©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2024; 12(6): 1050-1062
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1050
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1050
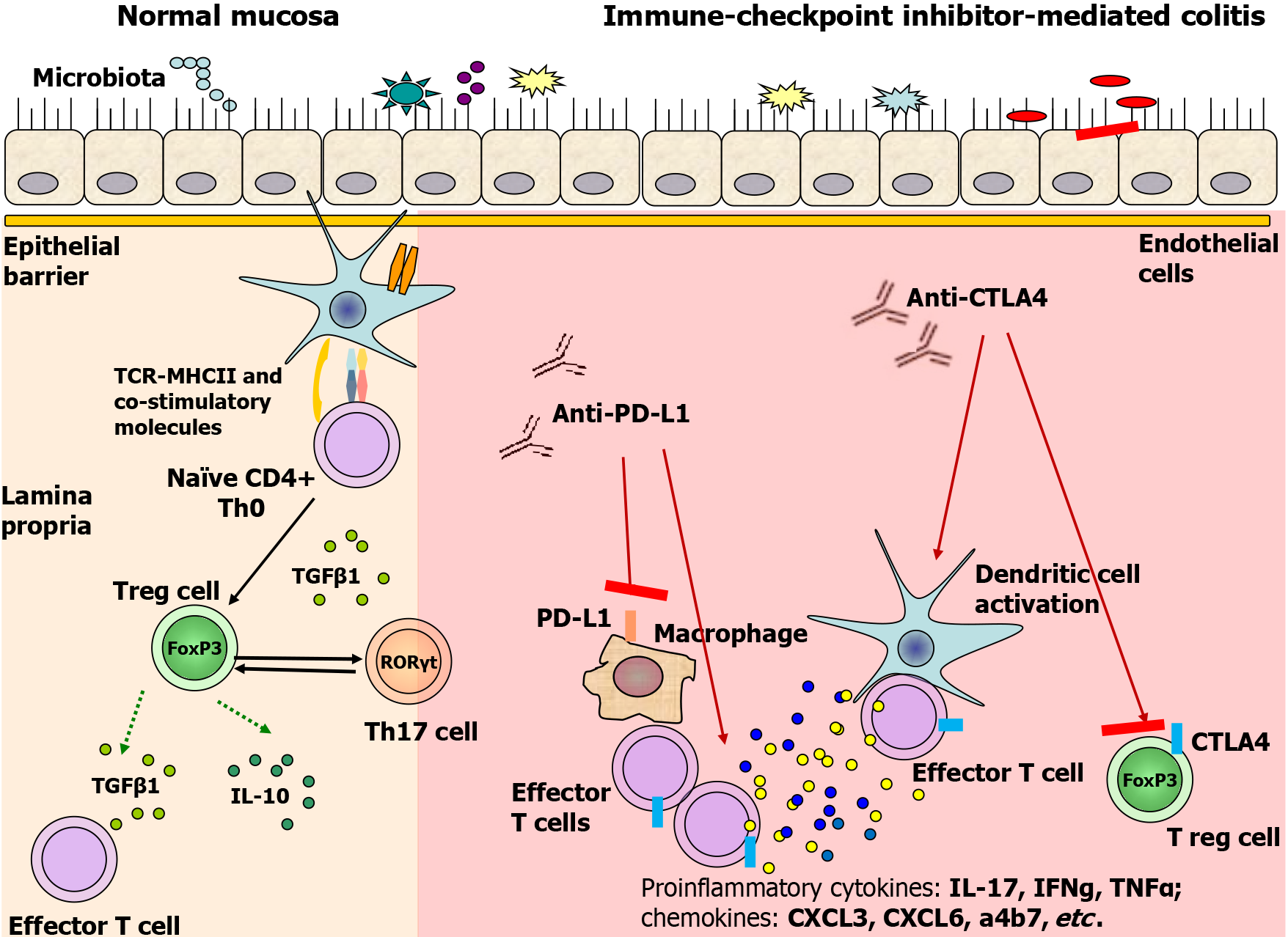
Figure 1 Proposed immune-mediated pathways of immune checkpoint inhibitor-mediated colitis.
