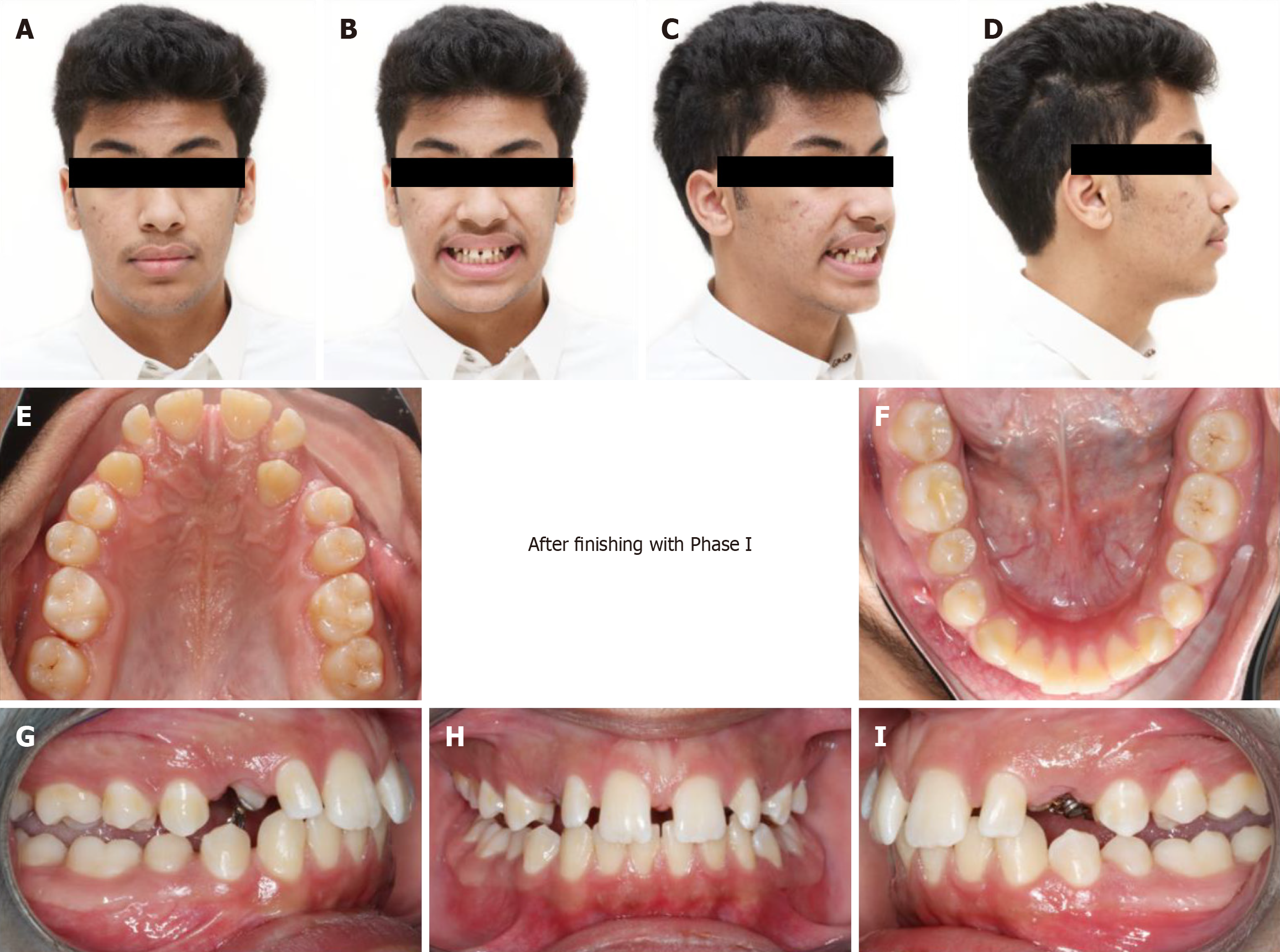
Figure 6 End of phase I treatment.
A-D: Facial pictures of the patient post twin block (TB) treatment (Note the improvement and chin and lips positions); E-I: Intra-oral photos post TB treatment showing significant improvement in overjet and improvement of maxillary canines positions.
