©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2024; 12(7): 1371-1377
Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1371
Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1371
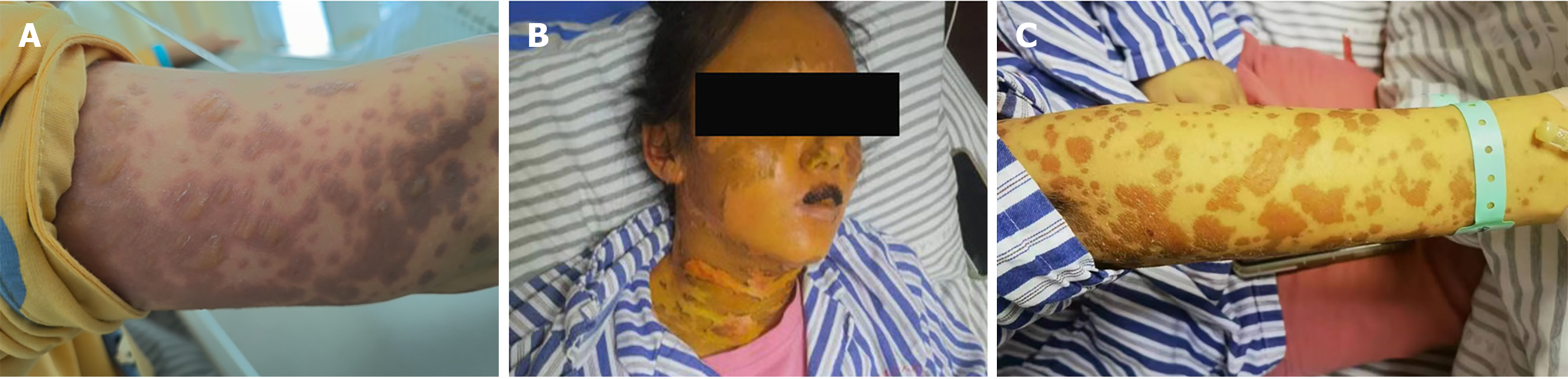
Figure 1 Facial symptoms of the patient with Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis after coronavirus disease 2019 diagnosis.
A: Skin injury on the upper arm on day 9 of the disease course; B and C: On day 13 of the disease course, the skin rash on her face and arm started falling off and was resolved after three courses of double plasma molecular adsorption system.
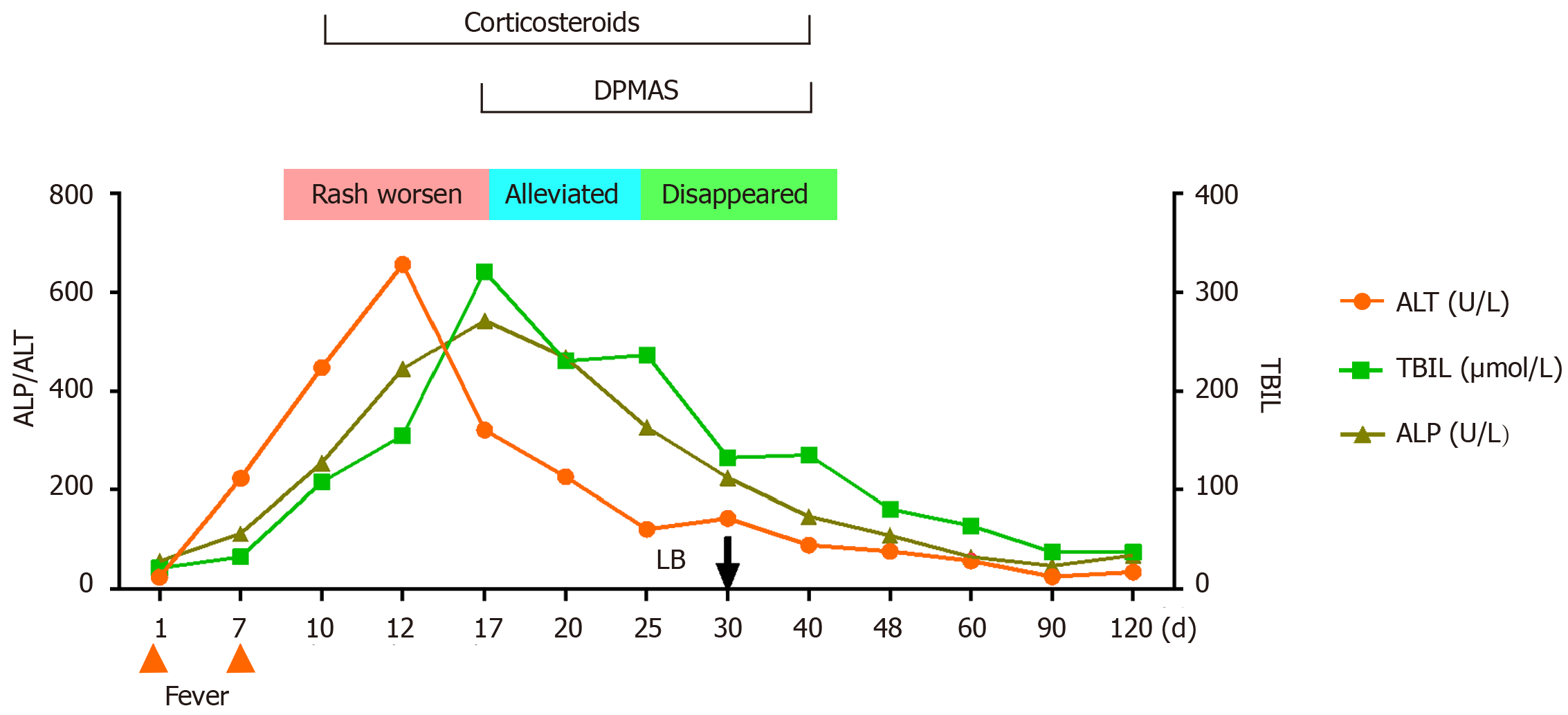
Figure 2 Disease flowchart.
