©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2024; 12(35): 6775-6781
Published online Dec 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i35.6775
Published online Dec 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i35.6775
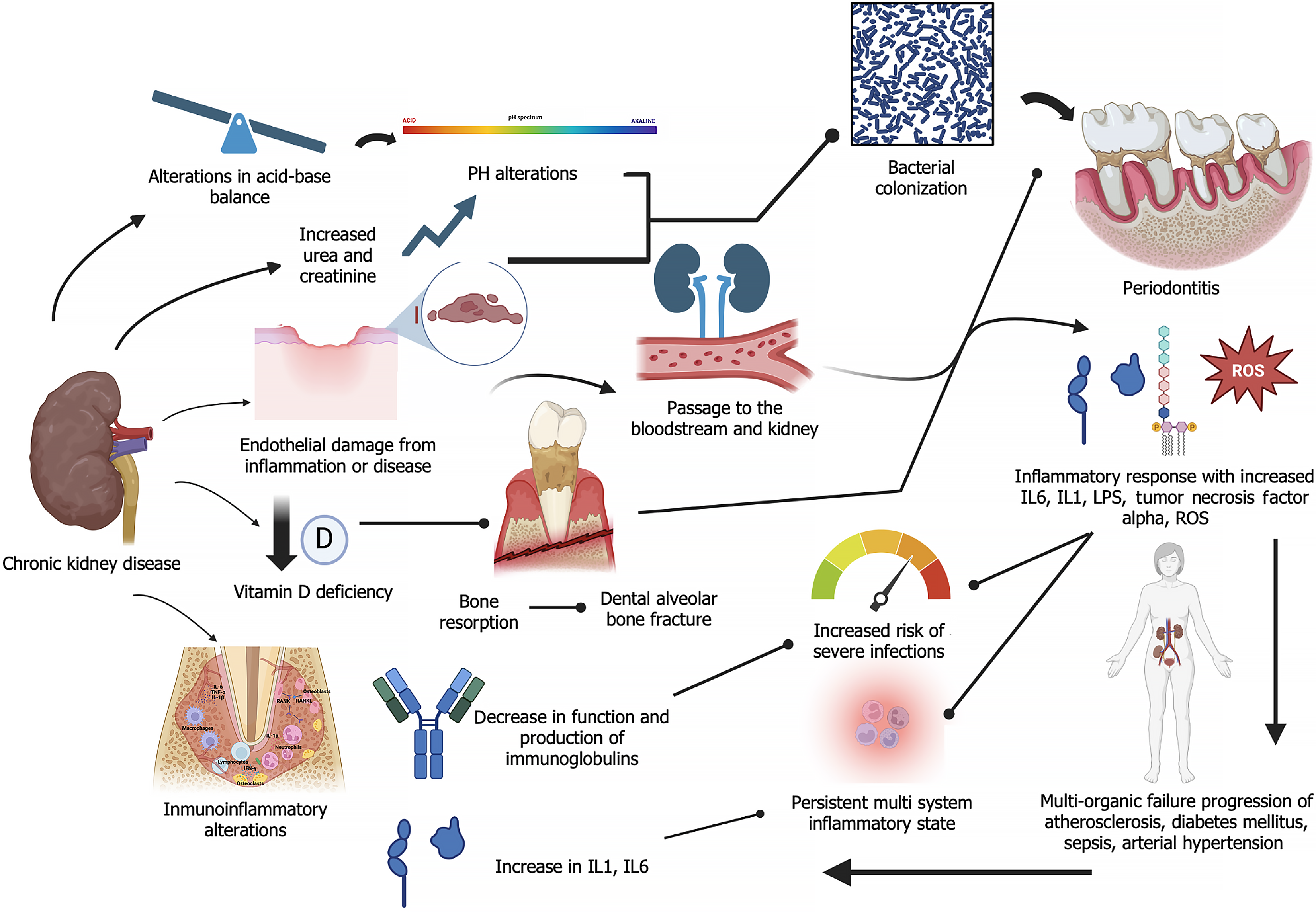
Figure 1 Image showing the main pathophysiological alterations in chronic kidney disease and periodontitis.
