©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2025; 13(30): 109212
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i30.109212
Published online Oct 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i30.109212
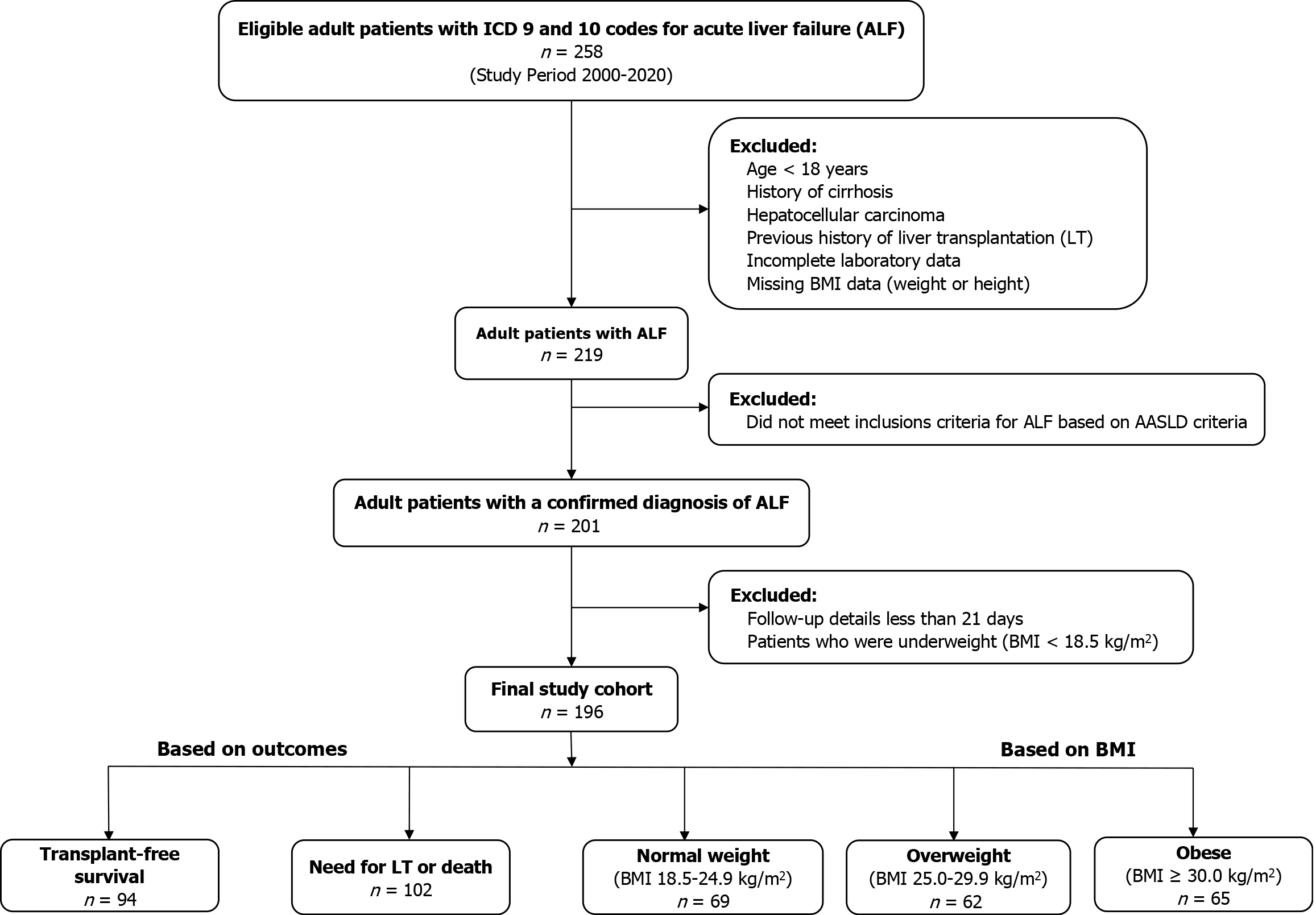
Figure 1 Study flow chart.
AASLD: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; ALF: Acute liver failure; BMI: Body mass index; LT: Liver transplantation.