In normal mucosa, T regulatory cells are fully capable of inducing tolerance while balancing pro-inflammatory cells and molecules (i.e. Th17 cells) and anti-inflammatory molecules (i.e. IL-10, TGFb, etc). By blocking cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) or programmed cell death ligand-1, immune checkpoint inhibitors promote pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokine production, Treg differentiation inhibition, and suppression of IL-10 and TGFb secretion. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier (https://smart.servier.com/) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported License (Supplementary material). CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand-1.
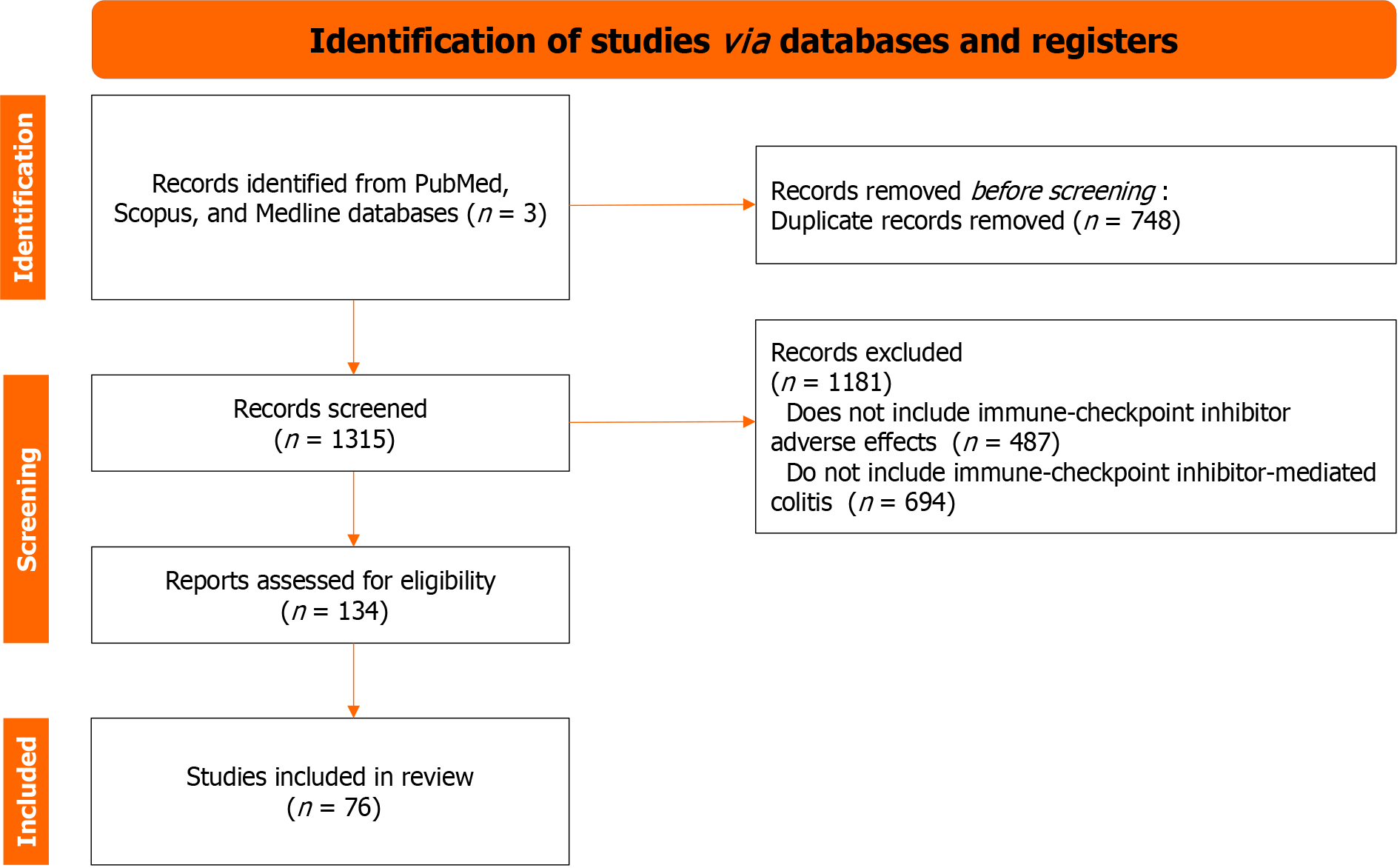
Figure 2 PRISMA-guided flow chart of the papers screened and included in the manuscript.