The green arrows illustrate the alterations in periodontal disease and how the association of both conditions predisposes the patient to a persistent inflammatory state and multi-organ damage (Created with BioRender.com). IL1: Interleukin-1; IL6: Interleukin-6; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
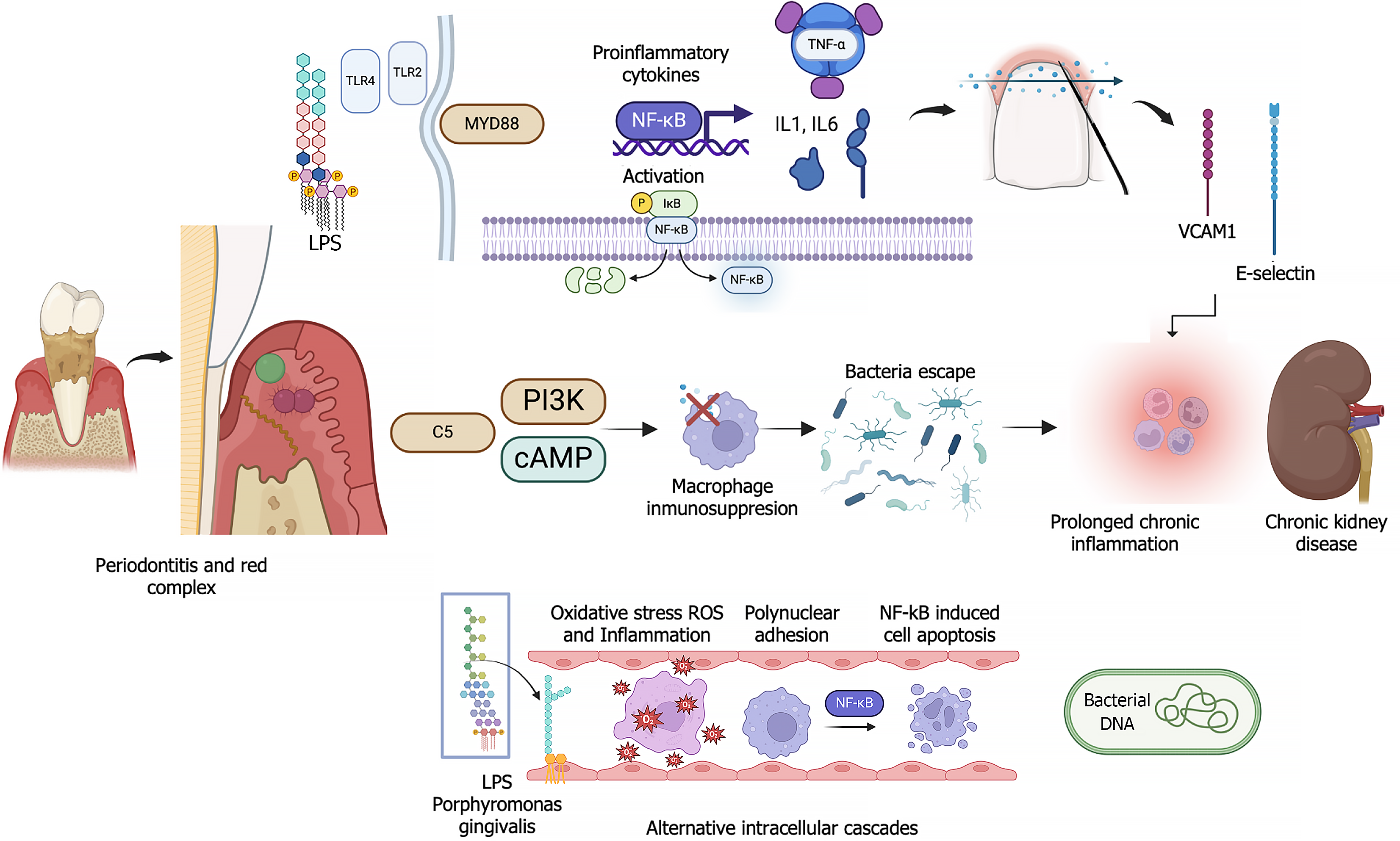
Figure 2 Bacteria from the "red complex" of periodontal disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, activate toll-like receptors-2 and toll-like receptors-4 on immune cells via lipopolysaccharide.
This activation triggers an inflammatory cascade mediated by MyD88 and nuclear transcription factor-kappa B (NF-kB), leading to the production of cytokines [interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)] and adhesion molecules (VCAM1 and E-selectins). Intracellular pathways such as PI3K and cAMP induced by complement factor C5 suppress macrophage immune responses, thereby allowing pathogen survival and causing persistent inflammation. Oxidative stress driven by the presence of lipopolysaccharide from P. gingivalis and the production of reactive oxygen species leads to inflammation, polymorphonuclear adhesion and cellular apoptosis induced by NF-kB, which directly target bacterial DNA. This cycle of inflammation and oxidative stress exacerbates periodontal disease and chronic kidney disease, thereby negatively impacting renal and periodontal health (Created with BioRender.com). LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TLR2: Toll-like receptors-2; TLR4: Toll-like receptors-4; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-kB: Nuclear transcription factor-kappa B; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL1: Interleukin-1; IL6: Interleukin-6; IkB: Inhibitory protein; VCAM1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; C5: Complement component 5; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Martínez Nieto M, De Leon Rodríguez ML, Anaya Macias RDC, Lomelí Martínez SM. Periodontitis and chronic kidney disease: A bidirectional relationship based on inflammation and oxidative stress. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(35): 6775-6781
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i35/6775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i35.6775