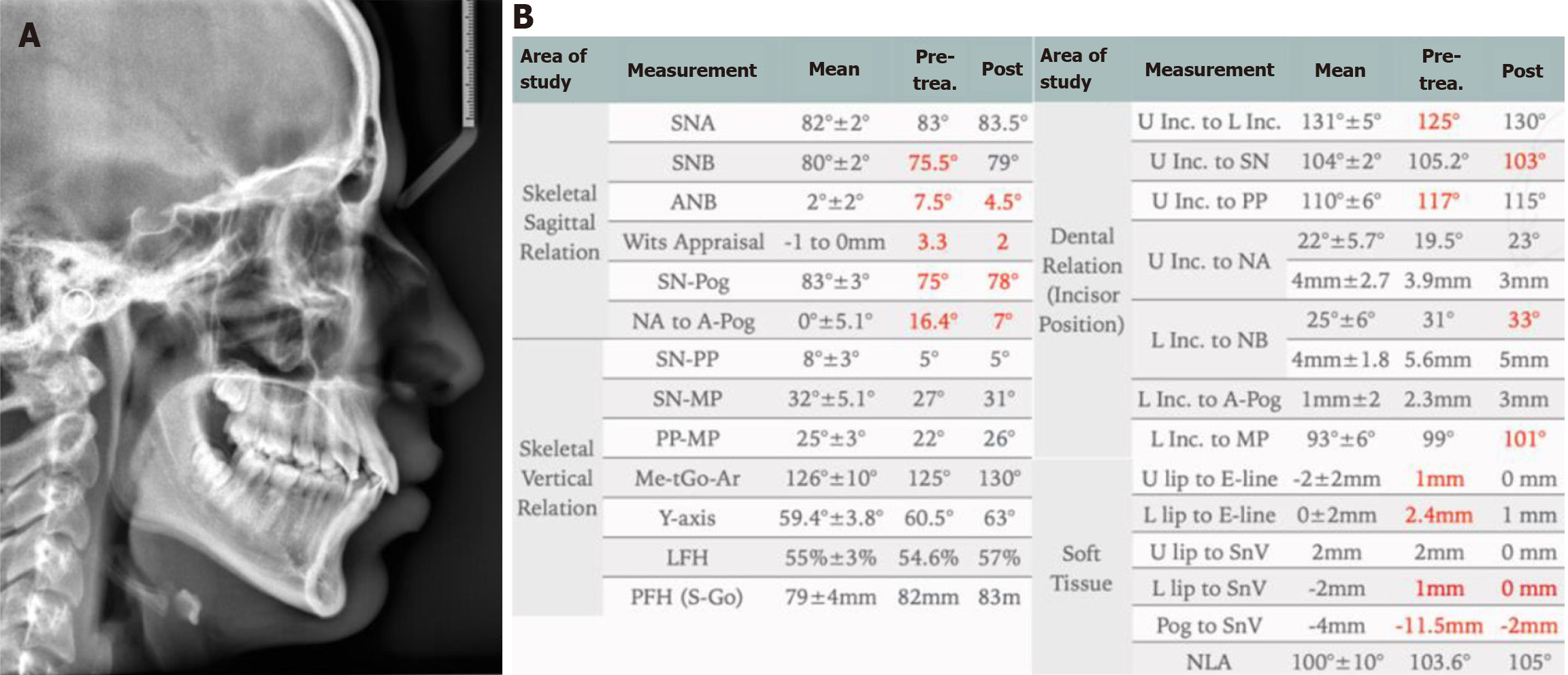
Figure 7 End of phase I lateral cephalometric radiograph.
A: Lateral cephalometric radiograph showing improvement of skeletal and dental positions; B: Cephalometric measurements for pre and post twin block treatment showing overall major improvement of skeletal and soft tissue measurements.