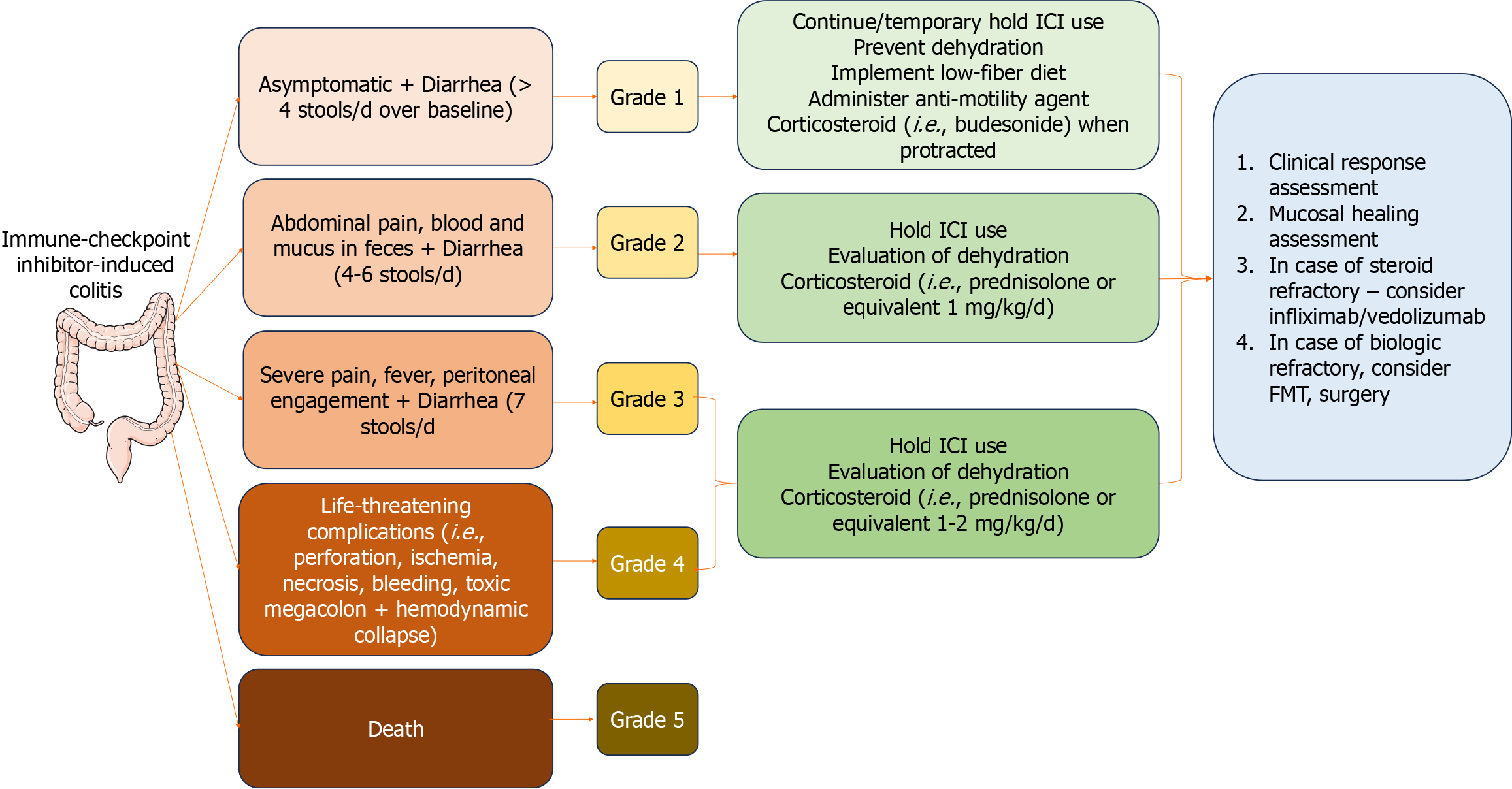
Figure 3 Grading the severity of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis and diarrhea and management.