DPMAS: Double plasma molecular adsorption system; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; LB: Liver biopsy.
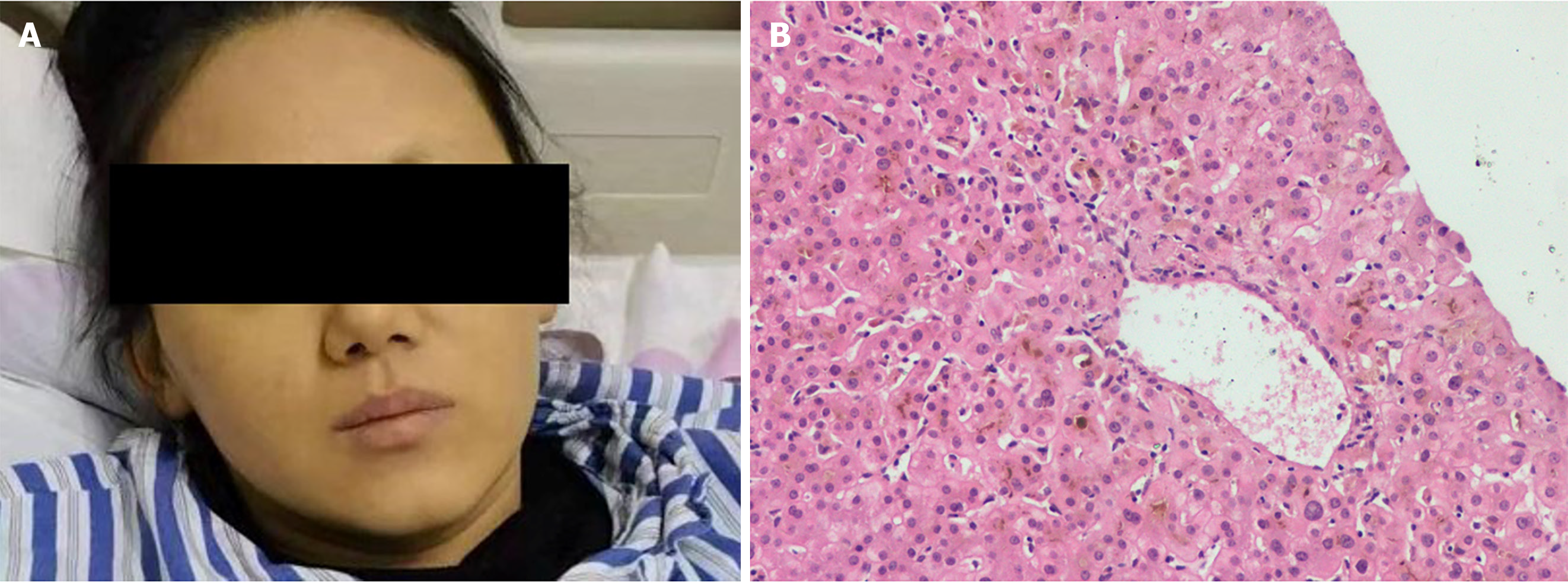
Figure 3 Skin changes after recovery, and histopathological features of the liver.
A: On day 40 of the disease course, the facial skin gradually returned to normal, but with pigmentation; B: Liver histopathology revealed cholestasis of central hepatocytes without apparent inflammation and necrosis.
Figure 4 After stopping the double plasma molecular adsorption system treatment, new skin lesions appeared.
A-C: New skin lesions on the inner thighs, arms, and face.
- Citation: Tan YW, Liu LP, Zhang K. Double plasma molecular adsorption system for Stevens–Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(7): 1371-1377
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i7/1371.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1371