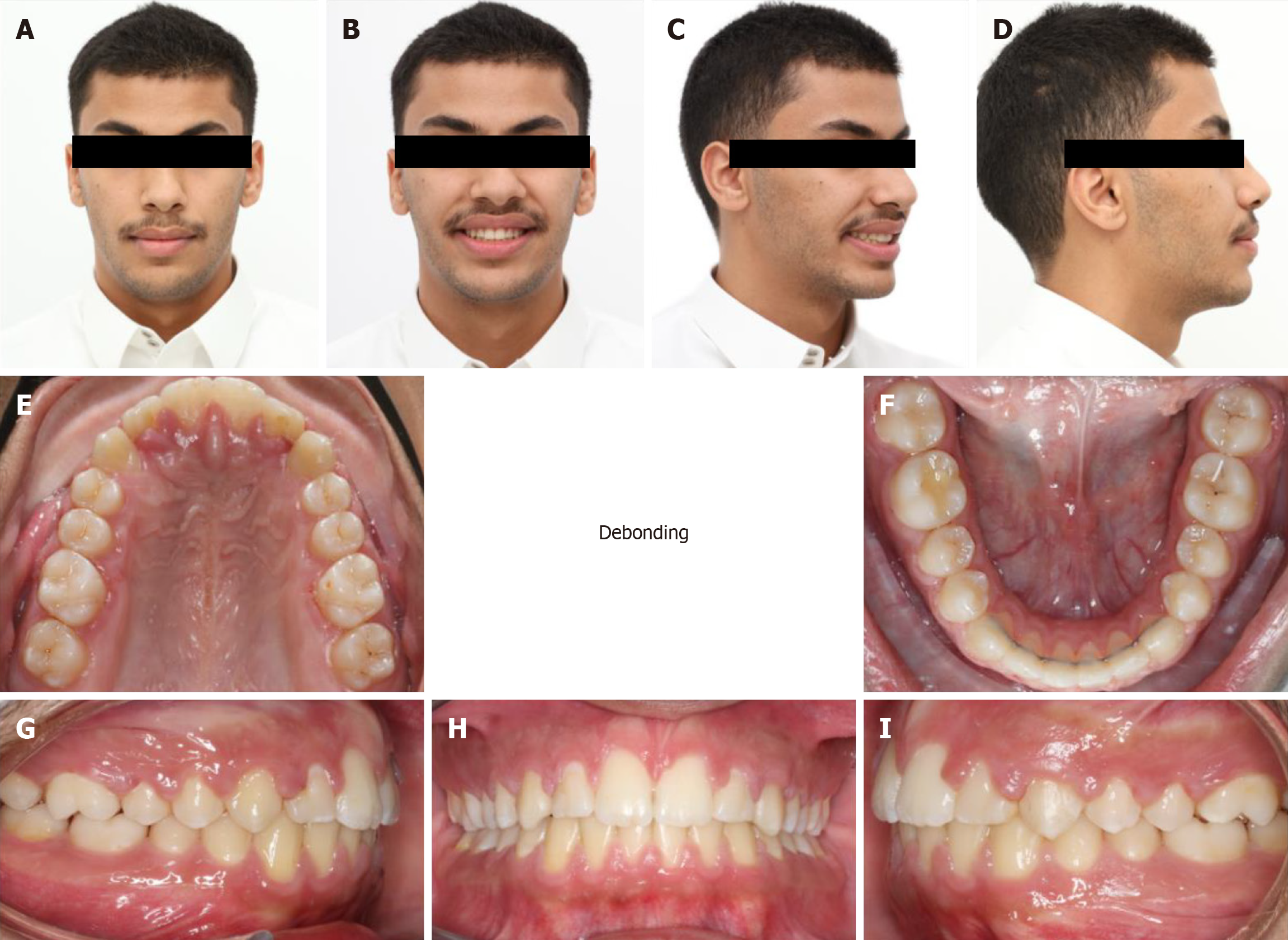
Figure 8 End of orthodontic treatment photos.
A-D: Facial pictures show a relaxed lip posture, reduced facial convexity, improved overall facial balance and harmony smile; E-I: Intra-oral photos show class I molar and canines relationship, good alignment of the teeth with the improvement of overjet and overbite.
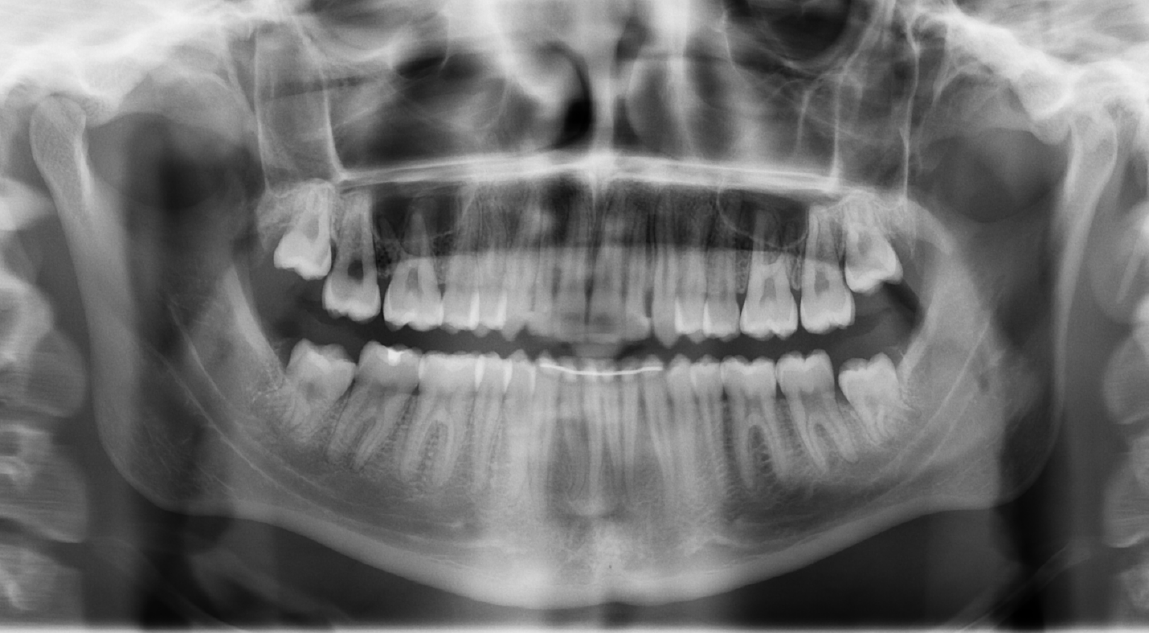
Figure 9 End of orthodontic treatment panoramic radiograph.