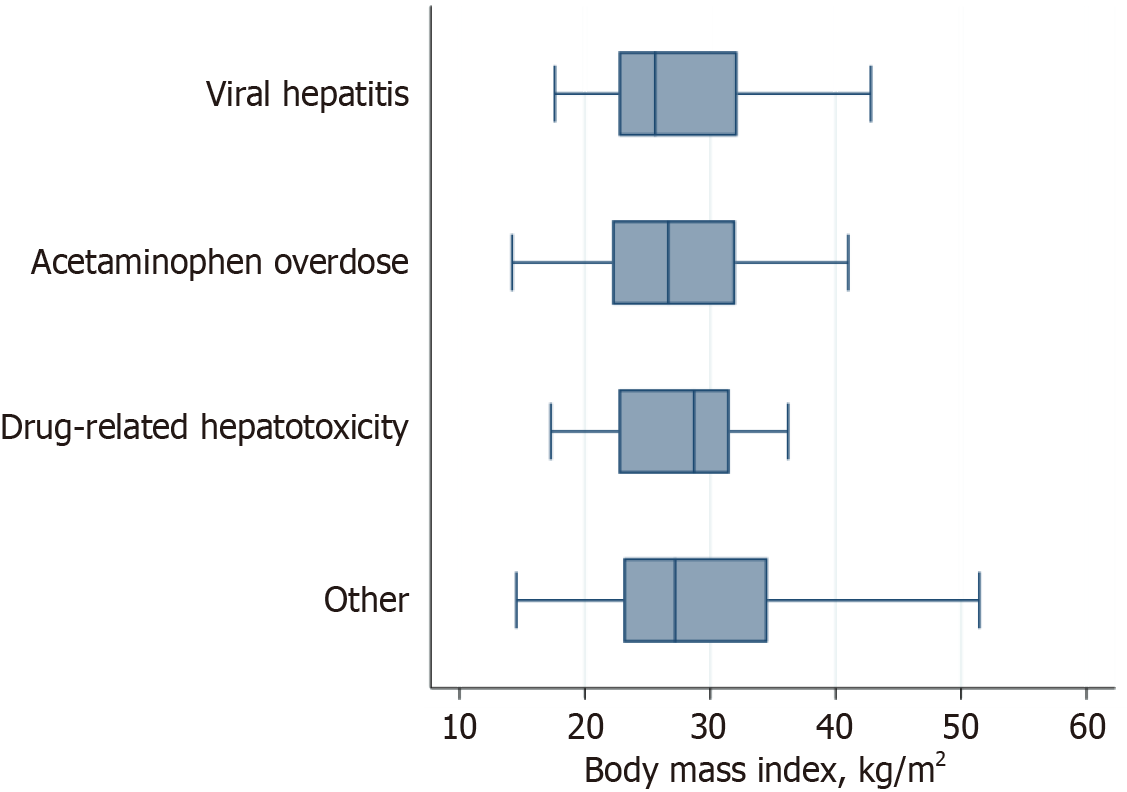
Figure 2
Boxplot of body mass index by etiology categories.
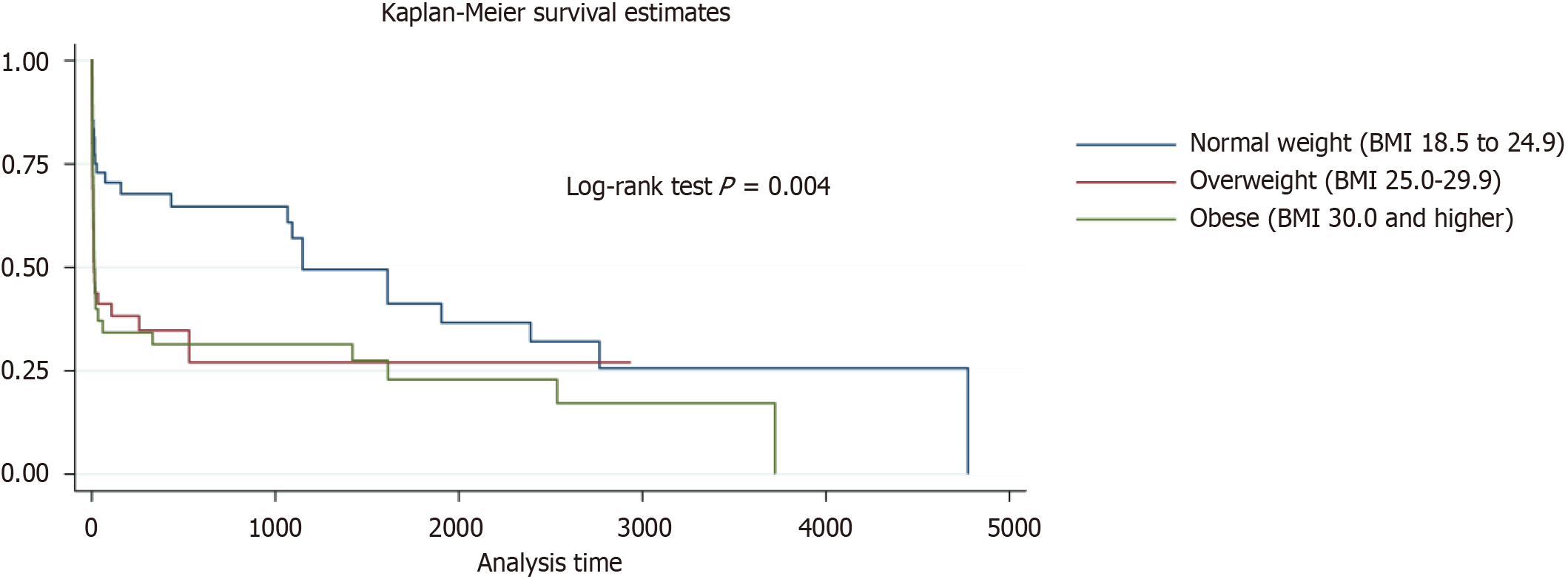
Figure 3 Kaplan–Meier survival analysis by body mass index comparing normal weight, overweight and obese.