After discontinuing immune checkpoint inhibitors, clinical response and mucosal healing assessment are needed, and then biologics, fecal microbiota transplantation or surgery are introduced. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier (https://smart.servier.com/) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported License (Supplementary material). FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation; ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitors.
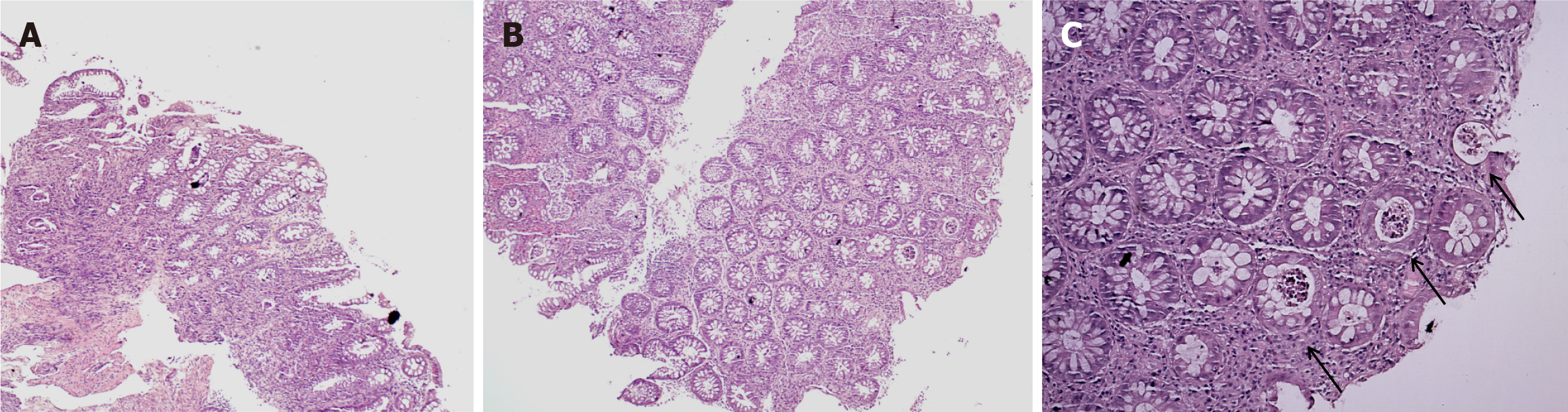
Figure 4 This colonic biopsy shows severe colitis highlighted by cryptitis and focal crypt microabscess (C-marked with an arrows), and surface epithelial injury without crypt atrophy.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) × 20; B: H&E × 50; C: H&E × 100.
Figure 5 Hematoxylin and eosin staining.
A and B: This colonic biopsy shows increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (lymphocytic colitis pattern of injury), mild focal active colitis and surface epithelial injury. Hematoxylin and eosin × 50 (A), × 100 (B).
- Citation: Velikova T, Krastev B, Gulinac M, Zashev M, Graklanov V, Peruhova M. New strategies in the diagnosis and treatment of immune-checkpoint inhibitor-mediated colitis. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(6): 1050-1062
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i6/1050.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1050