Panoramic radiograph shows good root parallelism of the teeth.
Figure 10 End of orthodontic treatment lateral cephalometric radiograph.
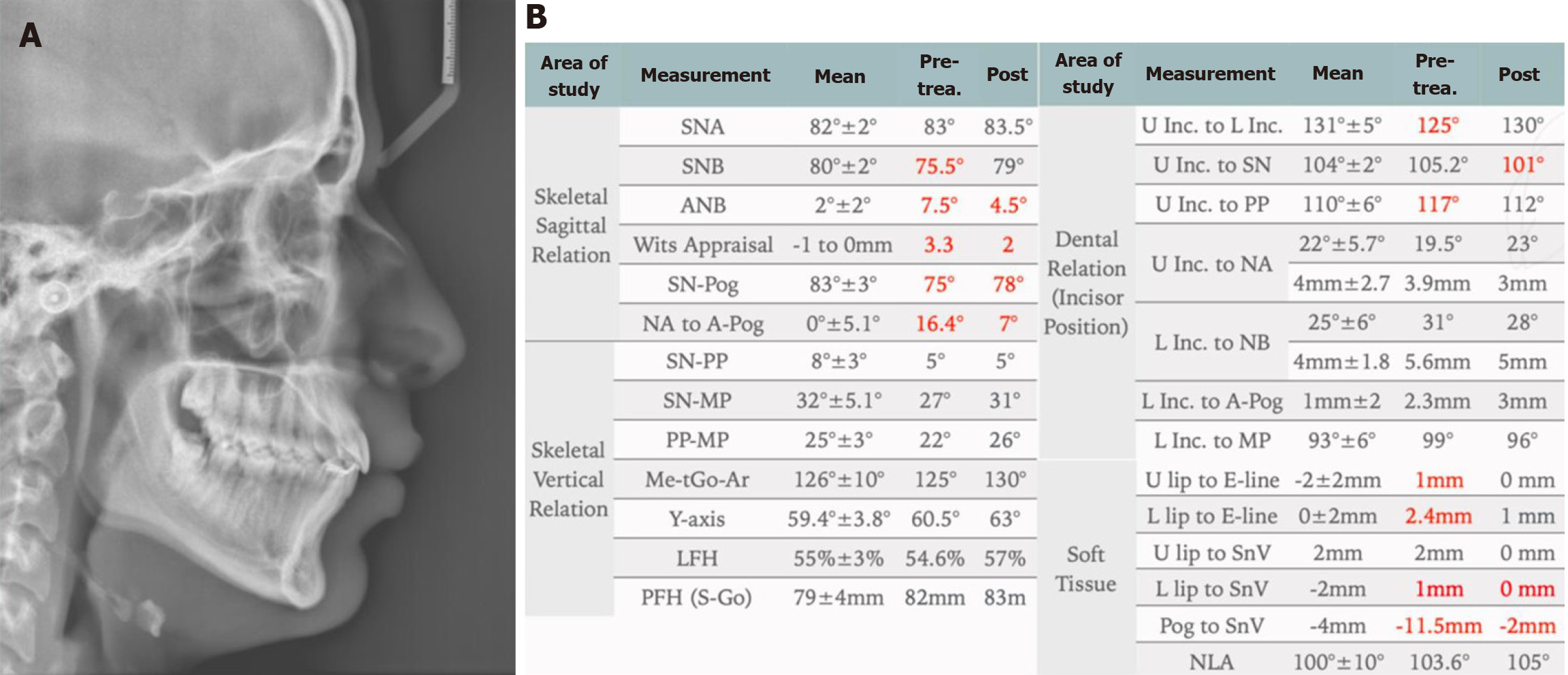
A: The lateral cephalometric radiograph shows significant improvements in skeletal and soft tissue positions, as well as in tooth positions; B: Cephalometric measurements for pre- and post-orthodontic treatment confirm that the overall improvement in skeletal and soft tissue measurements is maintained, as well as an improvement in the inclination of the upper and lower incisors.