BMI: Body mass index.
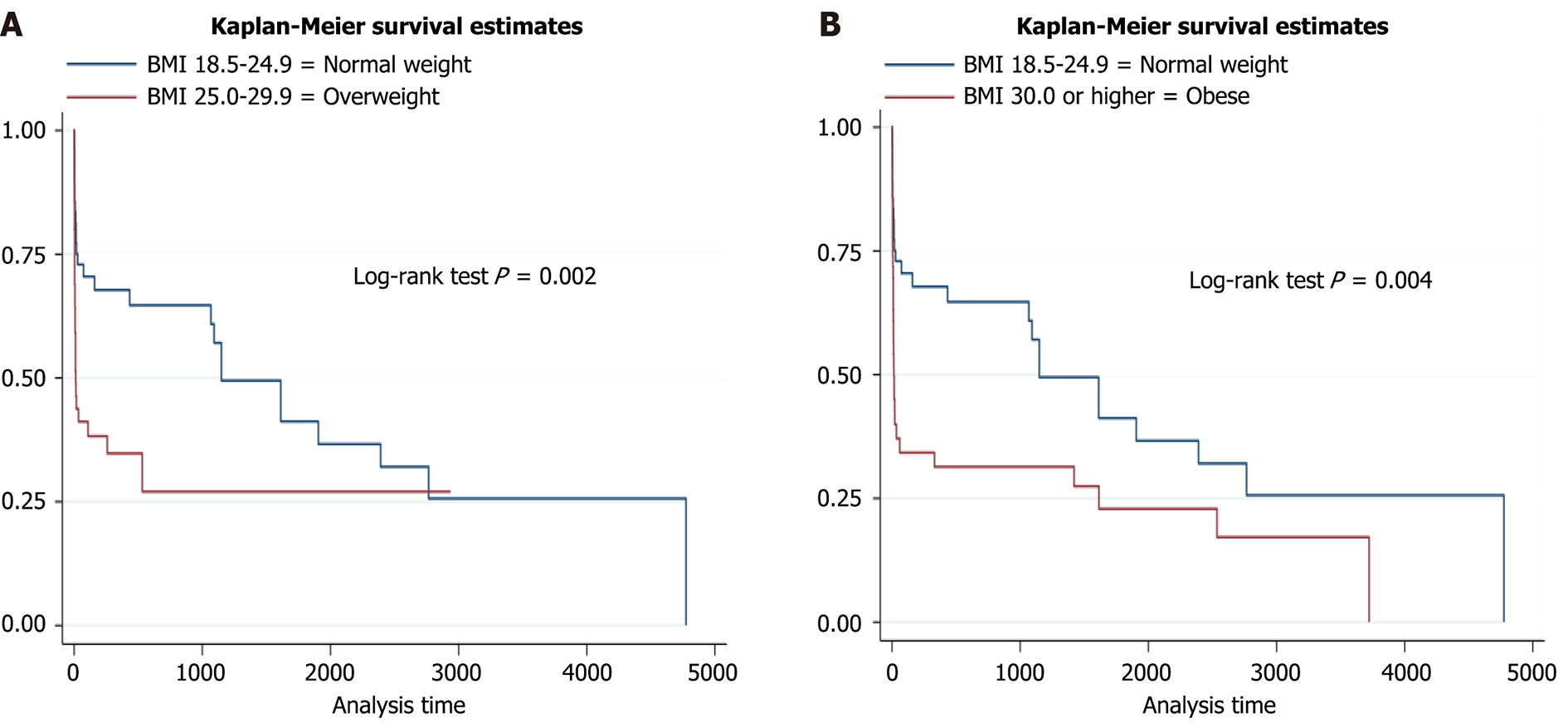
Figure 4 Kaplan–Meier analysis curve based on the patient's body mass index.
A: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis comparing normal weight [body mass index (BMI) 18.5-24.9 kg/m²] vs obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m²) patients with acute liver failure (ALF); B: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis comparing normal weight (BMI: 18.5-24.9 kg/m²) vs overweight (BMI: 25.0-29.9 kg/m²) patients with ALF. BMI: Body mass index.
- Citation: Krishnan A, Khan S, Gips J, Alqahtani SA, Vaidya D, Liu YS, Kim A, Su A, Gurakar A, Hamilton JP, Woreta TA. Body mass index and its association with clinical outcomes in acute liver failure. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(30): 109212
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i30/109212.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i30.109212