Figure 11 Cephalometric tracing and superimposition.
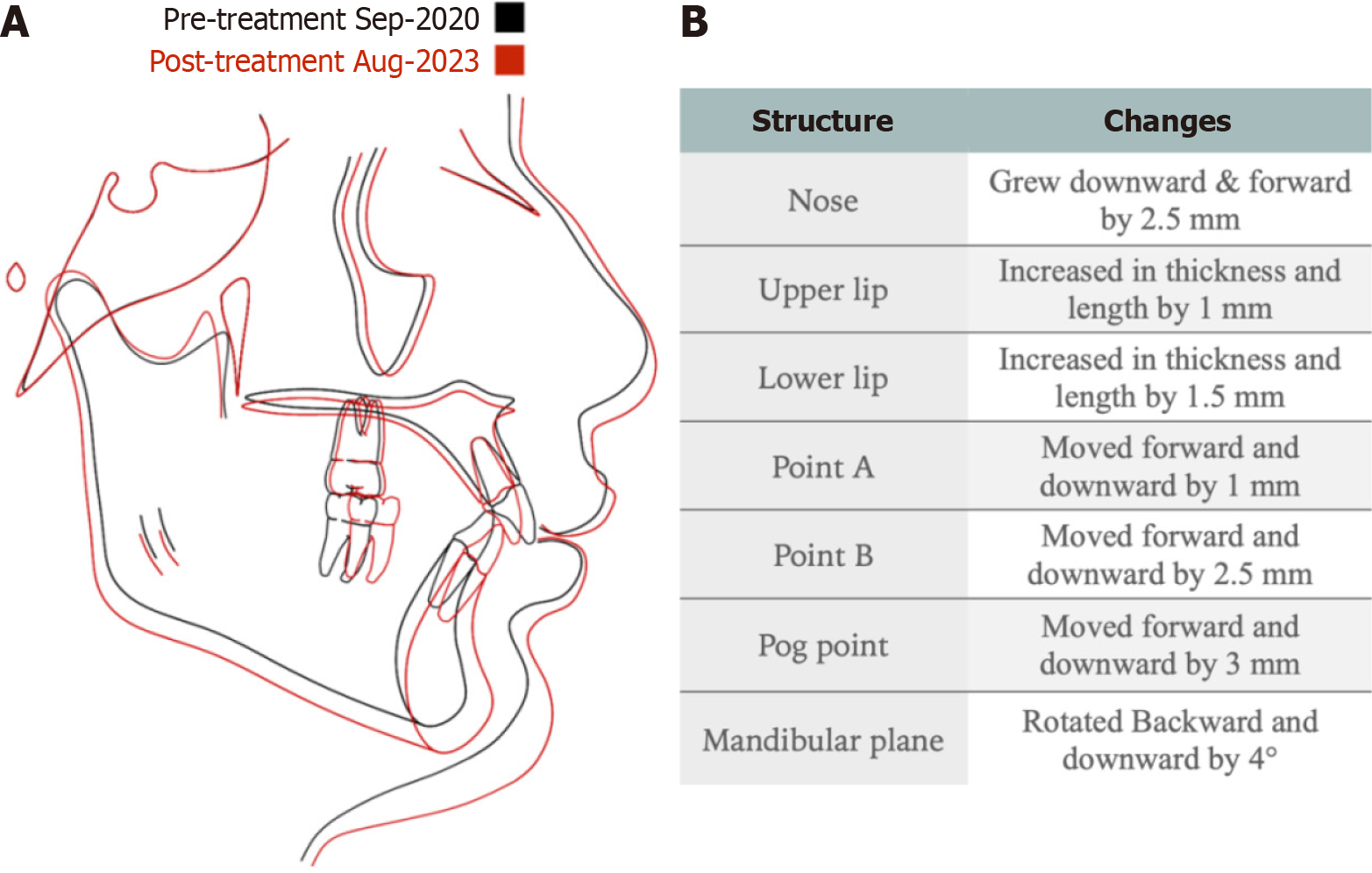
A: Cephalometric tracing before the start of orthodontic treatment (black) and after completion of orthodontic treatment (red), showing excellent downward and forward mandibular growth; B: Changes of main structures post orthodontic treatment.
- Citation: Alomair D, Halawani MR, Alsubaye S, Almajed AA. Treatment of class II malocclusion and ectopic maxillary canines: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(30): 109977
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i30/109977.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i30.109977